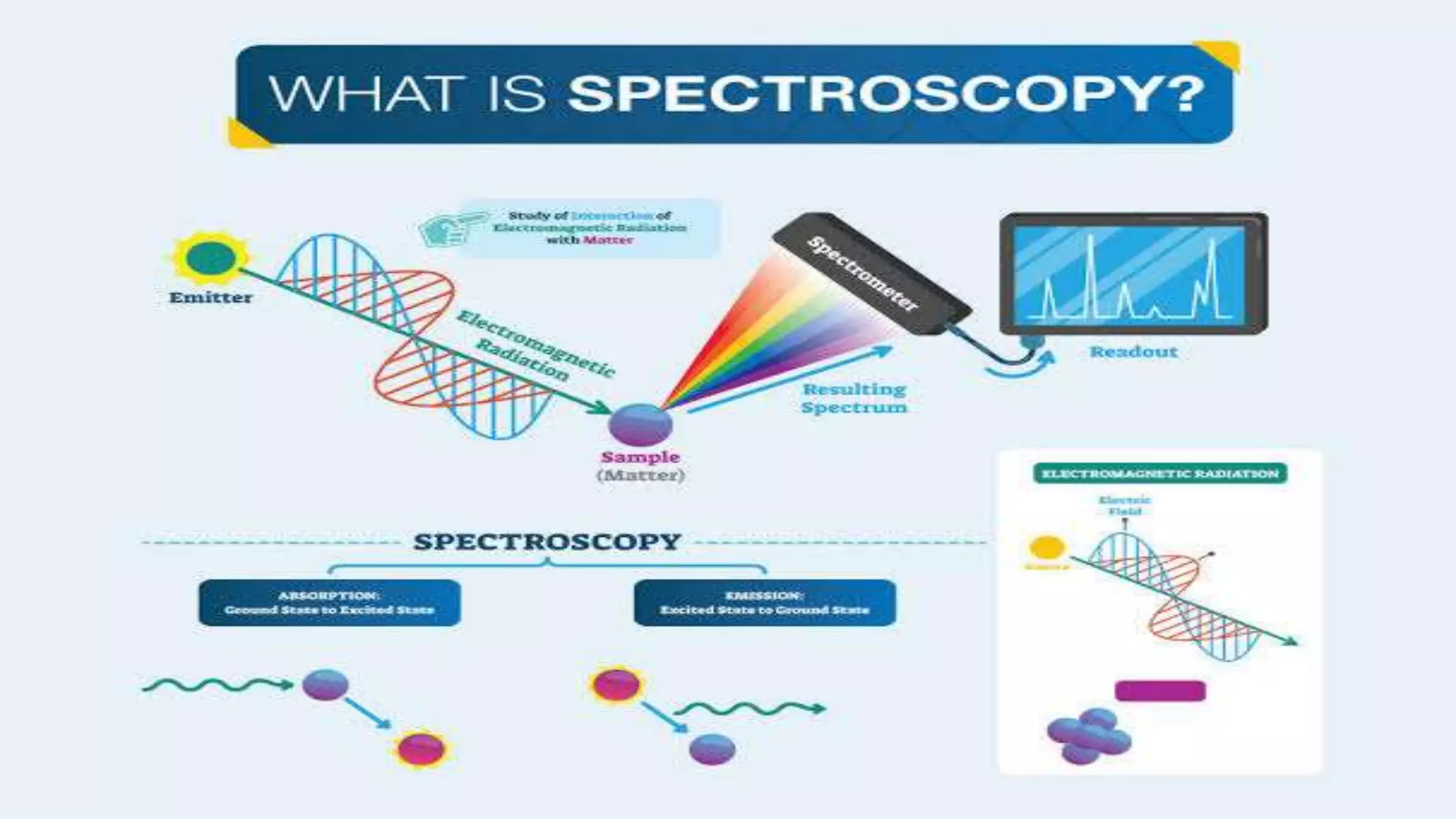
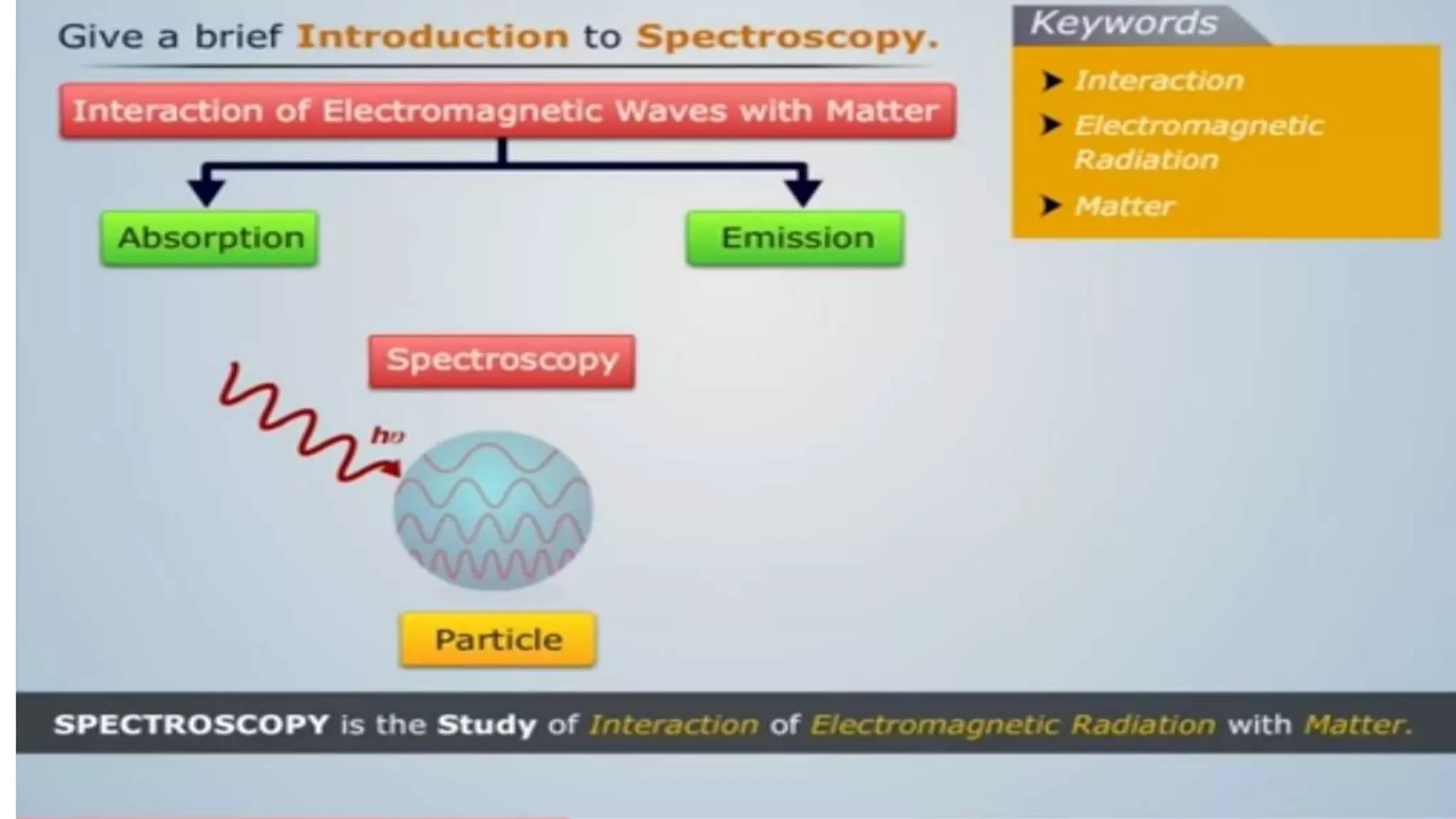
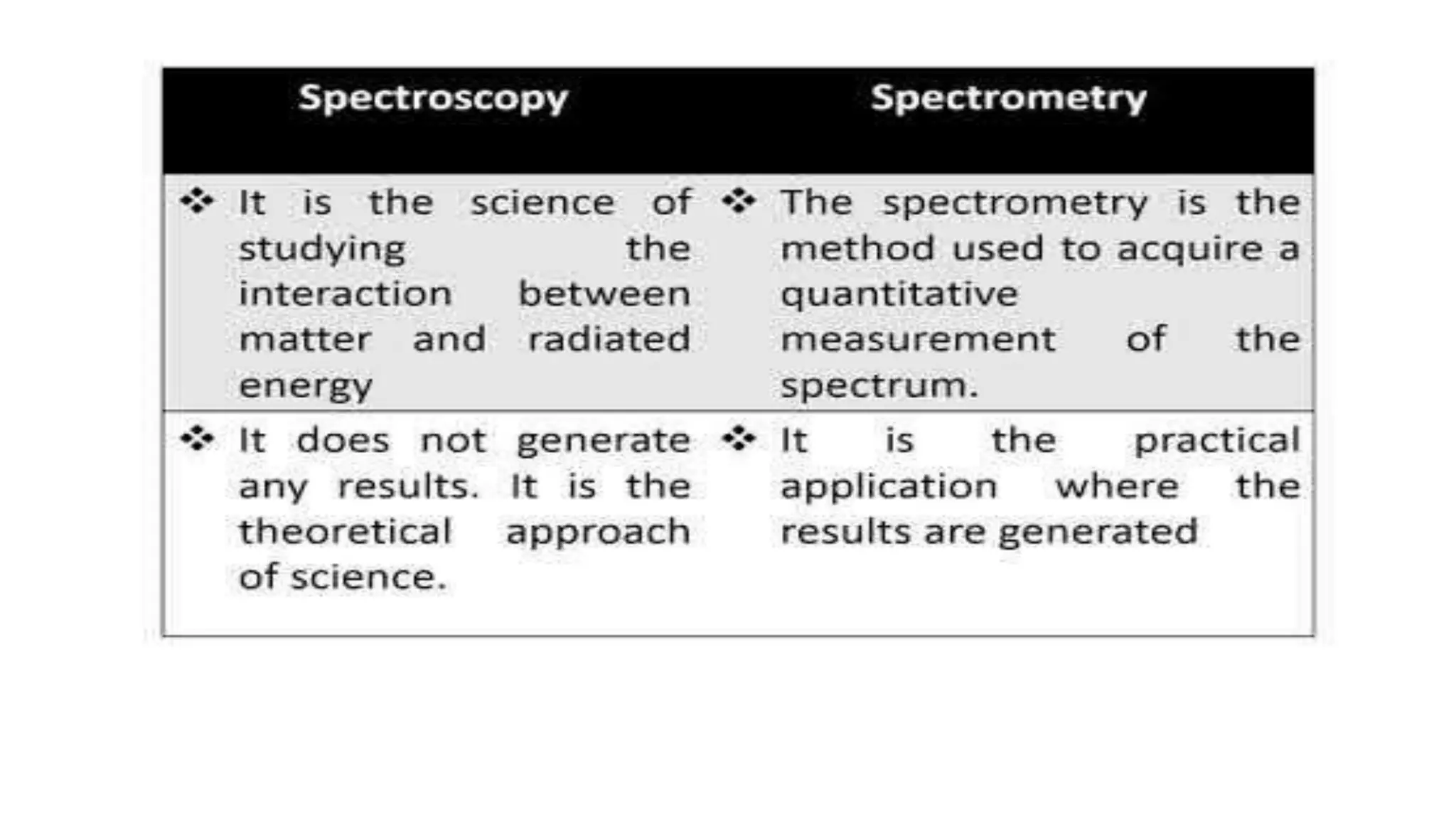
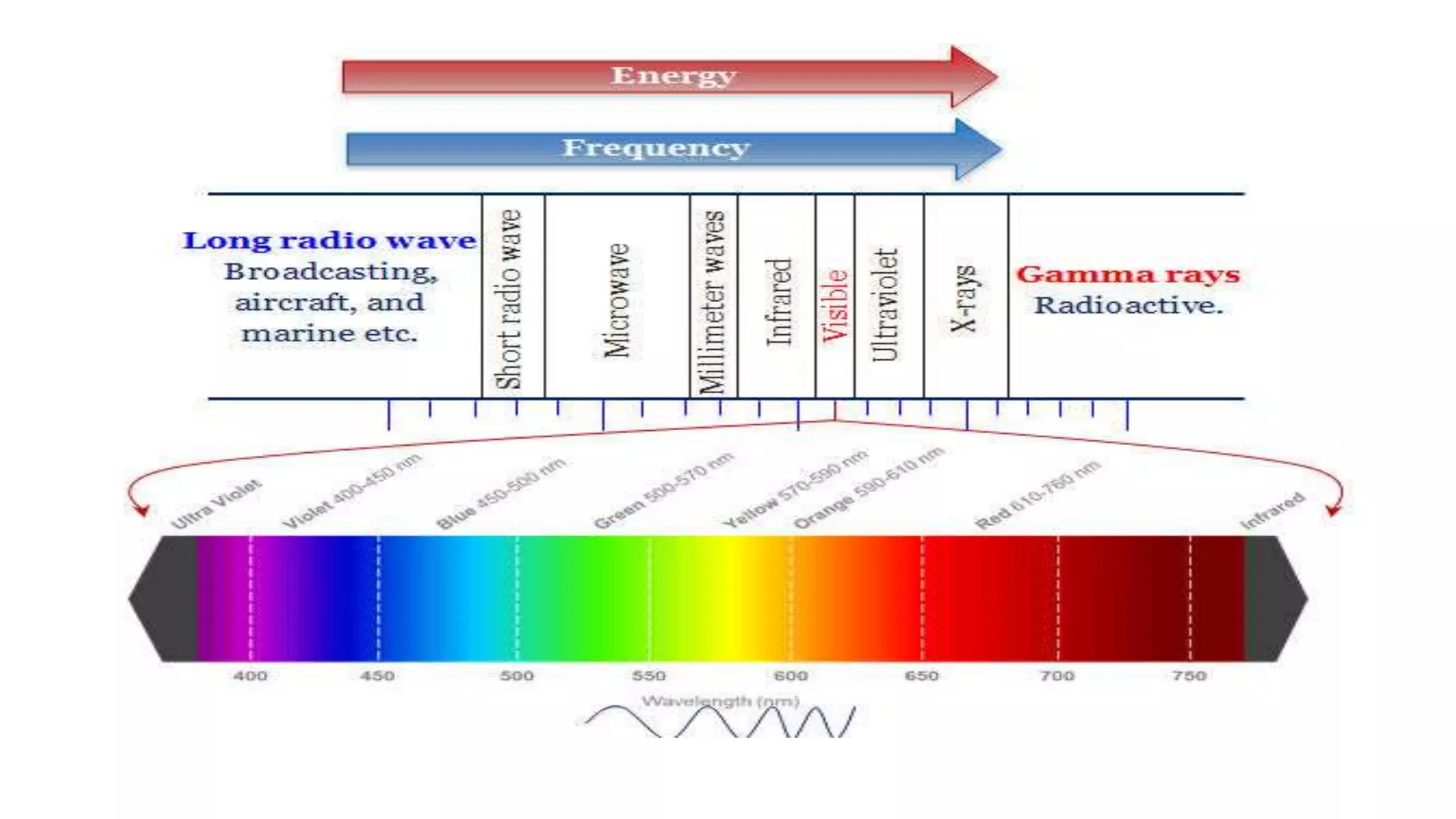
