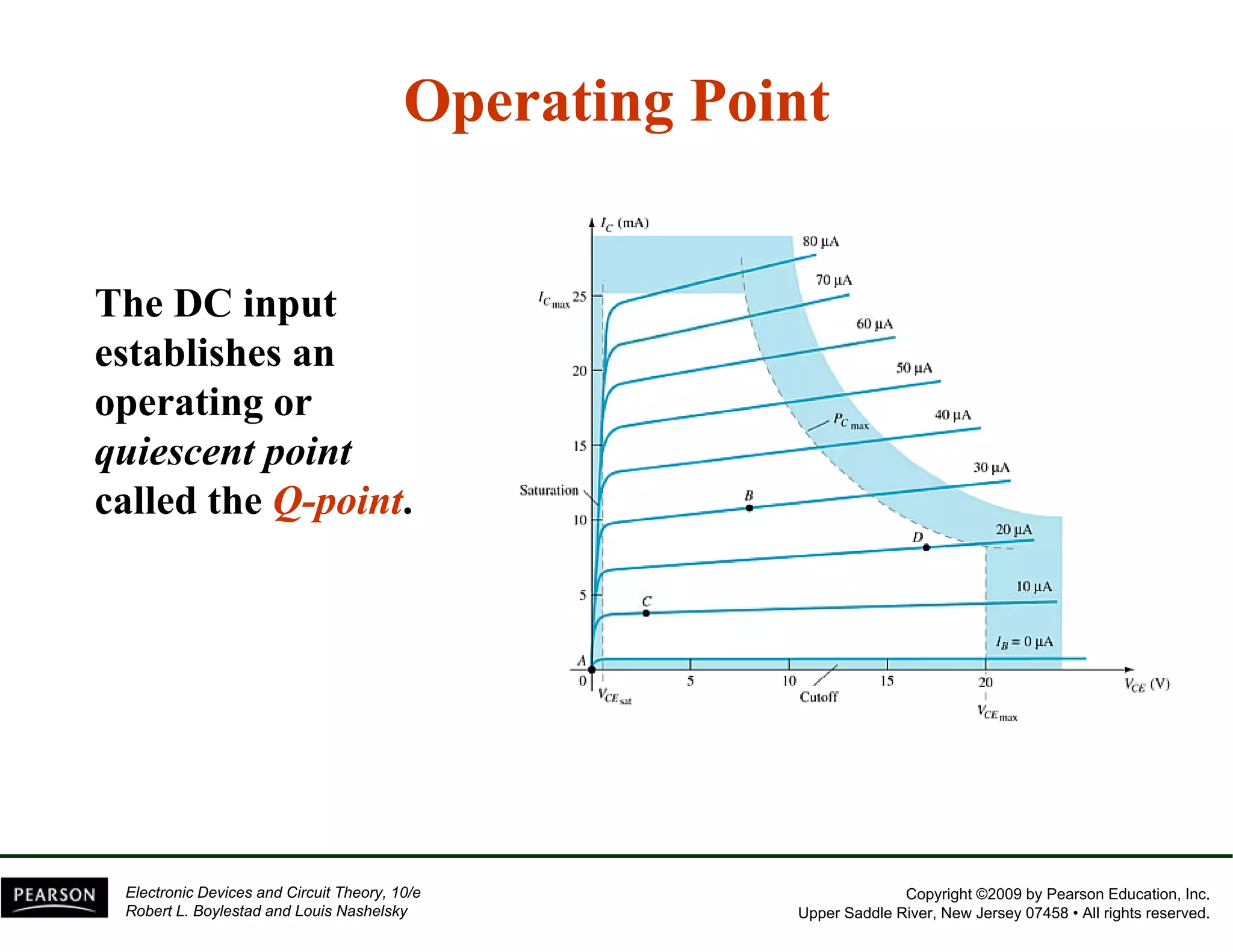
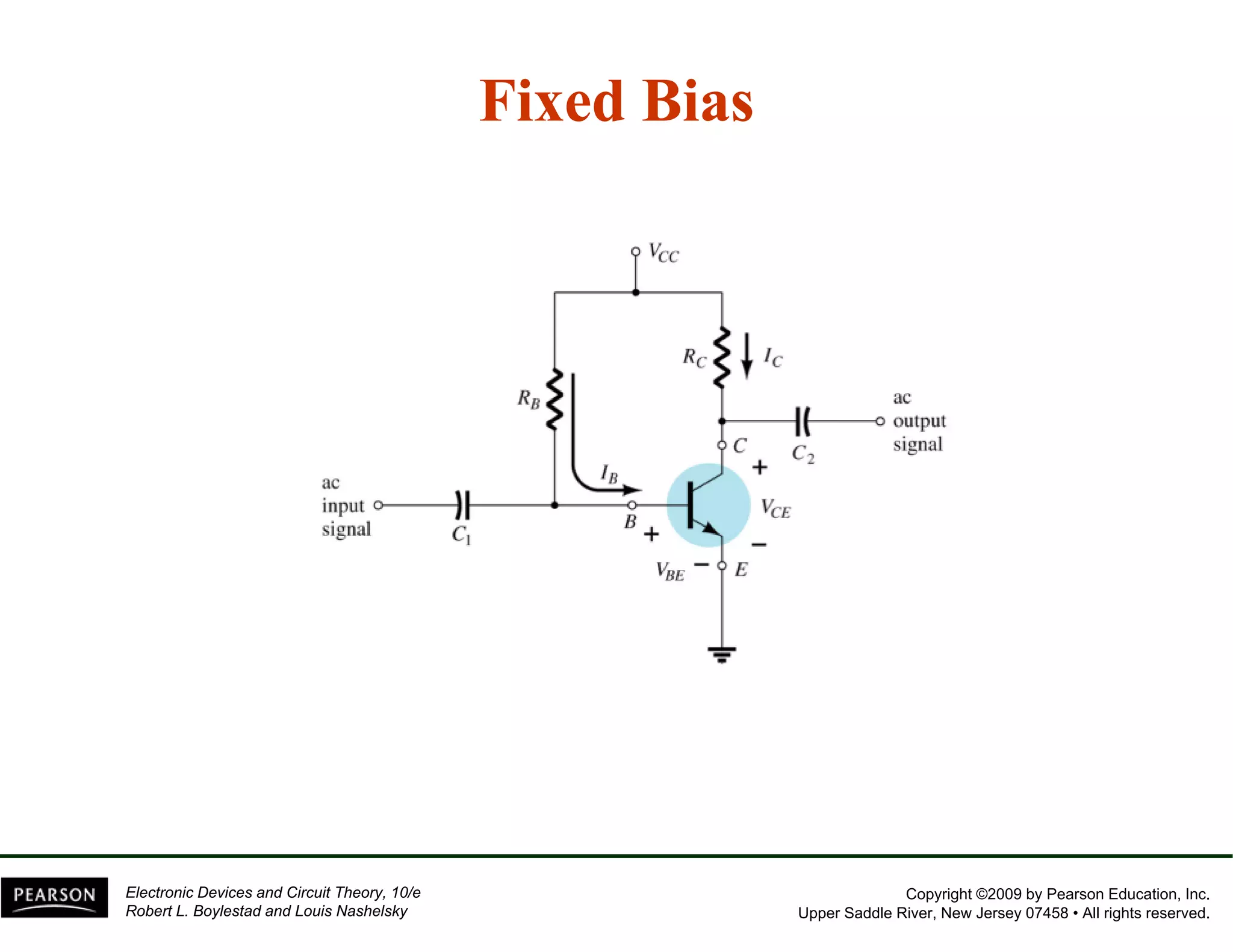
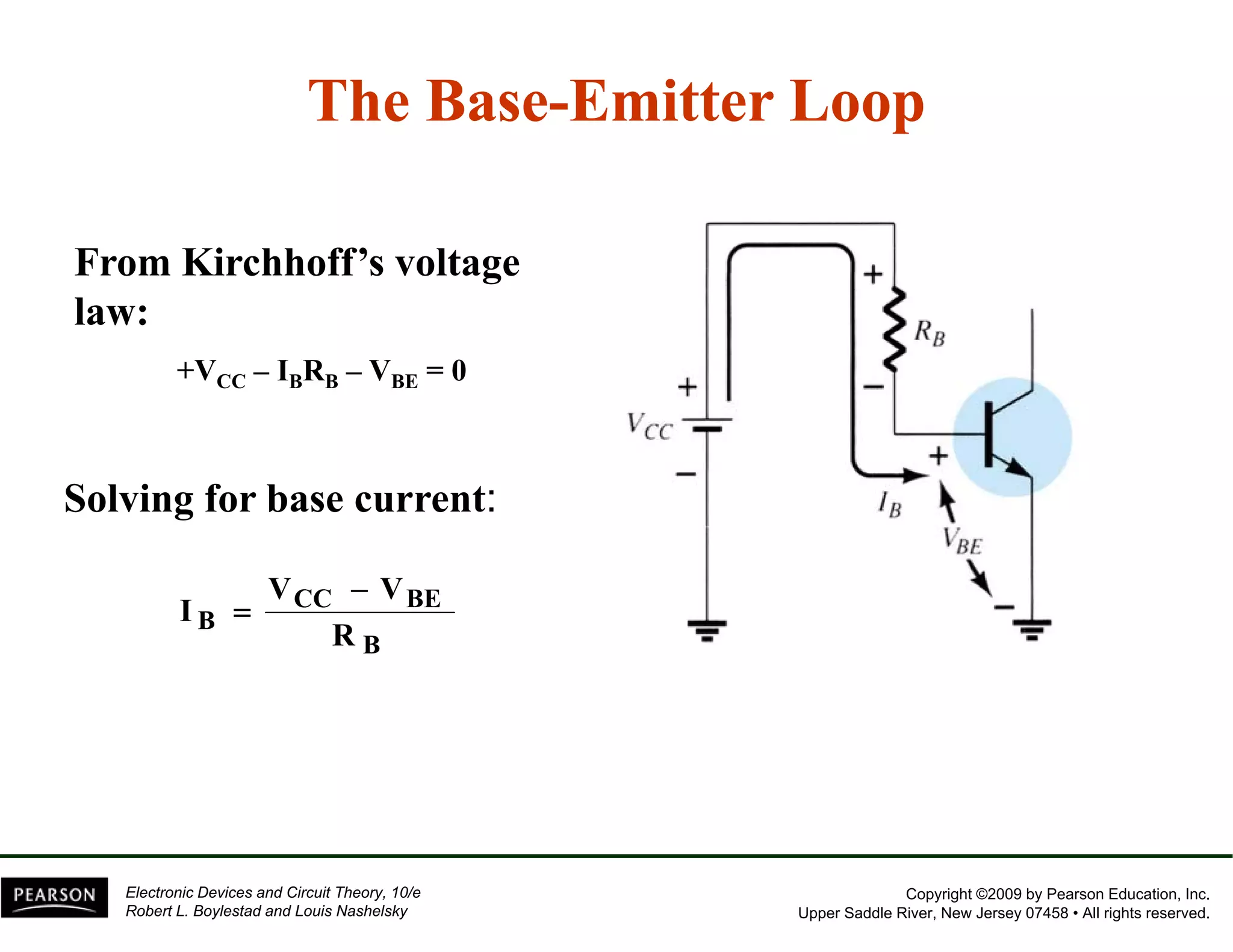
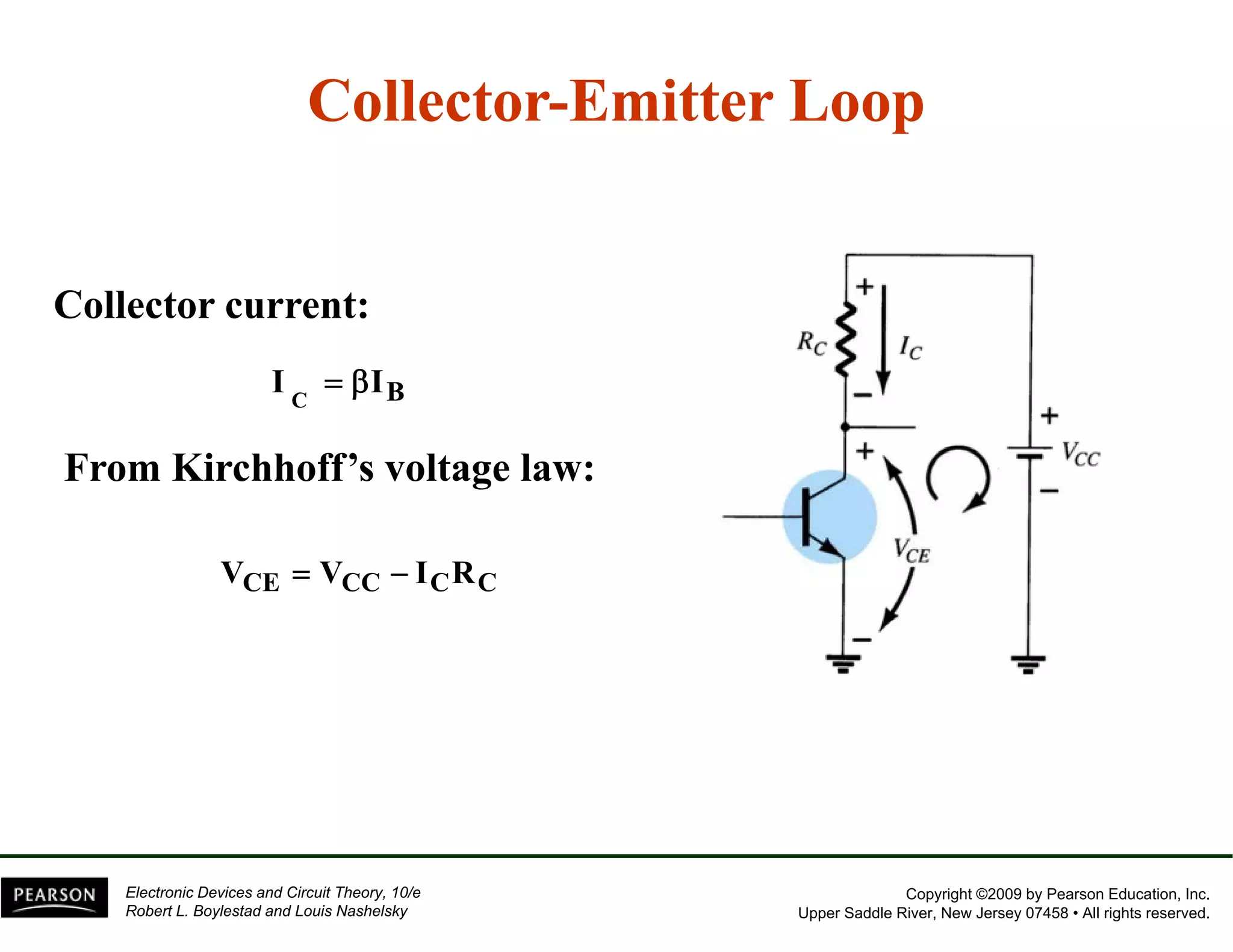
