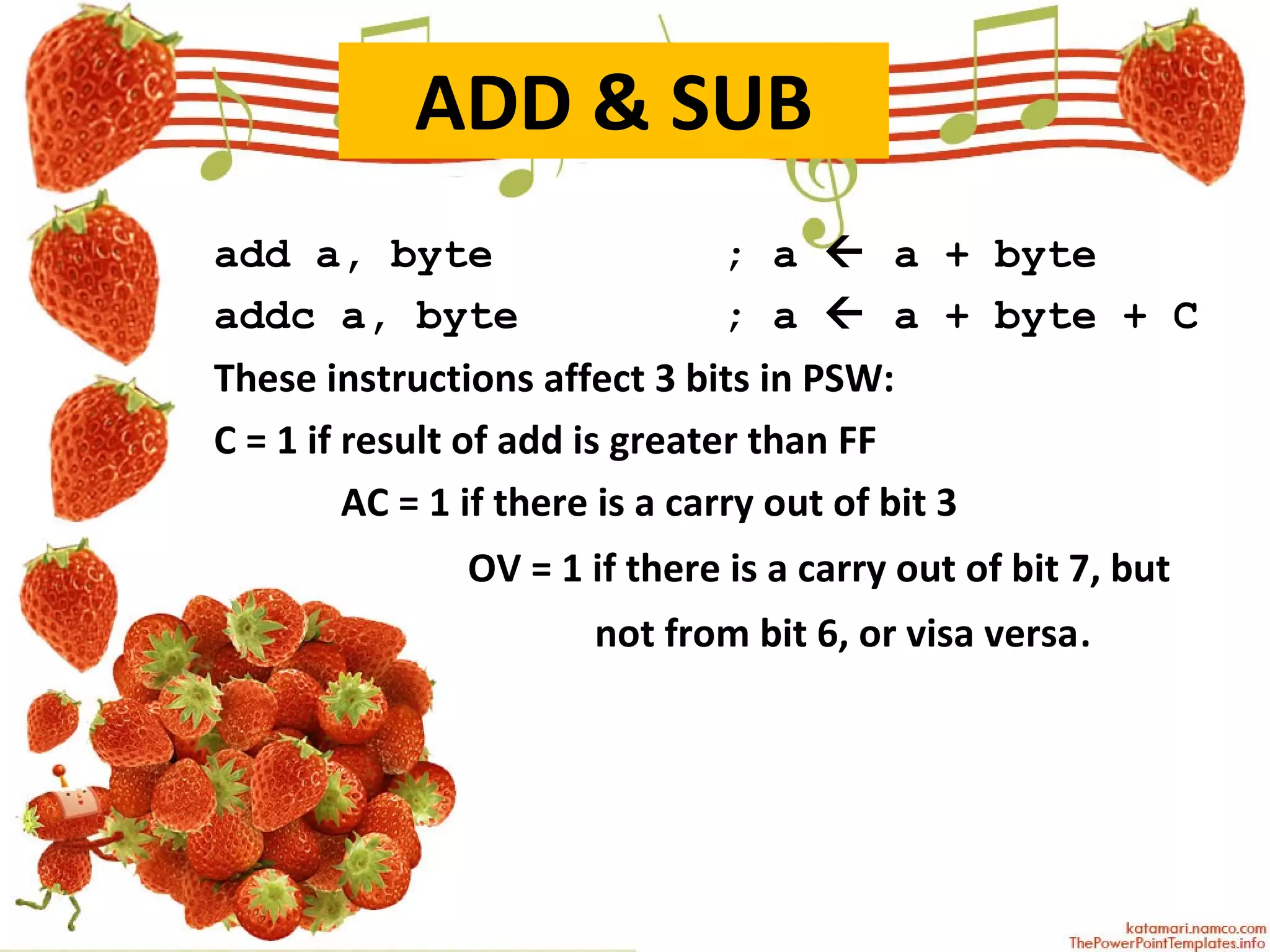
