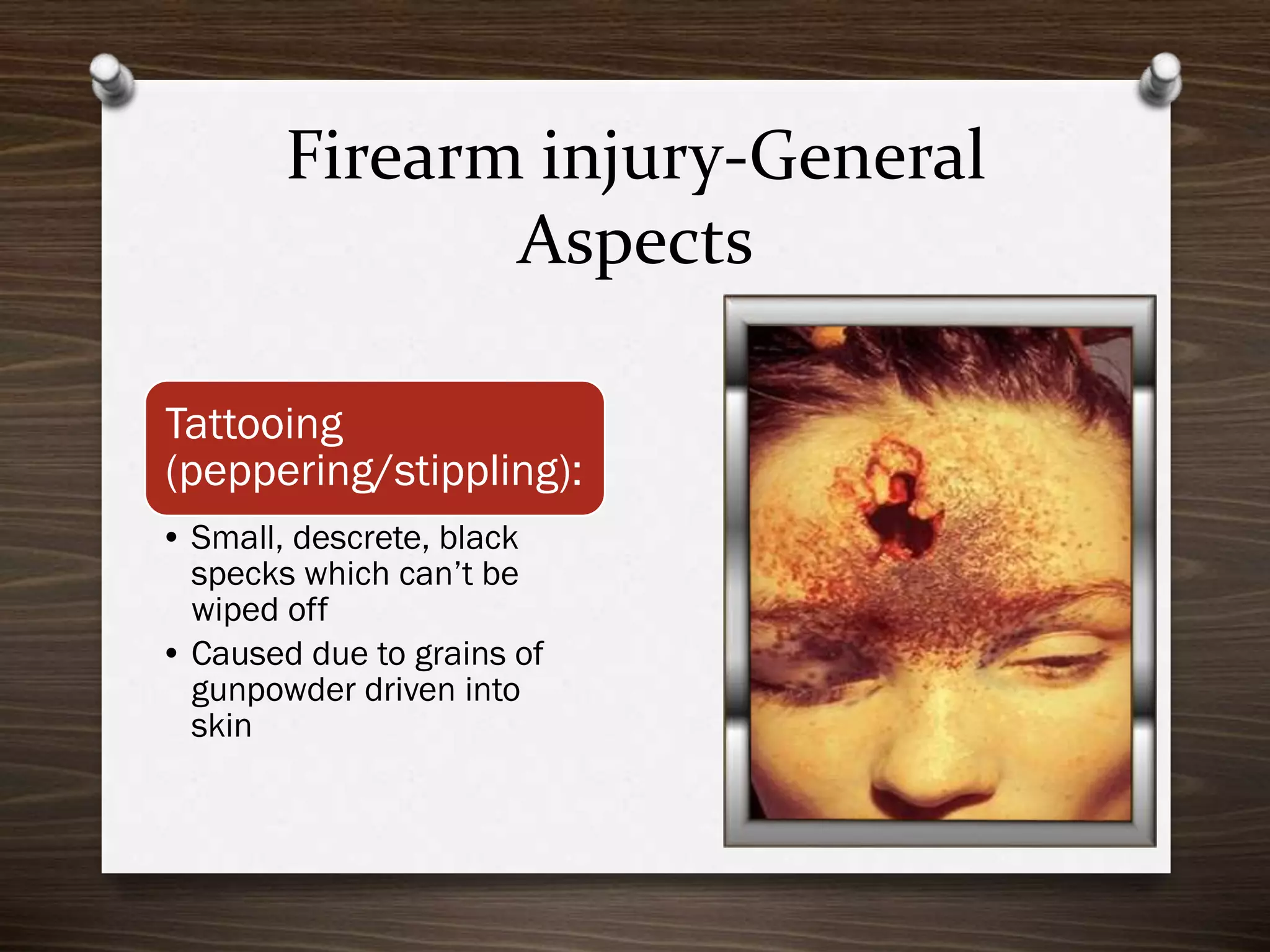
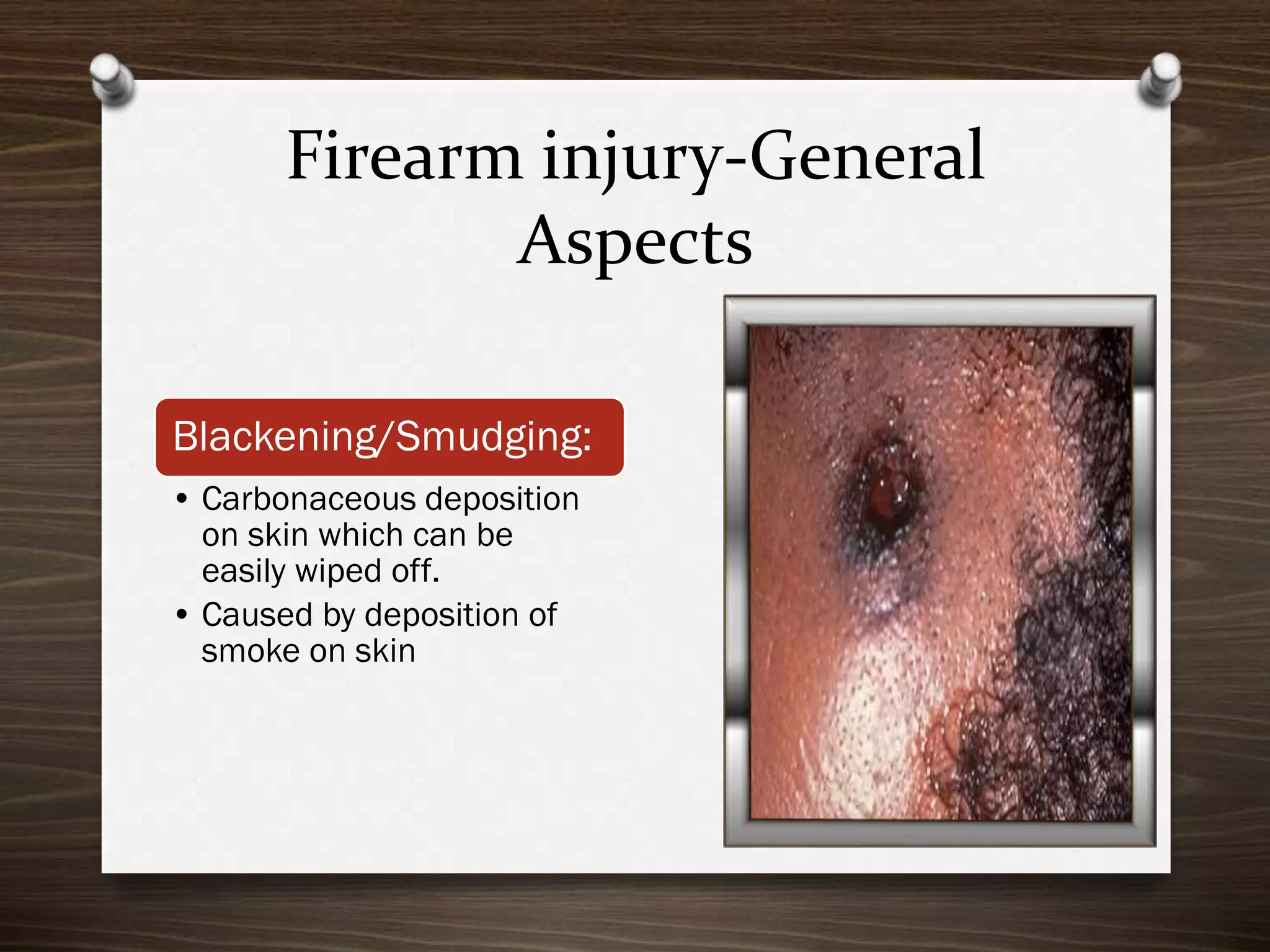
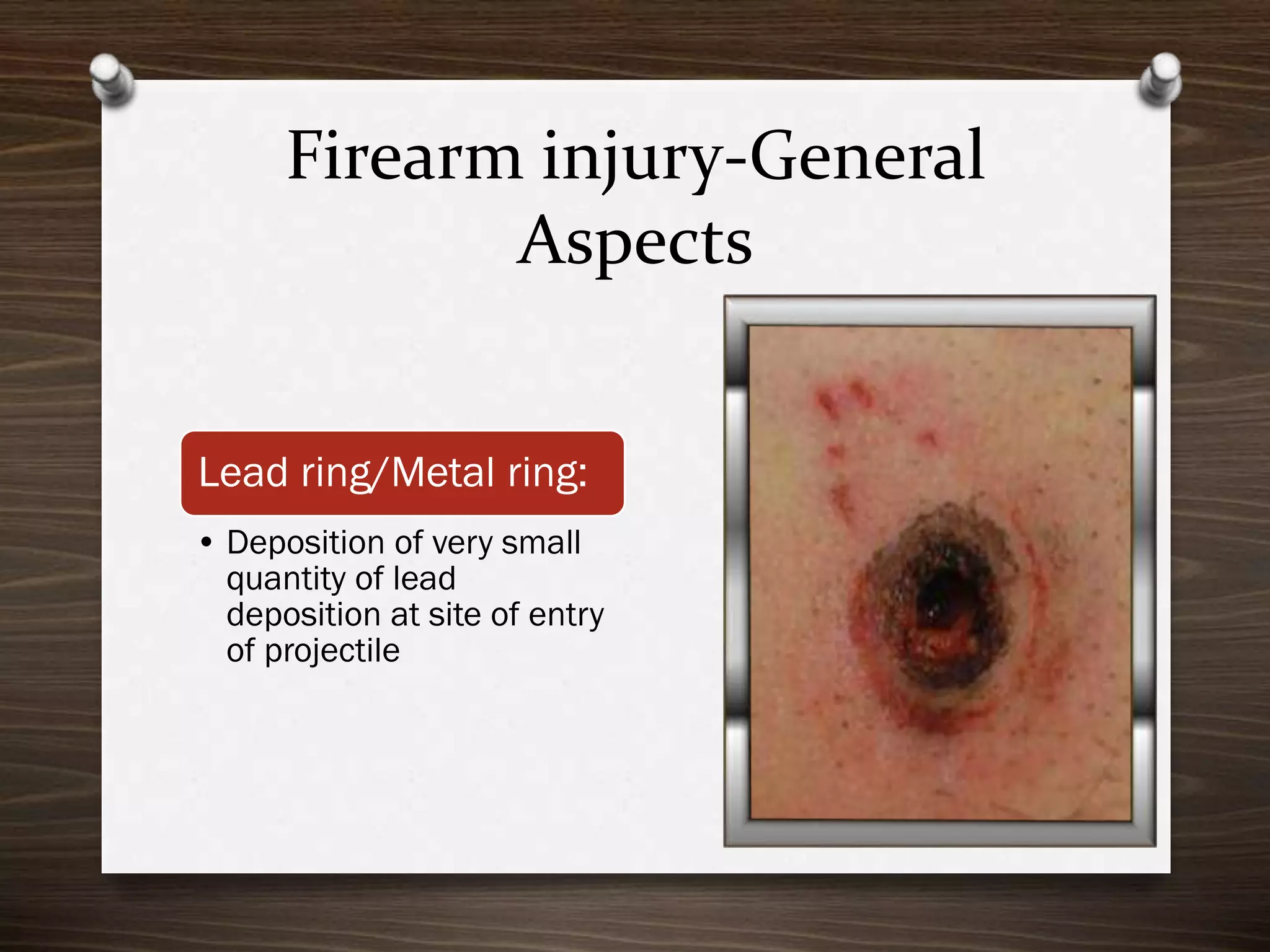
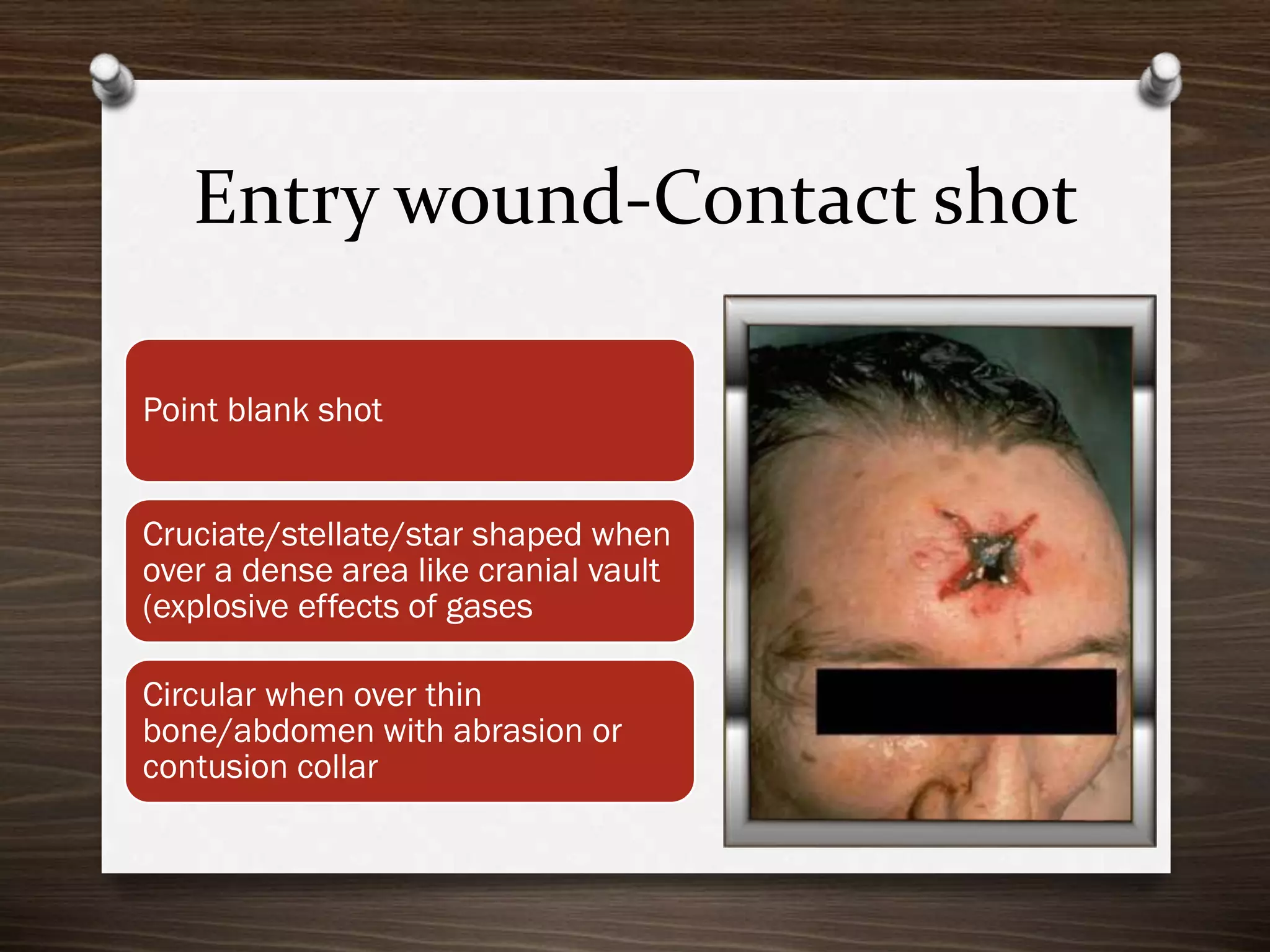
