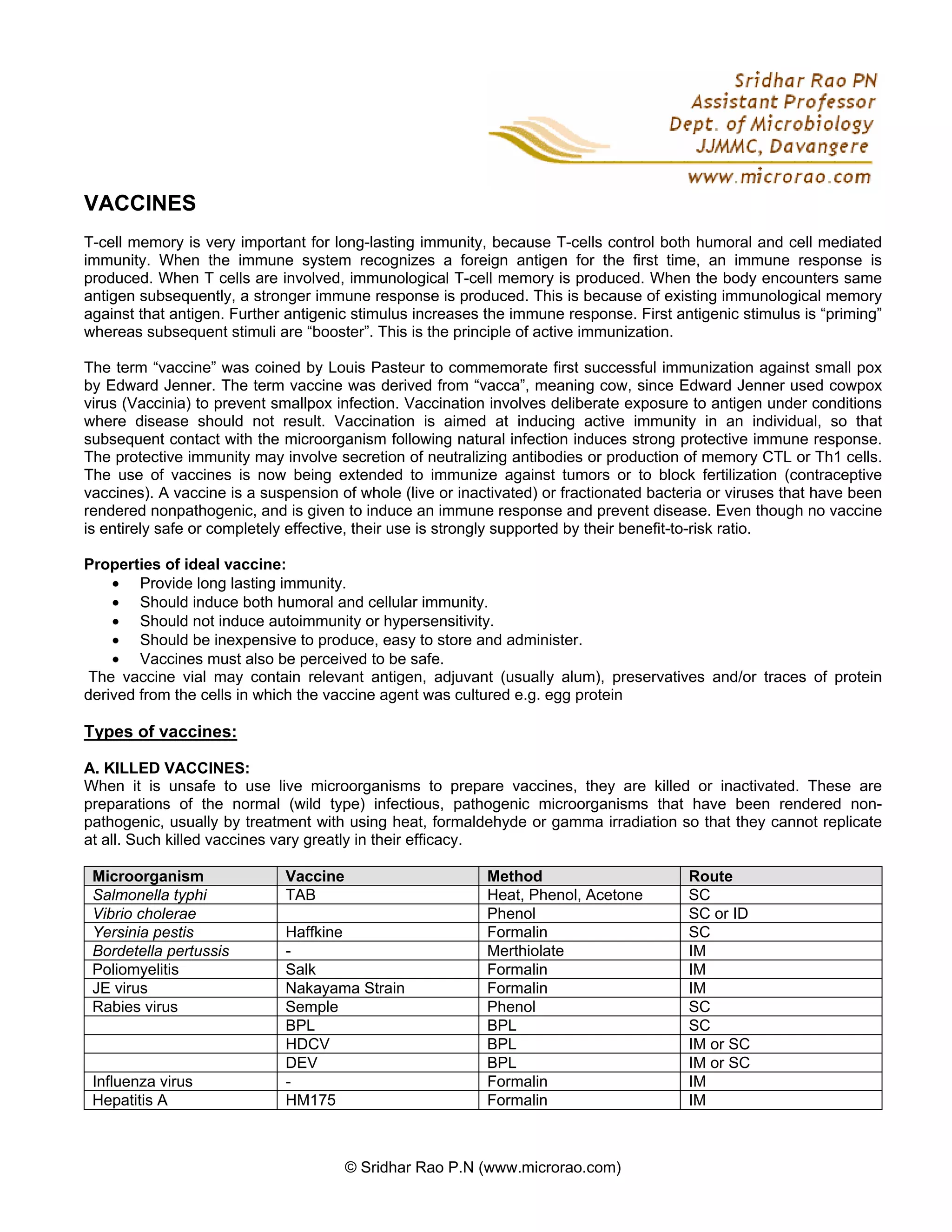
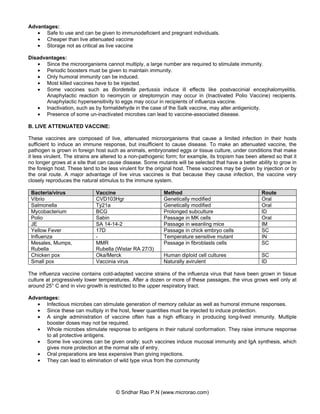
Vaccines work by inducing active immunity through exposure to antigens under controlled conditions. There are several types of vaccines including killed/inactivated vaccines which use dead pathogens, live attenuated vaccines which use weakened live pathogens, subunit vaccines which use purified antigens, conjugate vaccines which link polysaccharide antigens to proteins, recombinant vaccines which use genetically engineered antigens, and DNA vaccines which use genetic material encoding antigens. The ideal vaccine provides long-lasting immunity while being safe, inexpensive, and easy to produce and administer.