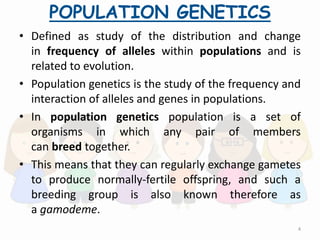
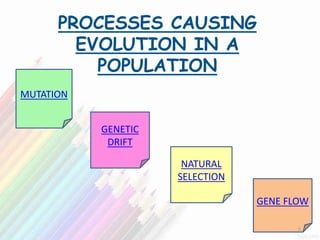
Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations. It examines how processes like natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation cause evolution in a population over time. The key concepts are:
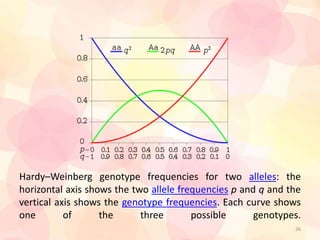
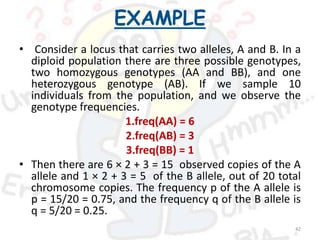
1) Hardy-Weinberg law states that allele and genotype frequencies remain constant in a population with no evolutionary influences.
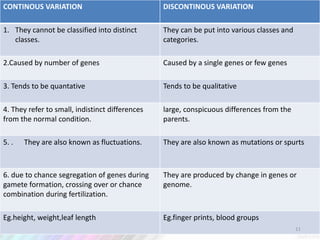
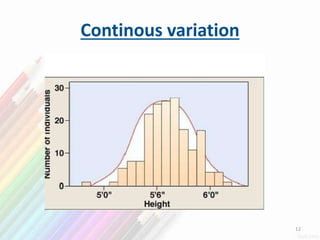
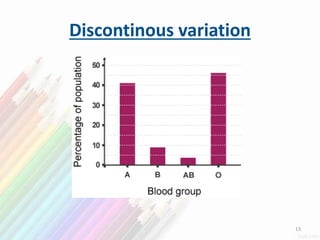
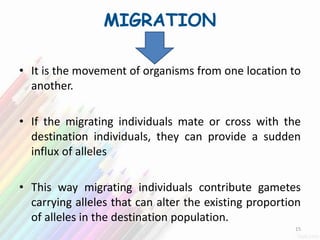
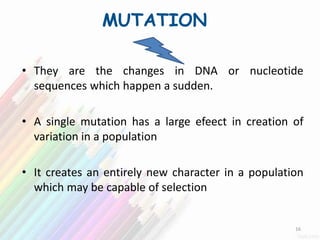
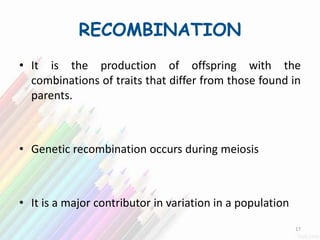
2) Variation within populations arises through migration, recombination, mutation, and gene flow.
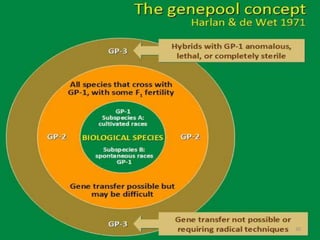
3) Gene pools are sets of genes found in related species that can be used in crop breeding. They are divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary pools based on ease of gene transfer.