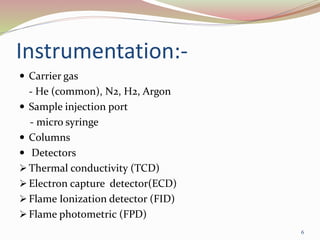
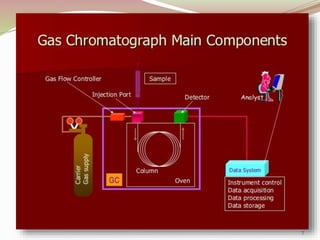
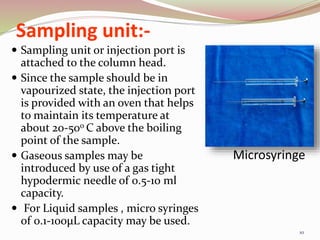
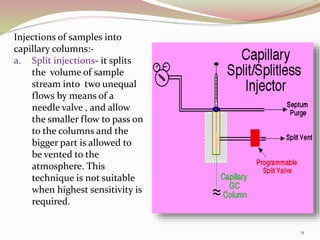
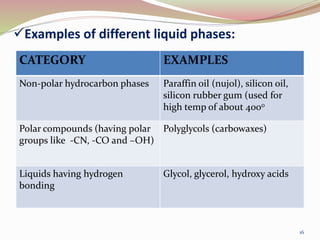
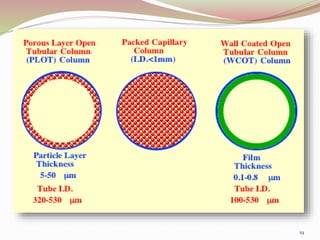
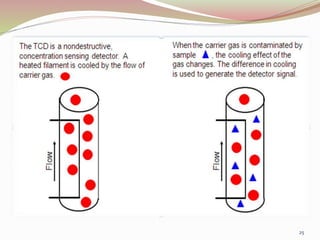
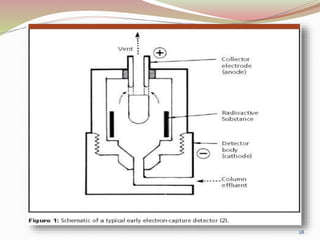
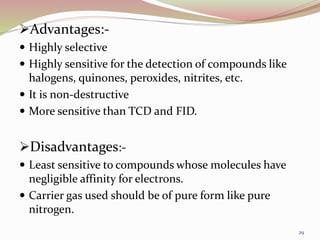
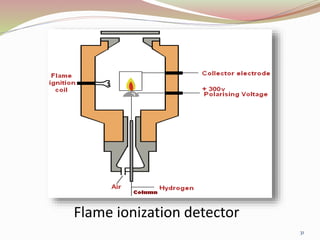
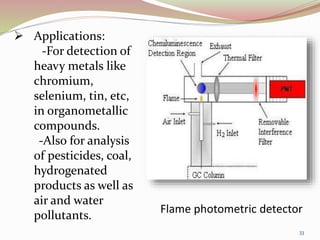
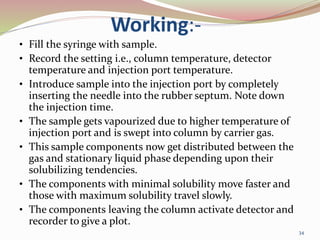
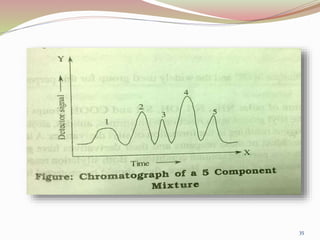
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate components of a mixture based on how they partition between a mobile gas phase and a stationary liquid phase. It involves vaporizing the sample and injecting it into a column containing a stationary phase, where components are separated as they are transported through the column by the mobile gas phase at different rates depending on their partition coefficients. Common detectors used at the end of the column include the thermal conductivity detector, electron capture detector, and flame ionization detector, which produce signals proportional to the concentration of eluting components. Gas chromatography has many applications in fields like pharmaceutical analysis, food testing, and environmental analysis.