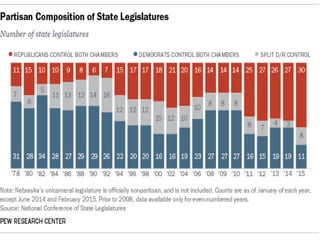
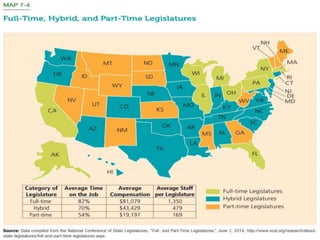
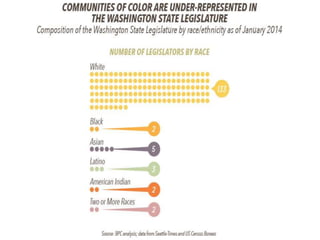
This document provides an overview of state legislatures, including their roles in lawmaking, representation, constituent services, oversight, appropriations, and impeachment. It discusses the structure of state legislatures, including the types and names of legislative chambers. The document also covers trends in legislative professionalism using Squire's measure of salaries, session length, and staff/resources. Additionally, it addresses redistricting approaches and the demographics of state legislative membership.