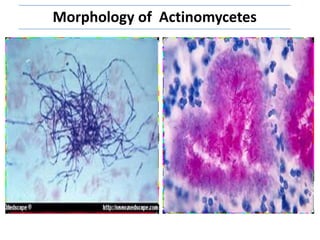
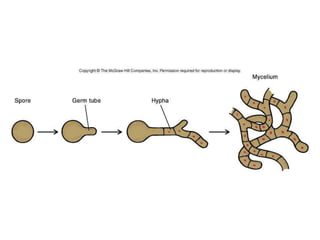
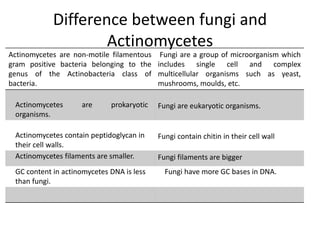
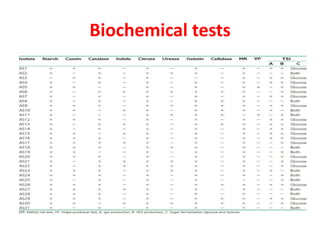
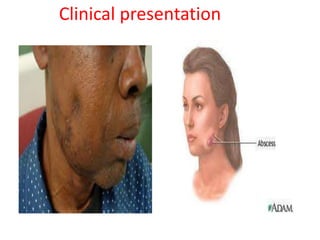
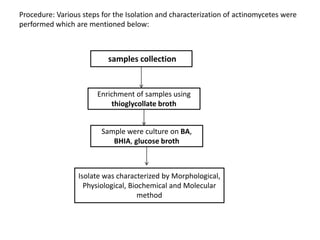
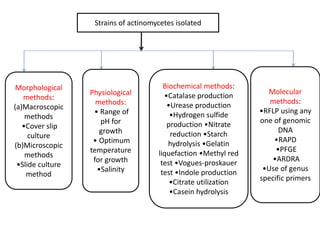
Actinomycetes are a diverse group of filamentous, gram-positive bacteria. They are classified within the domain bacteria and phylum Actinobacteria. Actinomycetes live predominantly in soil where they help break down recalcitrant compounds. While most species are harmless, some can cause infections in humans called actinomycosis. Important genera include Actinomyces, Nocardia, and Streptomyces. Actinomycetes are distinguished from fungi by being prokaryotic, containing peptidoglycan in their cell walls rather than chitin, and having smaller filaments. Diagnosis of actinomycosis involves identifying the pathogen's sulfur granules in biopsy samples