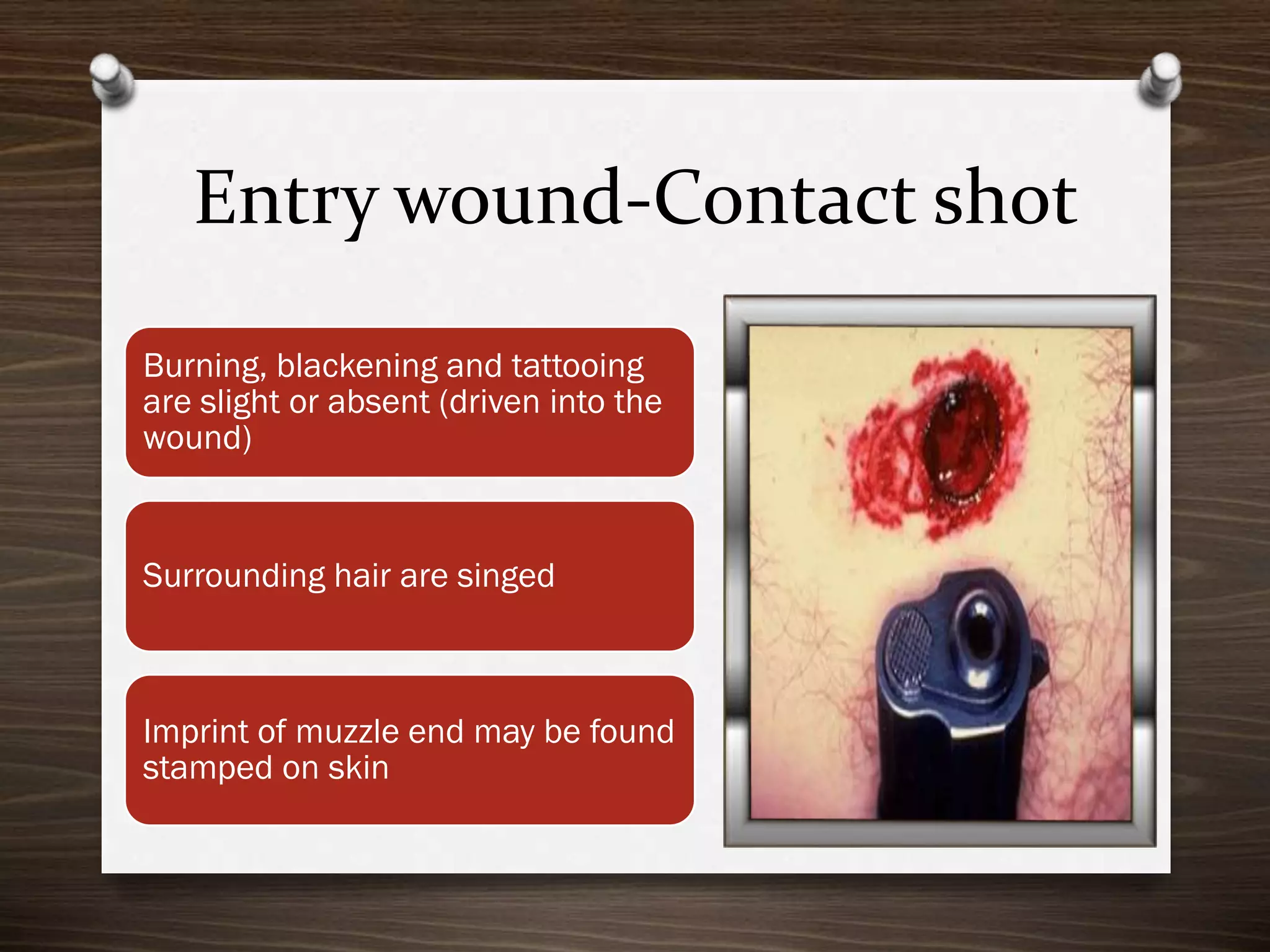
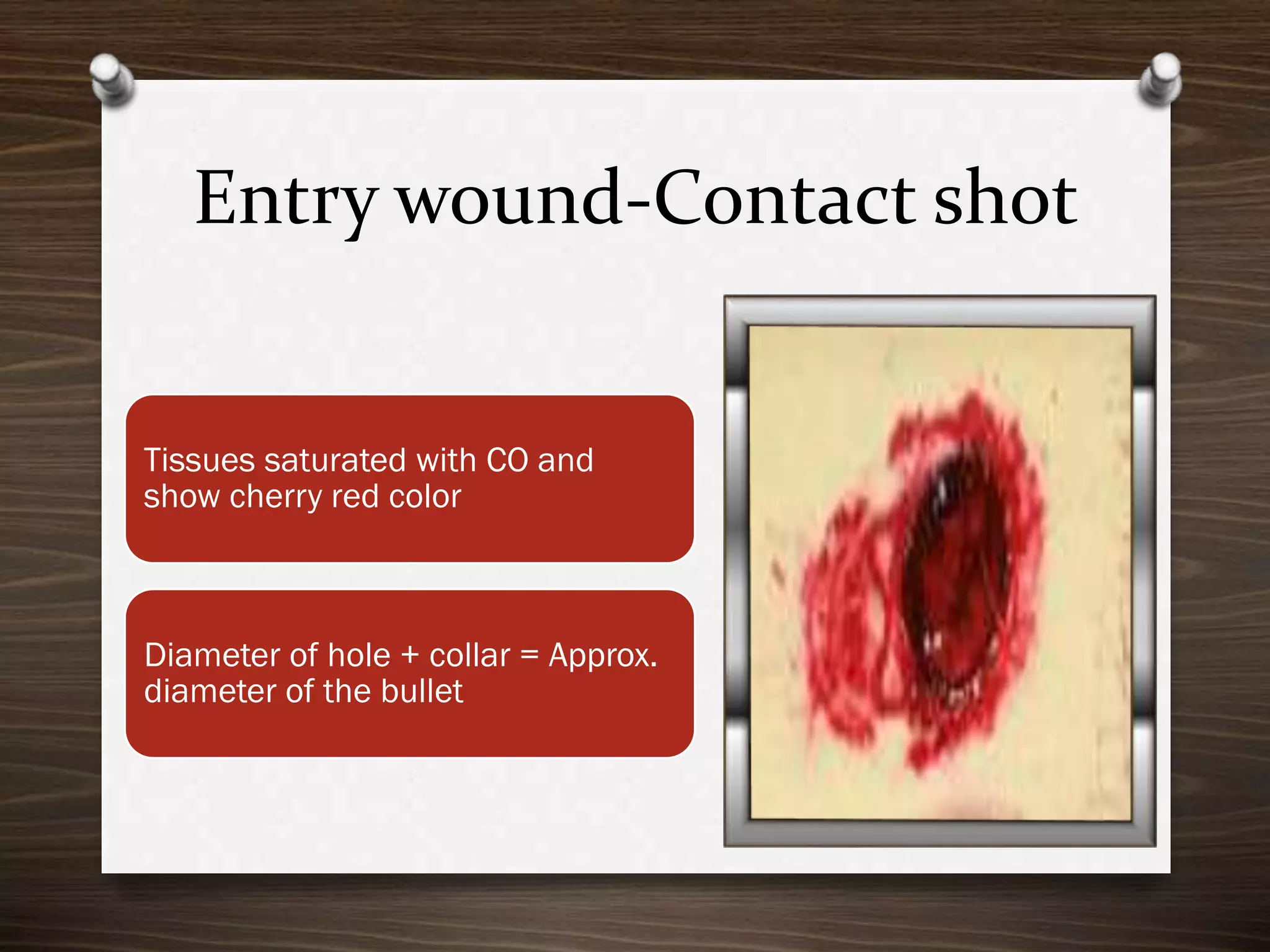
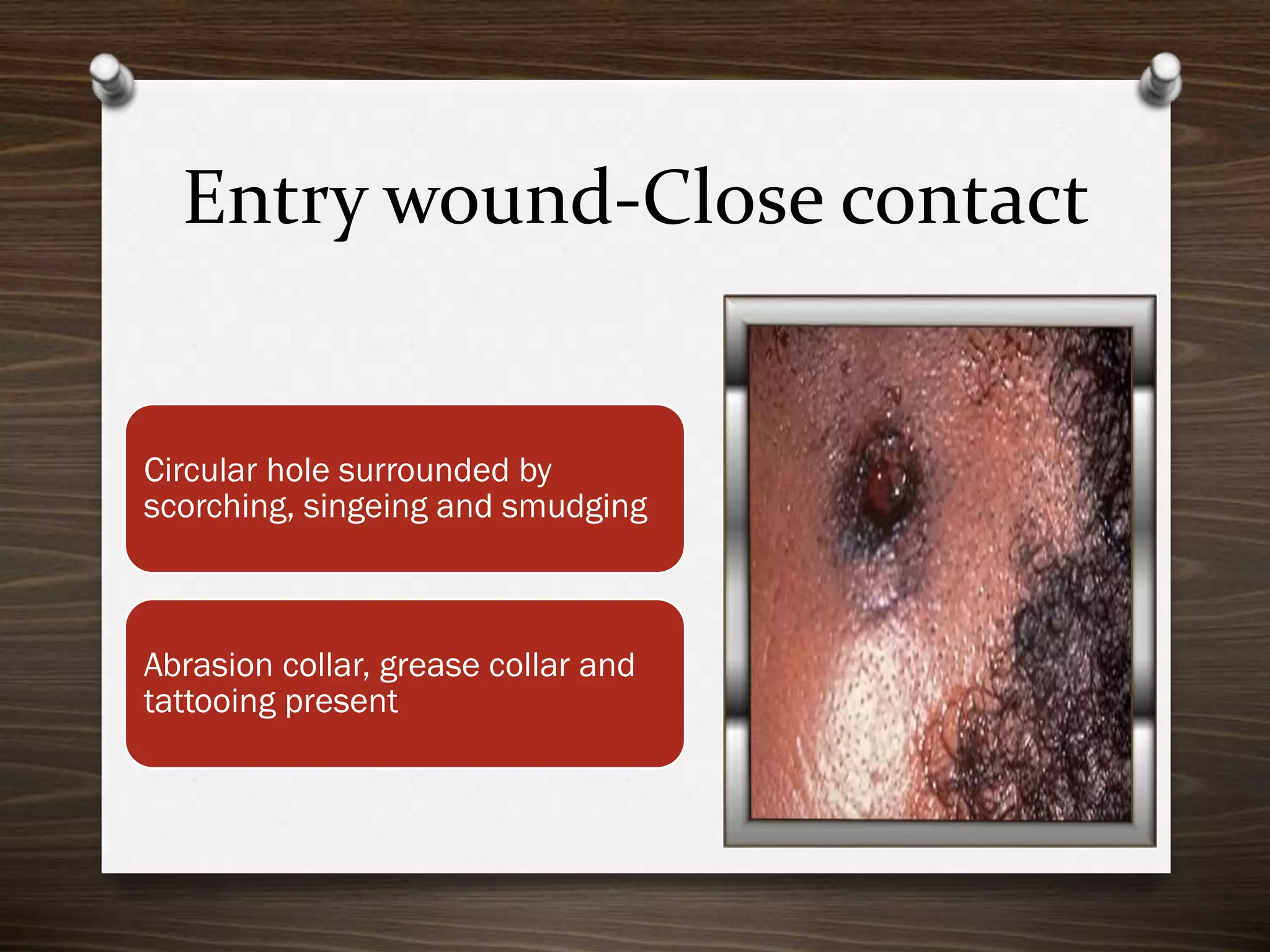
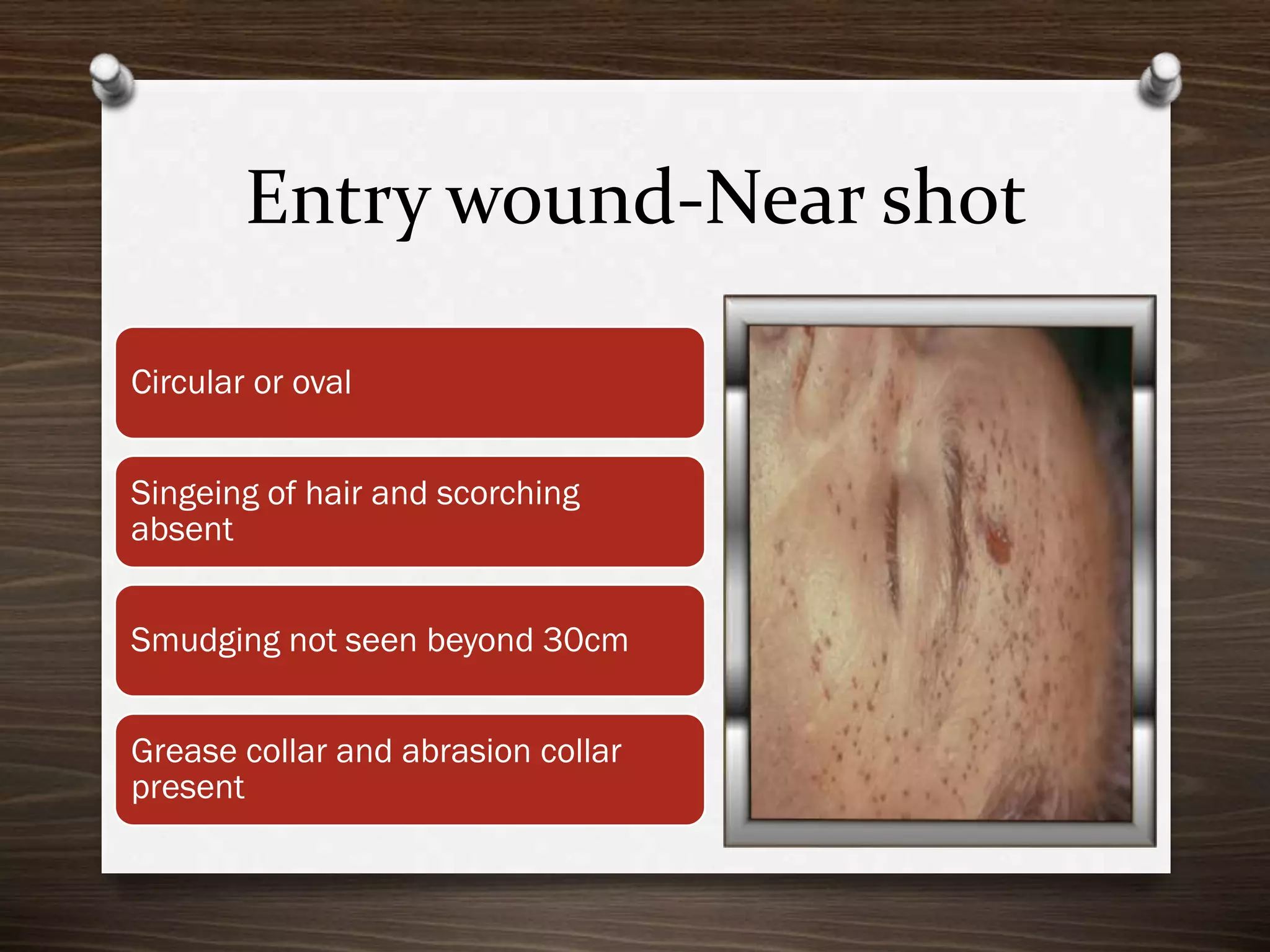
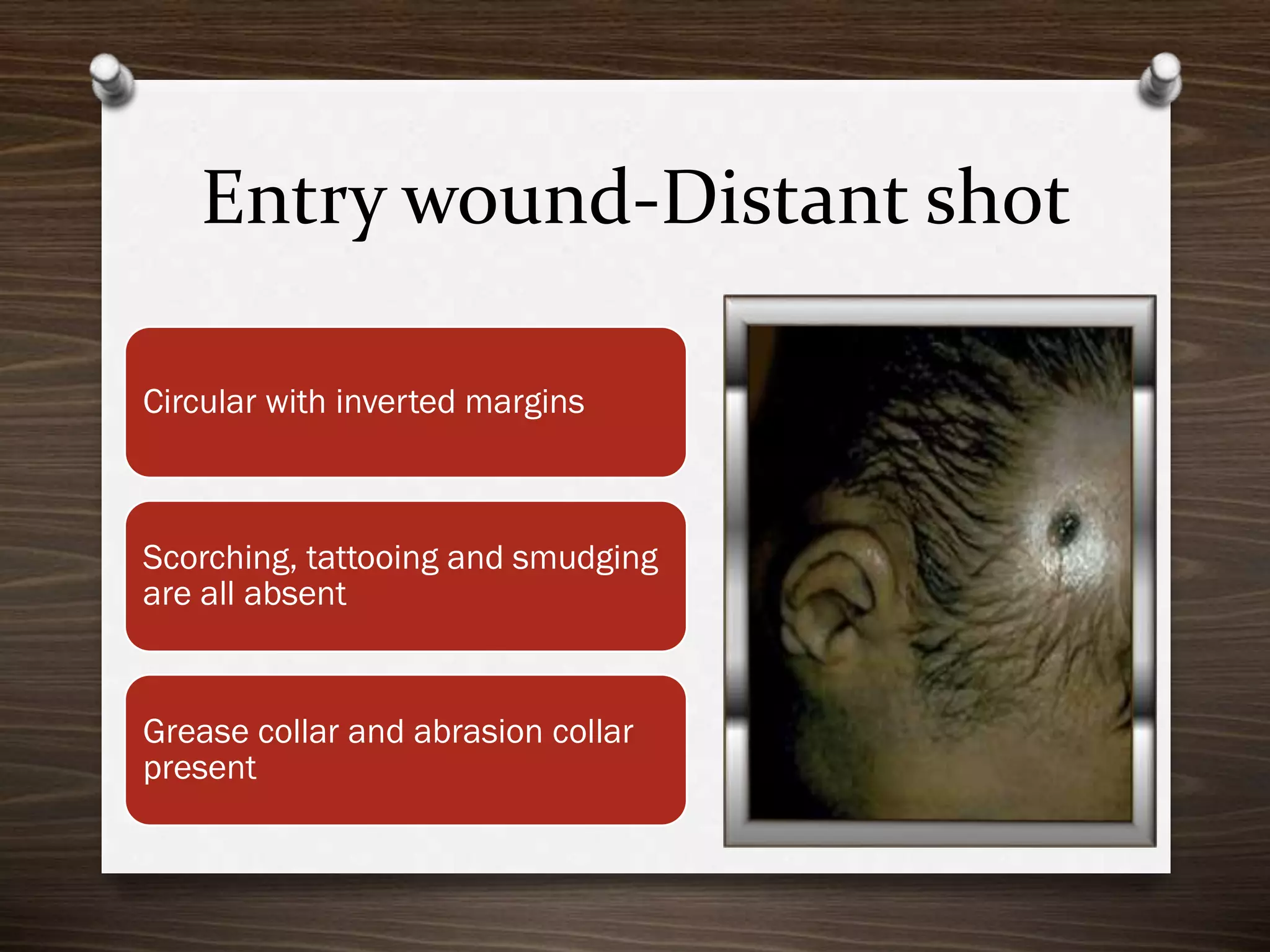
