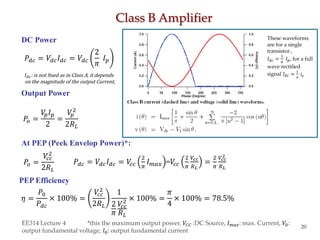
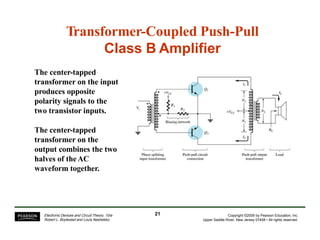
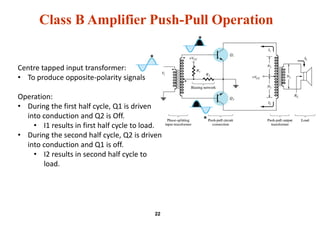
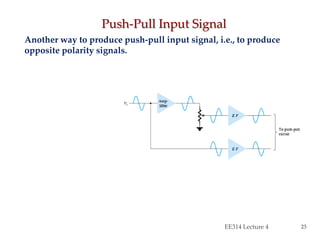
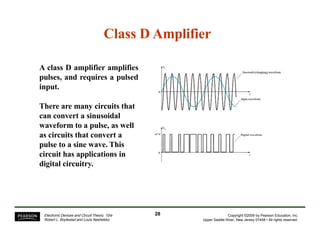
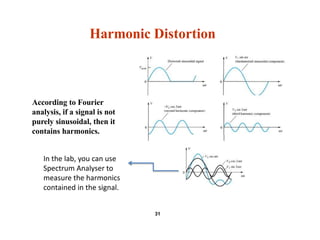
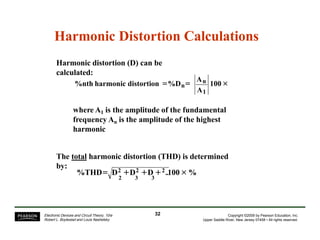
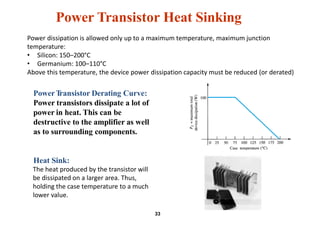
This document summarizes a lecture on power amplifiers, including:
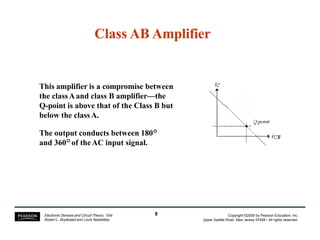
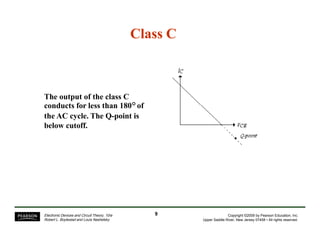
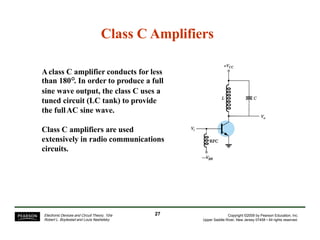
- Different classes of power amplifiers like Class A, B, AB, C, and D based on conduction angle.
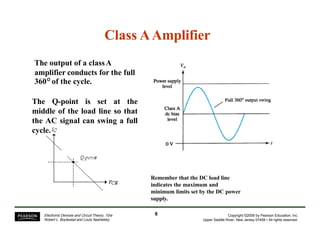
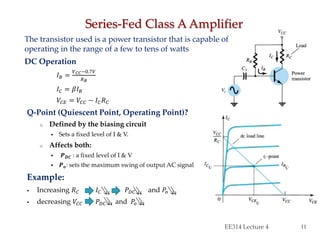
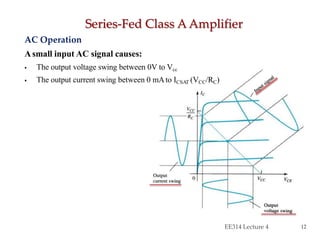
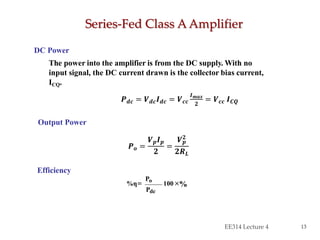
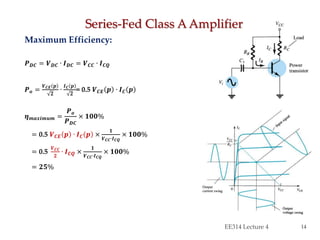
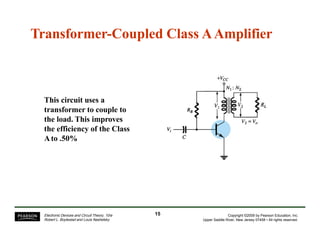
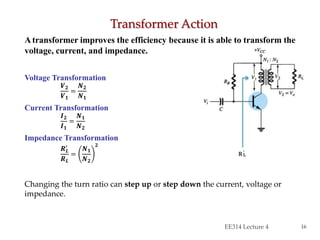
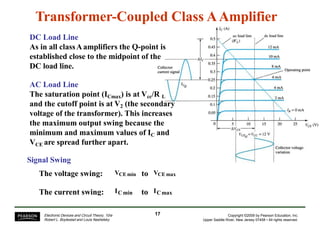
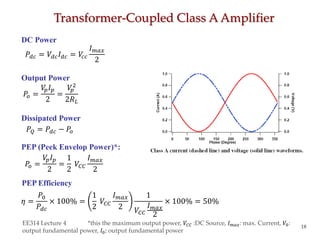
- Circuit designs for series-fed and transformer-coupled Class A amplifiers.
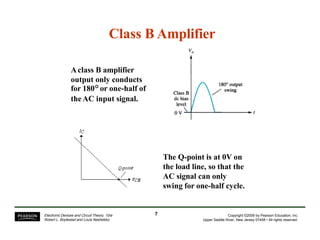
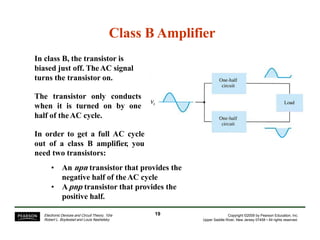
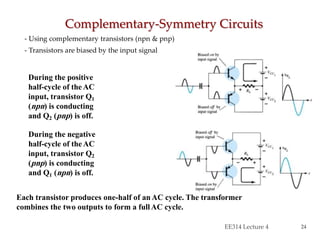
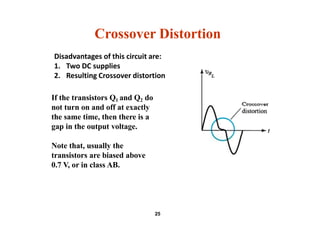
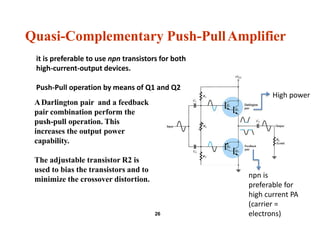
- Circuit designs for Class B amplifier using complementary pairs or a Darlington pair to achieve push-pull operation.
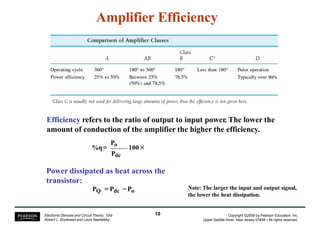
- Considerations for efficiency and maximum output power of different classes.