Embed presentation
Downloaded 121 times



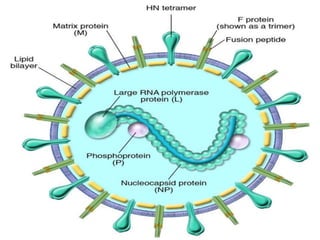



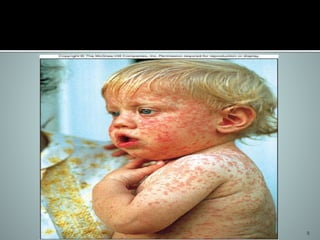

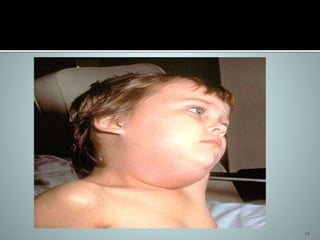



1. The document discusses two paramyxoviruses: measles and mumps. 2. Measles virus causes a fever and rash that begins on the forehead and spreads to the rest of the body. While measles itself does not directly kill, it can lead to secondary infections like pneumonia that do cause death. 3. Mumps virus causes painful swelling of the parotid glands, making it difficult to chew or swallow. Symptoms last about a week and are generally more severe in individuals past puberty. There is no vaccine for mumps, but it can be treated with ribavirin. Frequent hand washing can help decrease spread of the virus.












