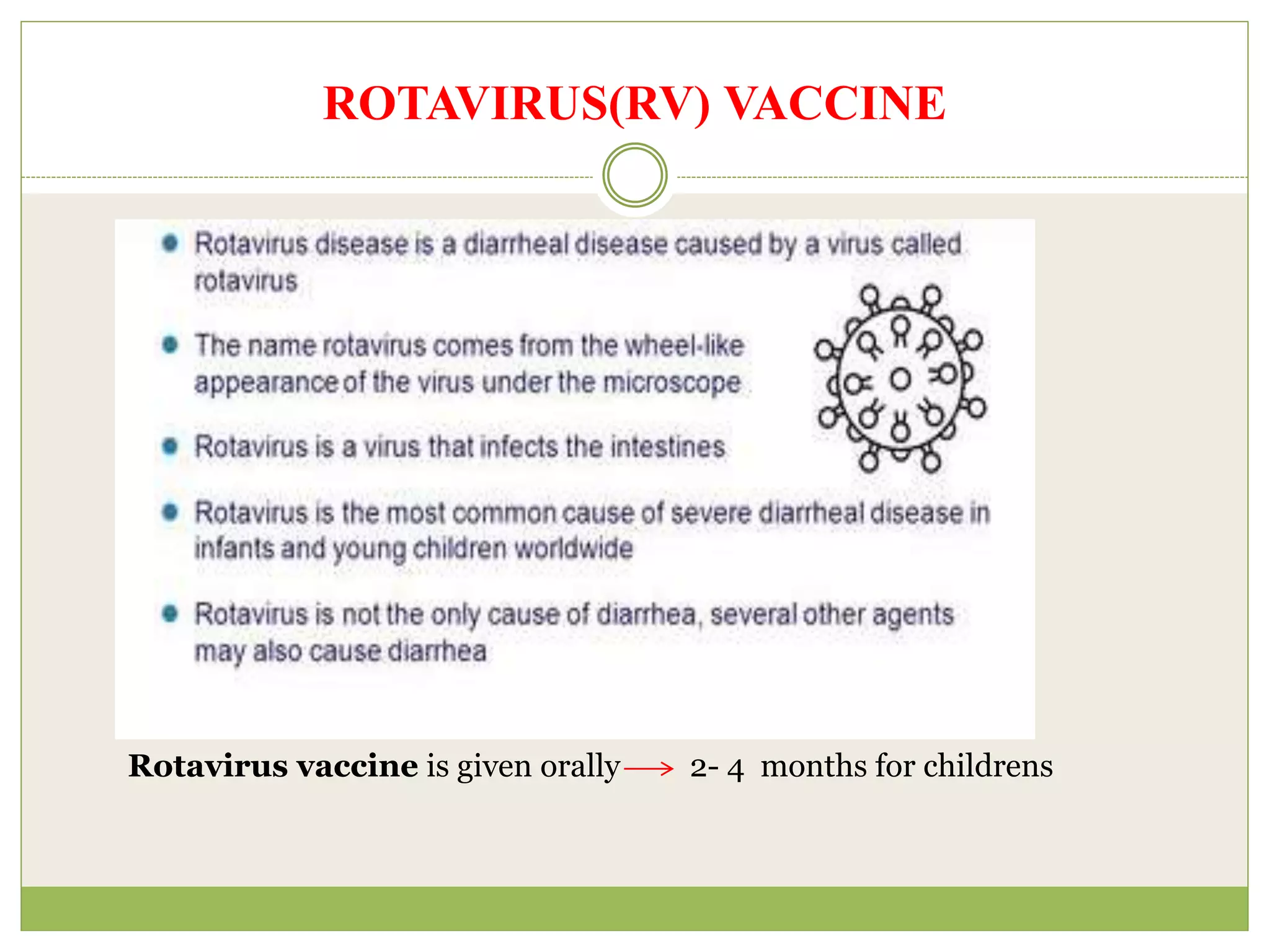
This document discusses several live attenuated vaccines:
1. Live attenuated vaccines work by attenuating (reducing virulence of) bacteria or viruses through prolonged abnormal culture conditions or chemical/heat treatment, selecting for mutants that can grow in these conditions but not cause disease.
2. Examples include the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis, developed by growing Mycobacterium bovis in increasing bile concentrations for 13 years until it was suitably attenuated.
3. Information is provided on administration routes and schedules for several live attenuated vaccines including BCG, oral polio, MMRV, rotavirus, and yellow fever vaccines.