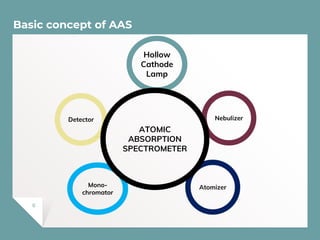
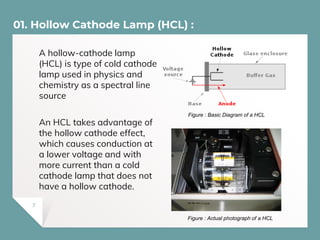
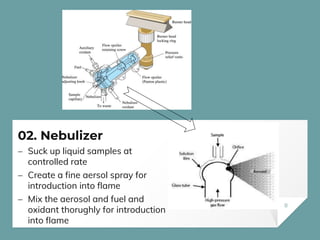
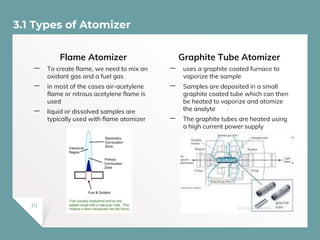
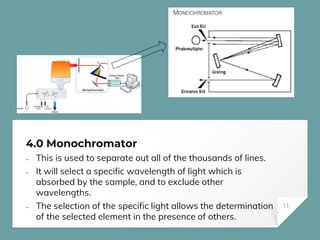
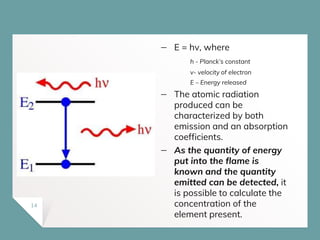
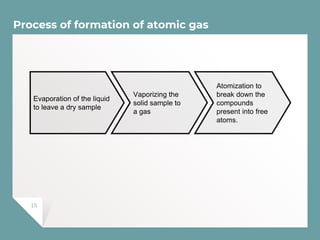
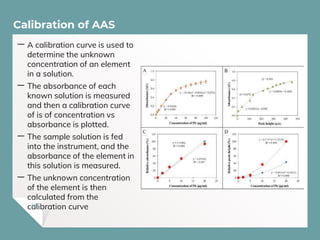
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is a technique for detecting metals and metalloids by measuring the absorption of light at specific frequencies by free atoms in a gaseous state. The process involves the use of a hollow cathode lamp, nebulizer, atomizer, monochromator, and detector to analyze concentrations of over 62 elements in various samples. AAS is applied in fields such as clinical analysis, environmental monitoring, pharmaceuticals, industry, and mining.