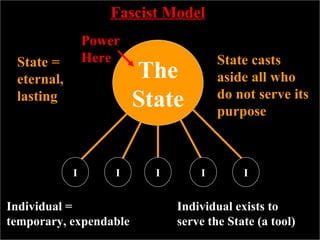
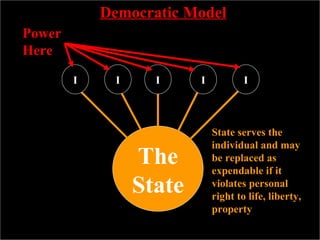
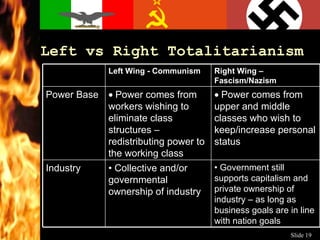
The document discusses the key characteristics and influences of totalitarian regimes. It defines totalitarianism as a form of government that seeks to subordinate all aspects of life to state authority. Totalitarian states view individuals as temporary and expendable, existing to serve the eternal state. The document also examines how World War I influenced the rise of totalitarianism in countries like Germany, Italy, and Russia by causing economic and political instability. It outlines common features of totalitarian regimes, including the use of propaganda, nationalism, and charismatic leaders to gradually increase state control and replace existing institutions.