This document discusses different classes of power amplifiers, including:
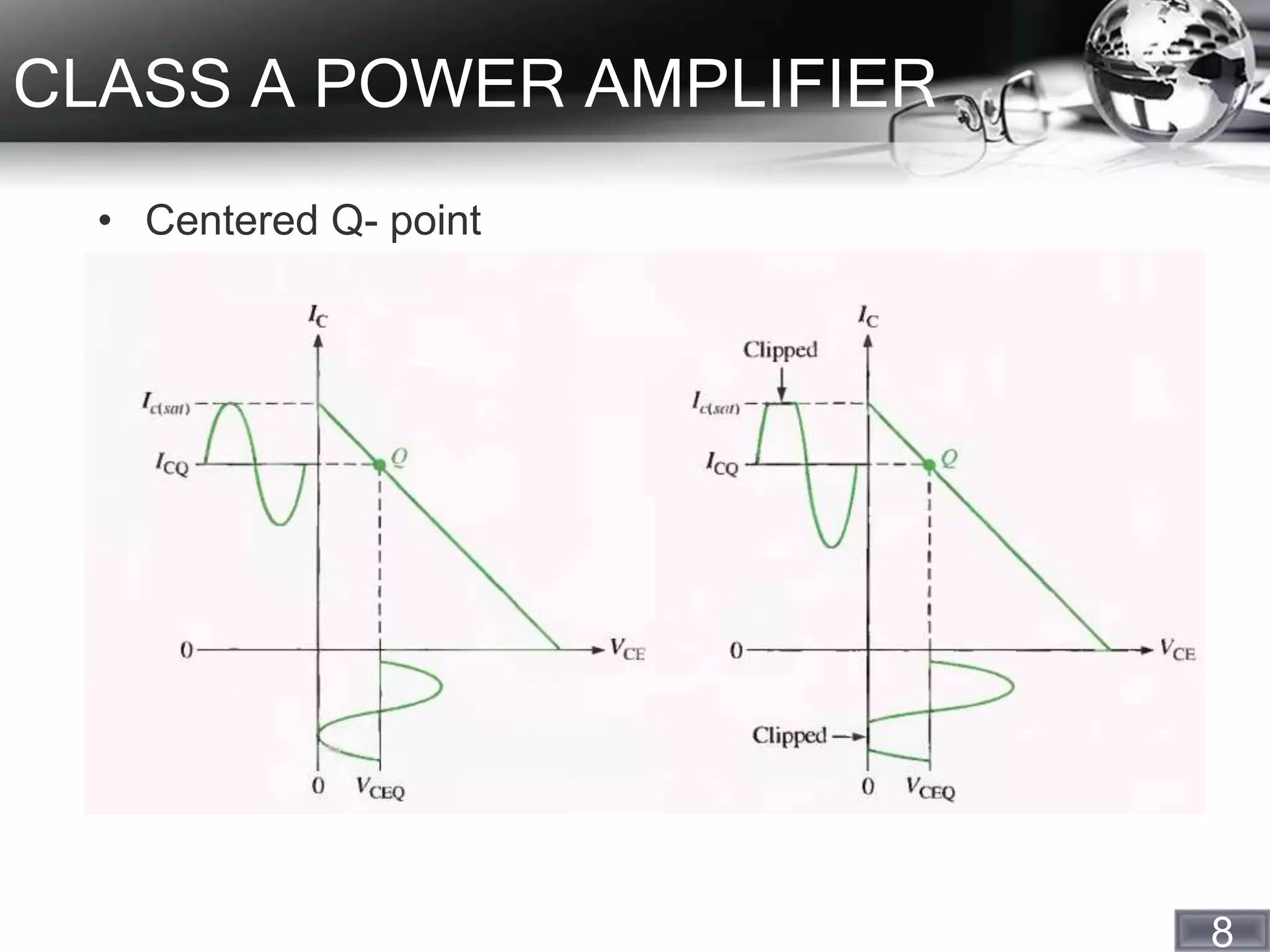
- Class A power amplifiers, which operate linearly for 360 degrees and have an efficiency of around 25%.