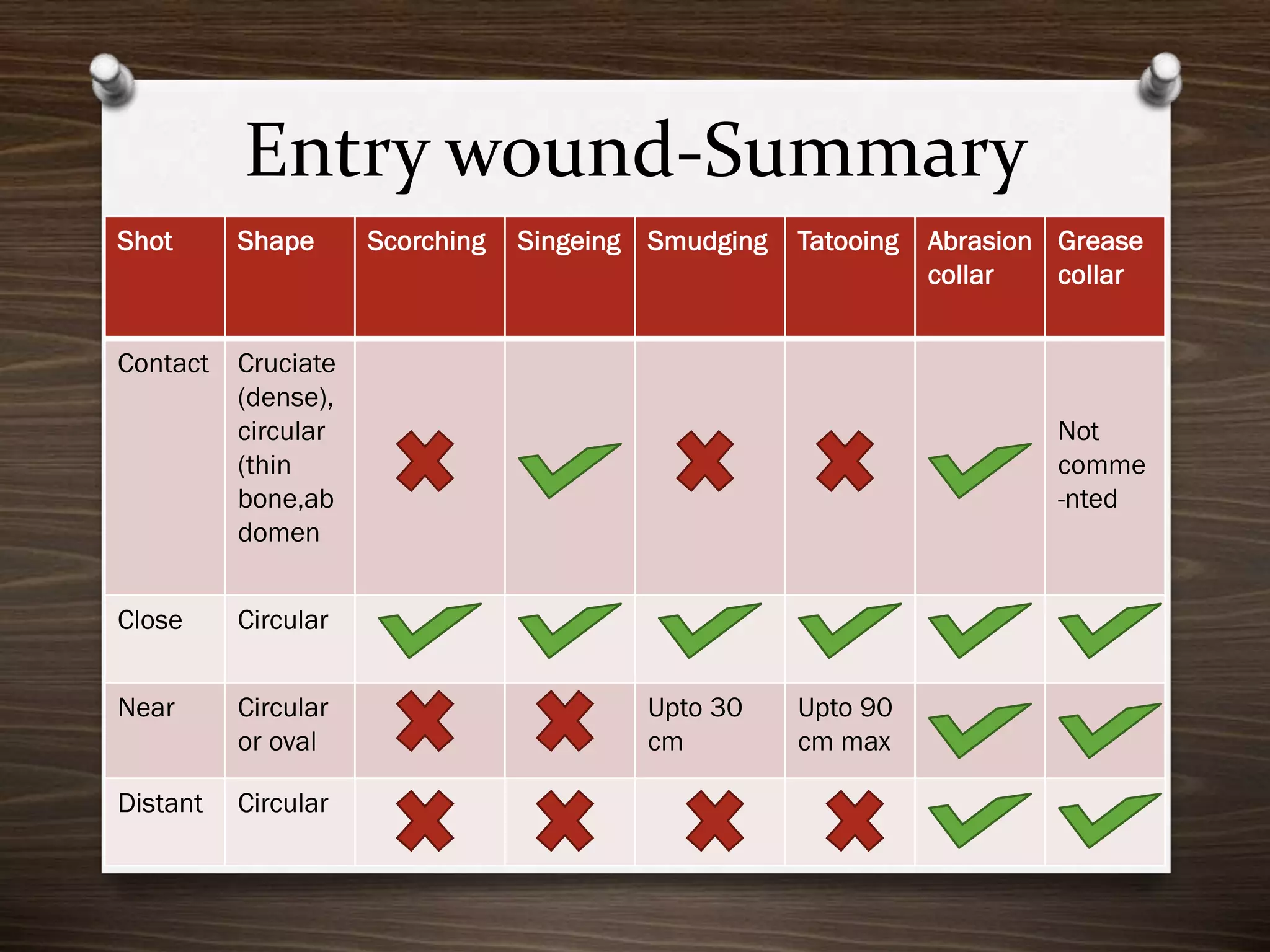
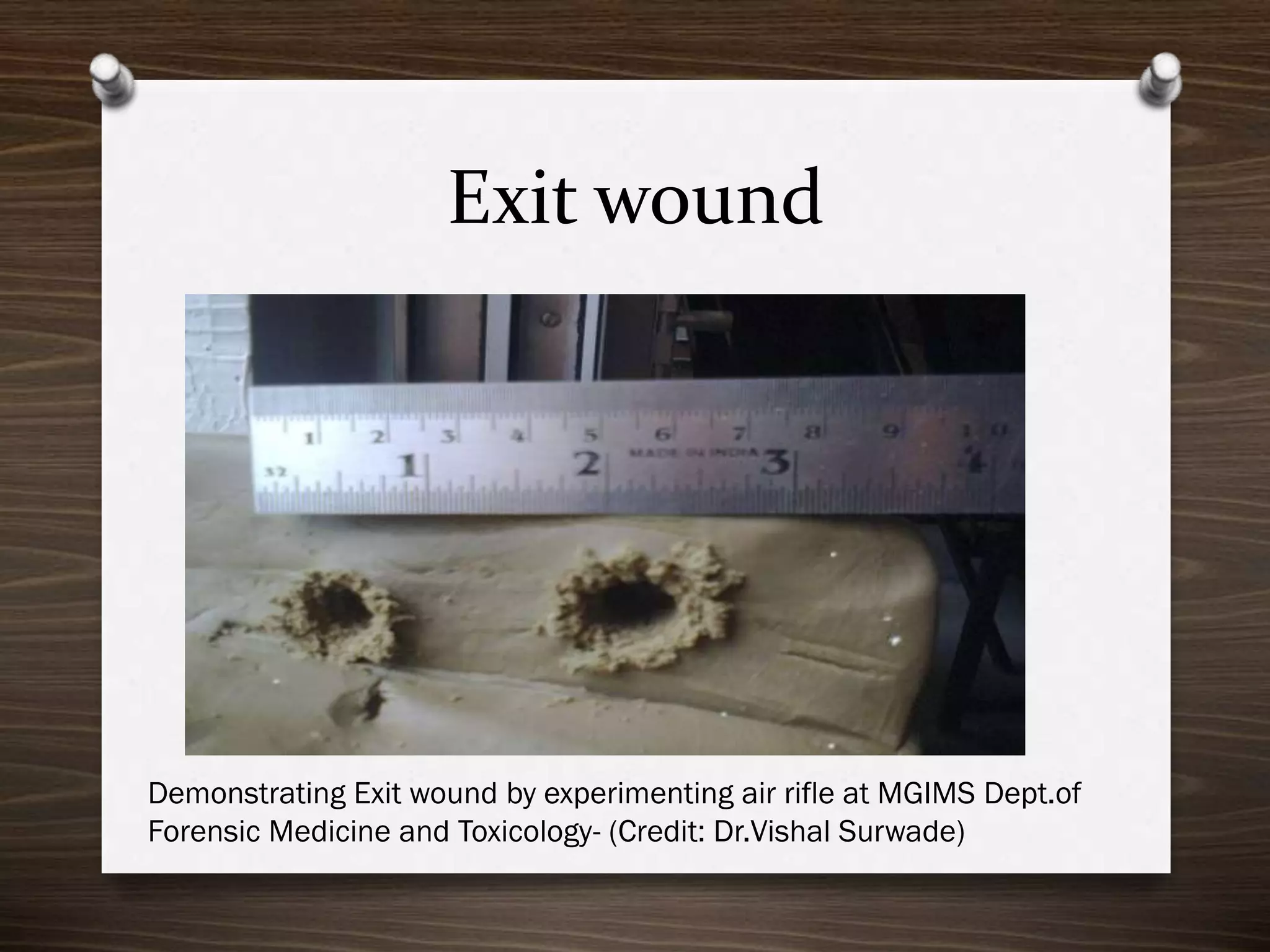
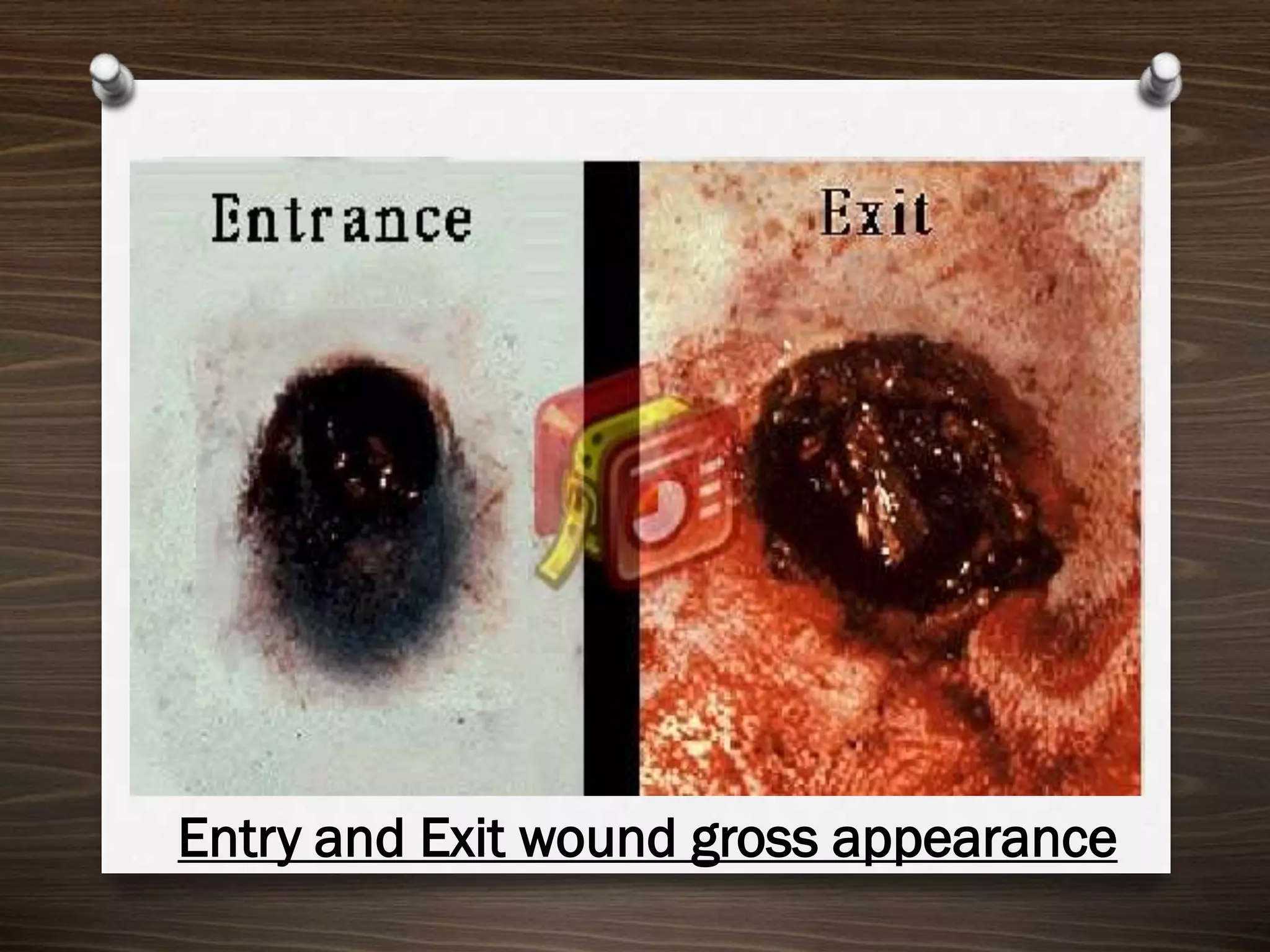
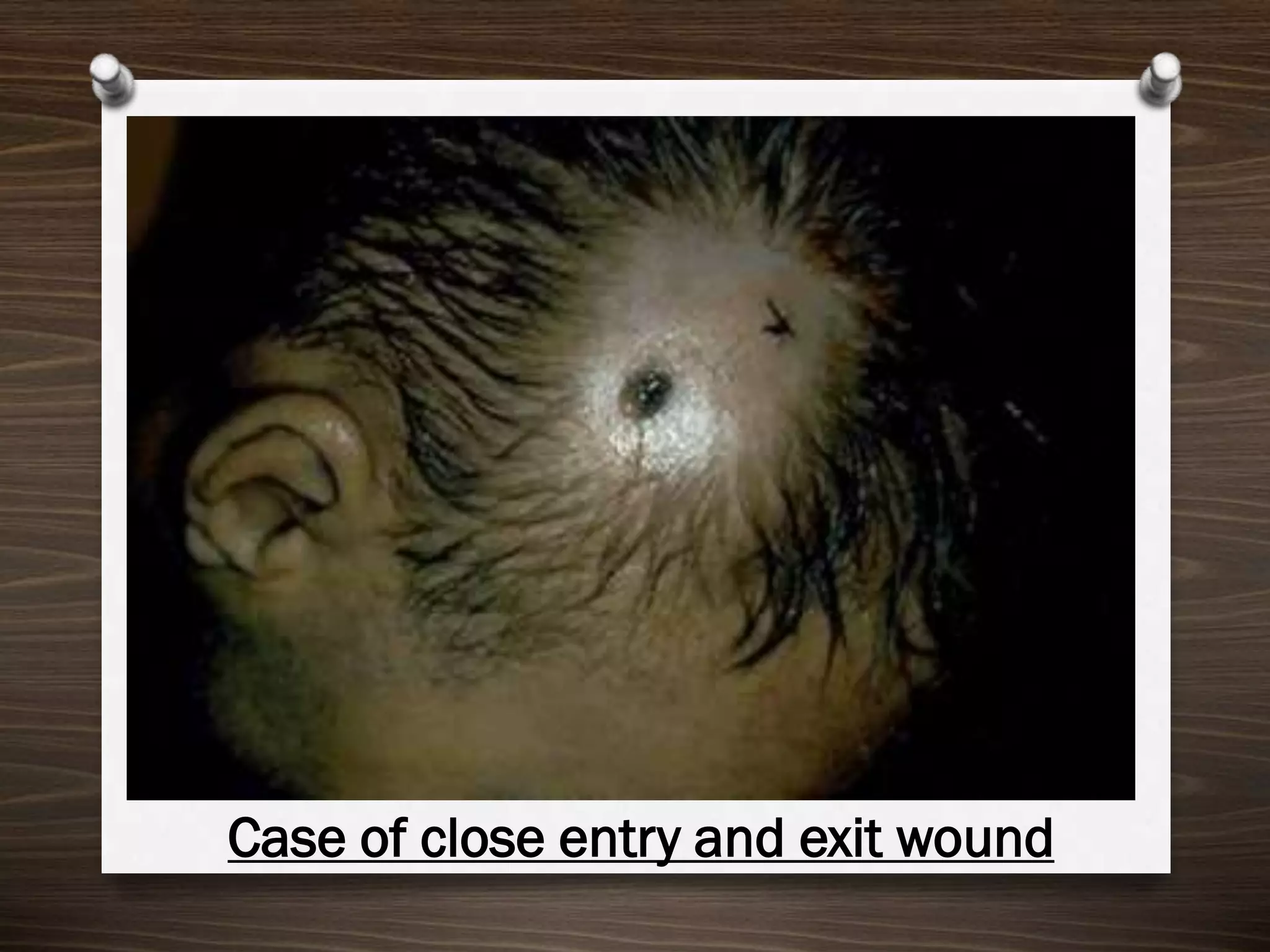
