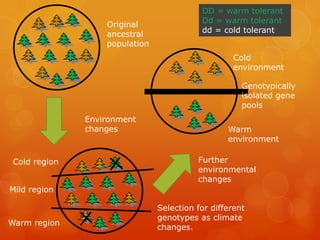
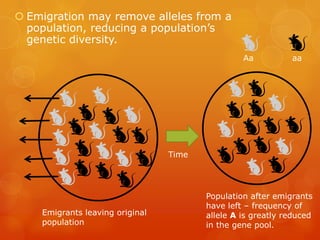
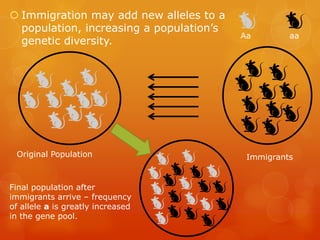
This document discusses factors that affect genetic variation and change in populations, including evolution, natural selection, mutations, migration, and genetic drift. It provides details on each factor and how they influence allele frequencies in a gene pool over multiple generations, leading to evolution and potentially new species. Examples are given to illustrate concepts like founder effects and bottleneck effects on small populations.