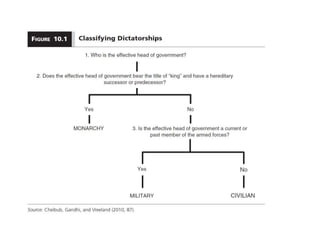
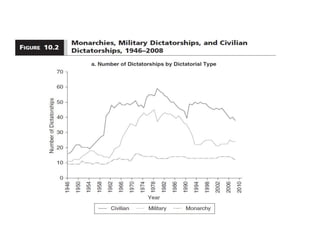
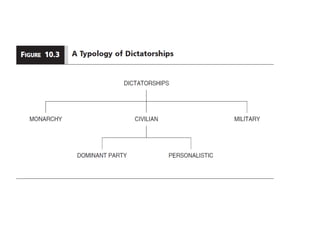
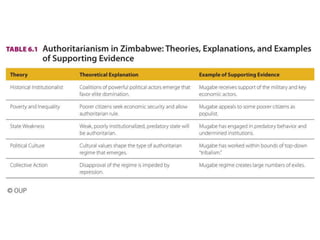
This document discusses different types of authoritarian regimes including totalitarian states, monarchies, and military and civilian dictatorships. Totalitarian states are characterized by a dominant leader and single ruling party that controls the media and uses violence. Military dictatorships typically seize power through coups and then hold sham elections to maintain control, while cracking down on dissent. Civilian dictatorships are either dominated by a single party or a personalistic leader, and rely on repressing opposition and controlling information. The document examines commonalities and differences between communist and fascist regimes as well as factors that contribute to the rise and persistence of authoritarian rule.