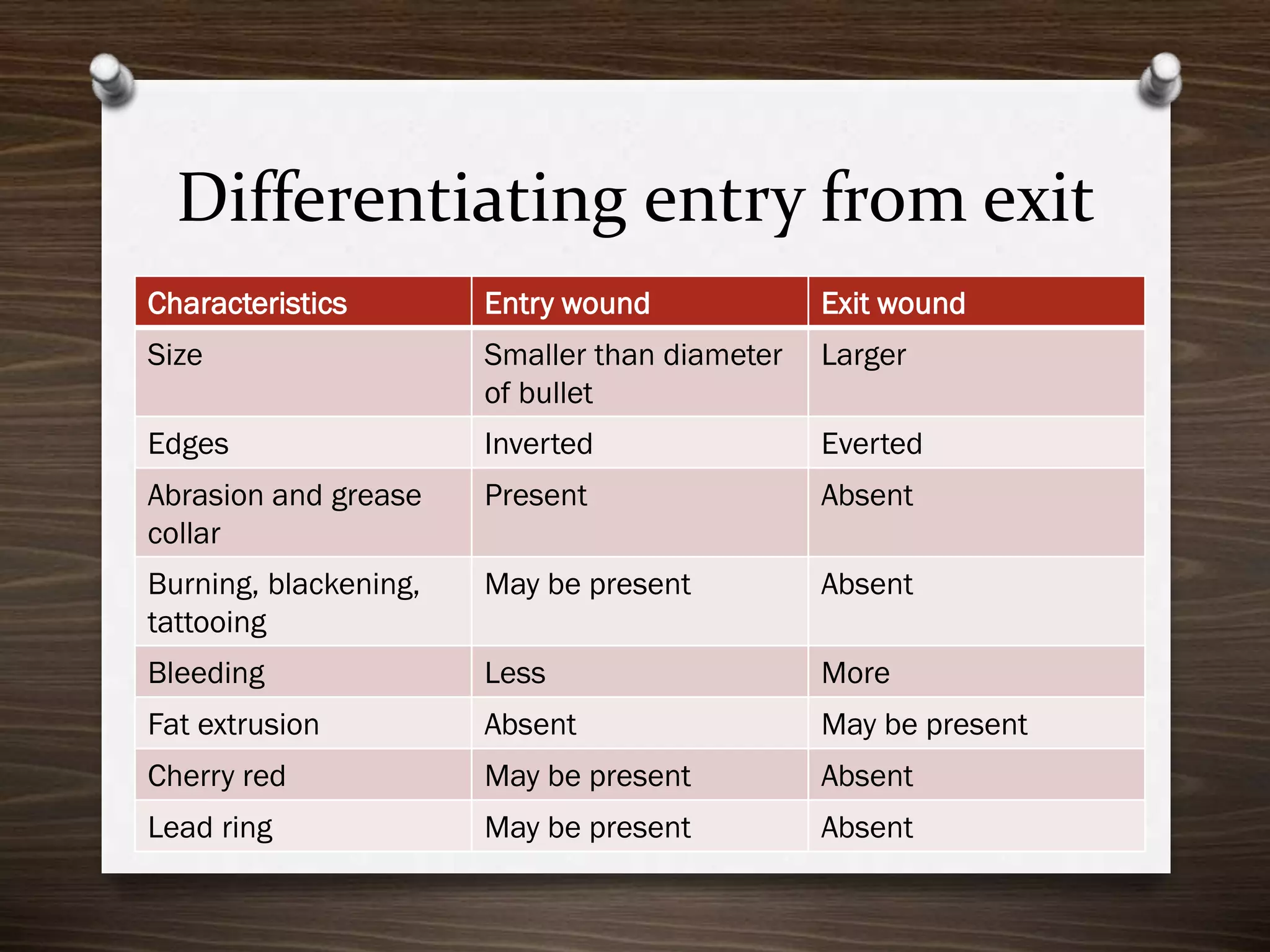
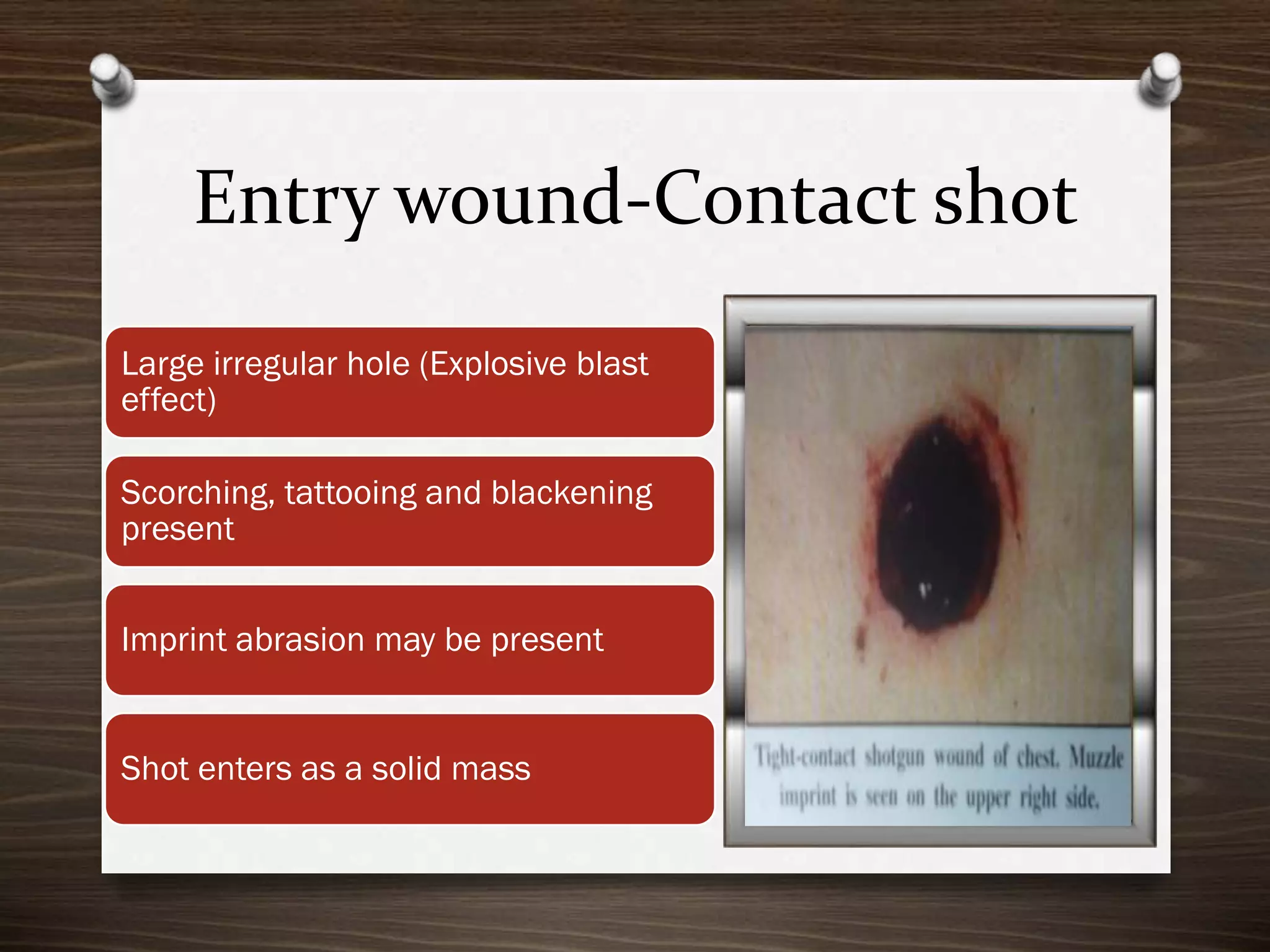
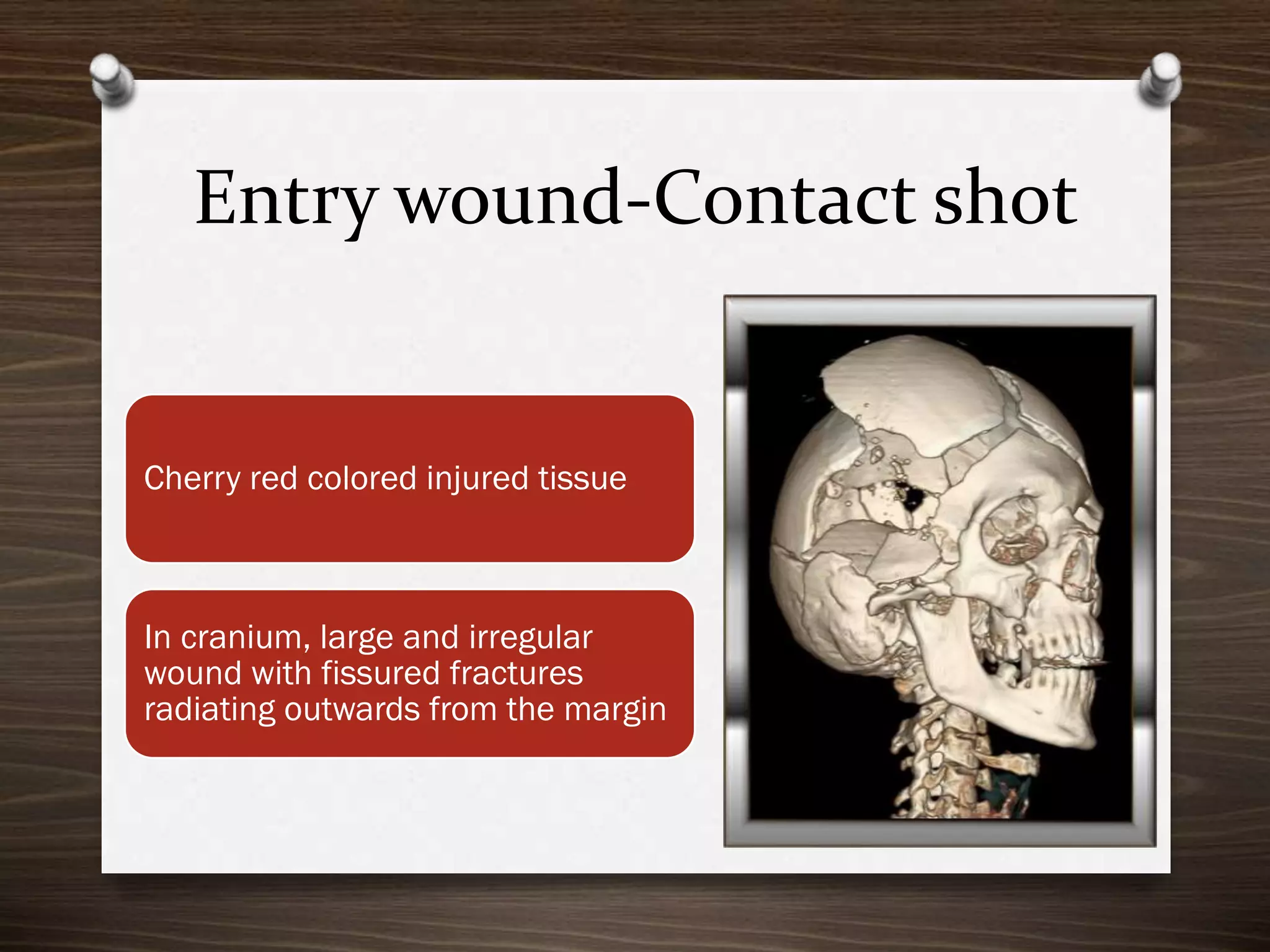
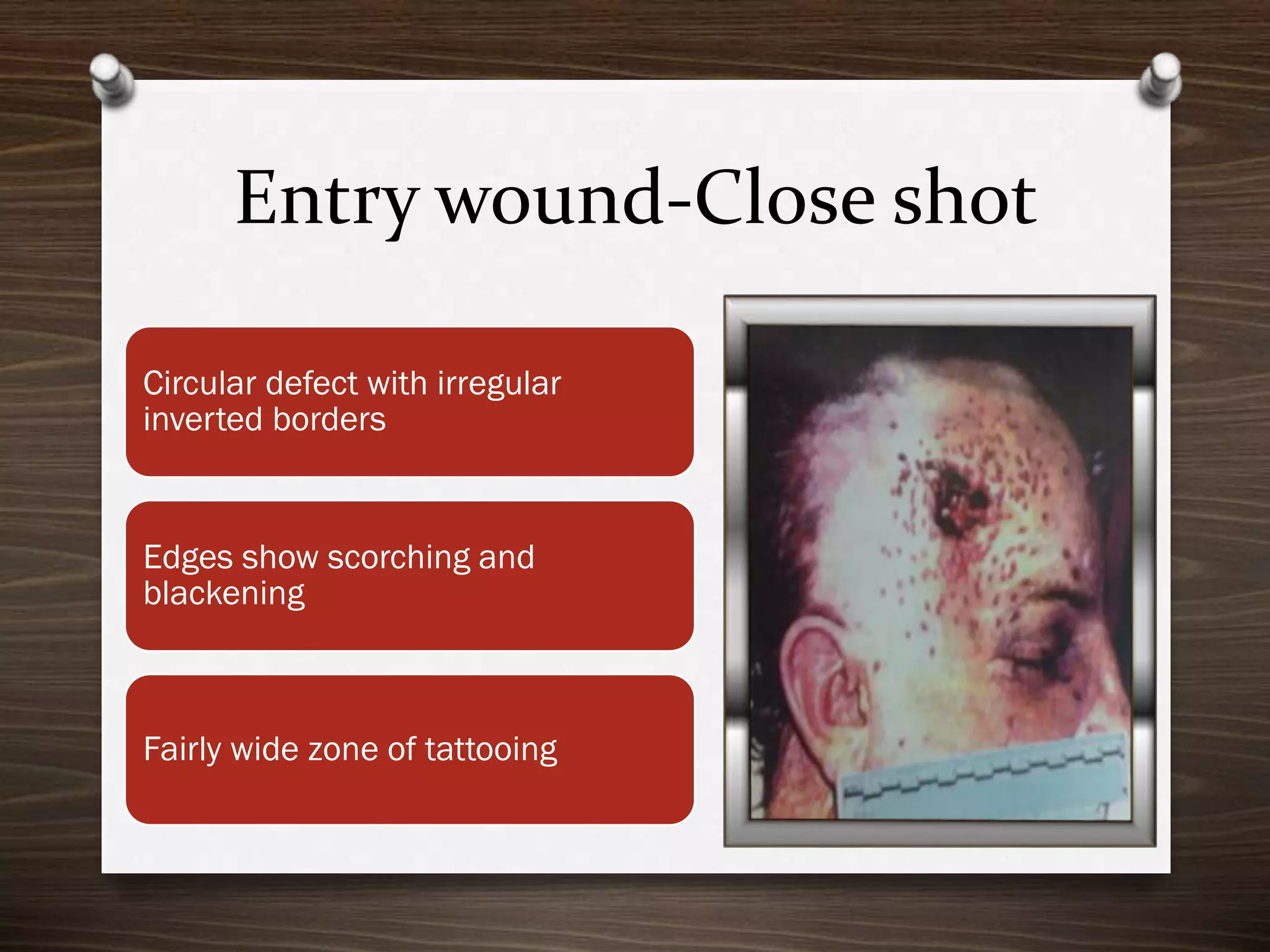