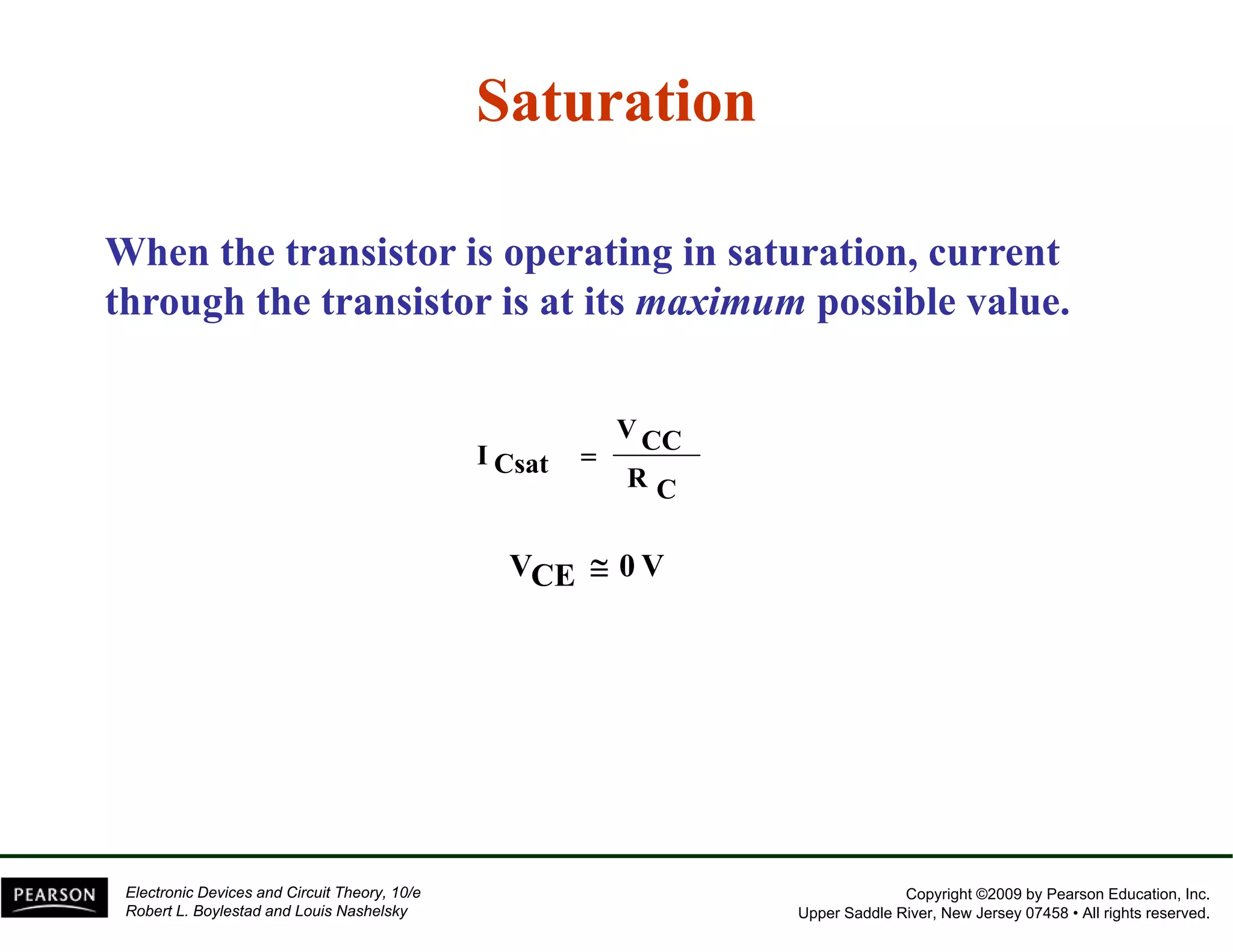
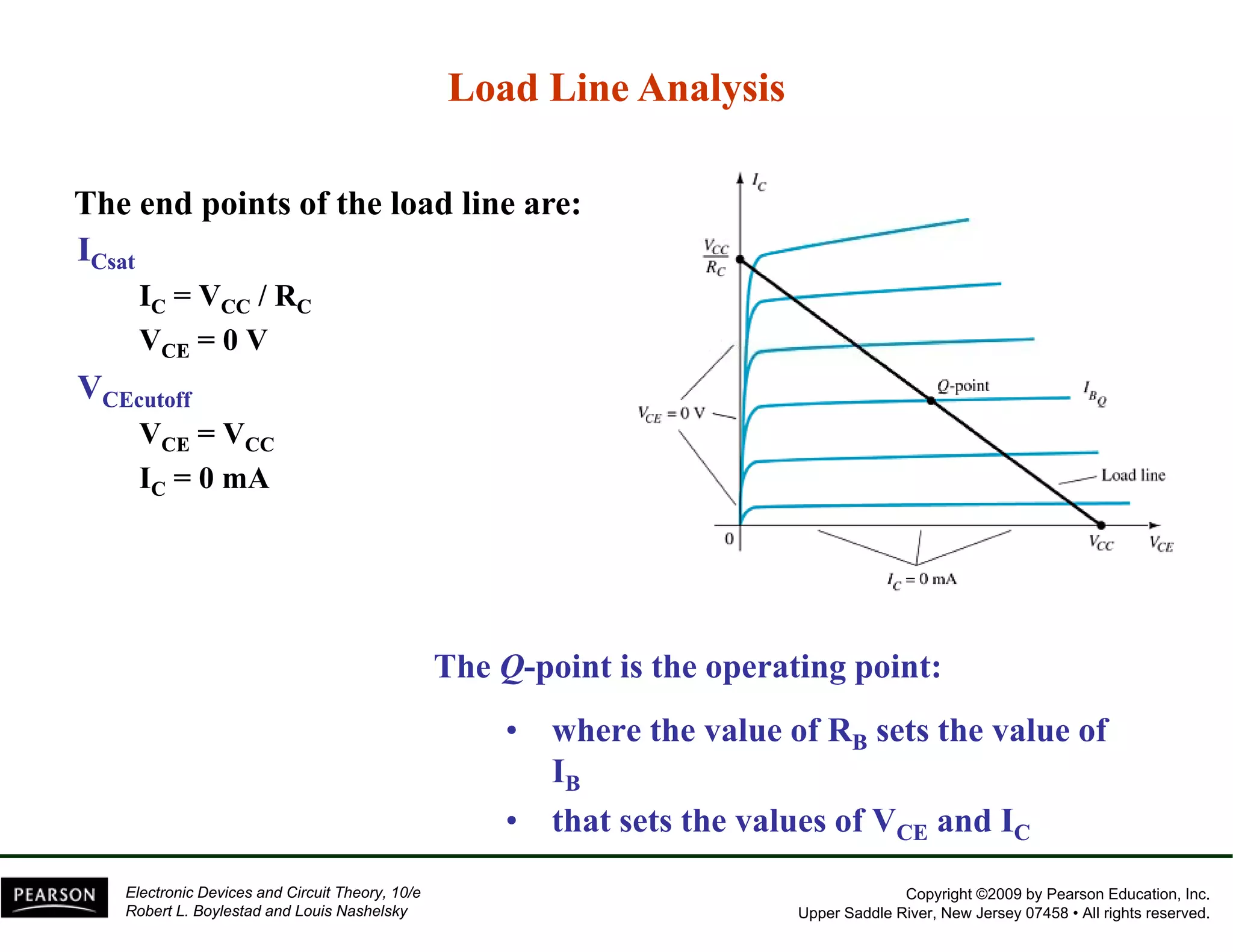
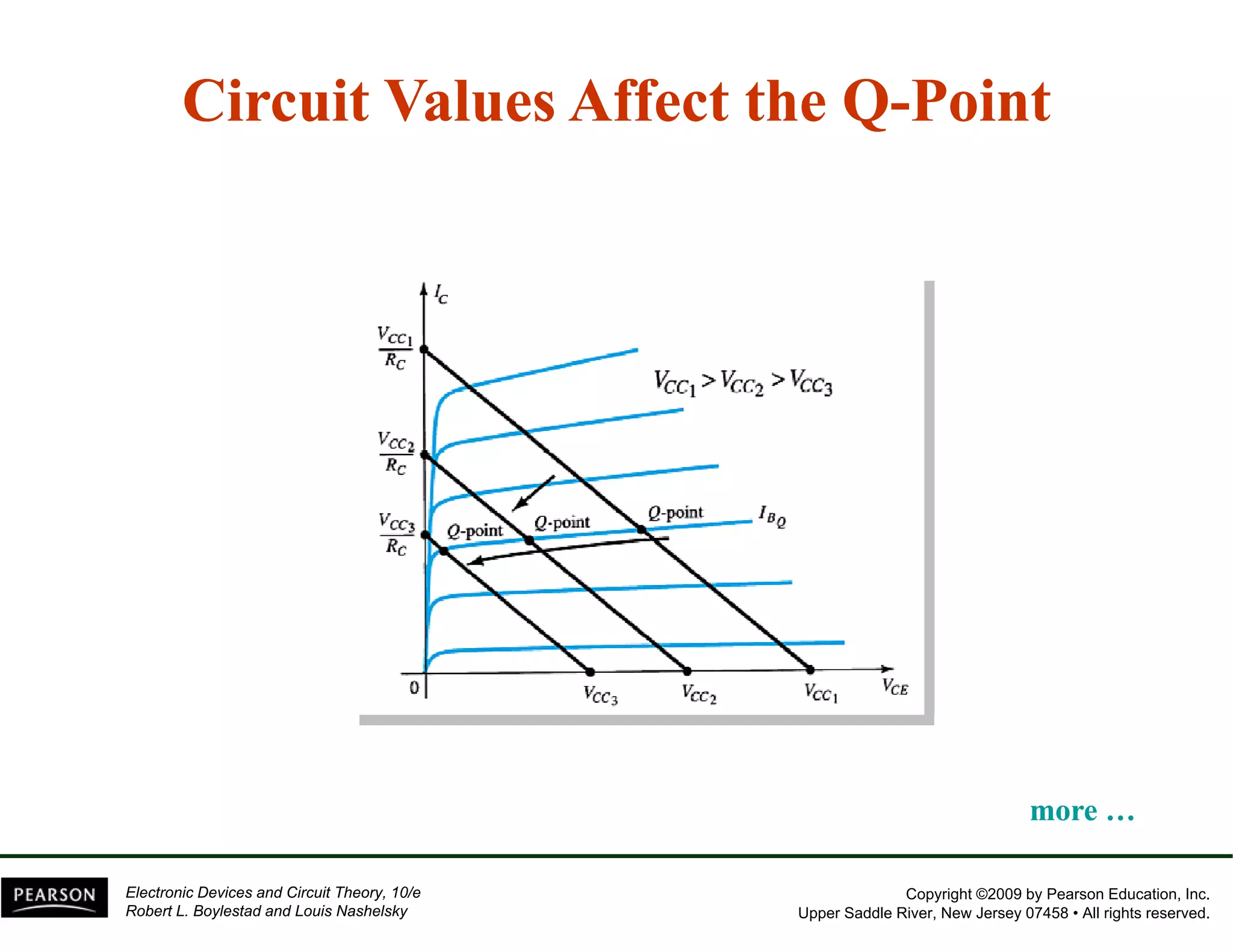
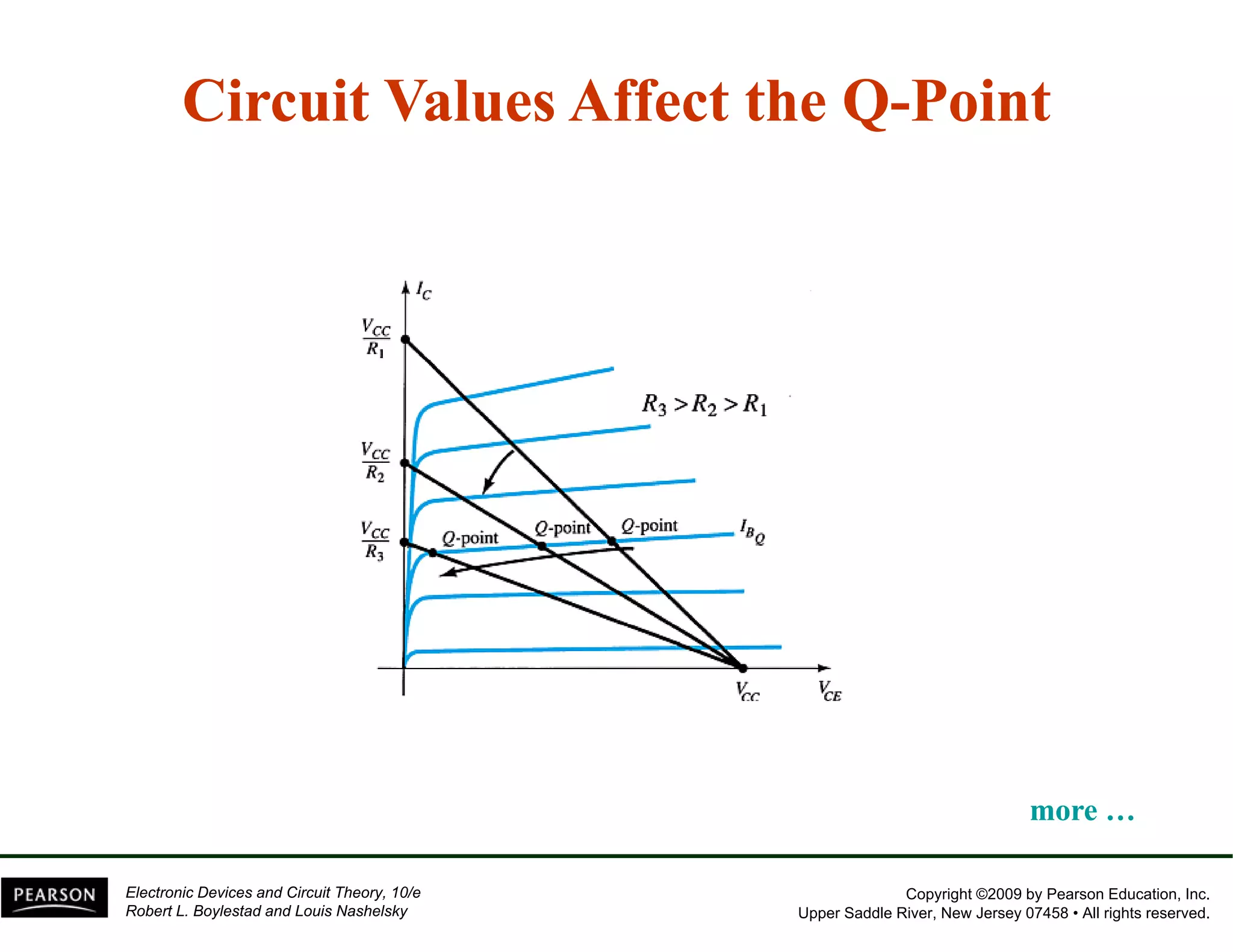
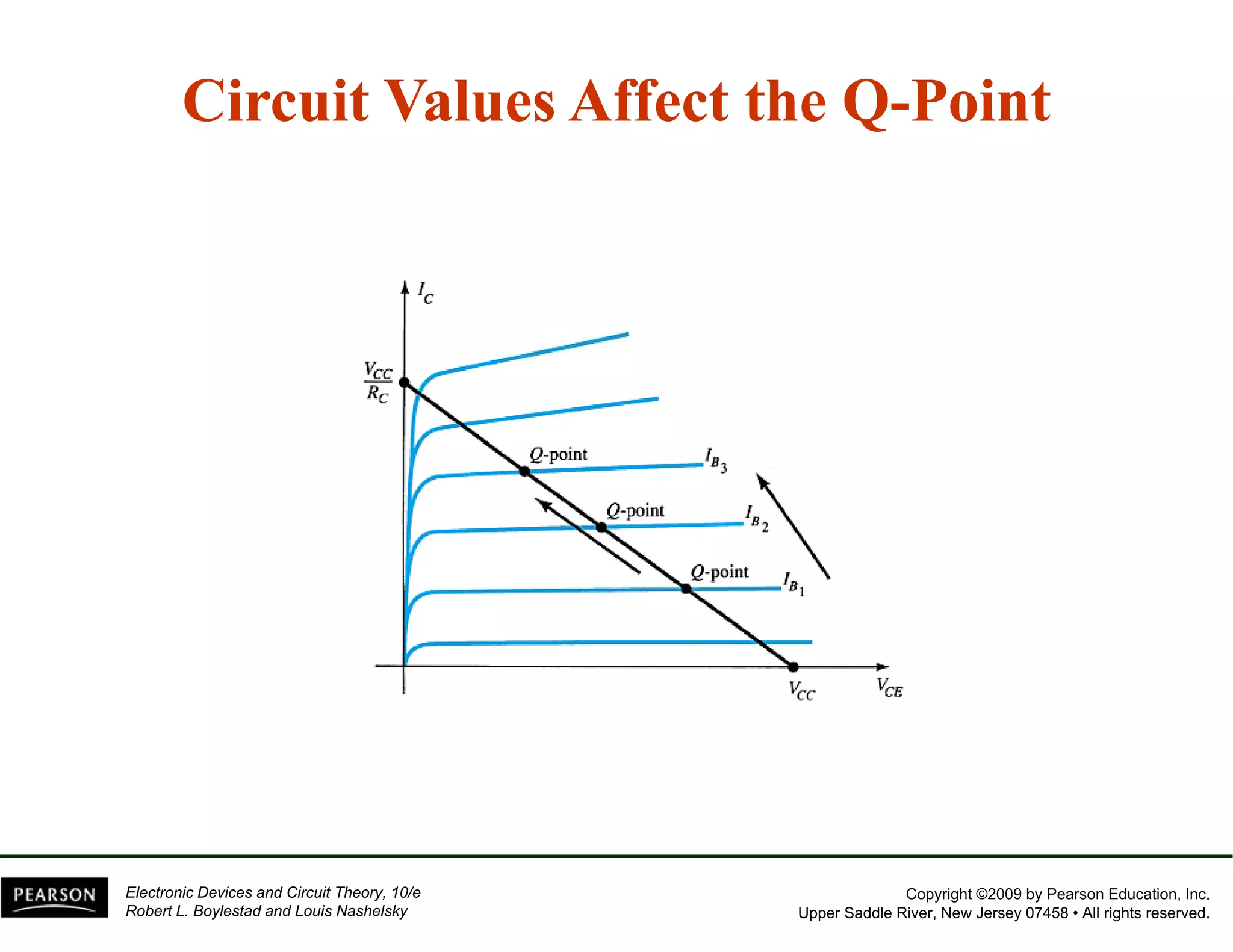