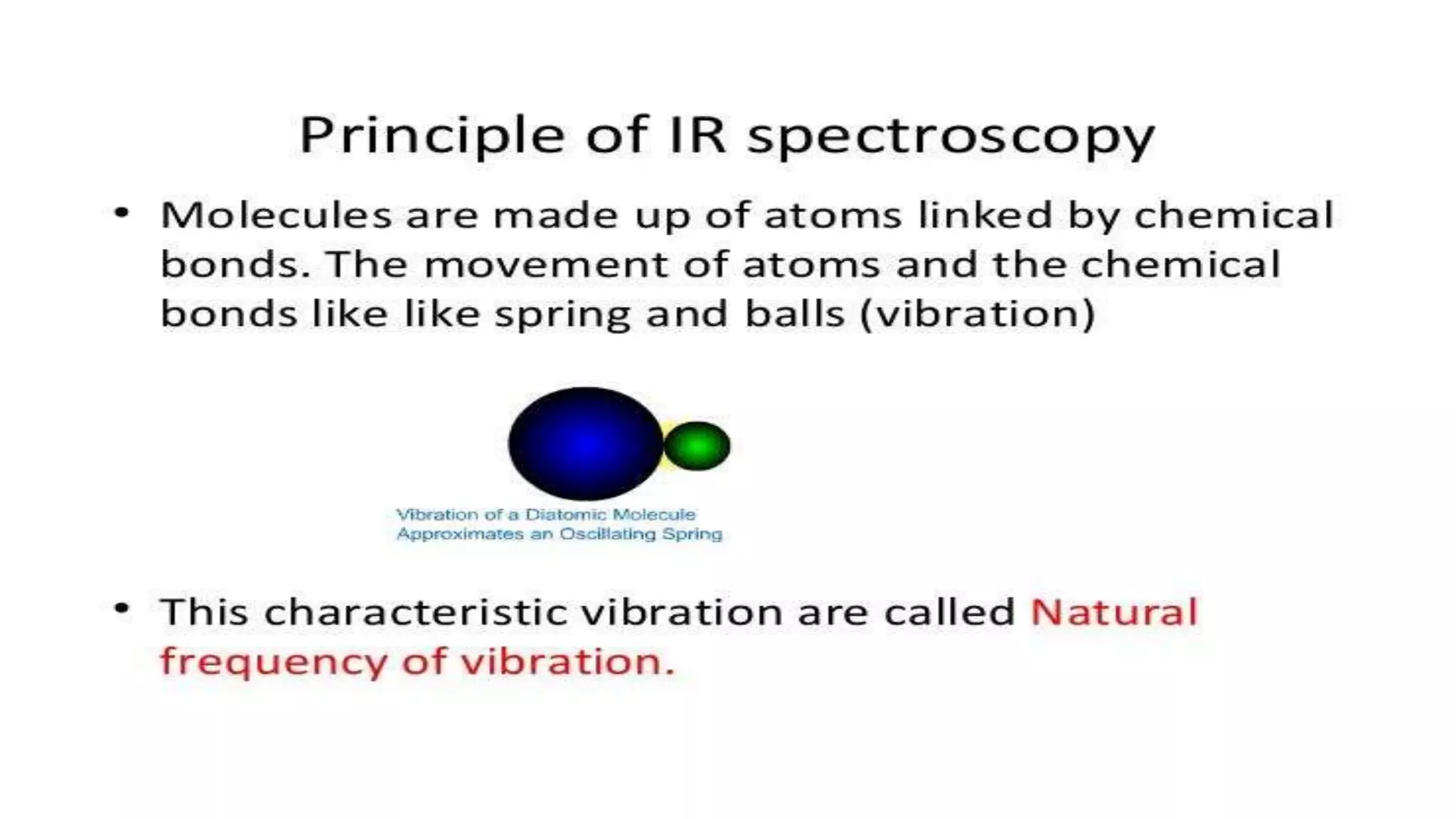
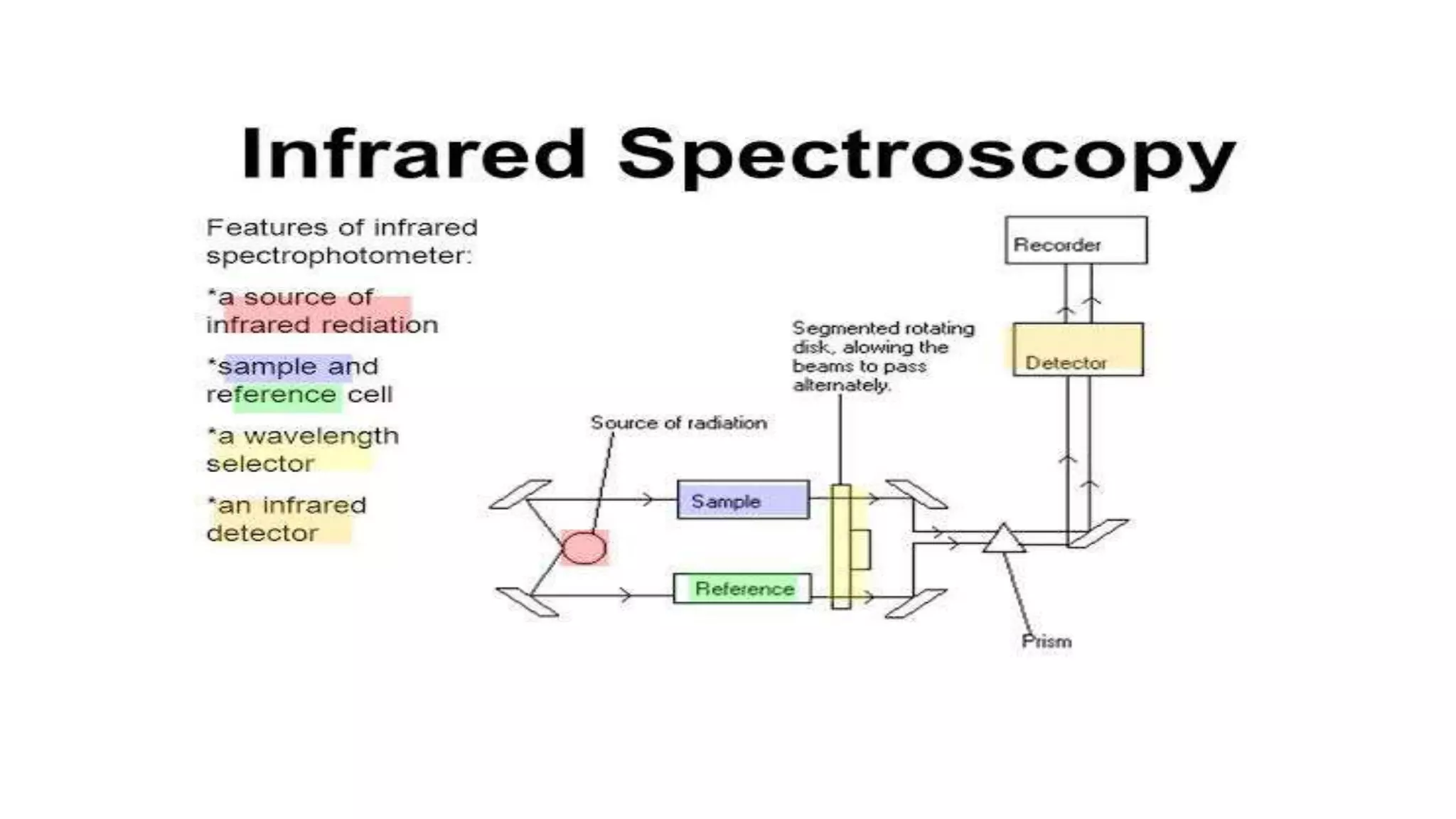
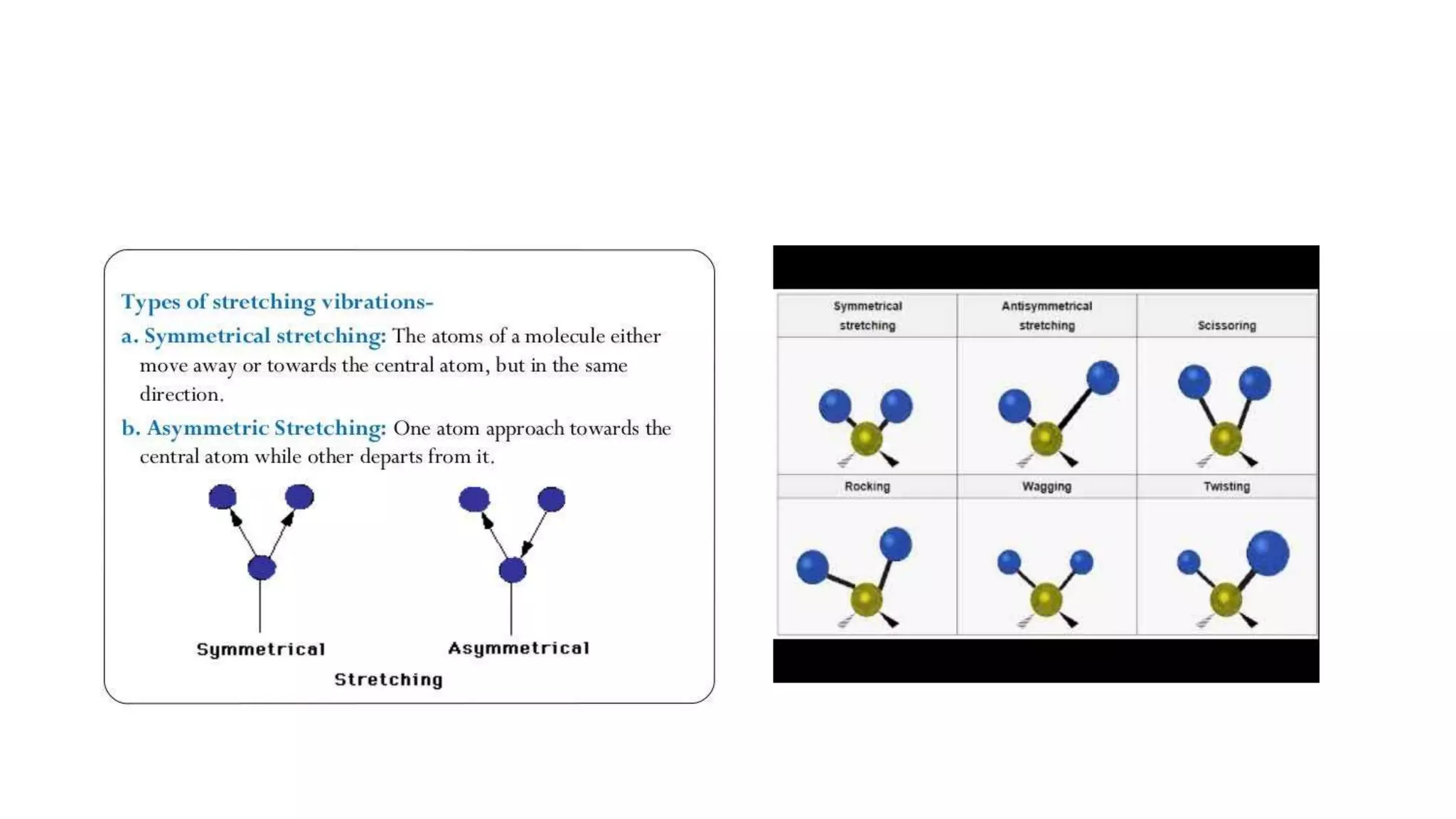
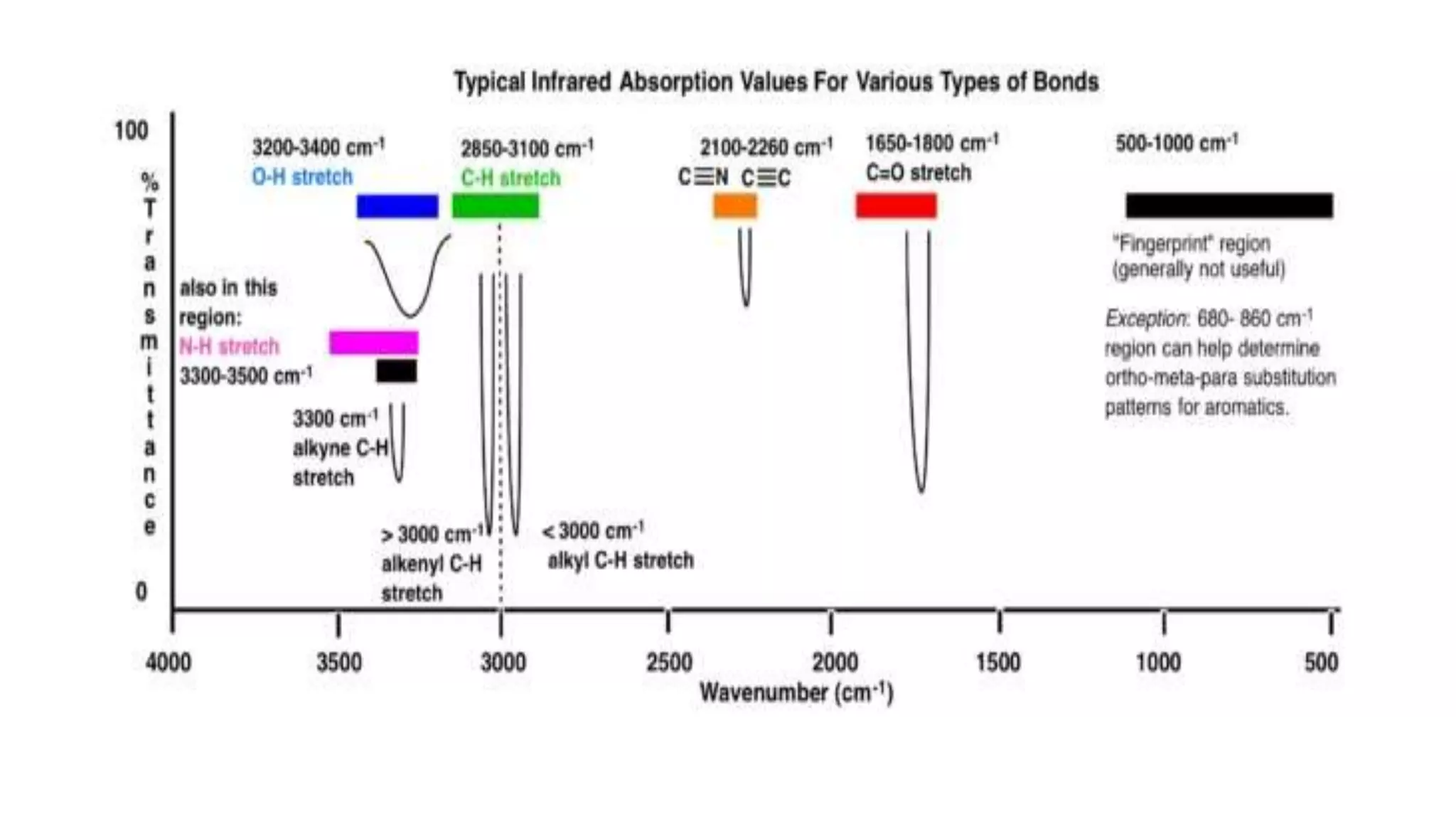
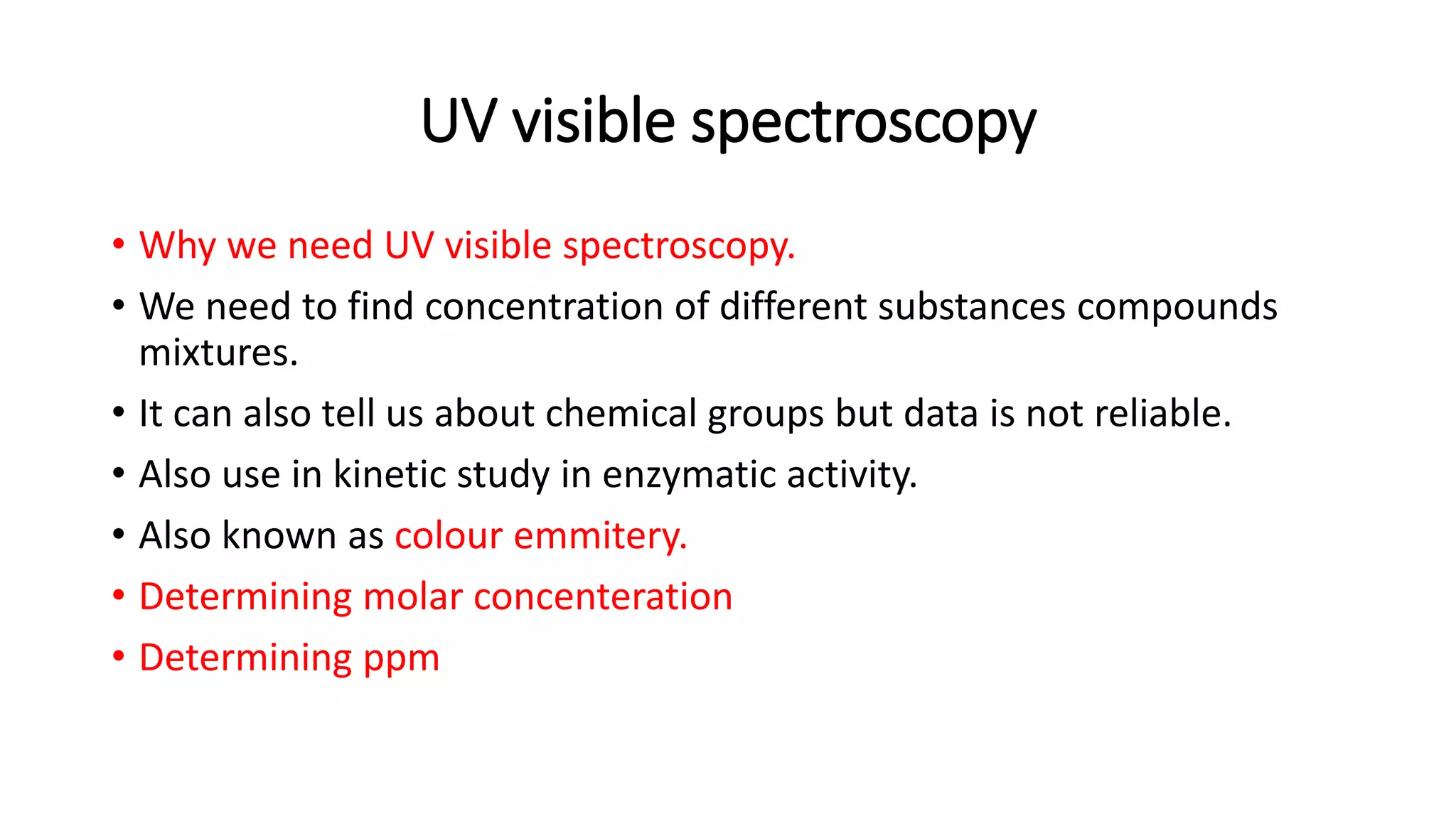