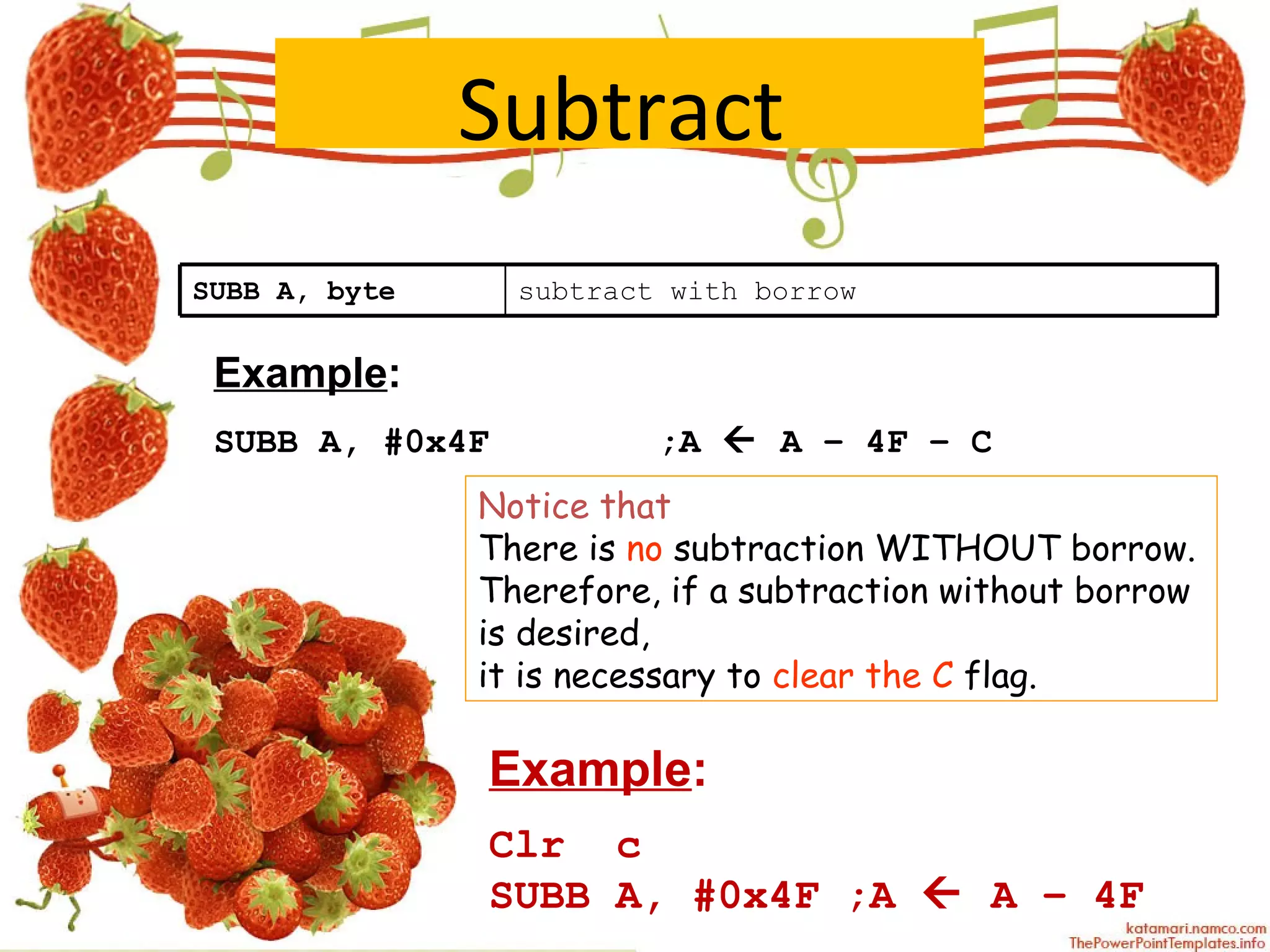