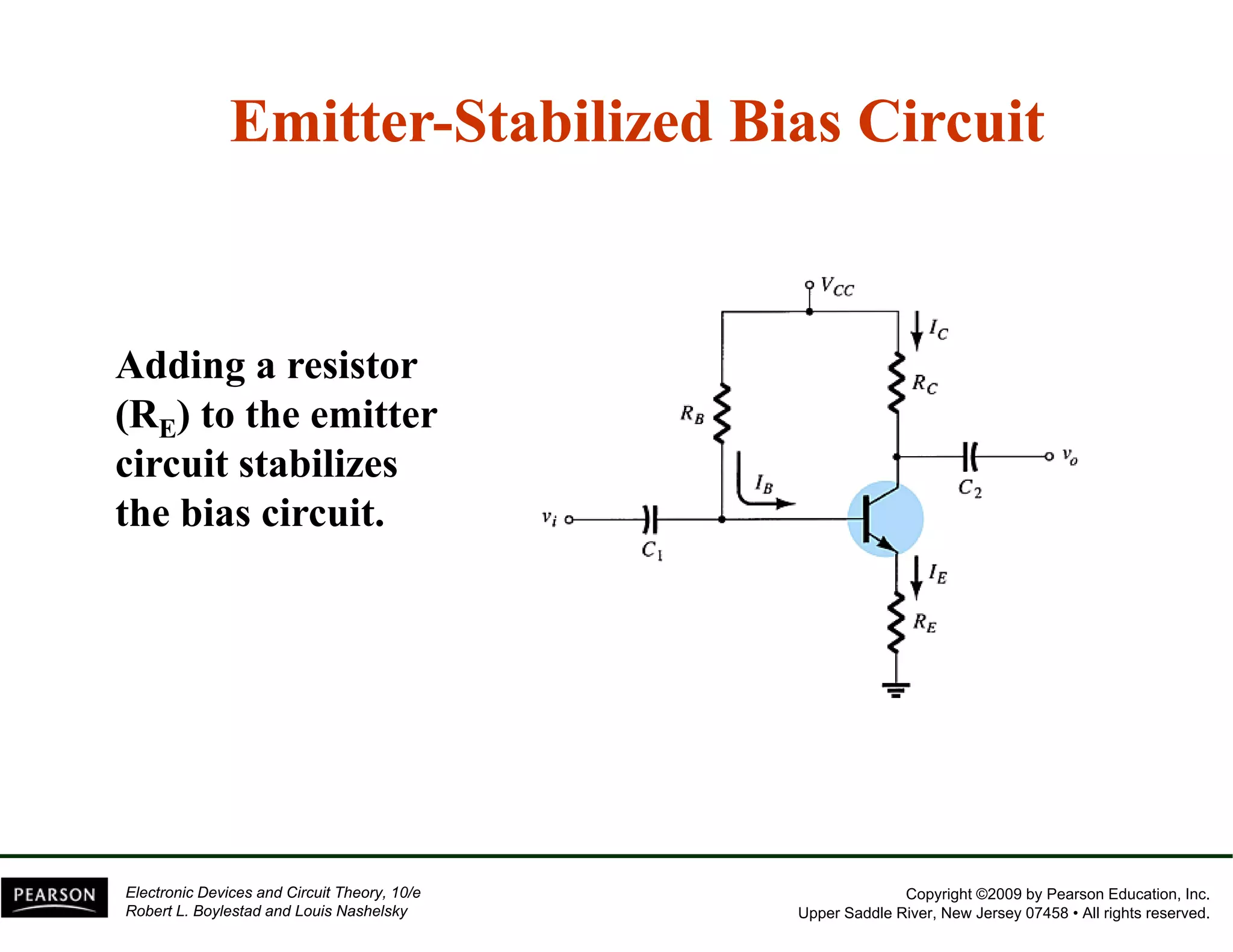
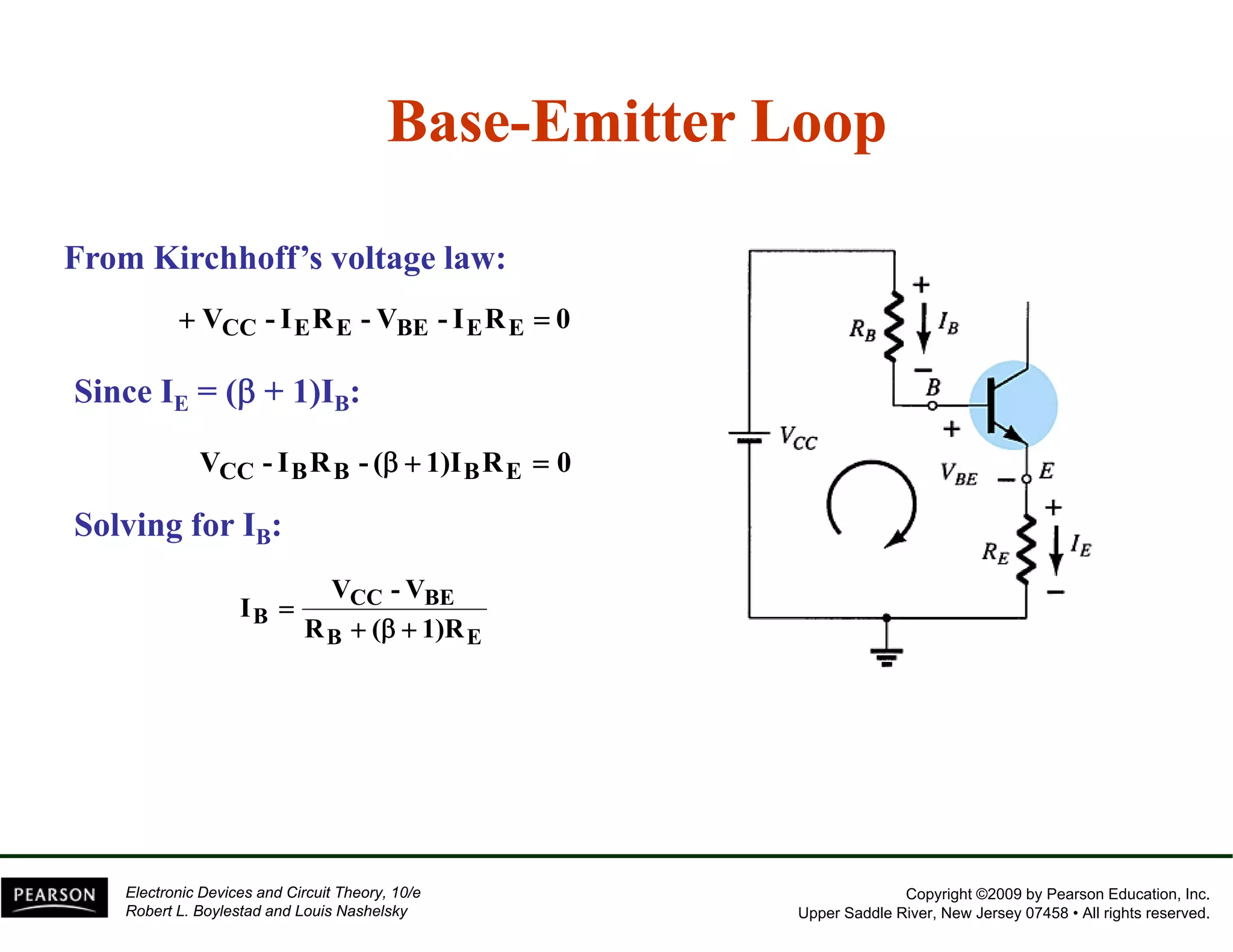
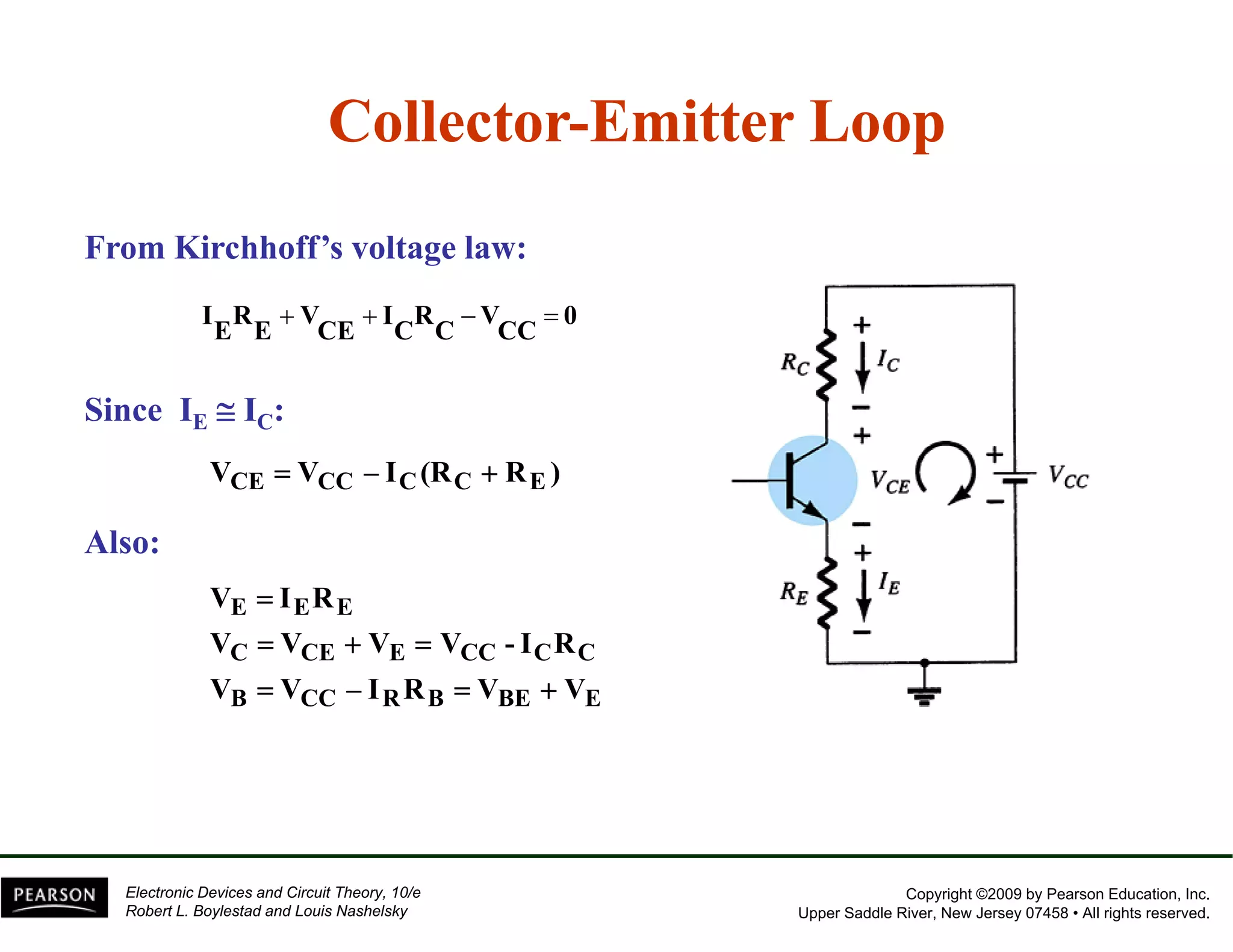
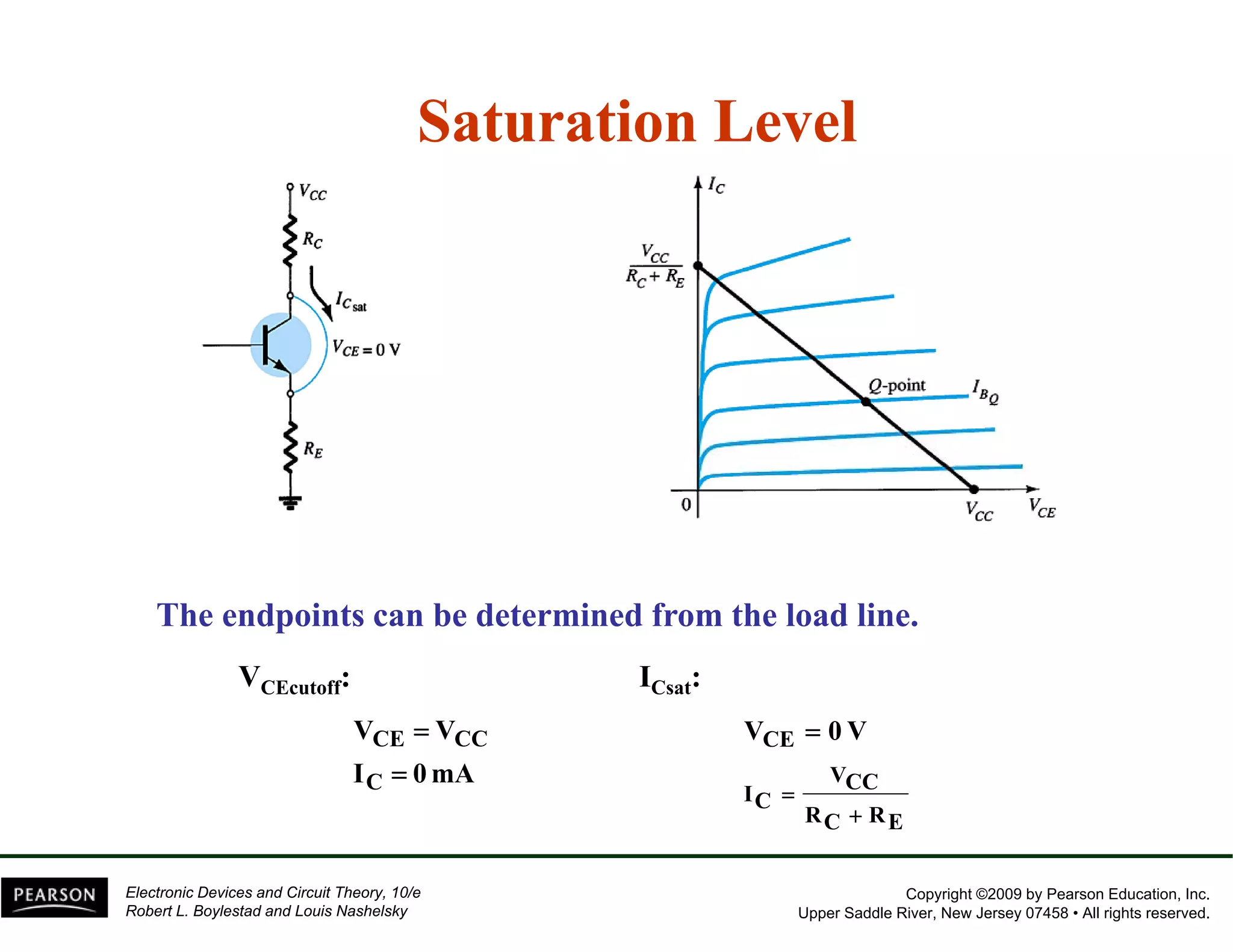