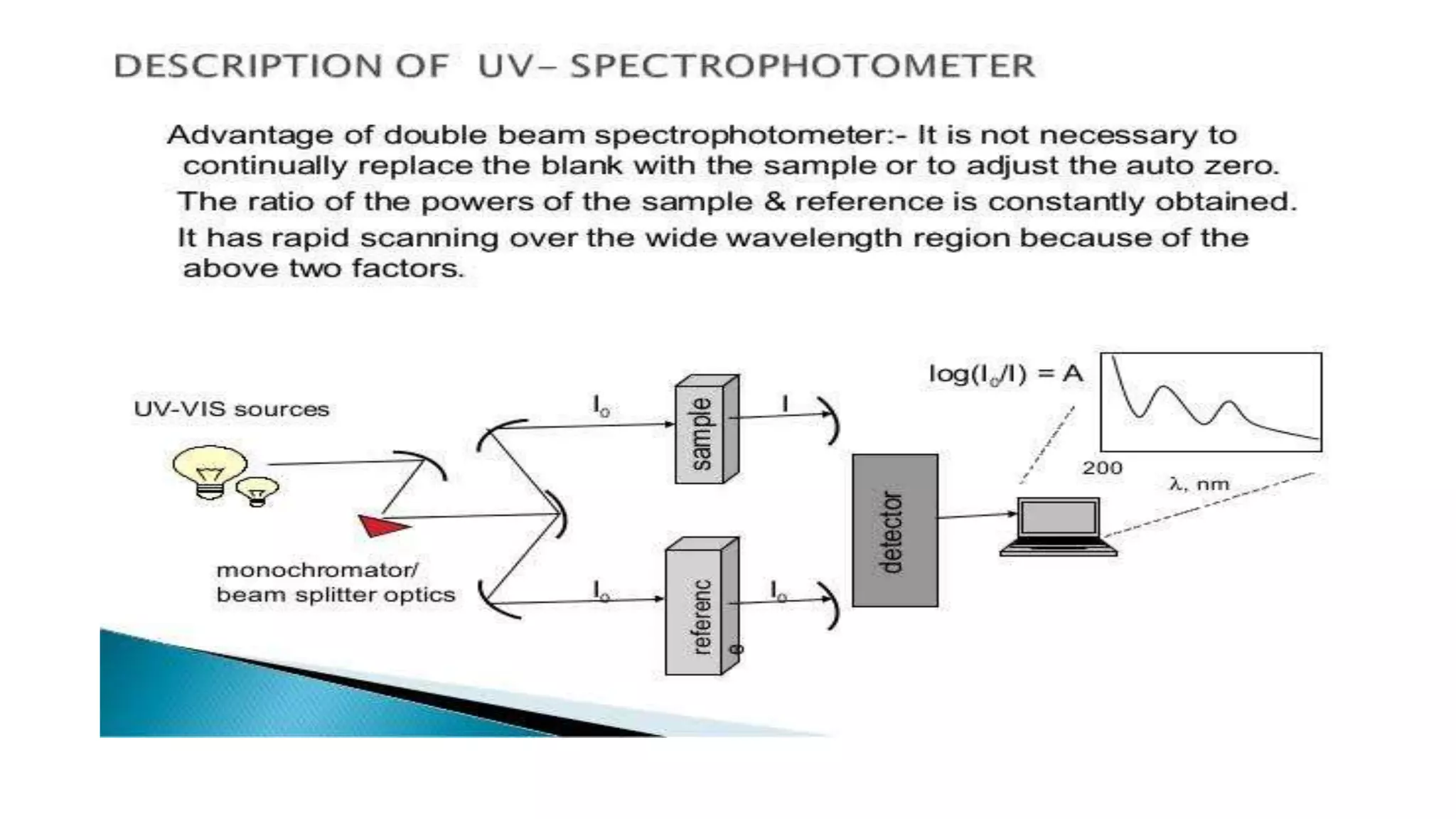
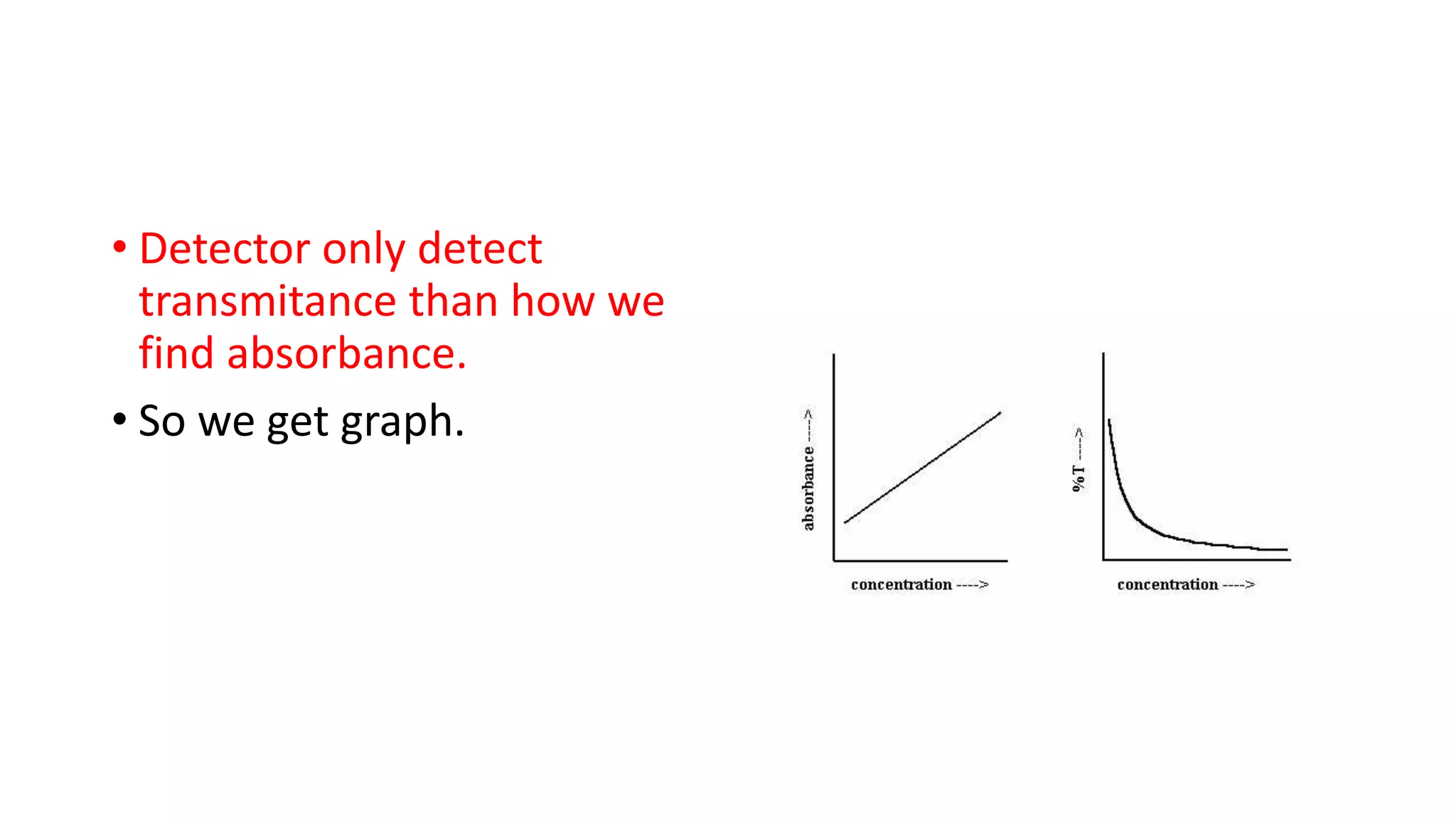
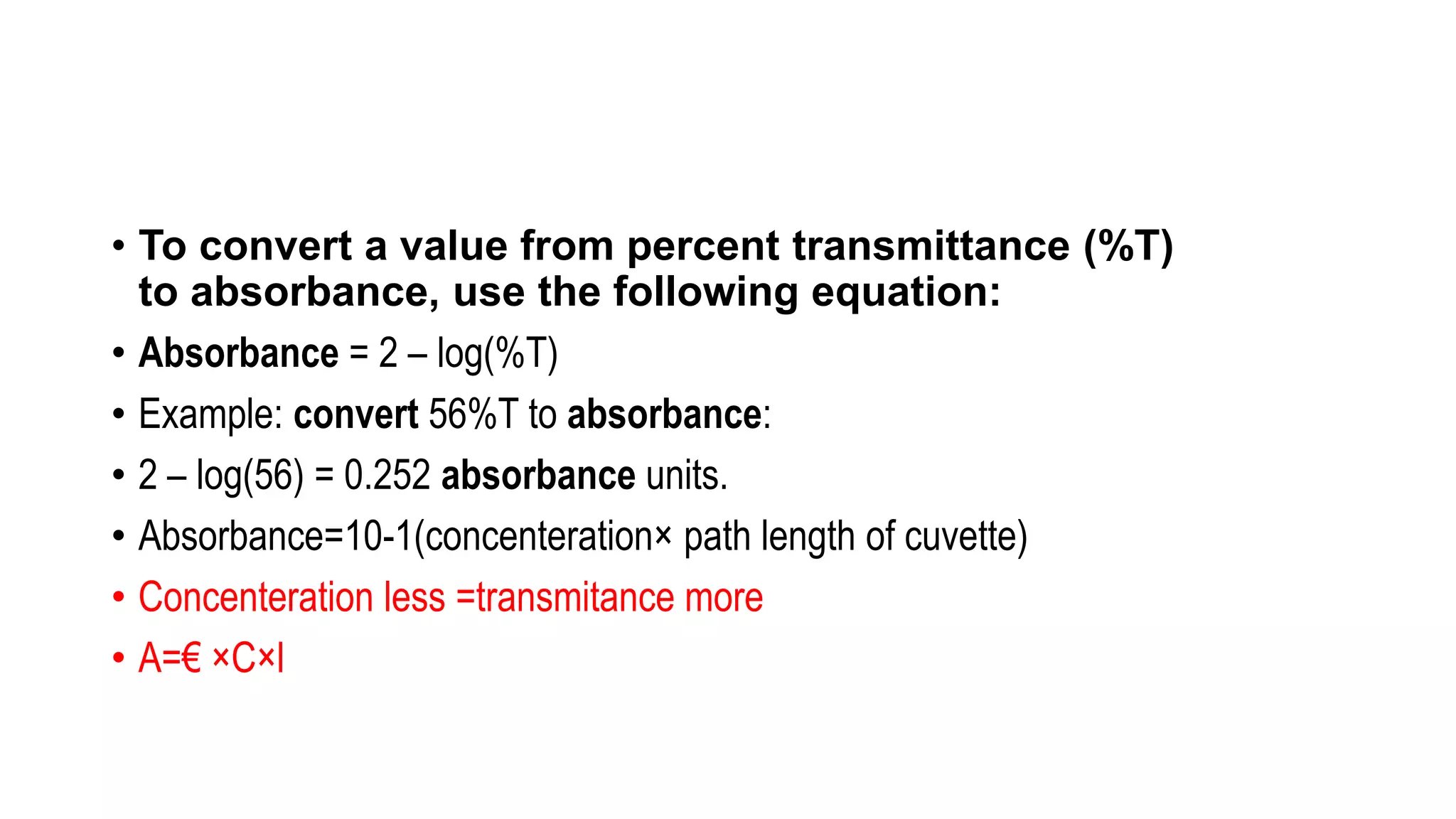
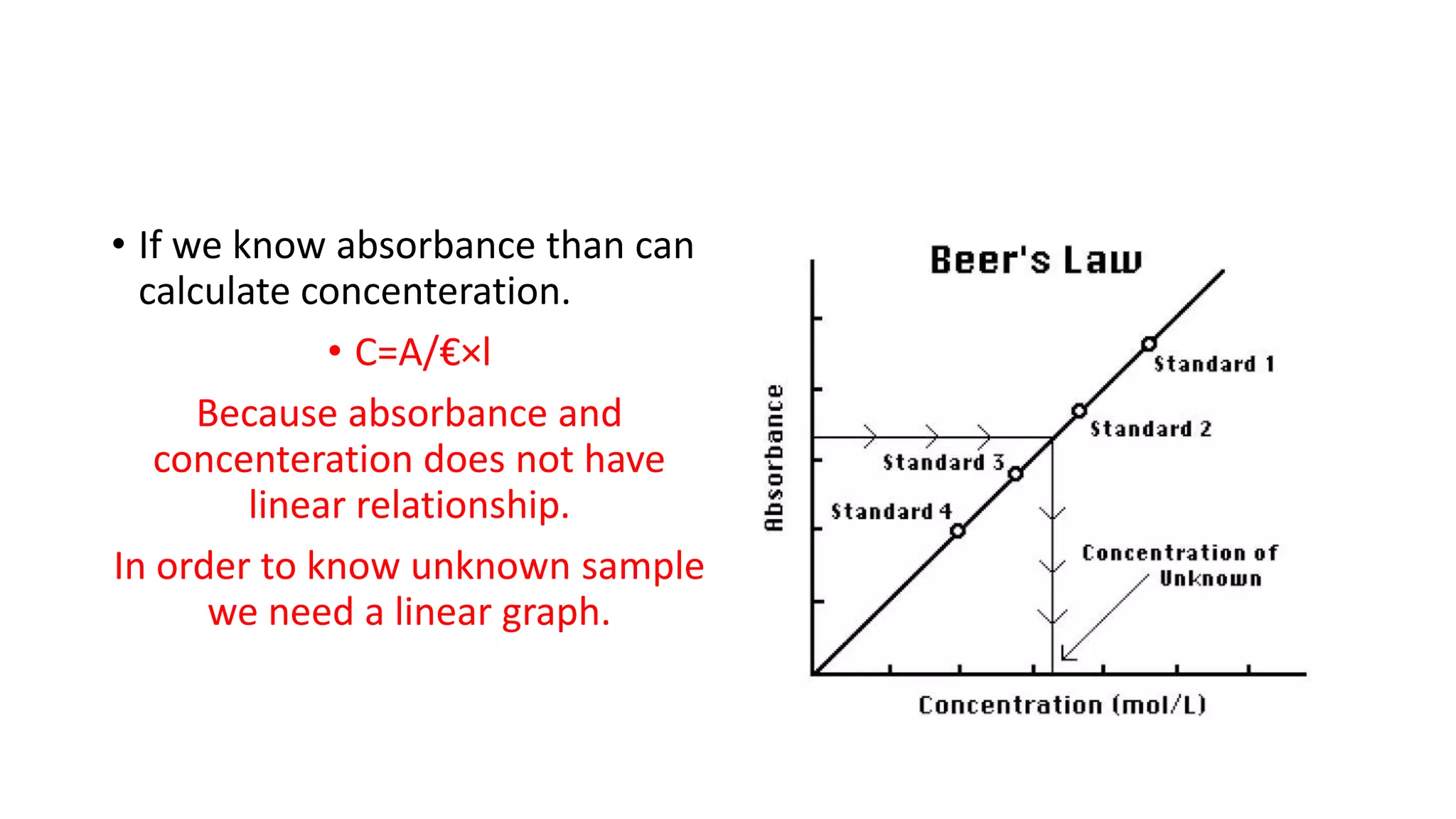