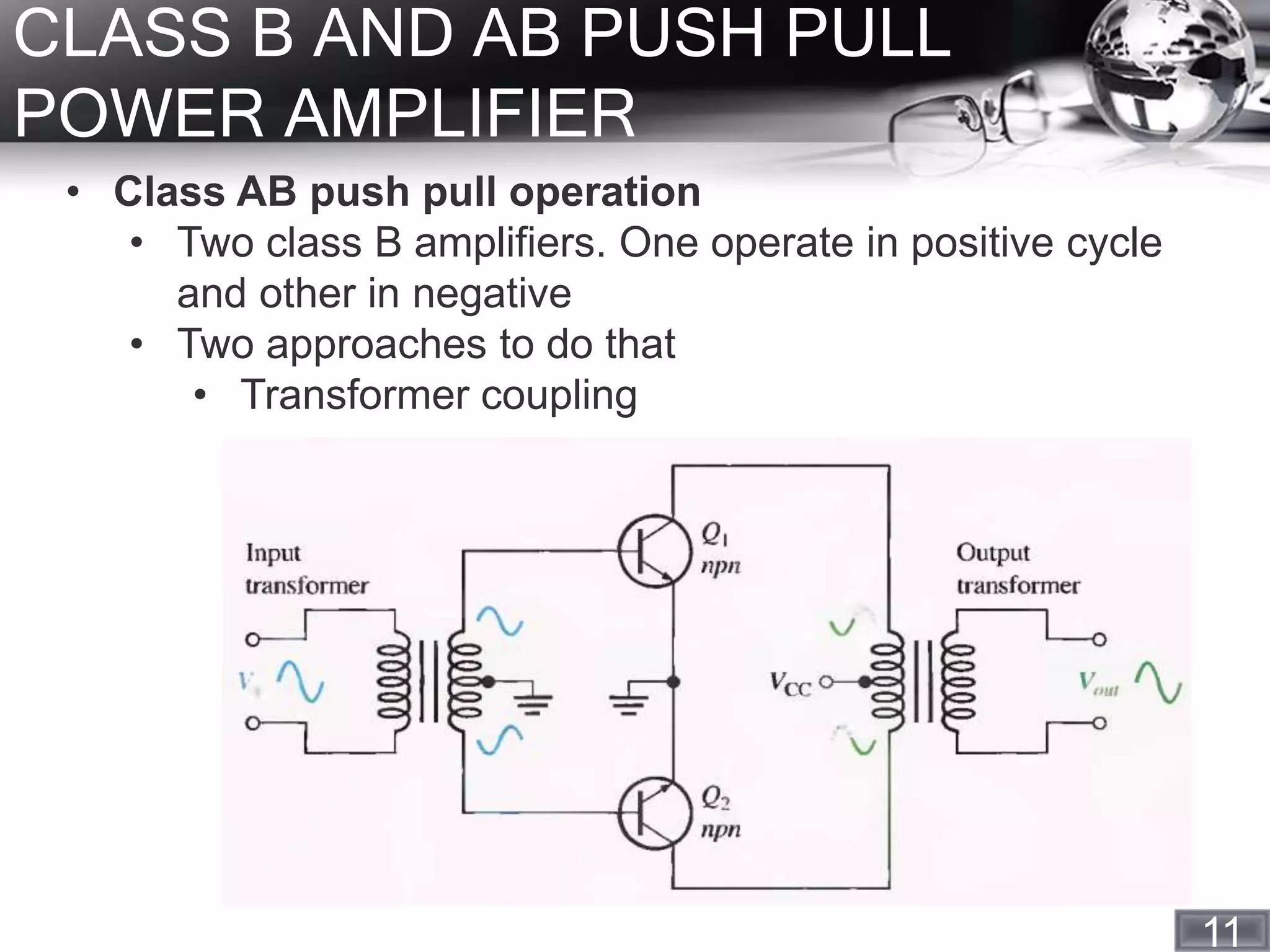
- Class B and AB push-pull amplifiers, which operate for more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees, and can have an efficiency near 79%.
