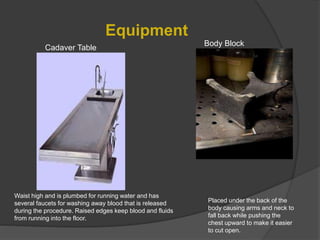
An autopsy, also known as a necropsy or postmortem examination, involves dissecting and examining a dead body and its organs to determine the cause of death. There are two main types - forensic autopsies which are performed as part of a police investigation, and clinical autopsies which are performed in hospitals by pathologists. The autopsy procedure involves examining and weighing the organs, taking tissue samples, and producing a report of findings to determine the manner of death - natural, accidental, homicide, suicide, or undetermined. Autopsies can provide valuable medical knowledge and legal evidence, help identify hereditary illnesses, and provide closure for families.