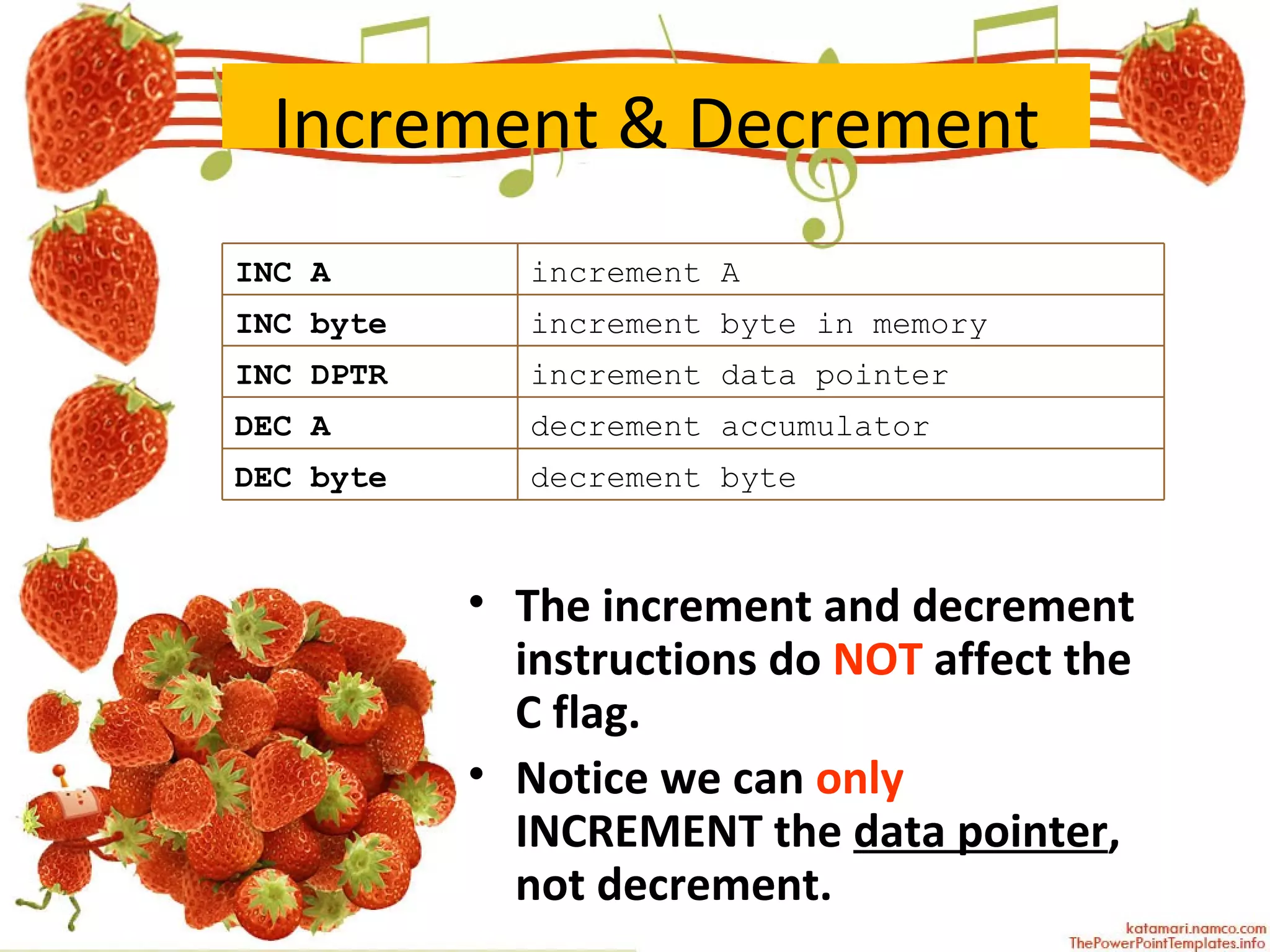