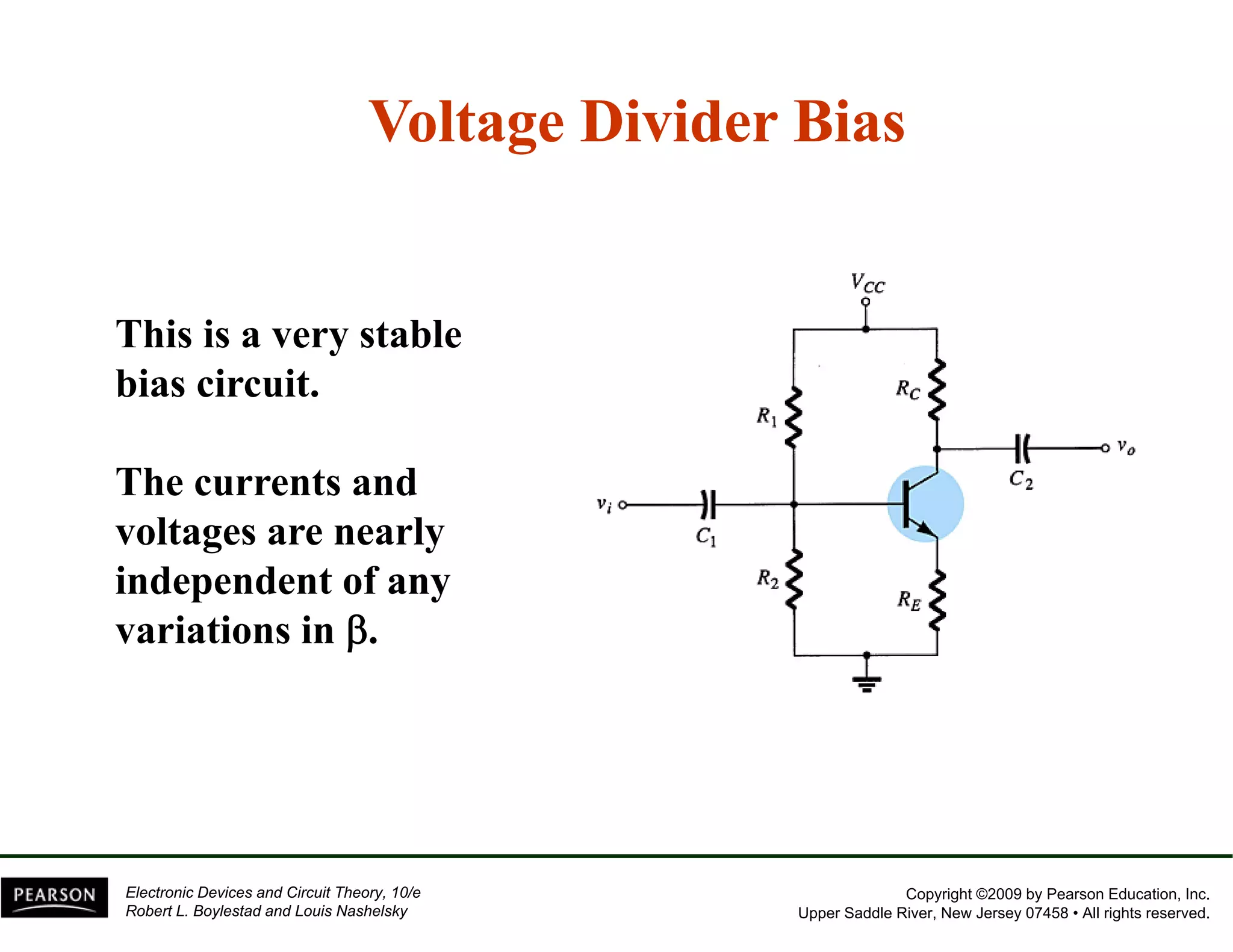
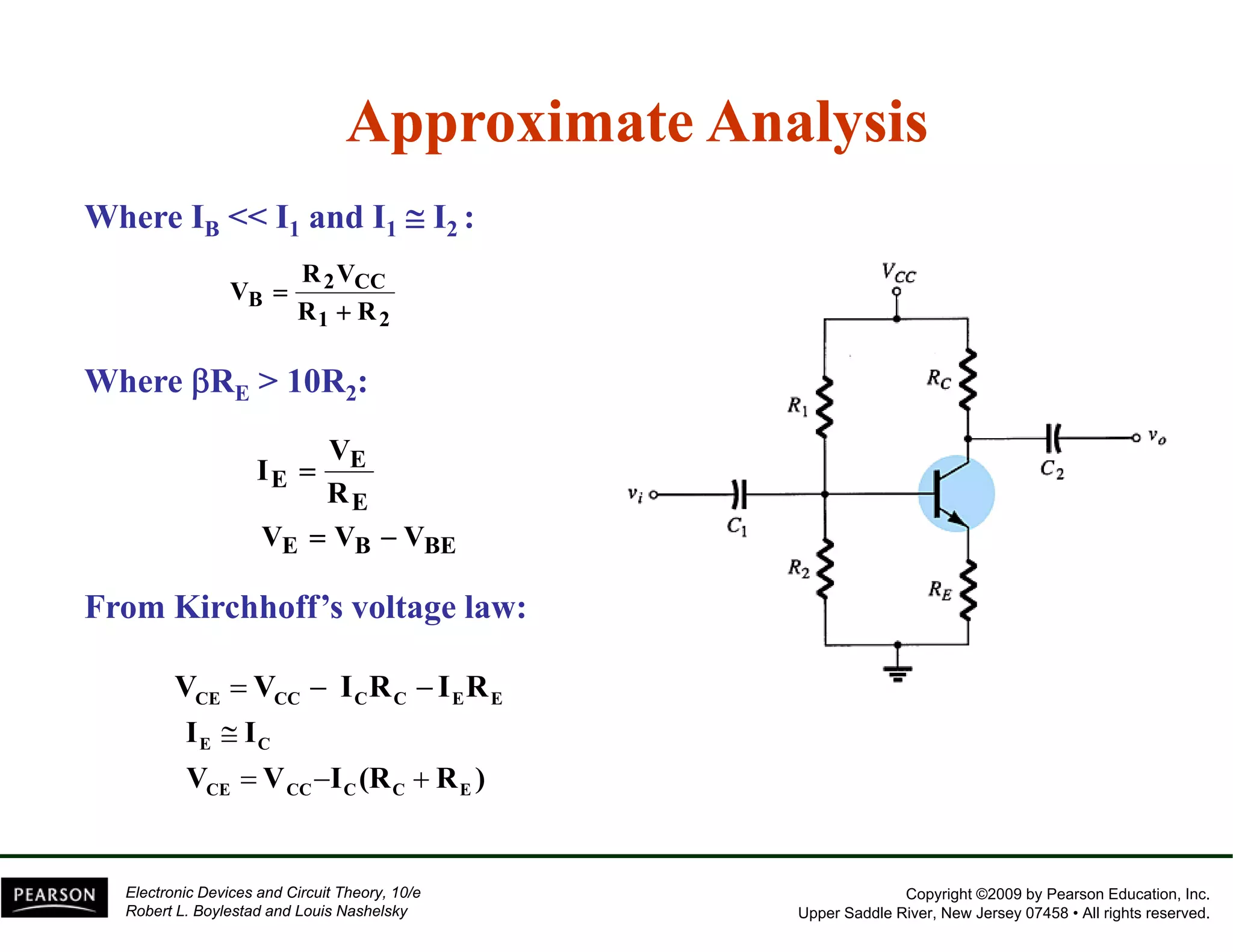
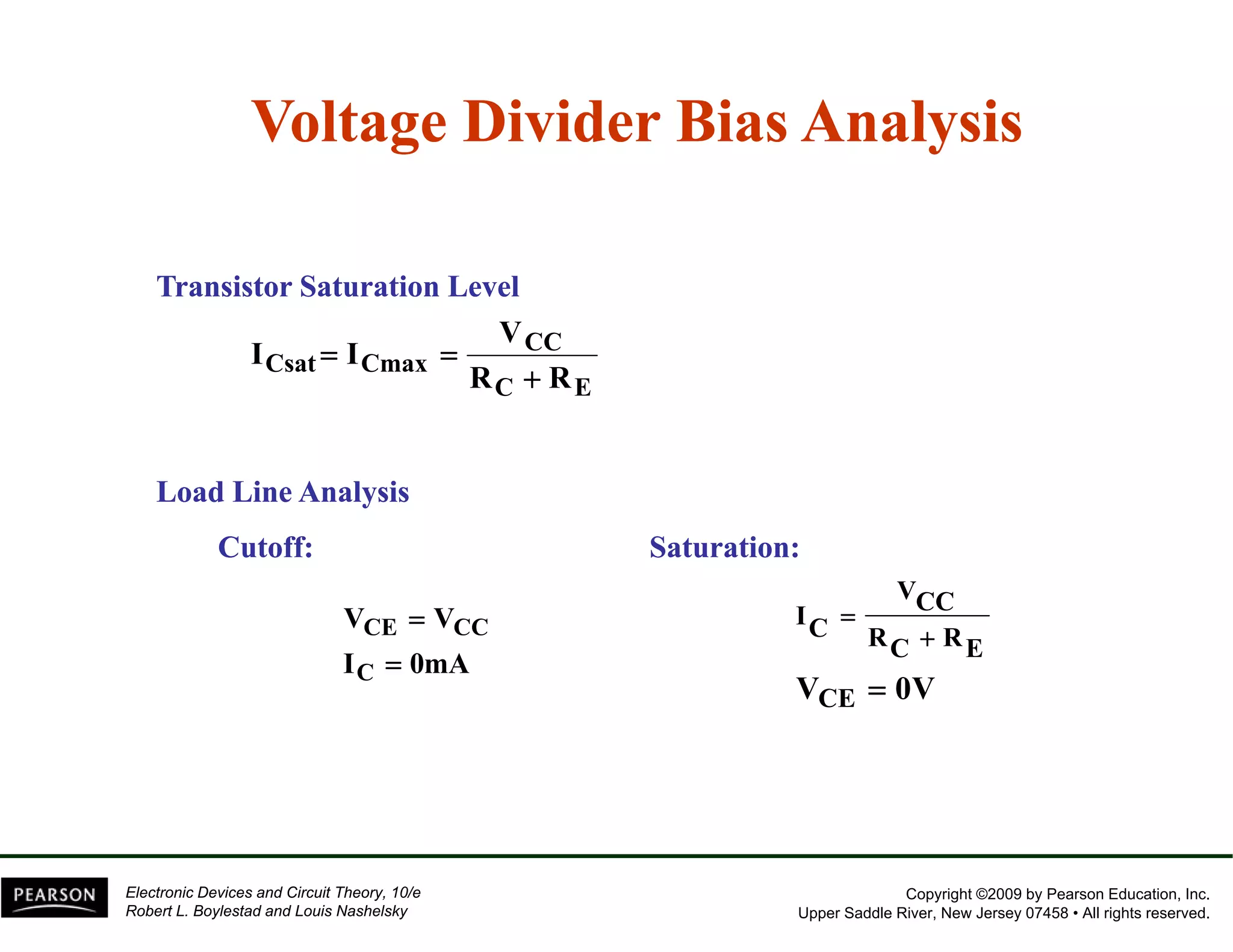
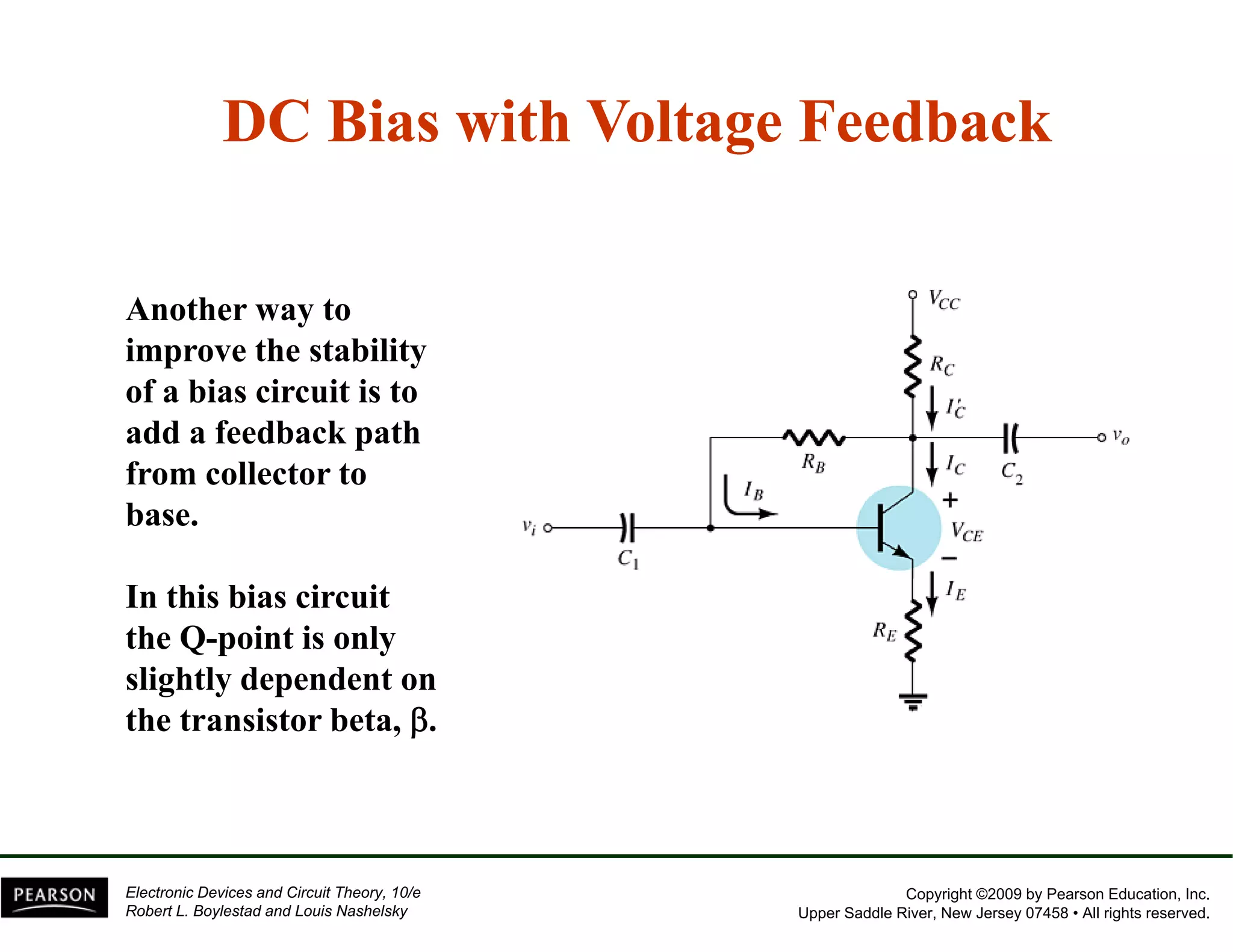
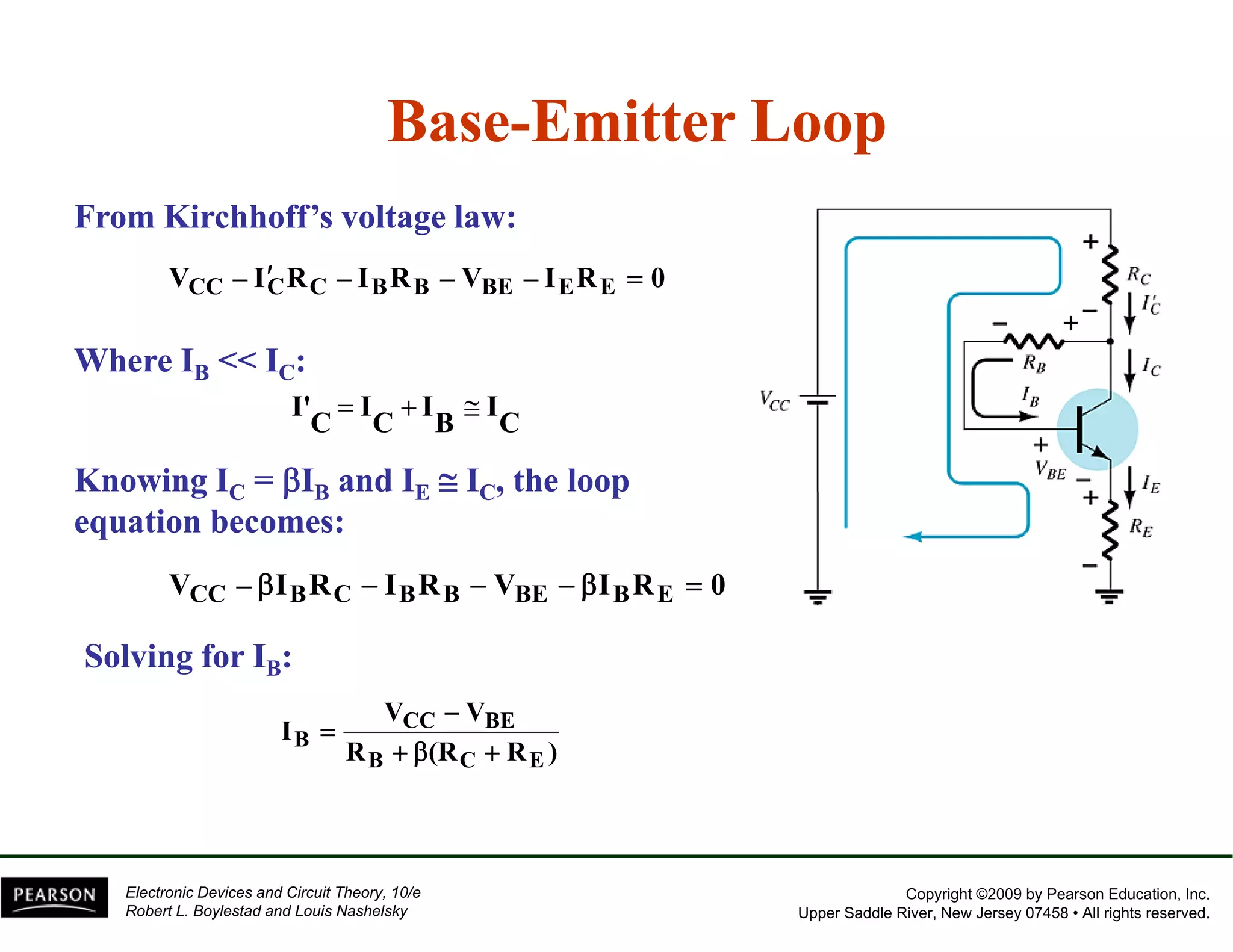
