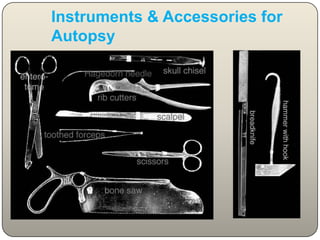
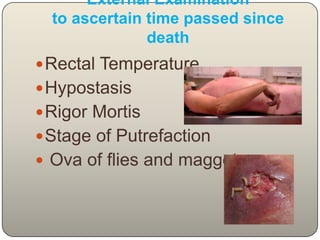
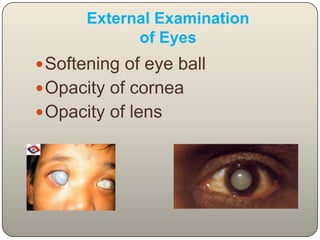
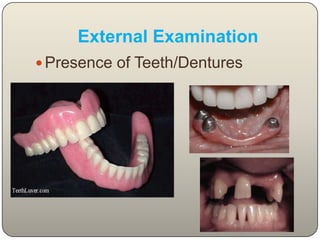
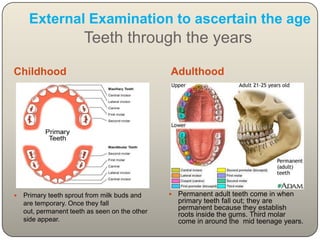
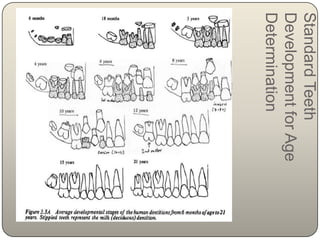
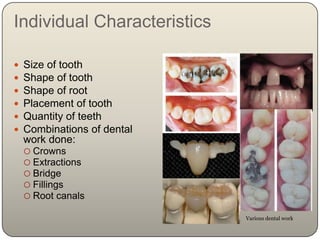
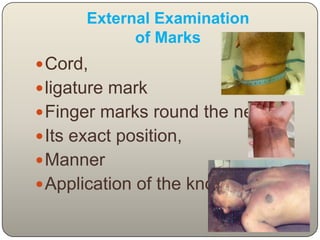
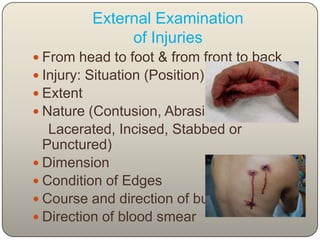
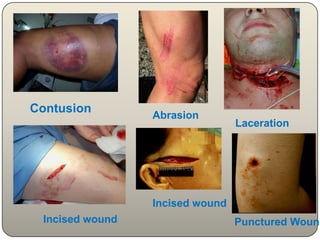
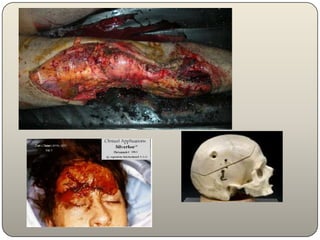
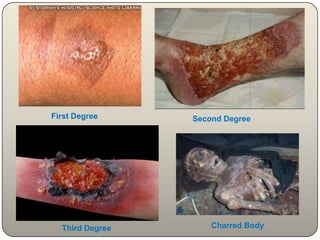
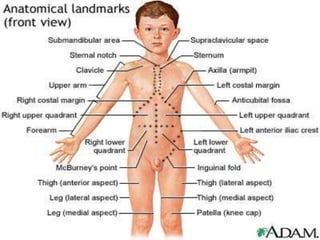
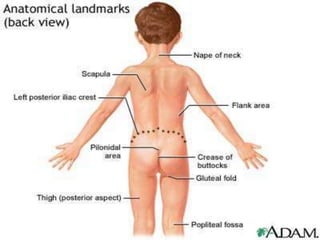
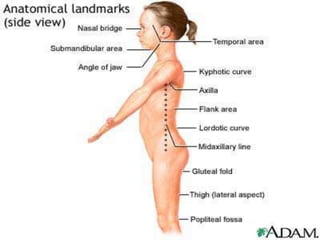
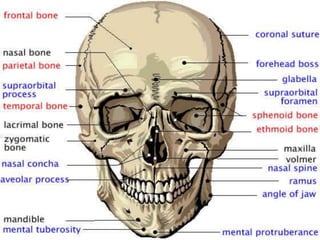
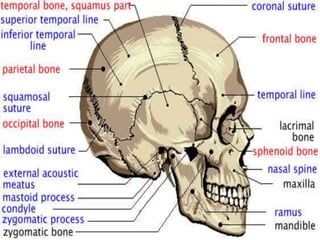
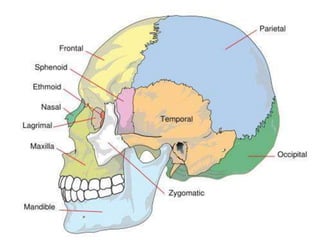
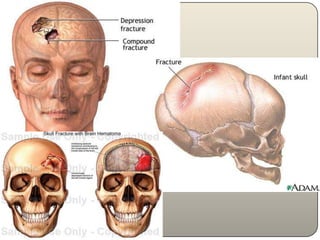
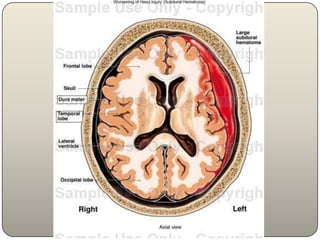
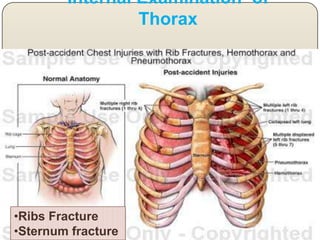
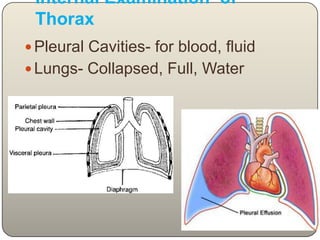
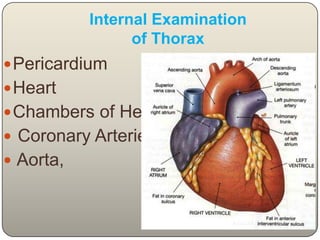
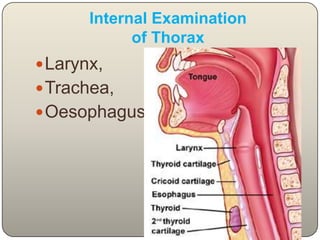
