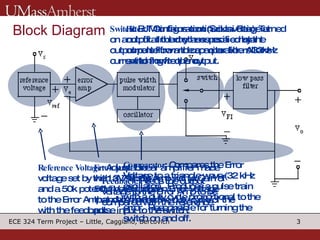
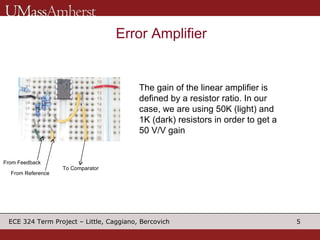
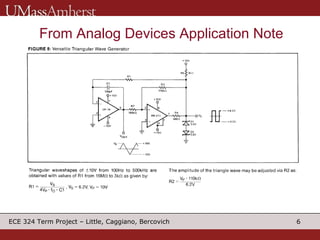
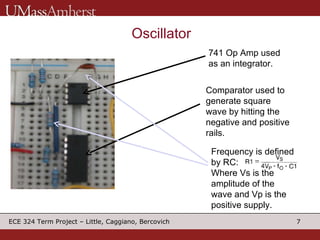
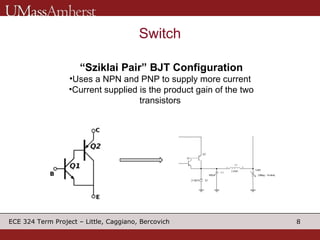
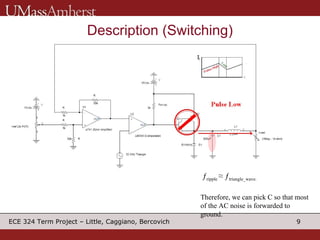
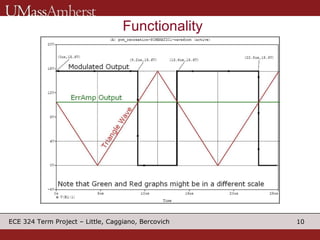
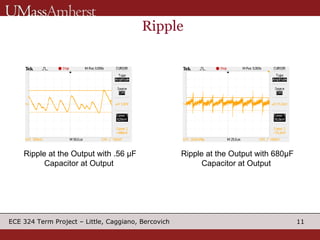
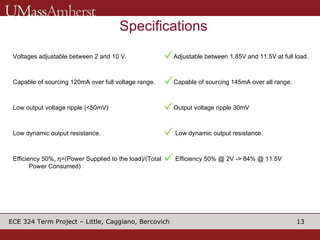
The document describes a switching voltage regulator circuit designed by a group of students. It includes a block diagram showing the main components: a reference voltage, error amplifier, comparator, switch, and filter. It assigns individual responsibilities for designing different components. The regulator is intended to output a adjustable voltage between 1.85-11.5V while supplying 145mA, with less than 30mV of ripple voltage. It provides specifications and a progress report on the design goals and notes for each section.