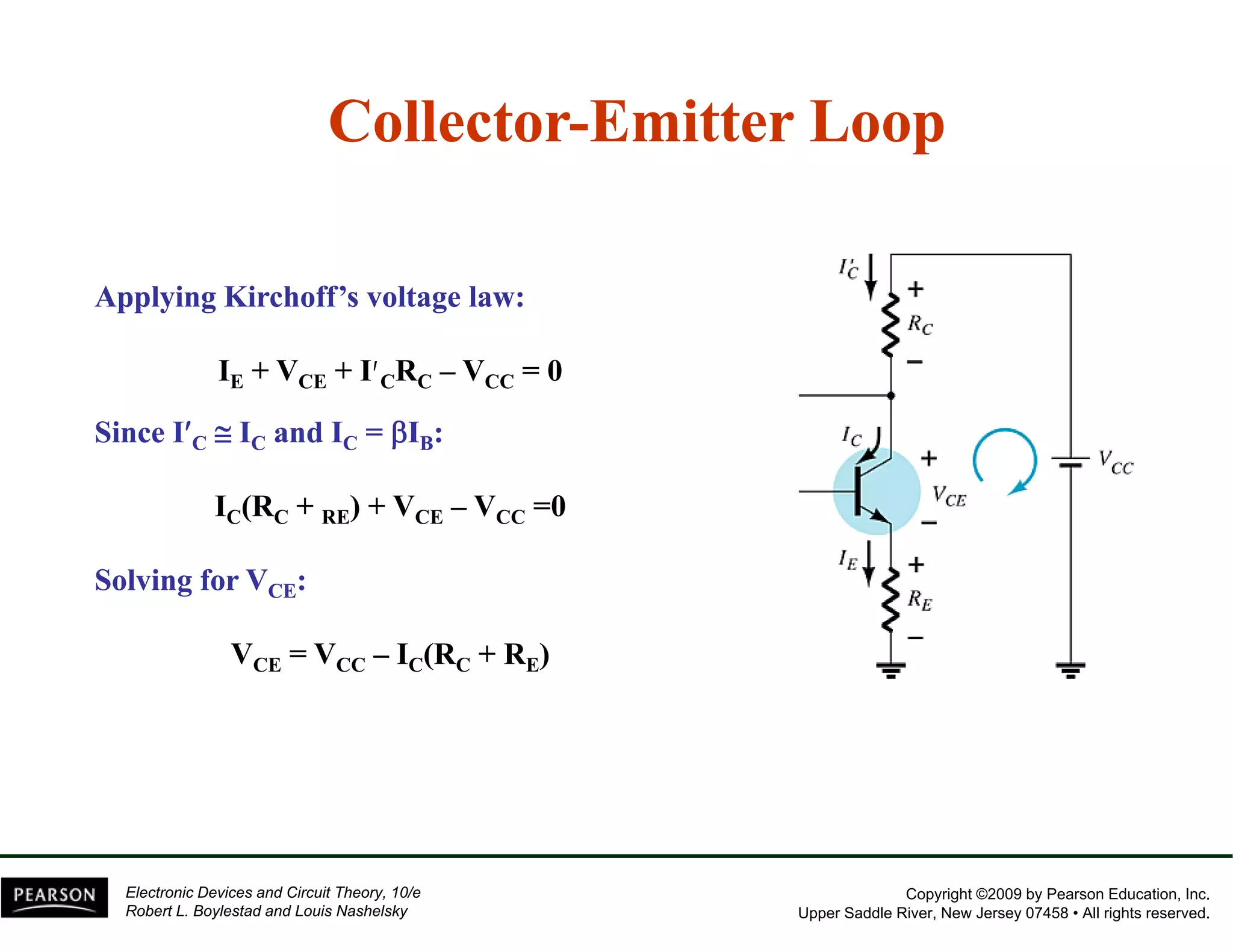
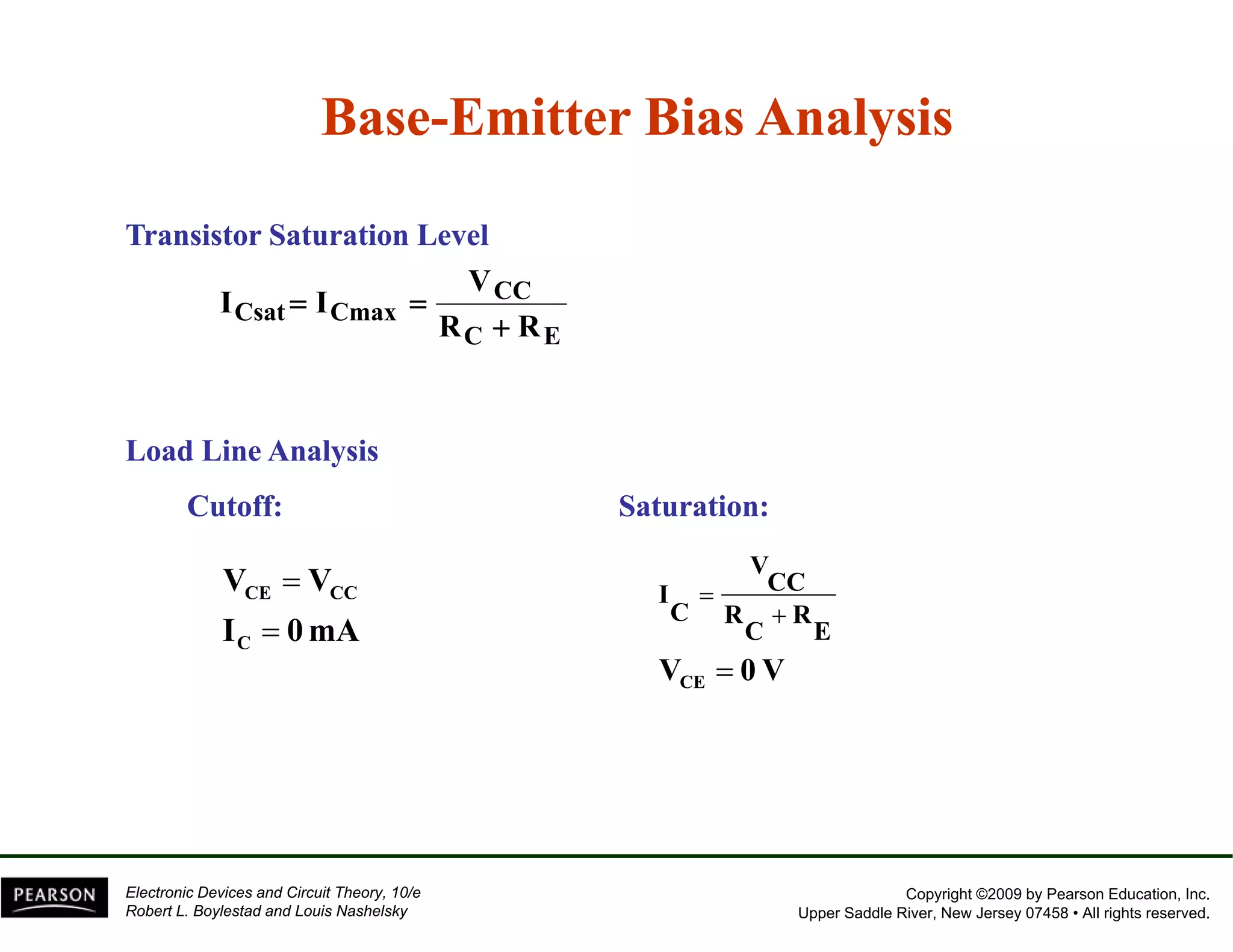
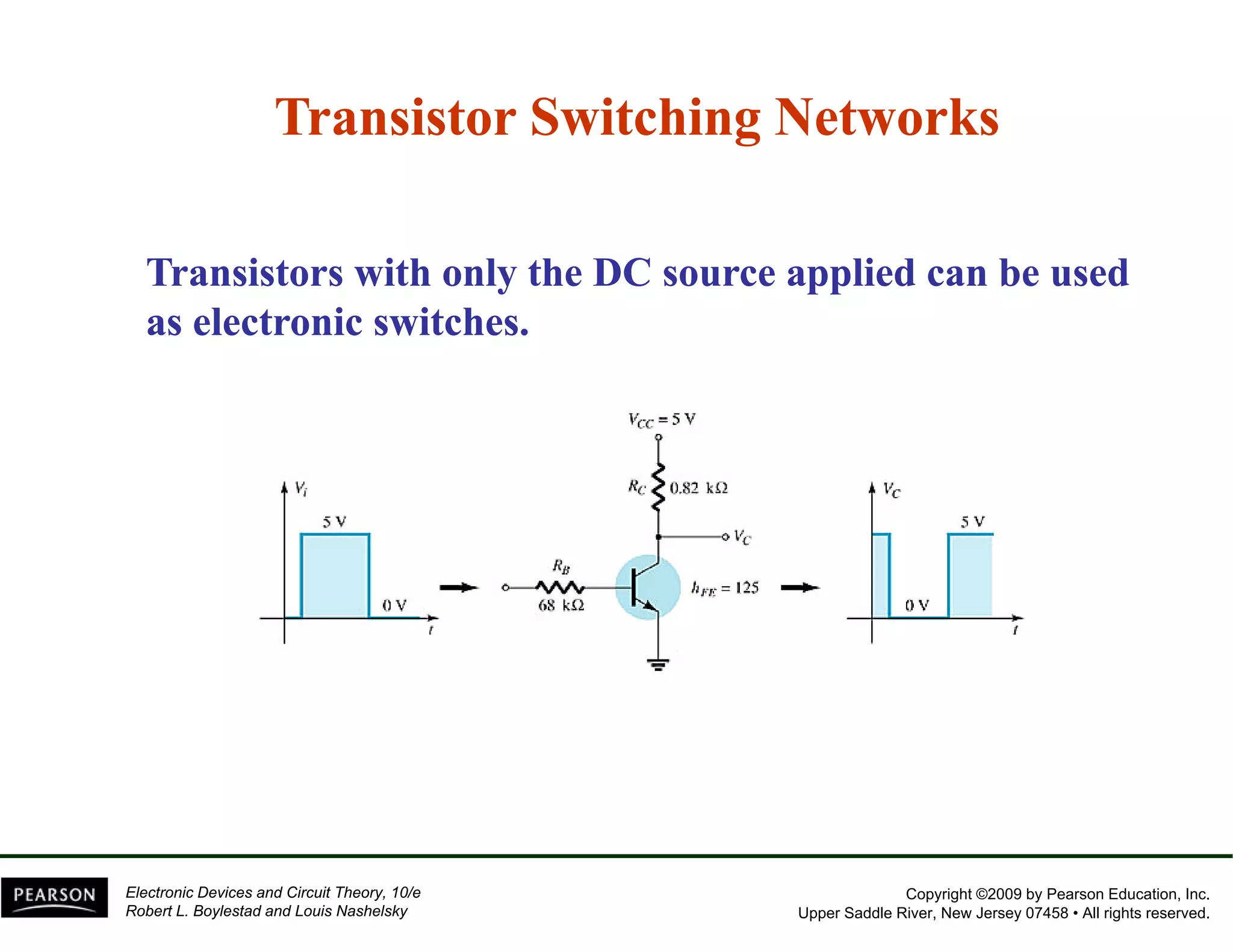
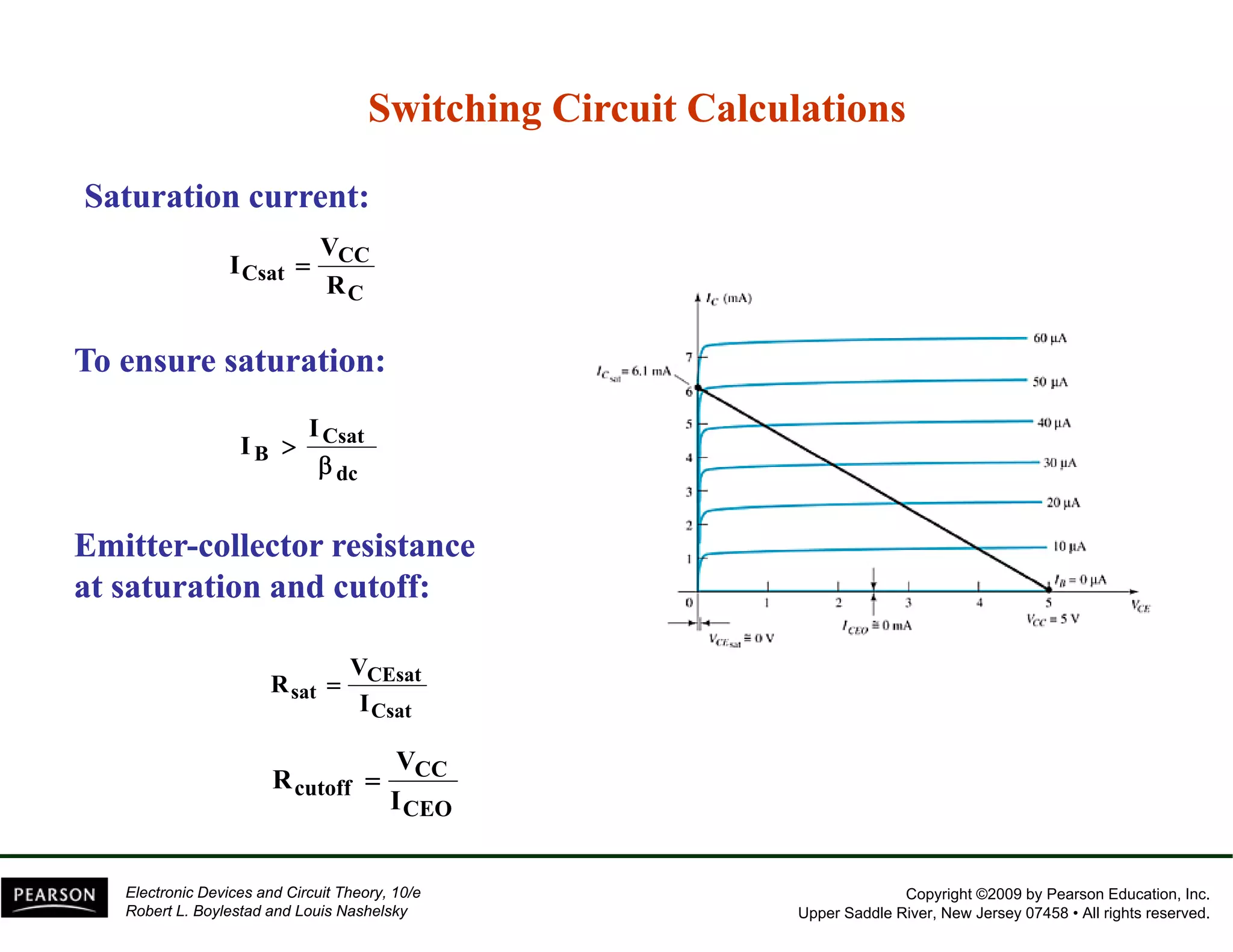
