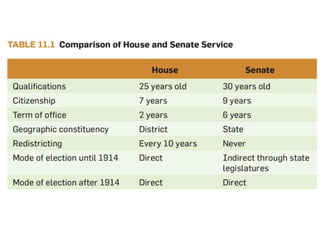
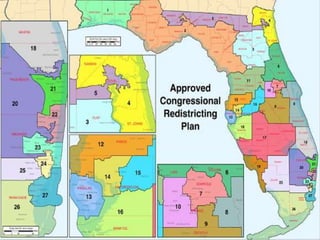
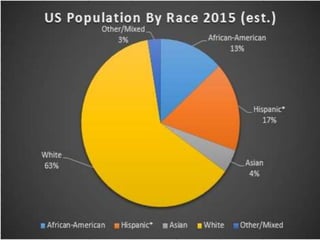
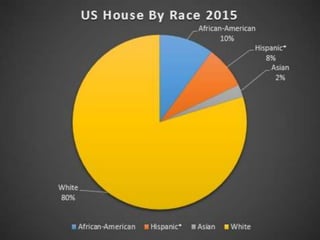
This document discusses the structure and functions of the United States Congress. It outlines that Congress is divided into two chambers, the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House has 435 voting members elected by population, while the Senate has 100 members with 2 per state elected via state legislatures. Congress passes laws, declares war, regulates commerce, and oversees the executive branch through powers enumerated in the Constitution. The document also examines congressional leadership positions, the committee system, and the legislative process.