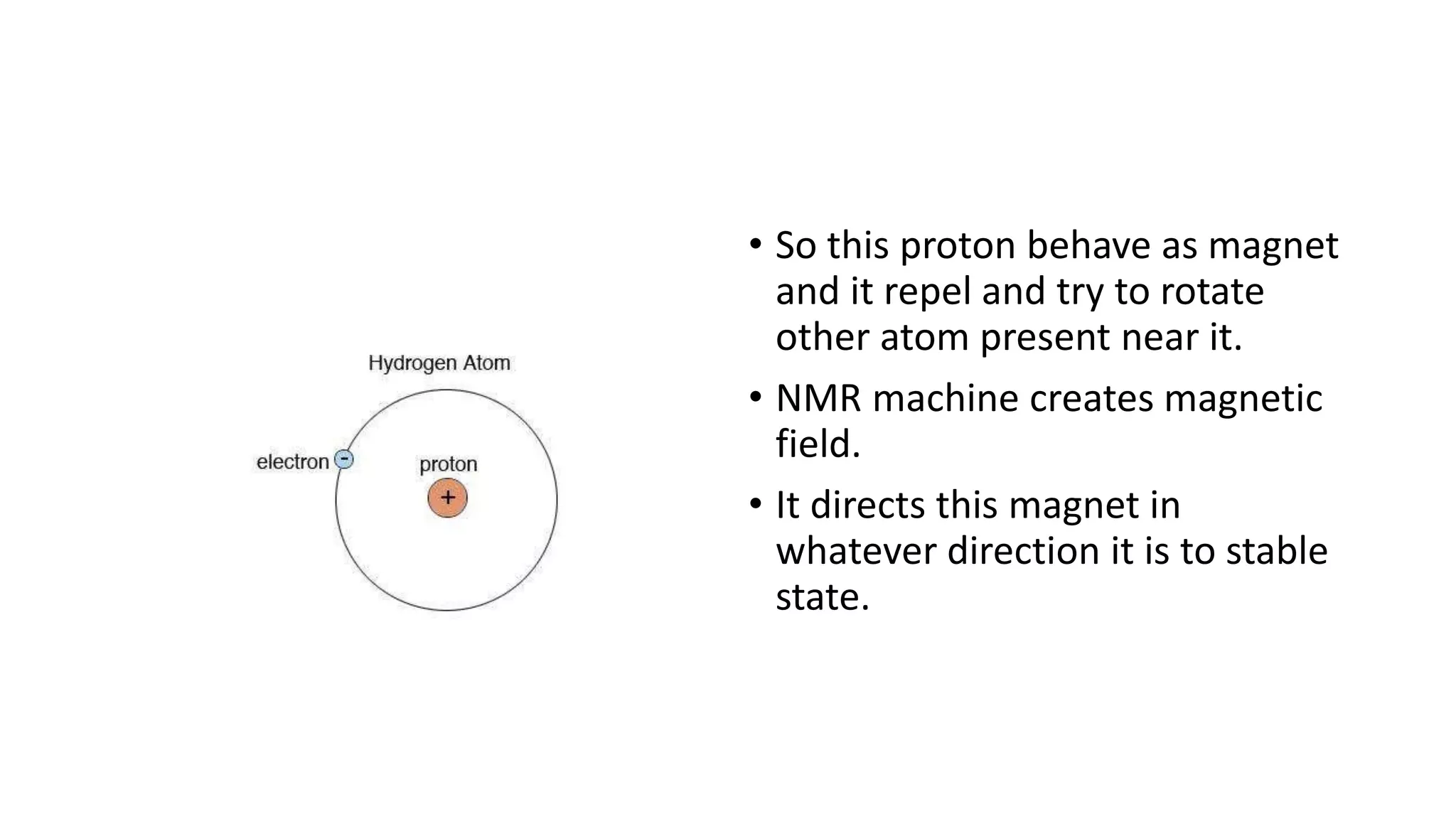
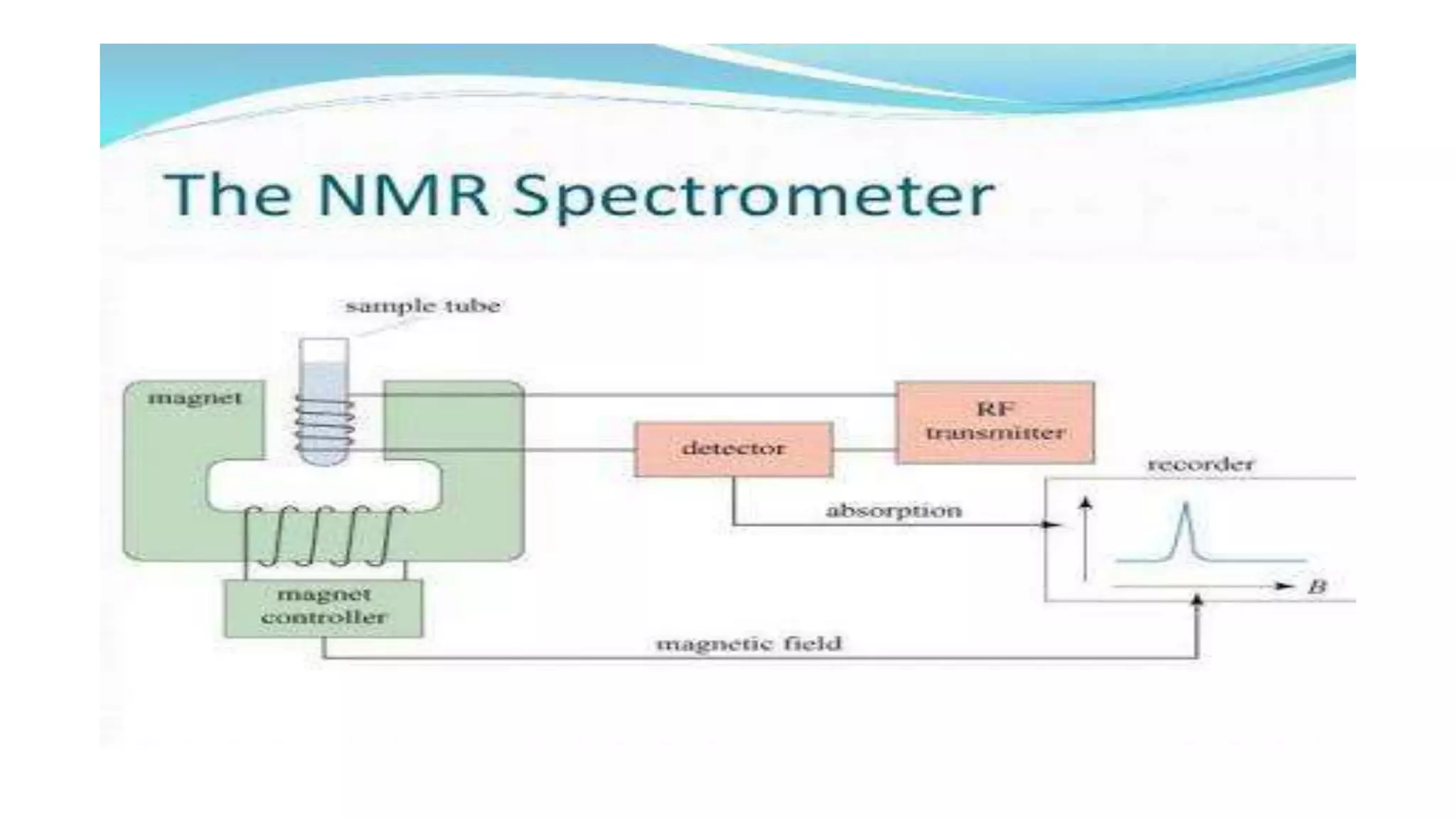
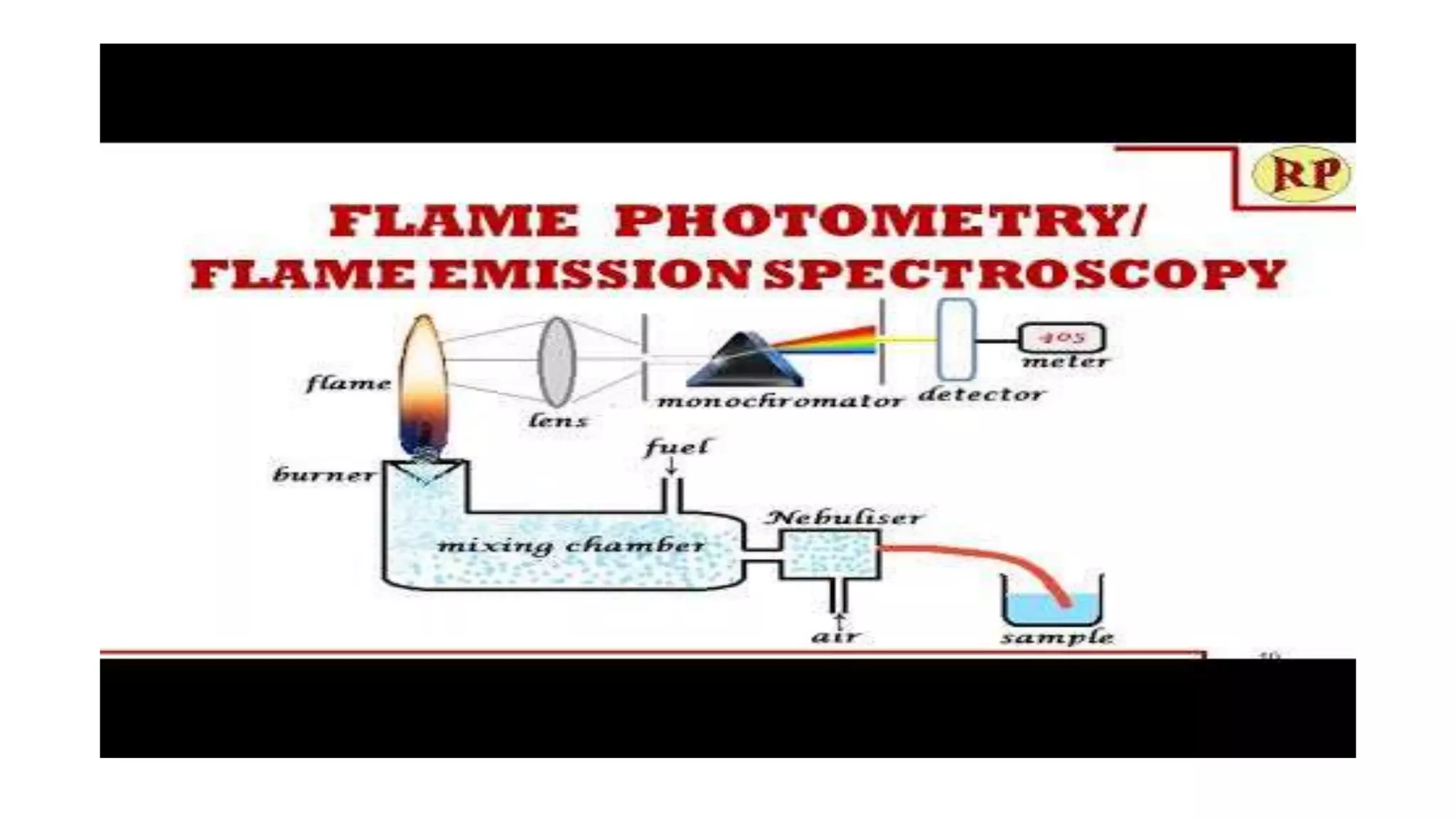
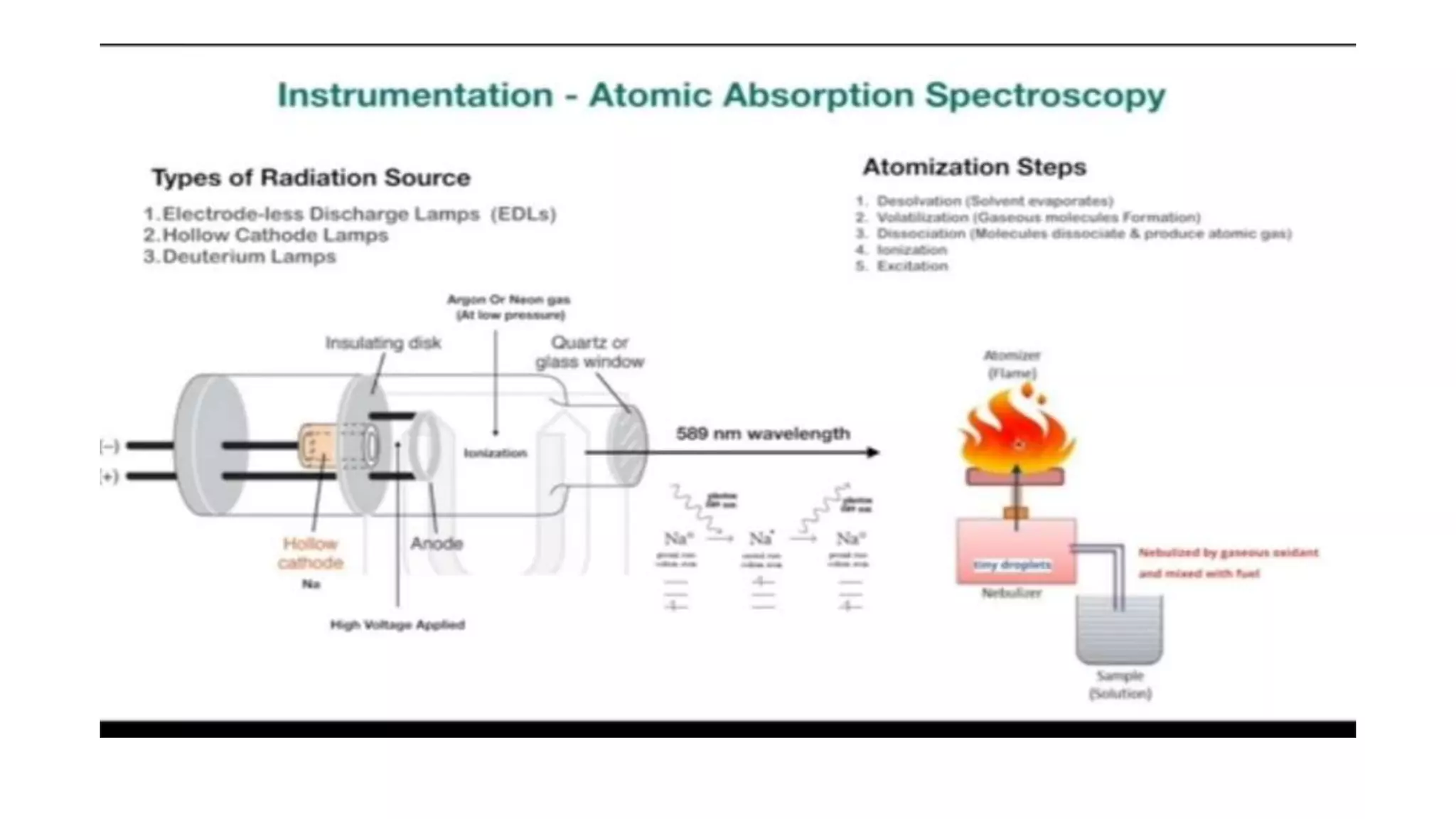
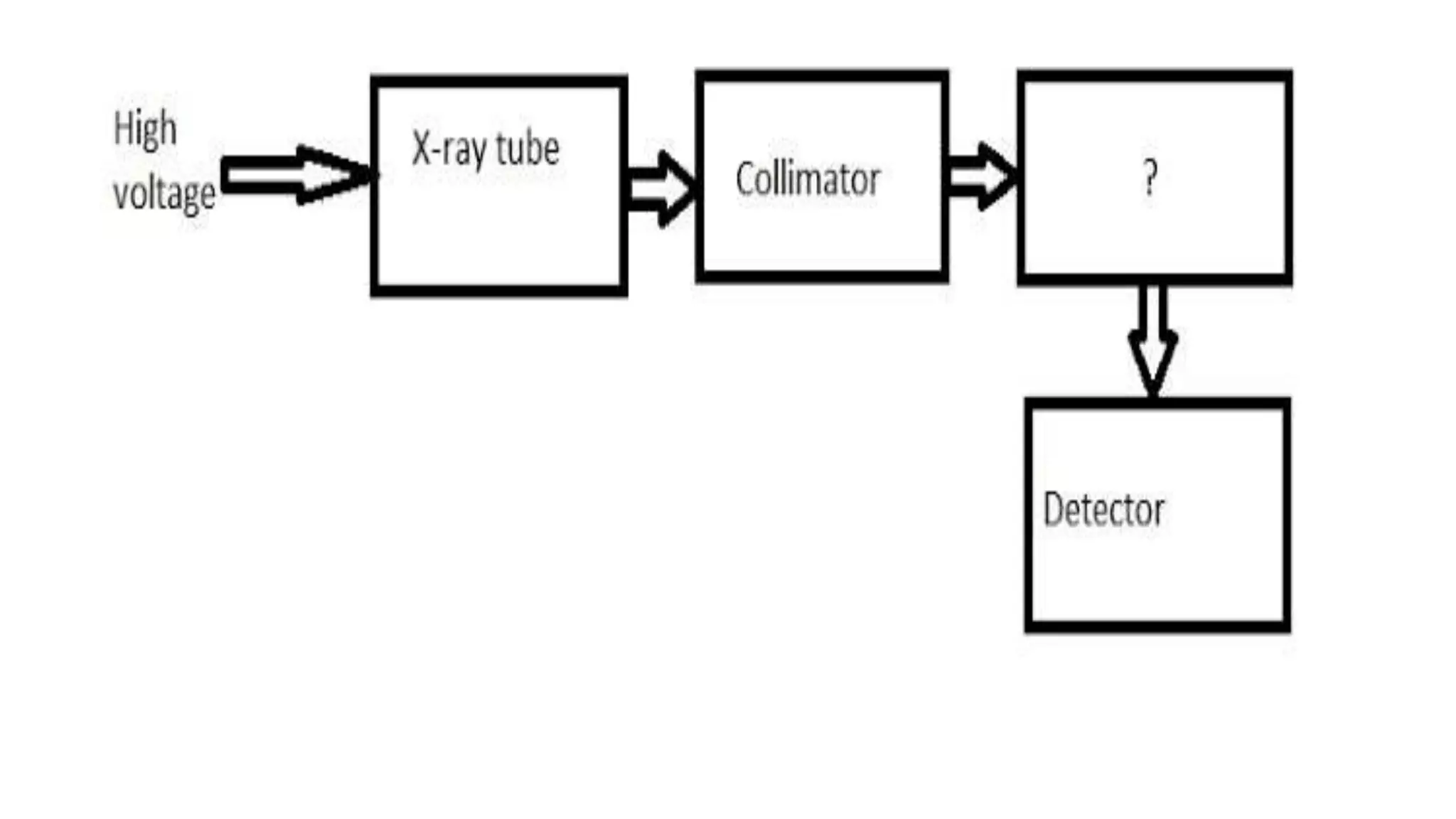
