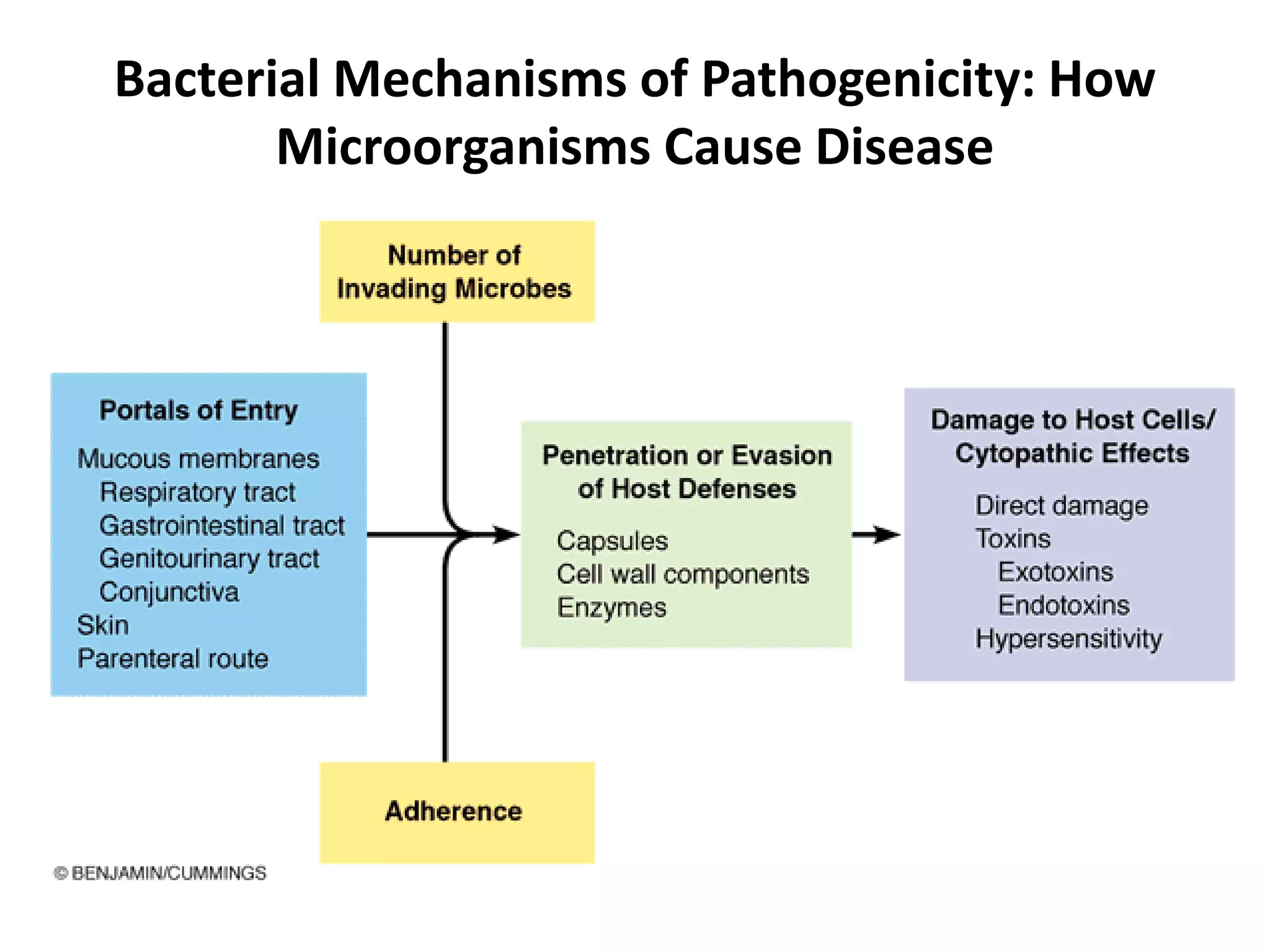
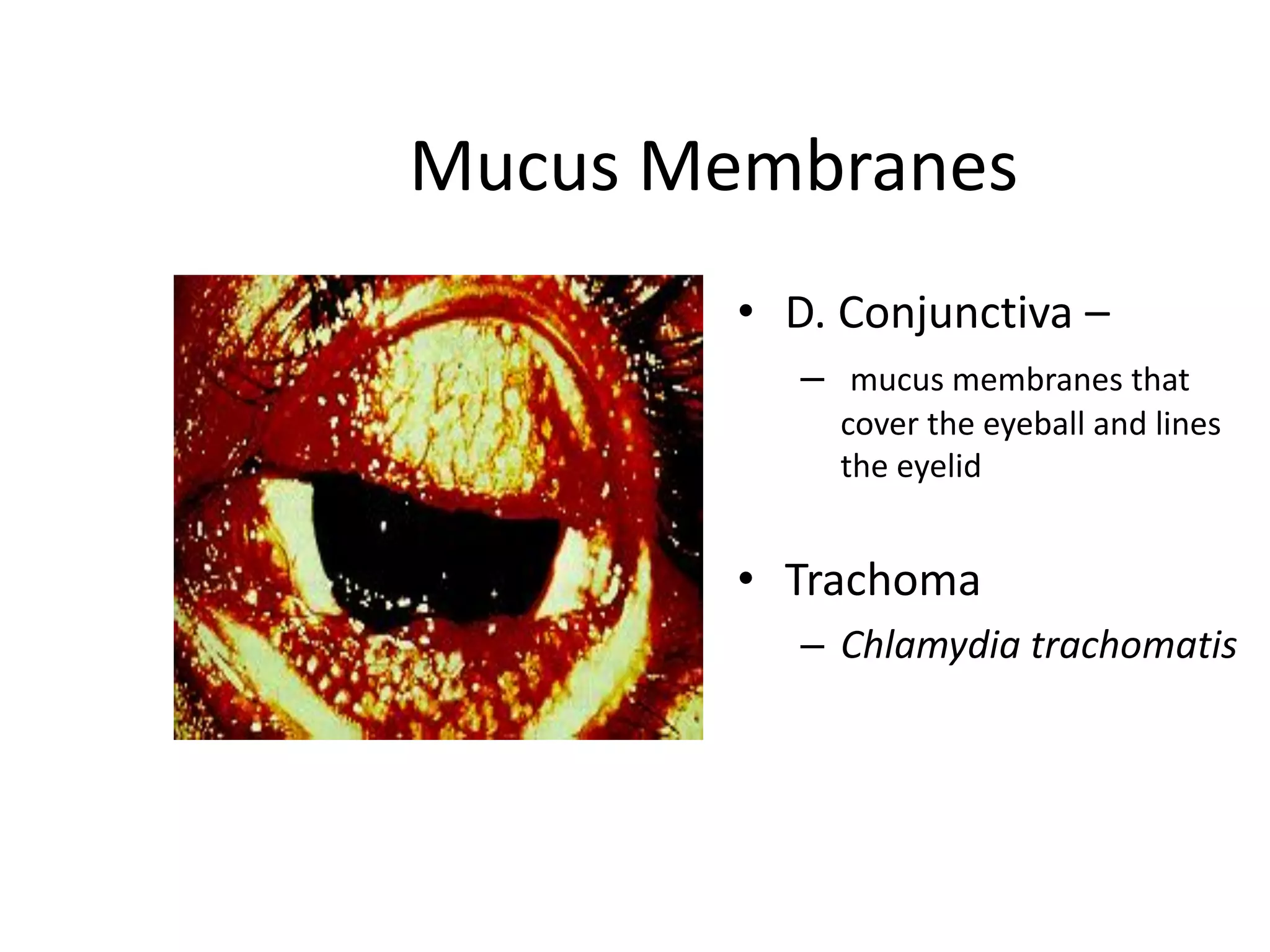
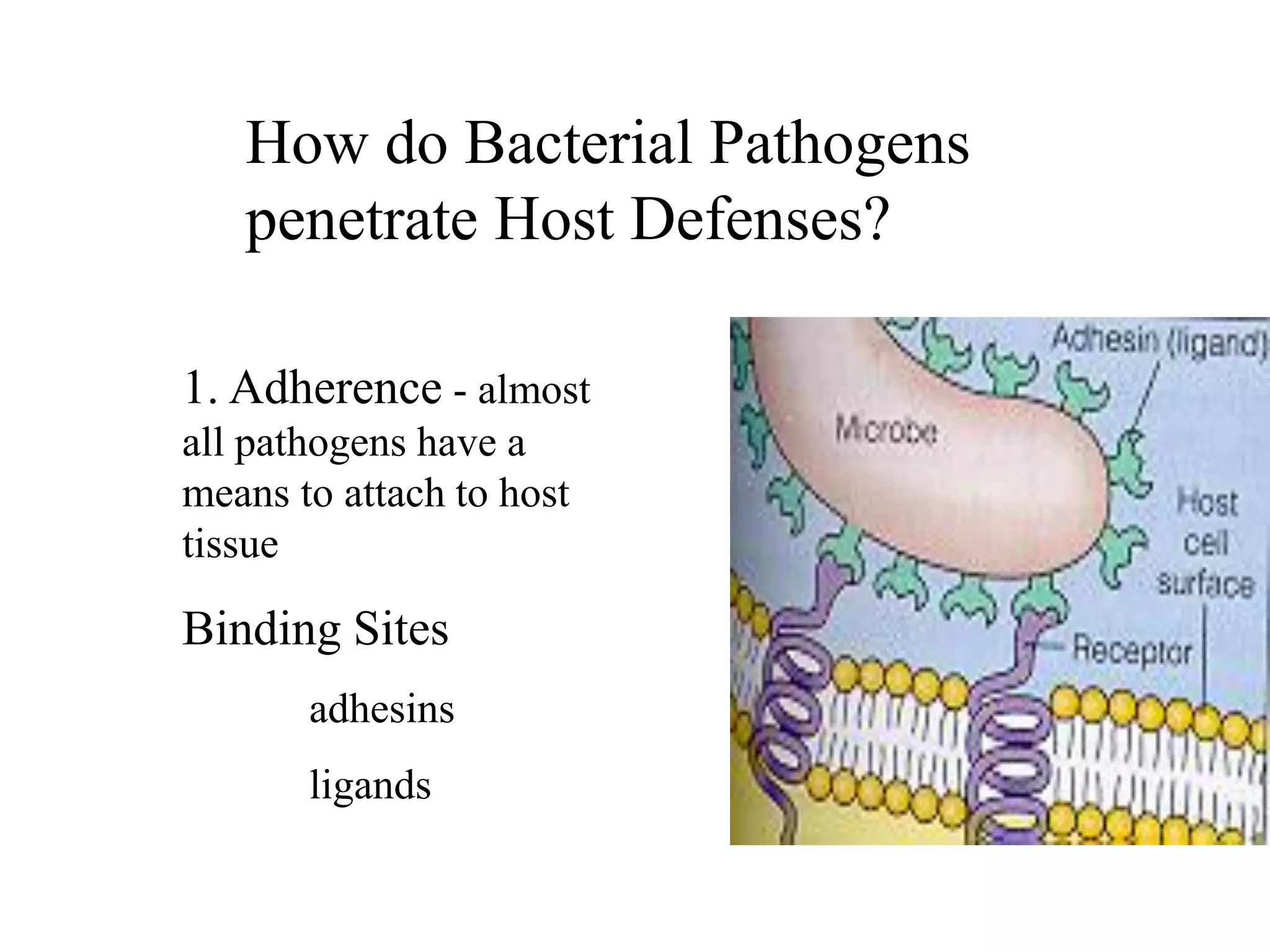