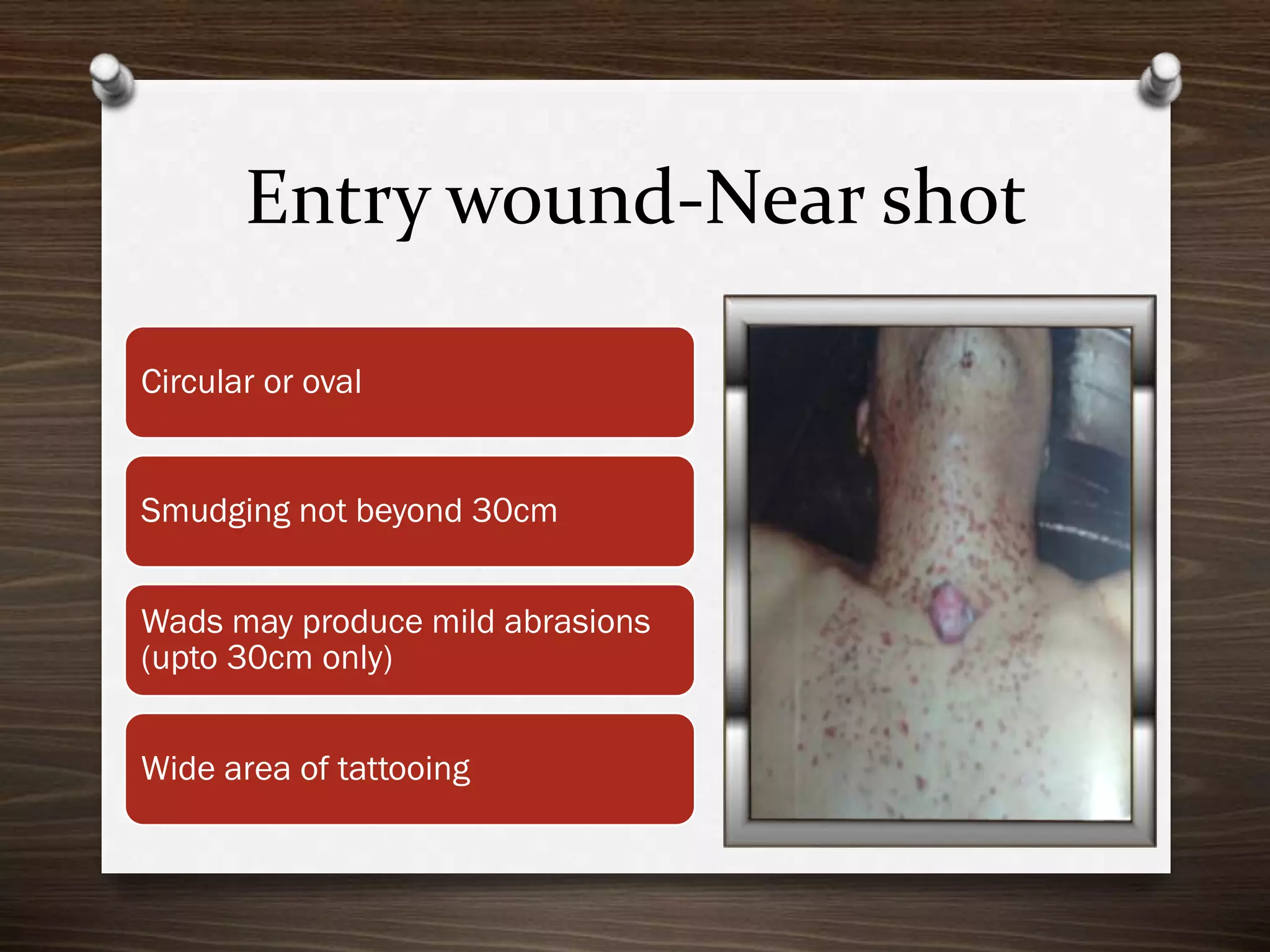
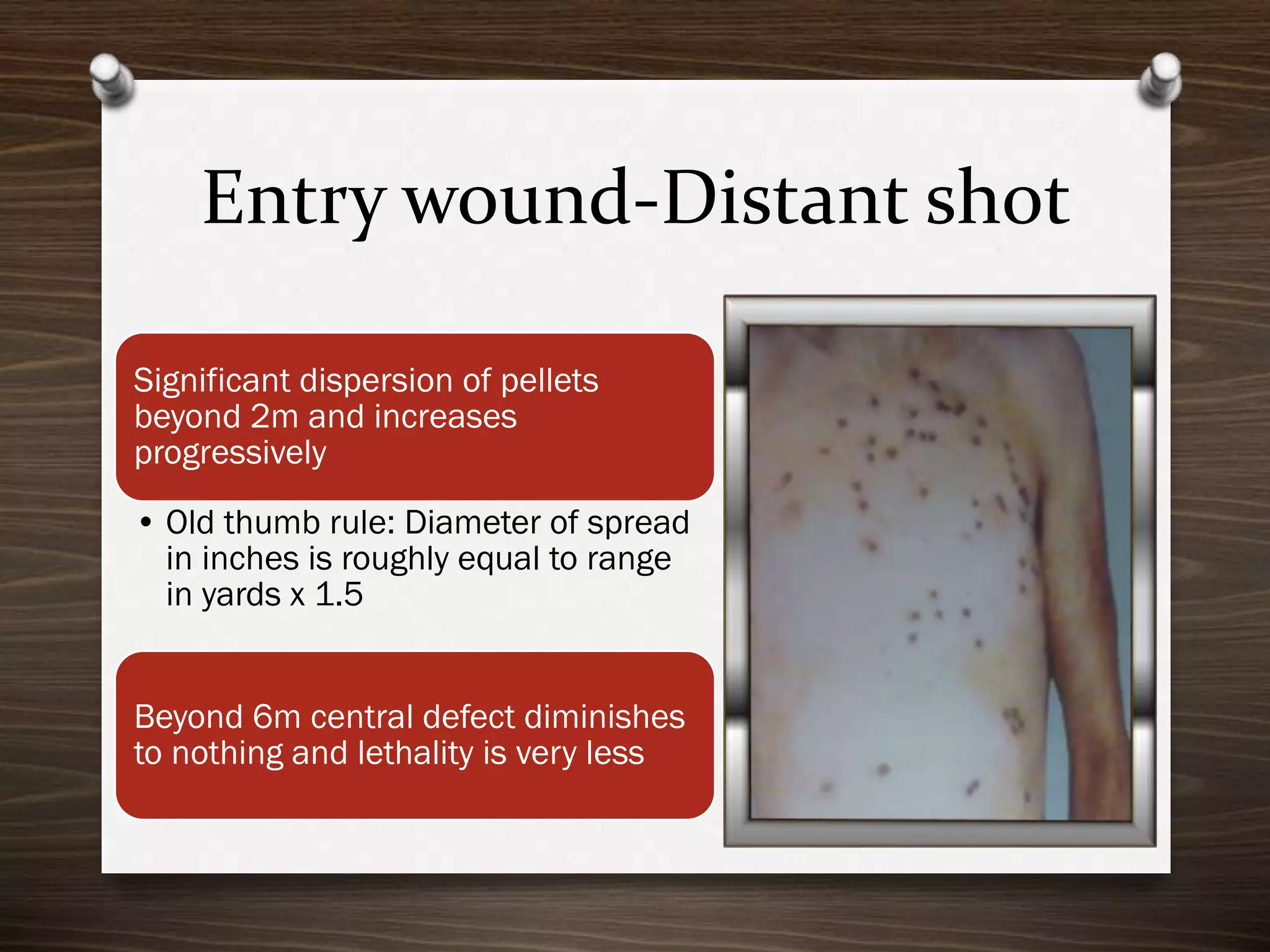
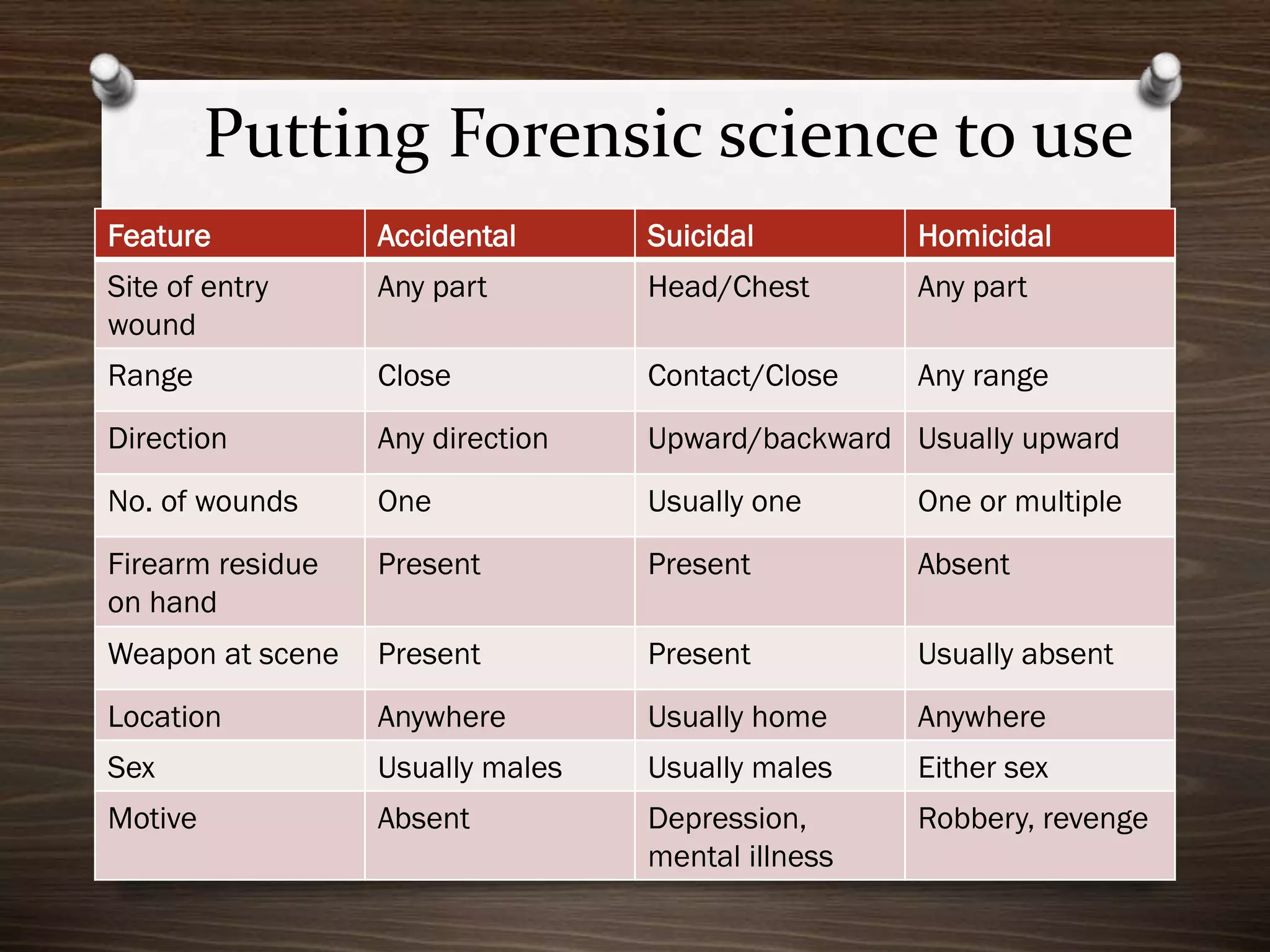
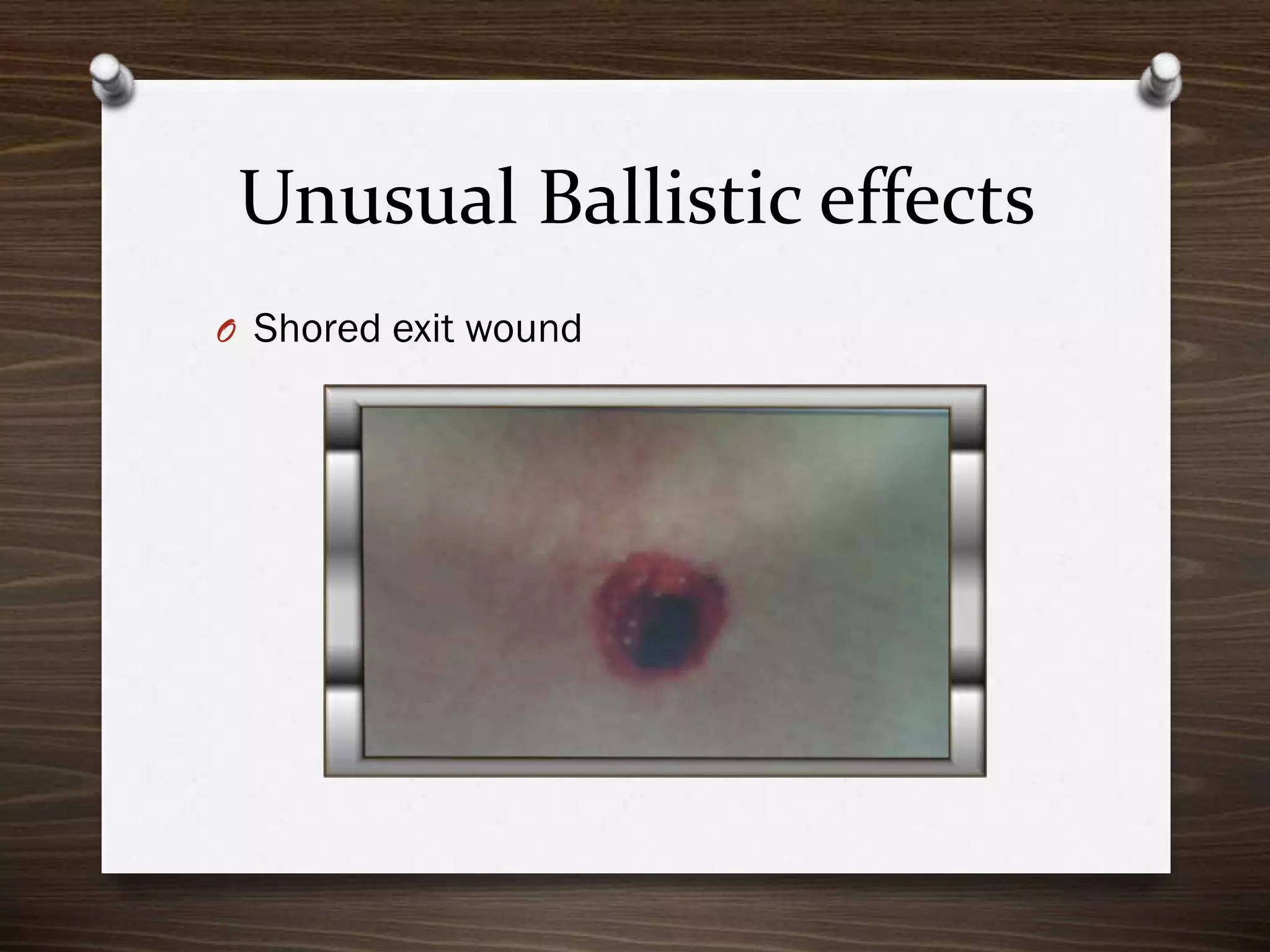
The document discusses various aspects of firearm injuries, including characteristics of entry and exit wounds, the effects of different types of firearms, and differential bullet impacts based on the range and firing conditions. It highlights the forensic significance of specific wound features, such as tattooing and blackening, and touches on the medicolegal implications of firearm injuries. Additionally, it briefly mentions notable historical firearm cases, particularly the assassination of John F. Kennedy and the controversy surrounding it.