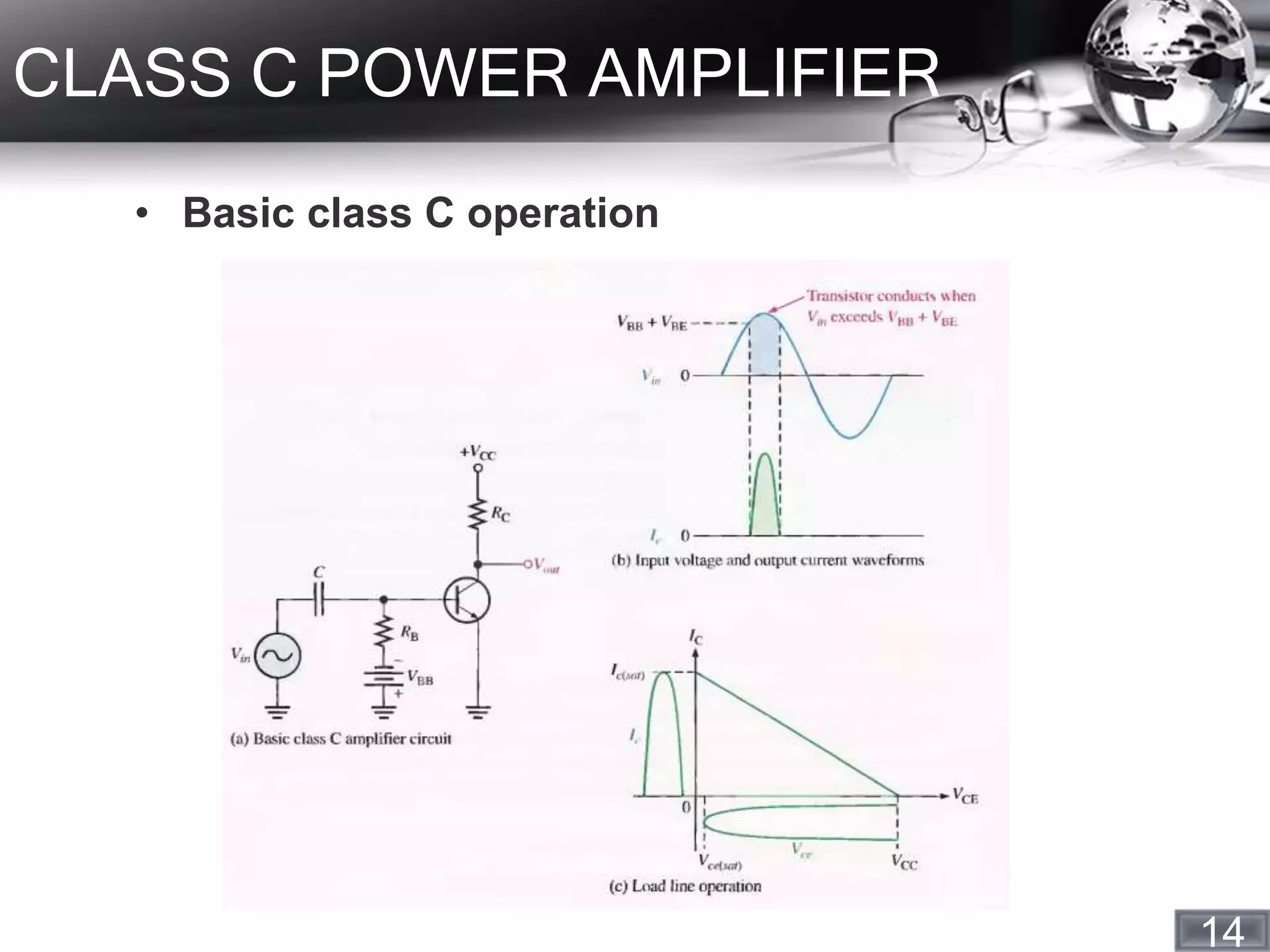
- Class C power amplifiers, which operate for less than 180 degrees but can have an efficiency near 100%, making them useful for applications like RF and oscillators.