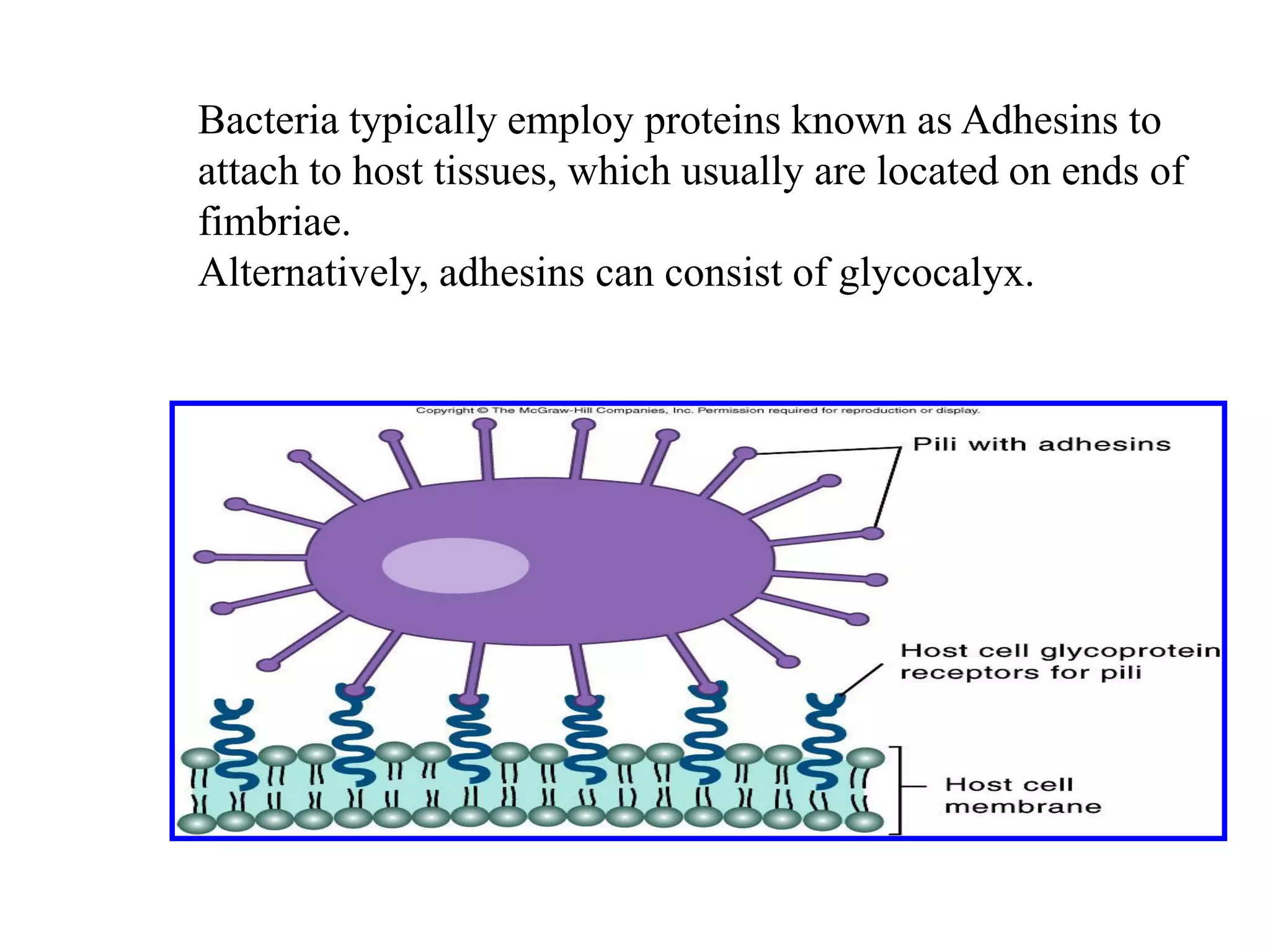
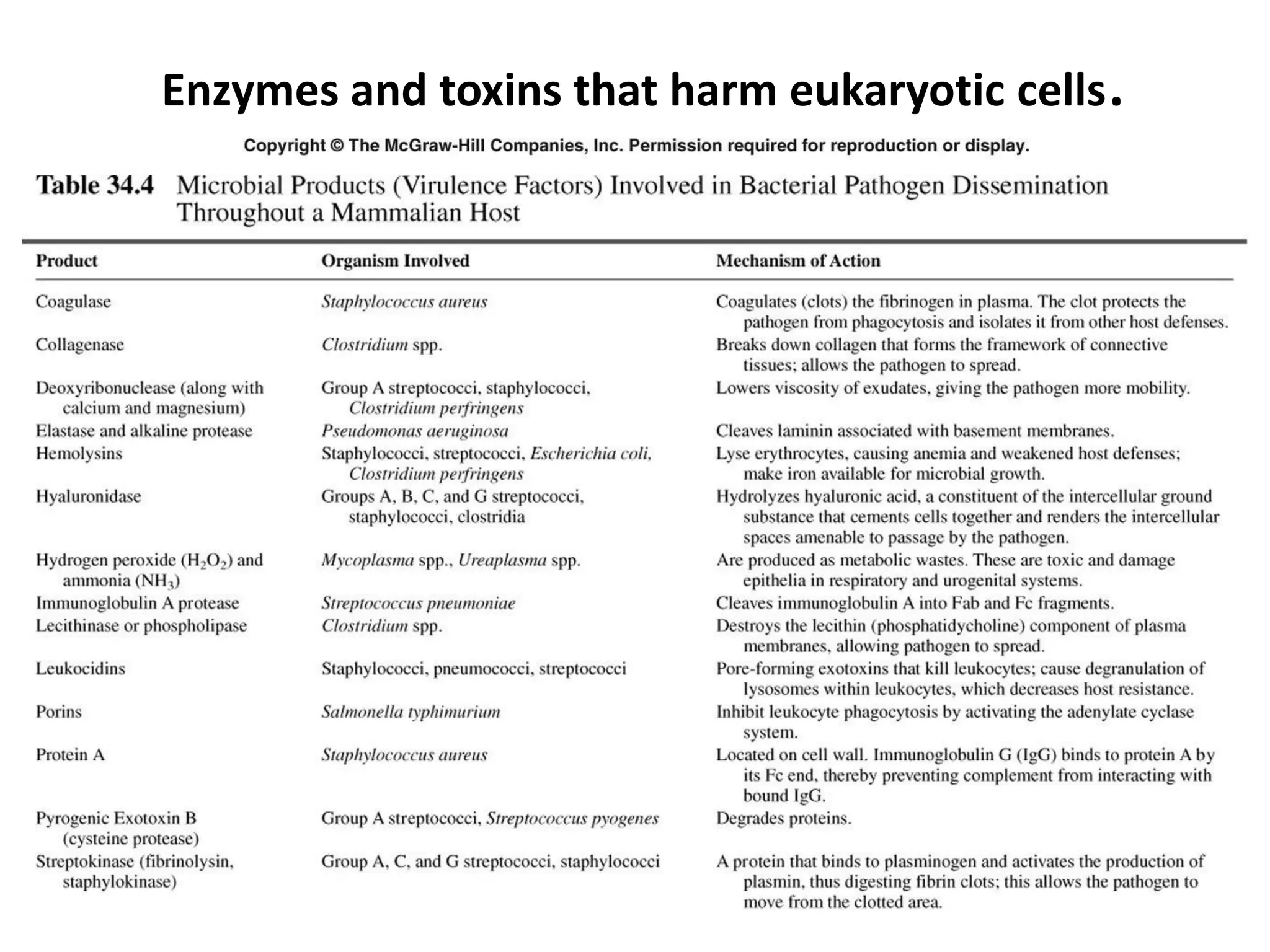