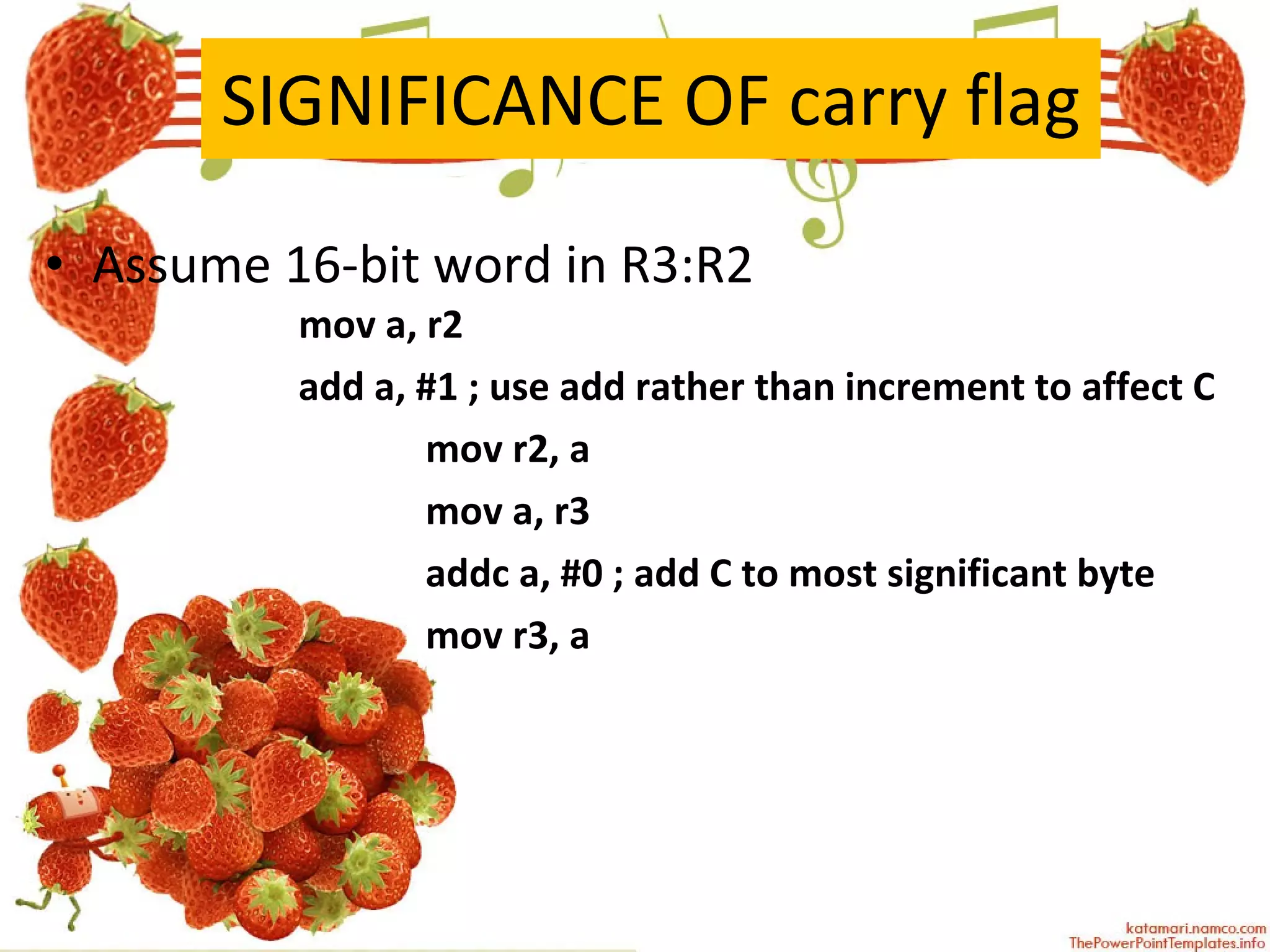