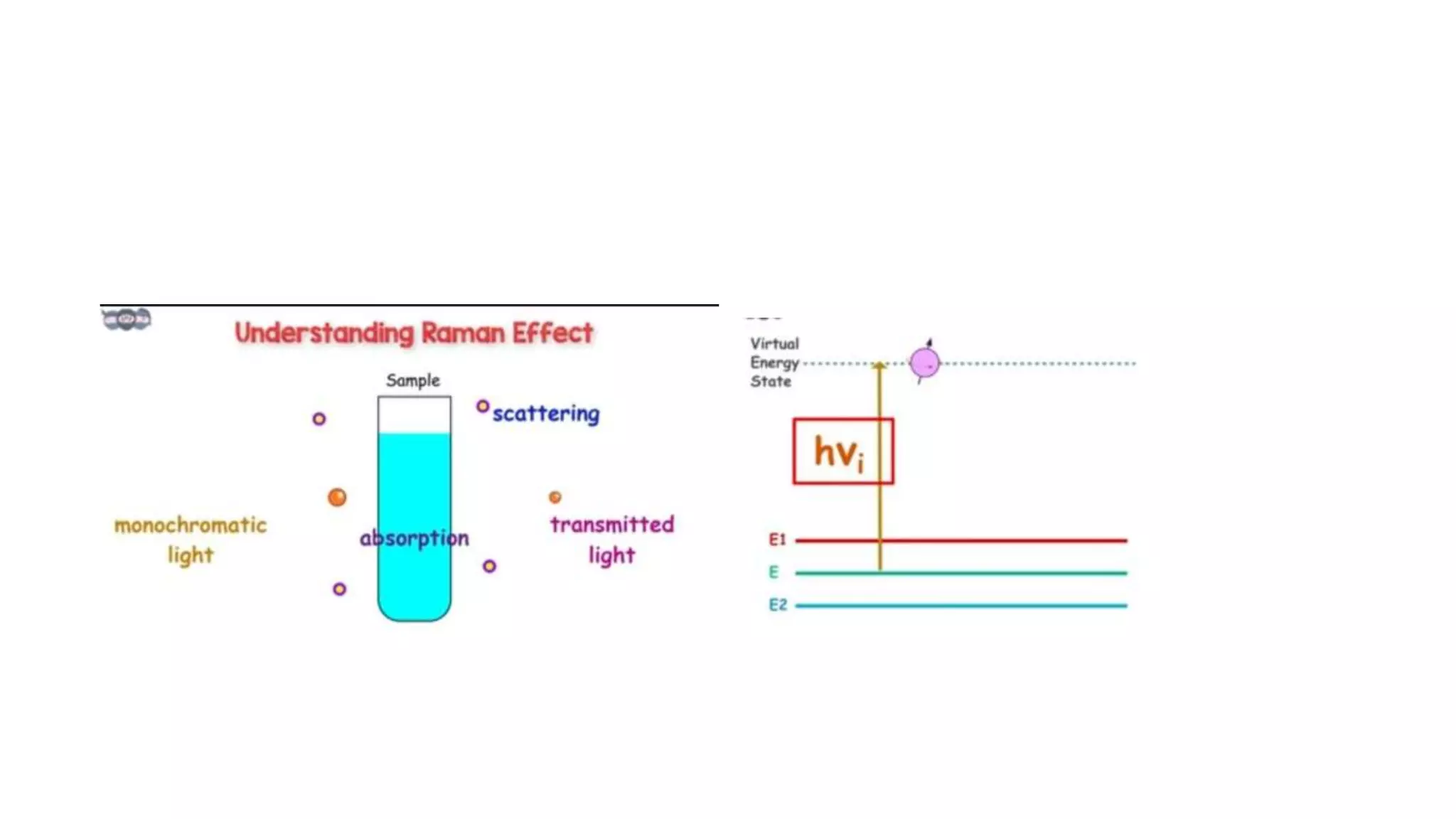
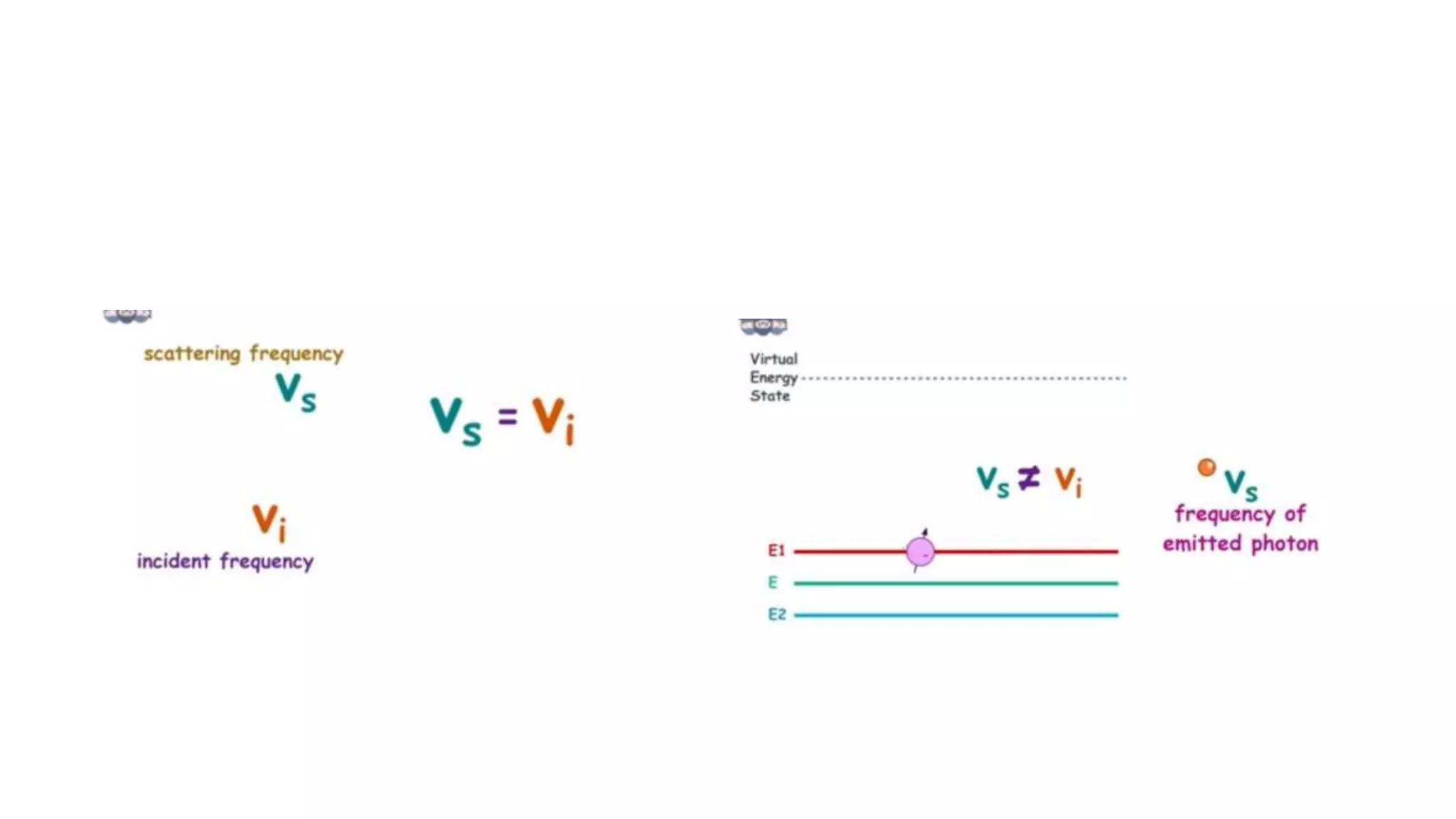
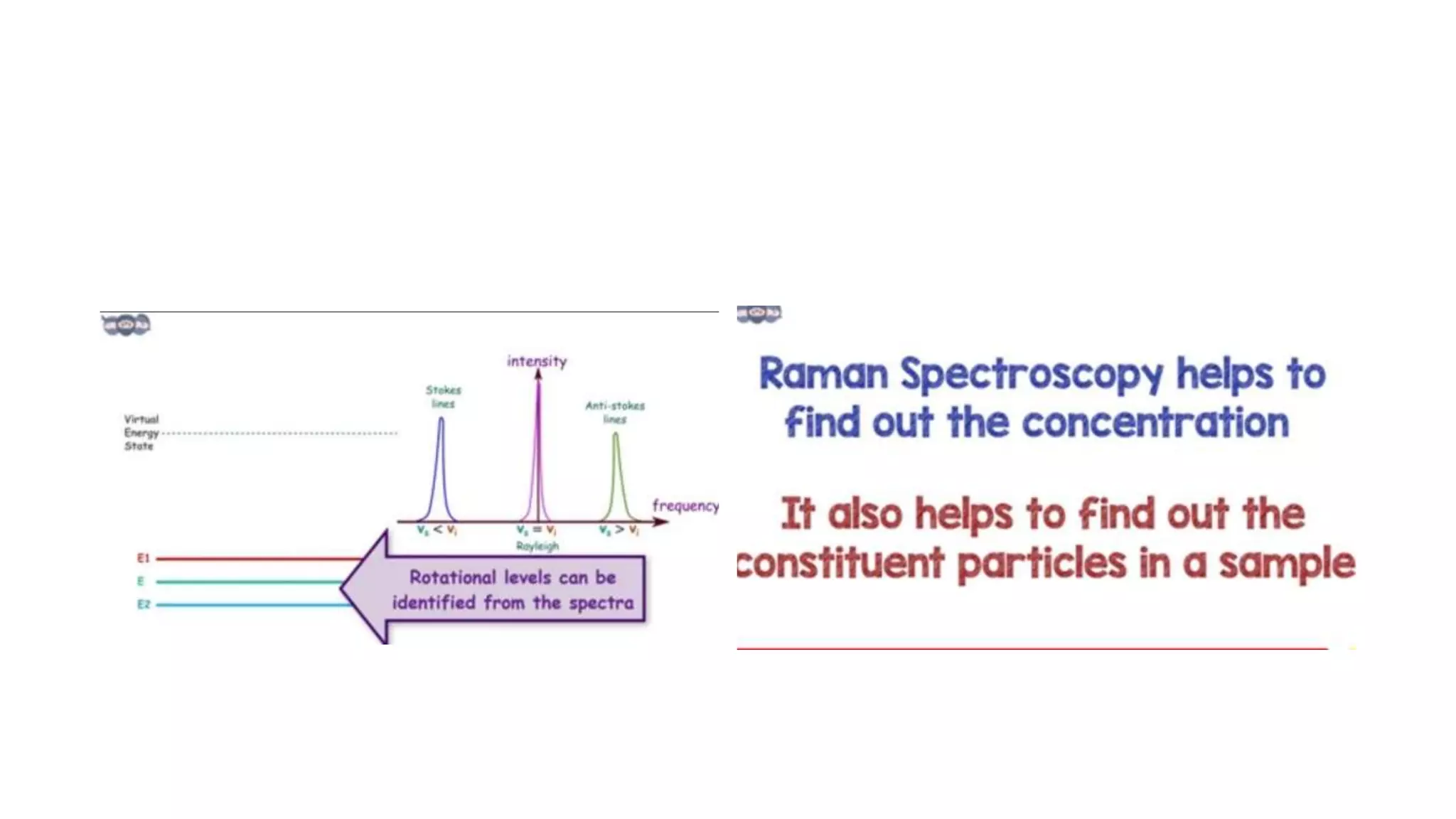
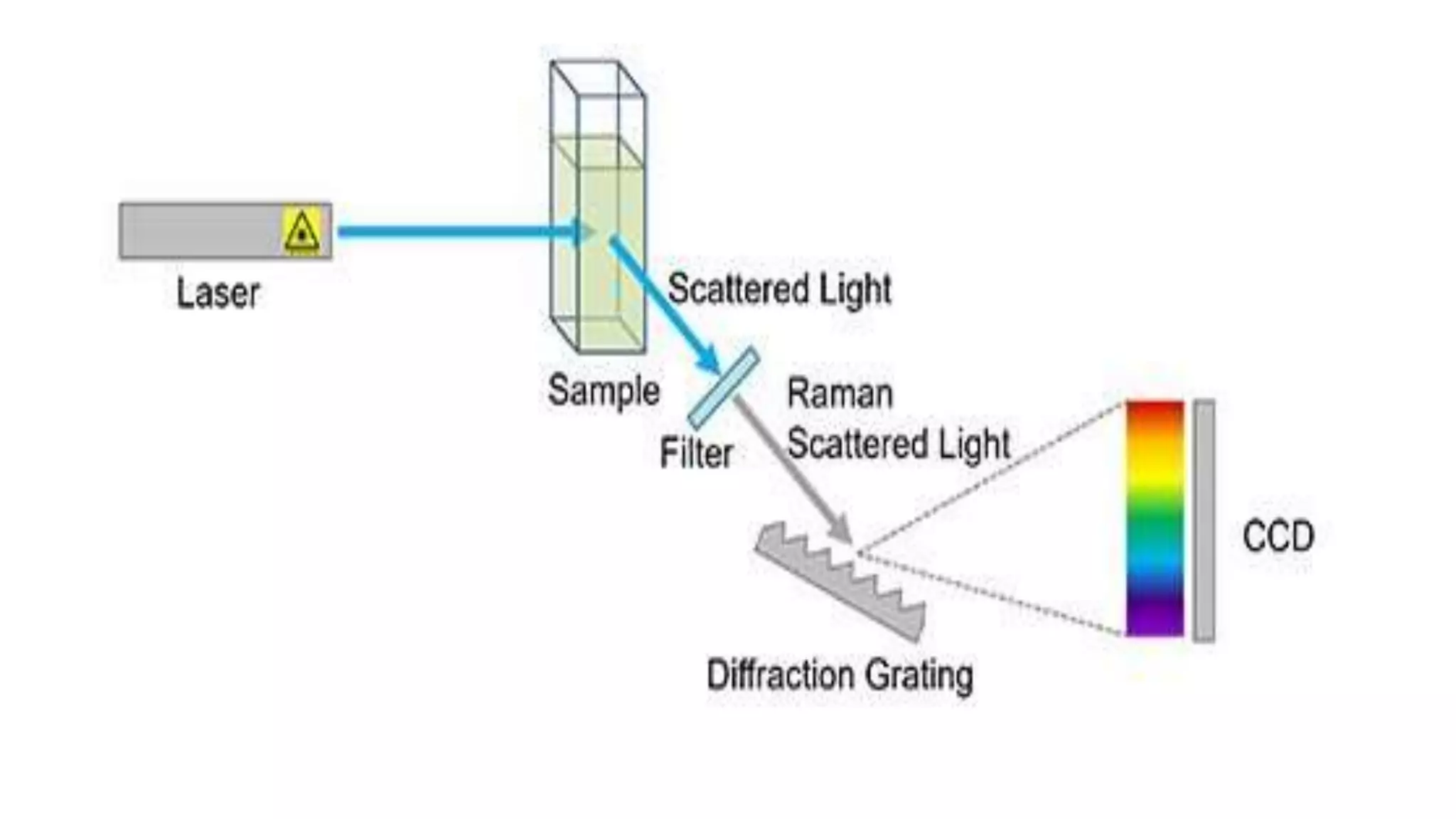