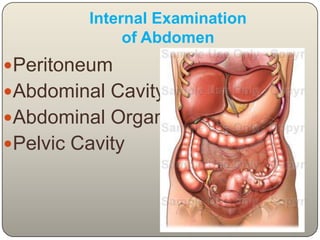
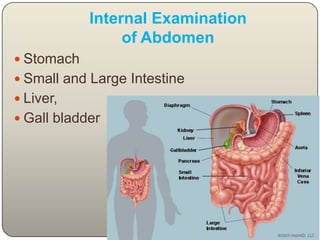
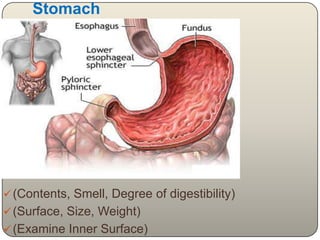
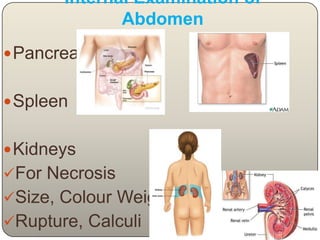
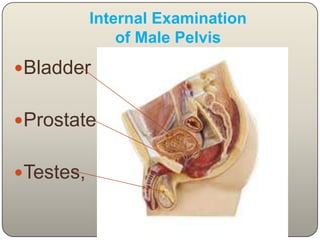
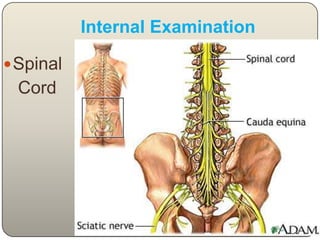
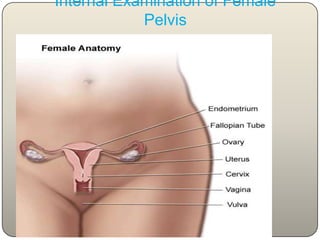
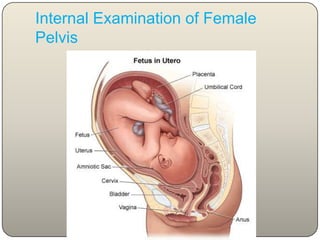
This document discusses the process and objectives of a post-mortem or autopsy examination. It describes the external and internal examination of the body to determine the cause and manner of death. The external examination involves inspecting the body for injuries, marks, signs of death. The internal examination involves opening the cranial, thoracic and abdominal cavities and examining the organs and tissues for any abnormalities, injuries, or diseases. Samples may be taken for further analysis. The goal is to establish the identity of the deceased and determine if death was natural, accidental, suicidal or homicidal.