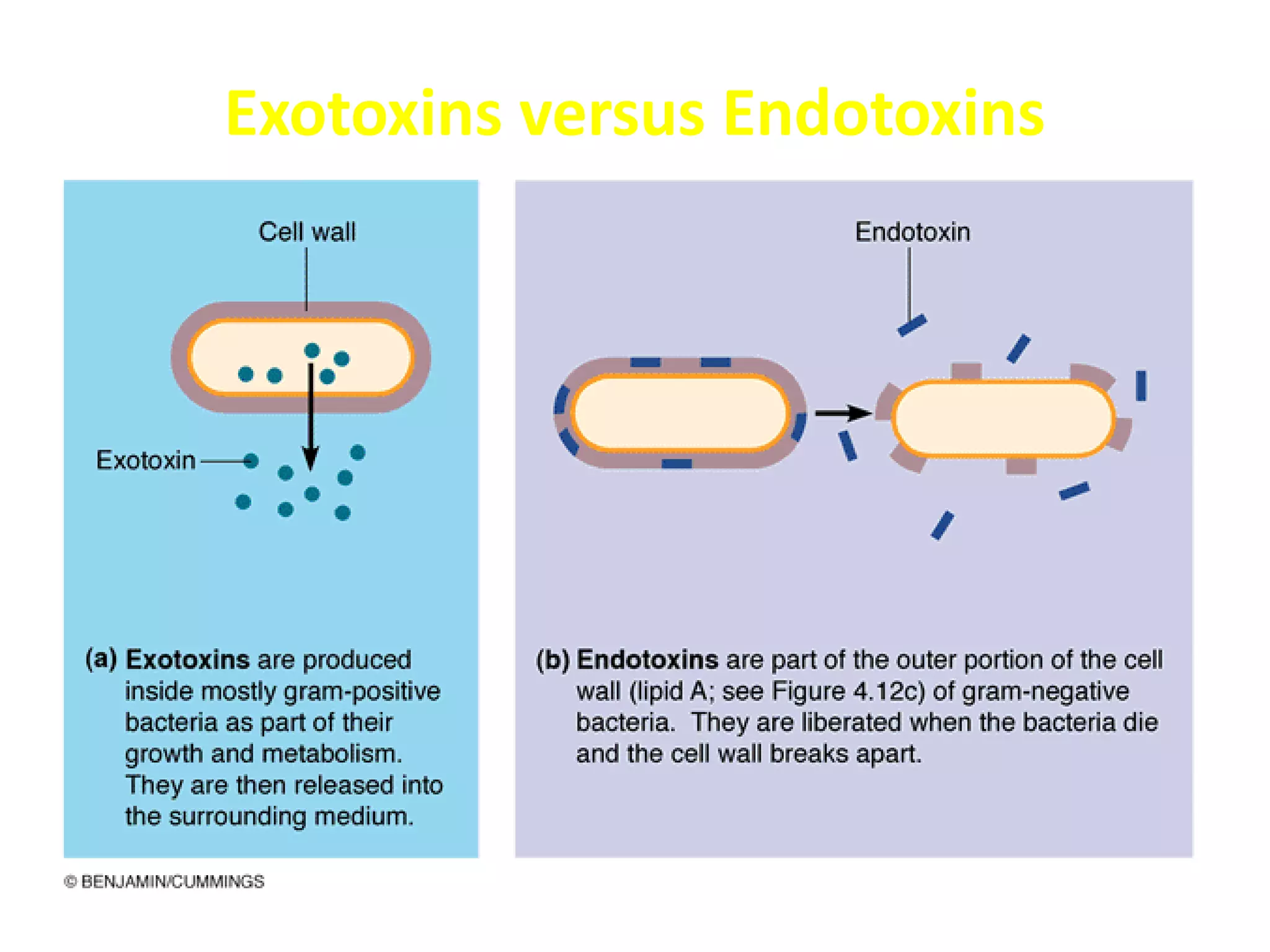
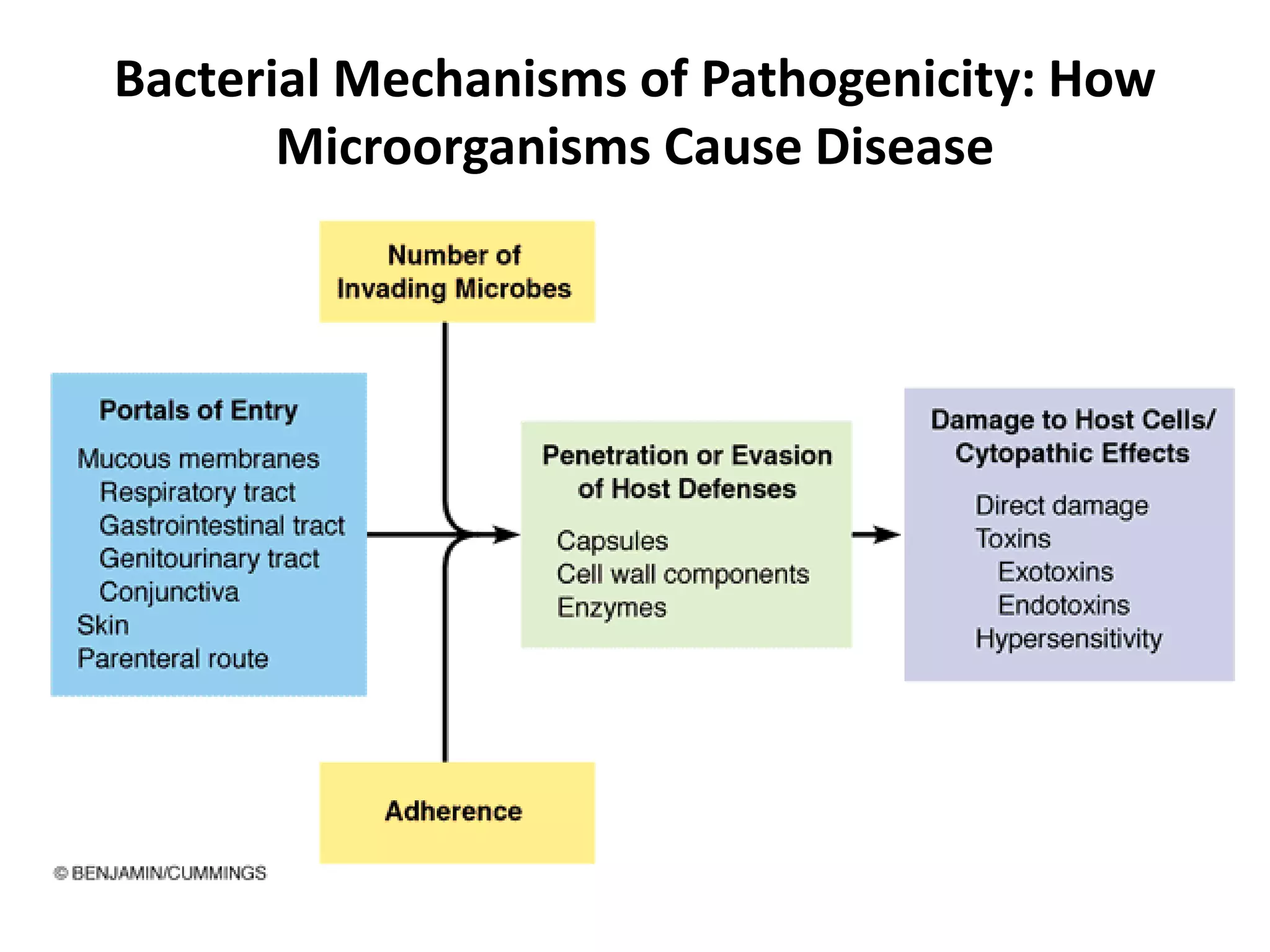
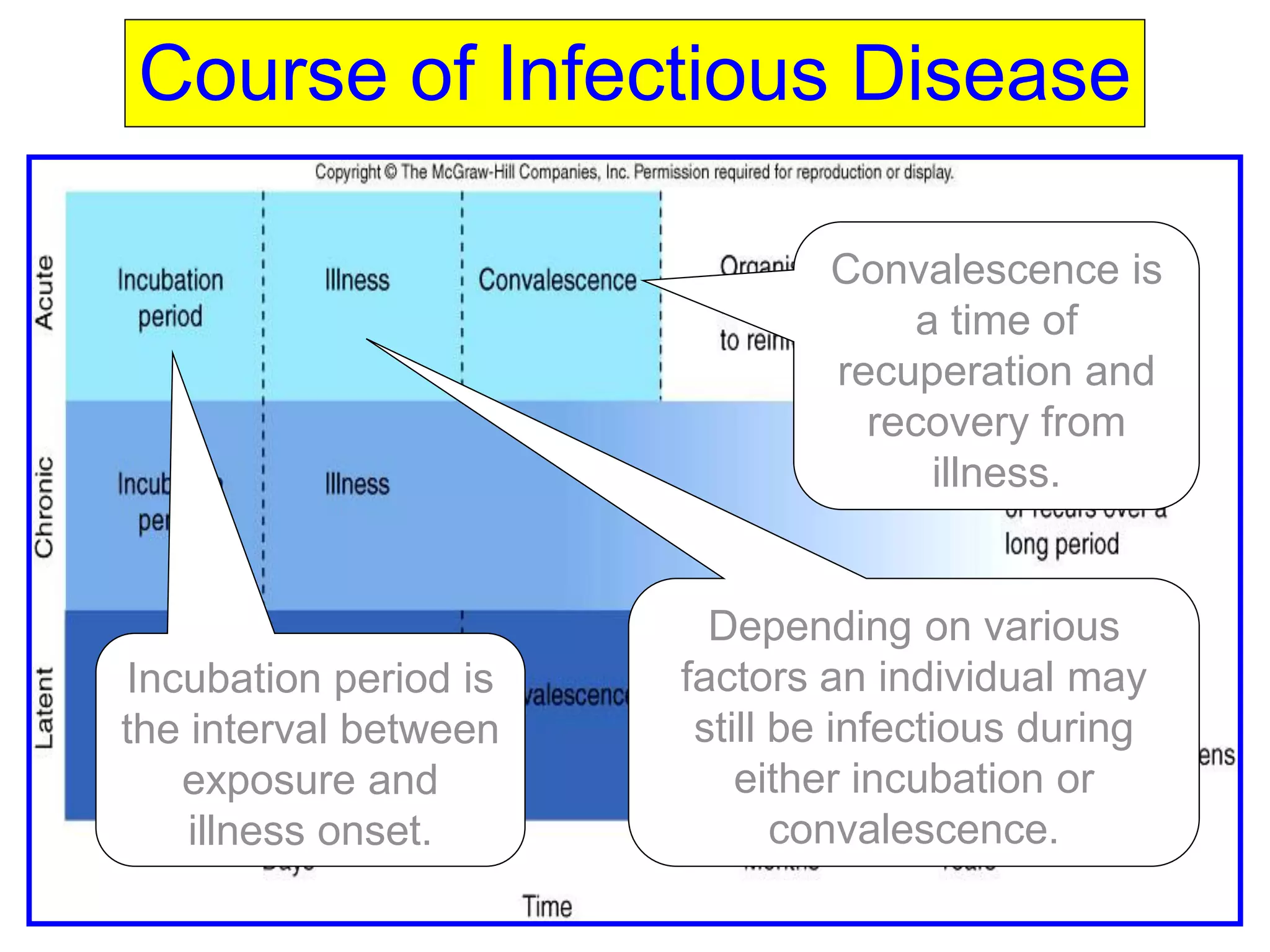
The document provides a comprehensive overview of bacterial mechanisms of pathogenicity, including definitions of key terms such as pathogenicity, virulence, and types of infections. It outlines how bacteria enter the host, evade defenses, and produce toxins, detailing the classification of infections and the various ways transmission occurs. Additionally, it explains the disease progression from incubation to convalescence and highlights the importance of understanding these mechanisms in the context of infectious diseases.