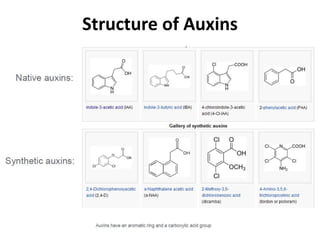
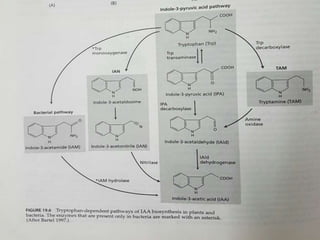
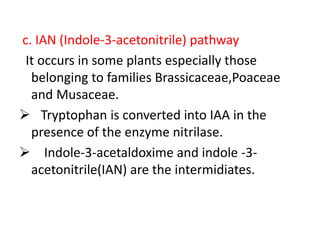
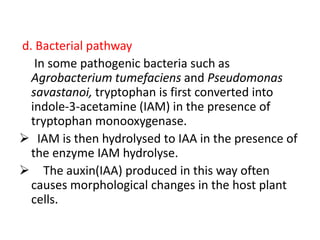
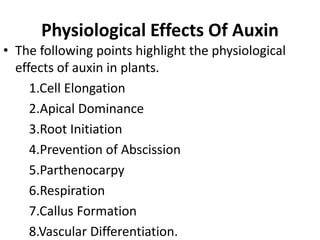
Auxin is the first plant hormone discovered. It is produced throughout the plant and regulates many growth processes. There are two main pathways for auxin (IAA) biosynthesis - tryptophan-dependent and tryptophan-independent. Auxin's mechanism of action involves binding to receptor proteins and promoting proton pumping, which acidifies the cell wall and activates expansin proteins, leading to cell wall loosening and elongation. The physiological effects of auxin include stimulating cell elongation, controlling apical dominance, initiating root formation, preventing abscission, and promoting callus growth and vascular differentiation.