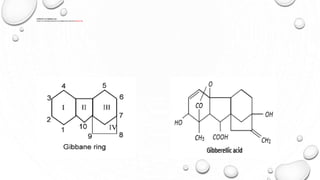
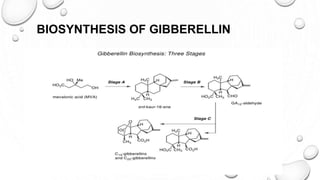
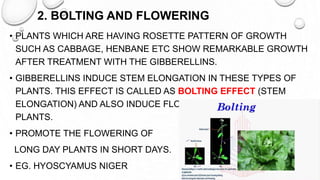
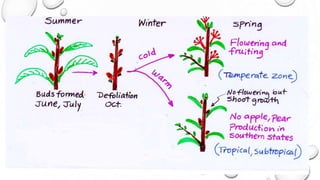
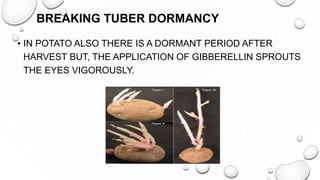
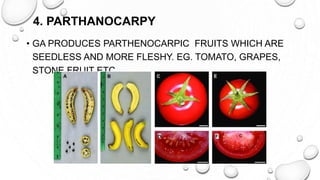
This document discusses gibberellins, a class of plant hormones. It was first discovered in 1928 by a Japanese scientist who observed rice plants infected by the fungus Gibberella fujikuroi showed excessive stem elongation. There are over 70 known forms of gibberellins that regulate various plant developmental processes such as stem elongation, germination, flowering, and fruit development. Gibberellins are widely distributed in plants and are involved in many physiological roles including stem elongation, bolting, seed germination, breaking bud and tuber dormancy, parthenocarpy, and flowering.