Embed presentation
Downloaded 40 times




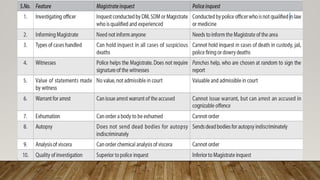


There are two types of inquests conducted in India to investigate unnatural or suspicious deaths: police inquests and magistrate's inquests. Police inquests are conducted by an investigating police officer of a certain rank or higher and involve notifying the magistrate, inspecting the death scene, questioning witnesses, and preparing a report on the cause of death. Magistrate's inquests are conducted by district or metropolitan magistrates and are required for deaths in police custody, prison, or other circumstances indicating foul play. Both inquest types aim to determine the cause and circumstances of unnatural deaths.






