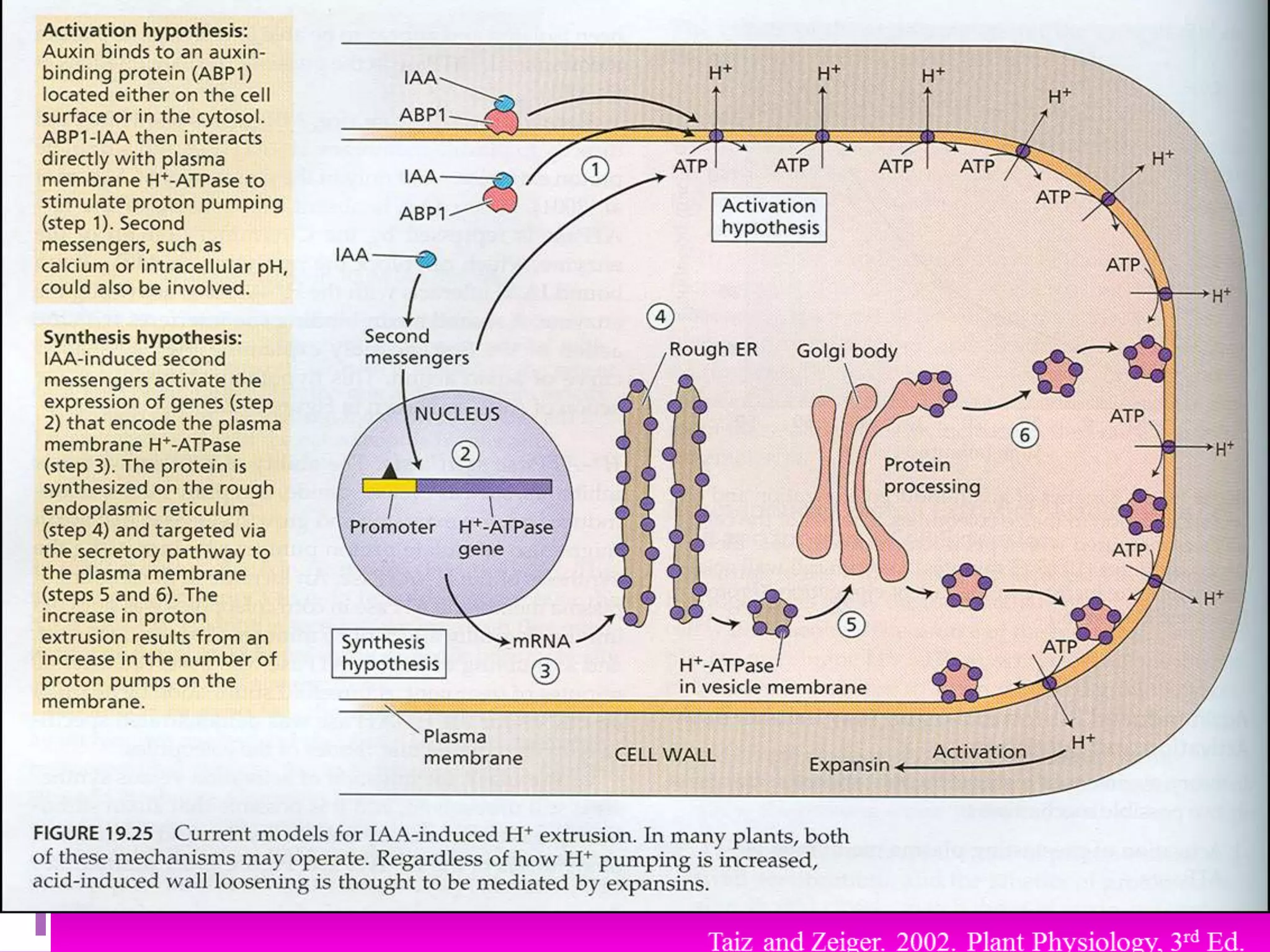
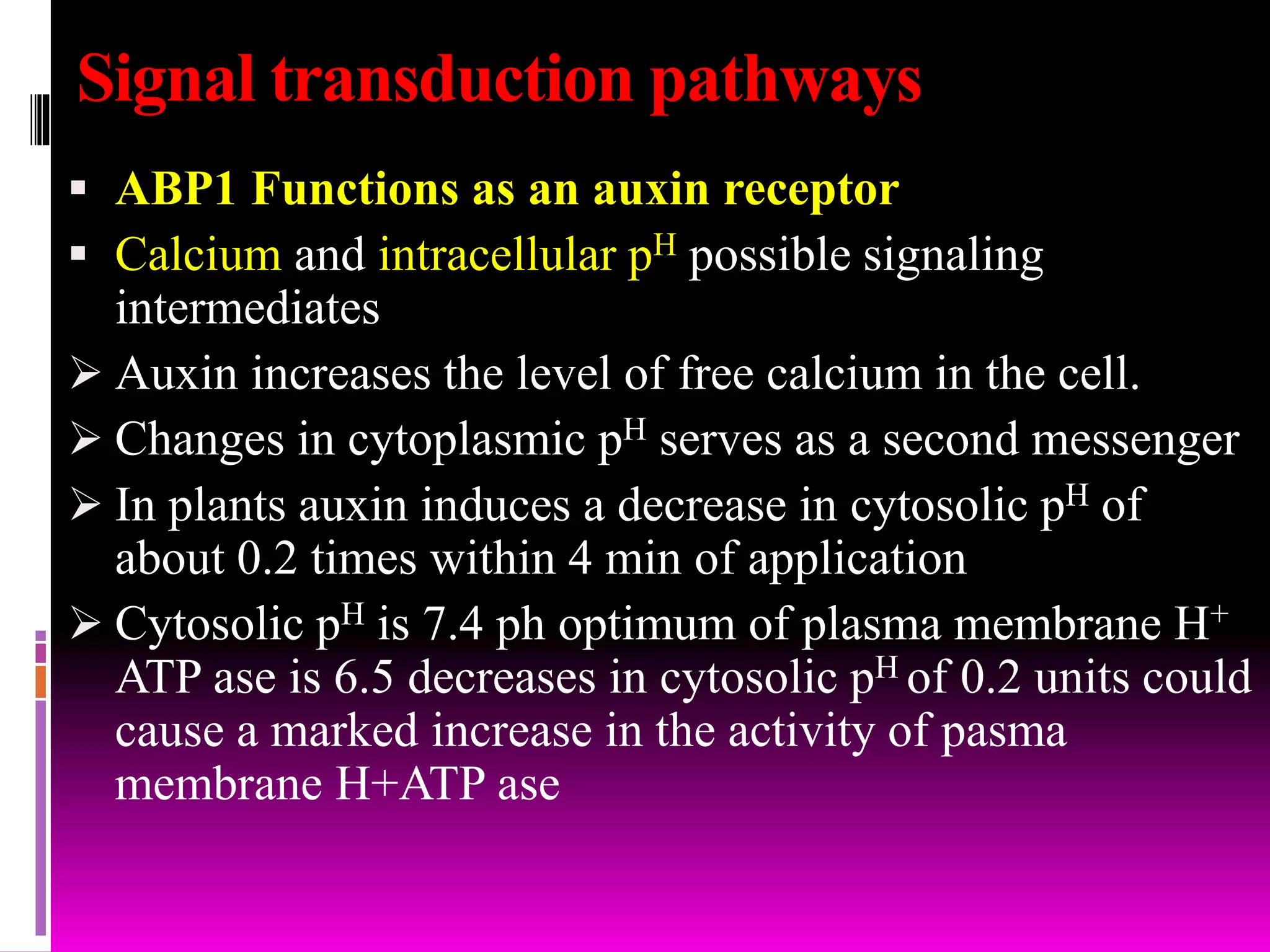
This document discusses auxin signaling and its role in cell elongation. It notes that auxin promotes growth in stems by increasing cell wall extensibility. This is achieved through auxin-induced proton pumping, which acidifies the cell wall and activates wall-loosening factors. The document outlines several pathways involved in auxin signaling, including the AUX/IAA, SAUR and GH3 gene families that are early auxin response genes regulating growth and development. It also discusses intracellular messengers like calcium and pH in auxin signaling and the roles of these pathways in mediating the cell's response to auxin.