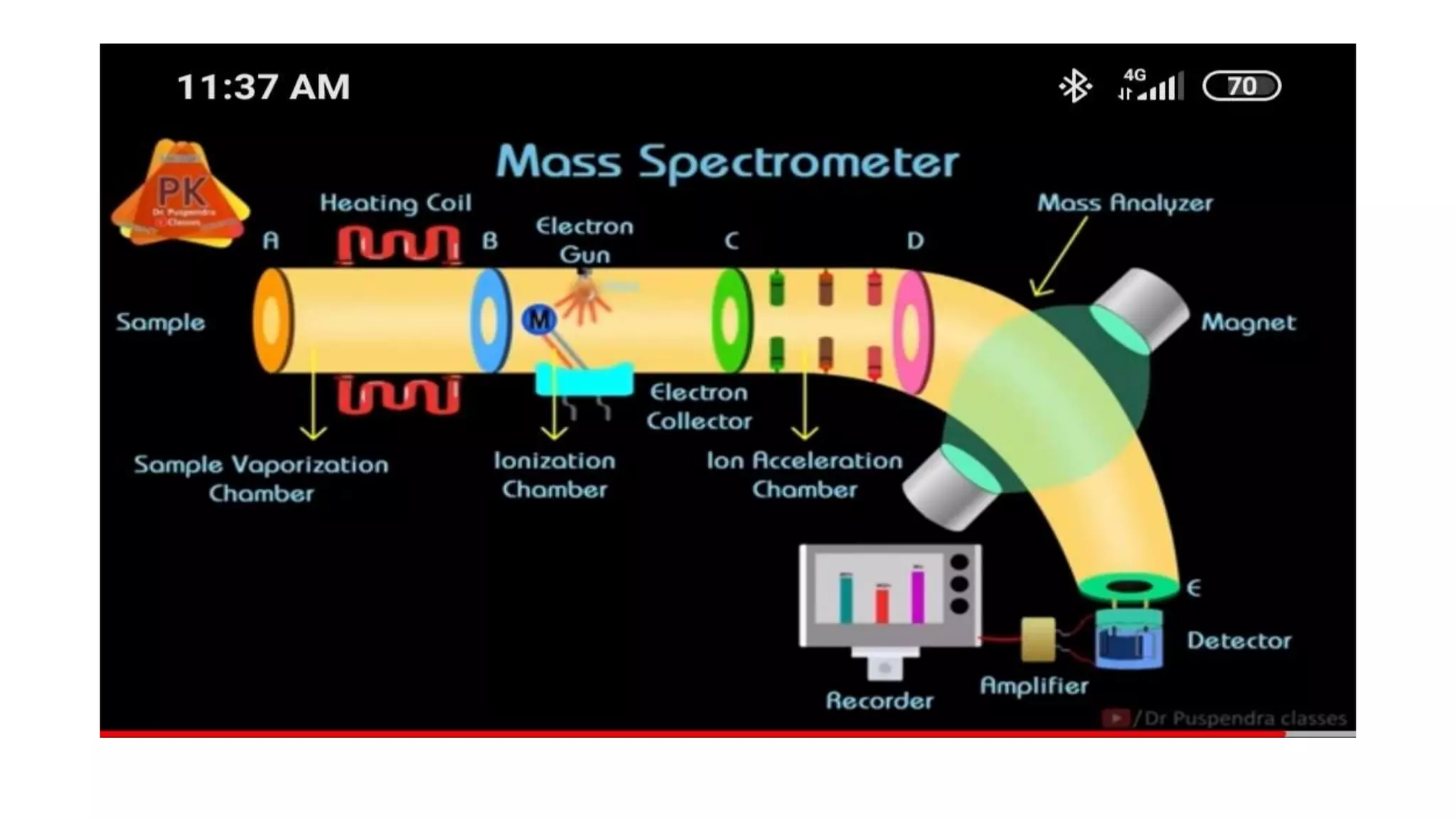
The document outlines the principles and applications of spectroscopy, which involves studying the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. It covers various techniques such as infrared, UV-visible, NMR, and fluorescence spectroscopy, detailing their uses in determining substance concentrations, molecular structures, and identifying compounds. Additionally, the document explains the functioning of spectrometers and how they analyze the emitted or absorbed light to extract essential chemical information.