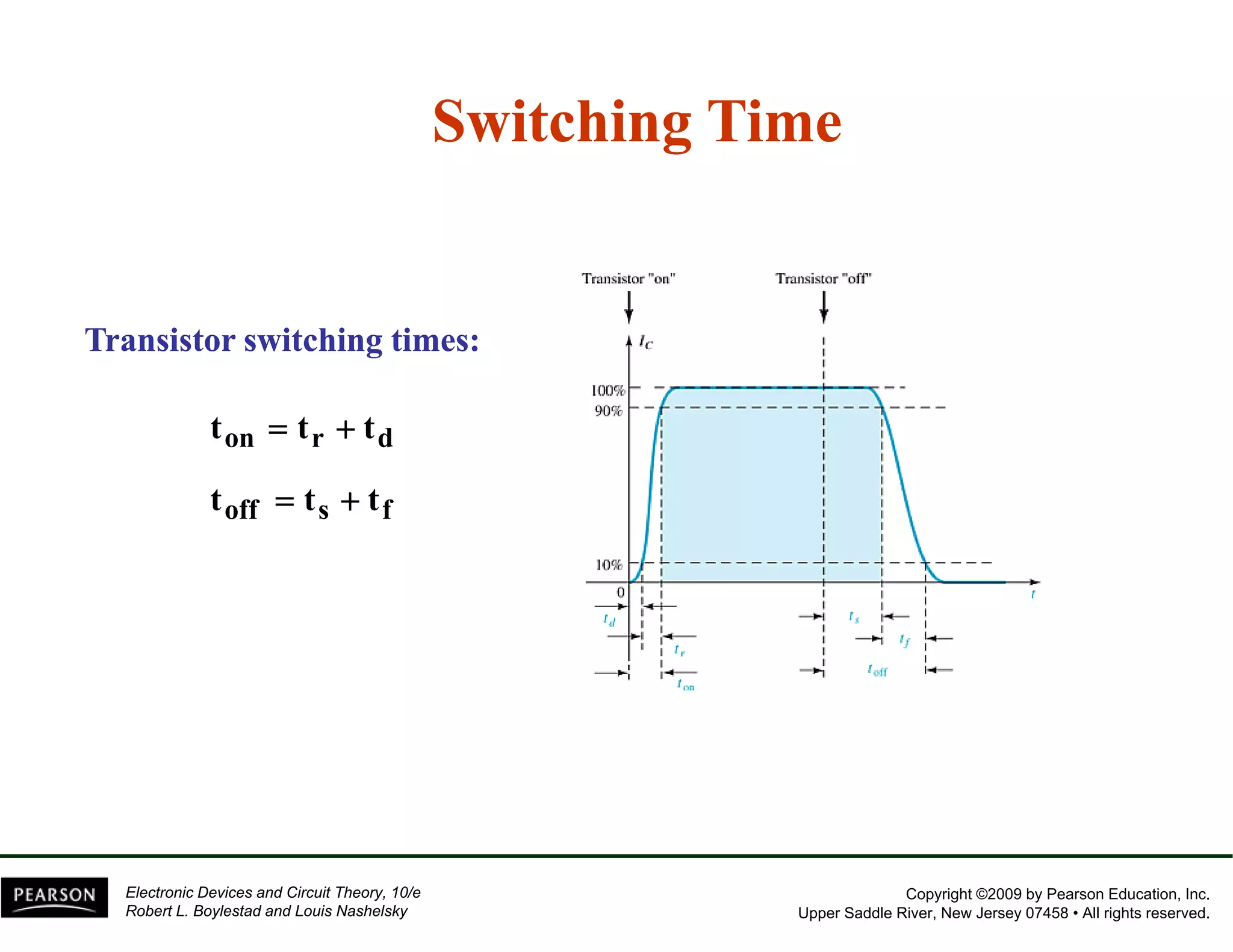
This document discusses different methods of biasing BJT transistors, including fixed bias, emitter-stabilized bias, and voltage divider bias circuits. It explains how the DC bias voltages establish an operating point (Q-point) for the transistor in either the active, cutoff, or saturation regions. Load line analysis is used to determine the transistor's Q-point based on the bias circuit components and supply voltage. Feedback circuits are also introduced to improve stability against variations in the transistor's beta value.