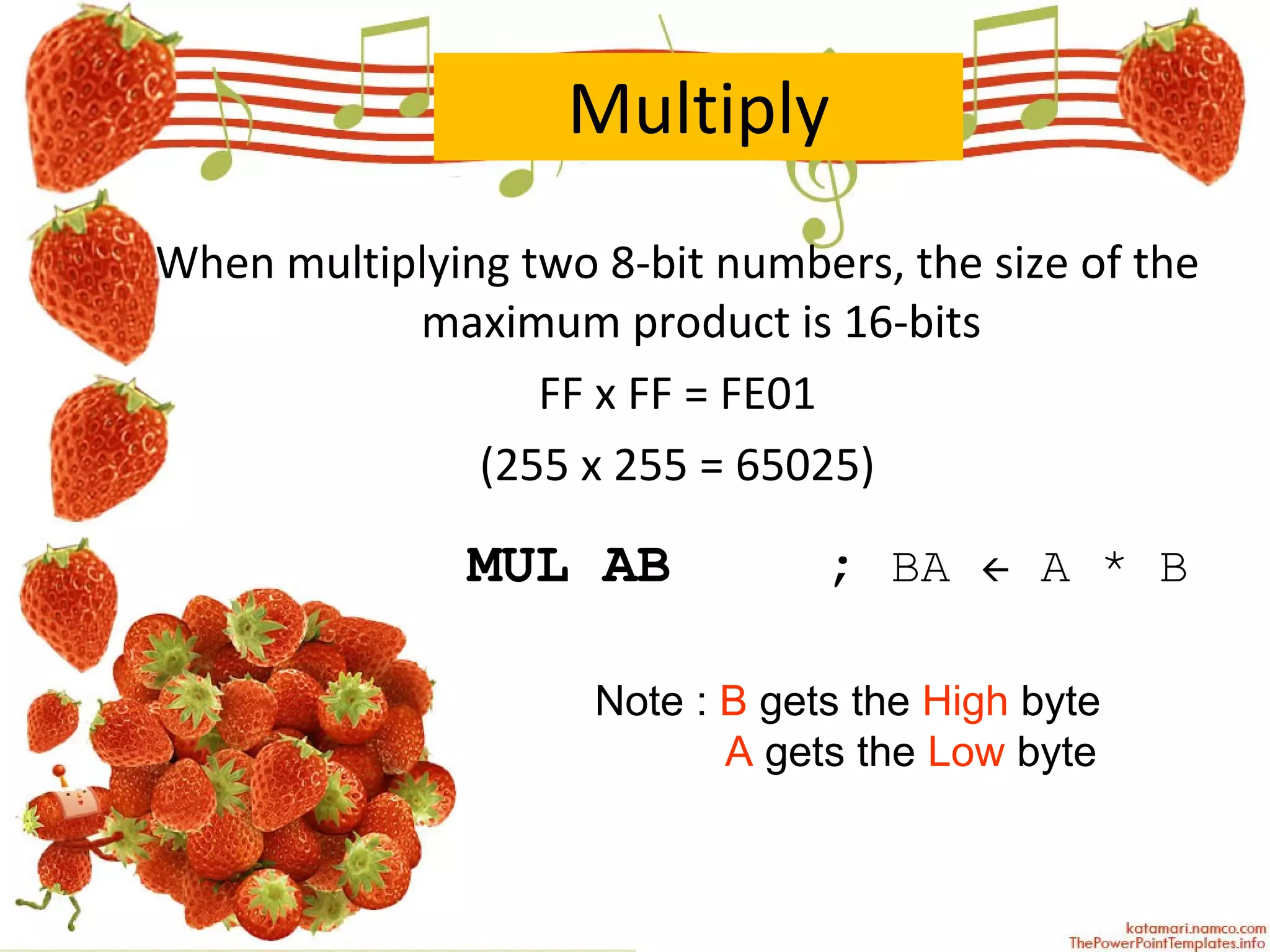
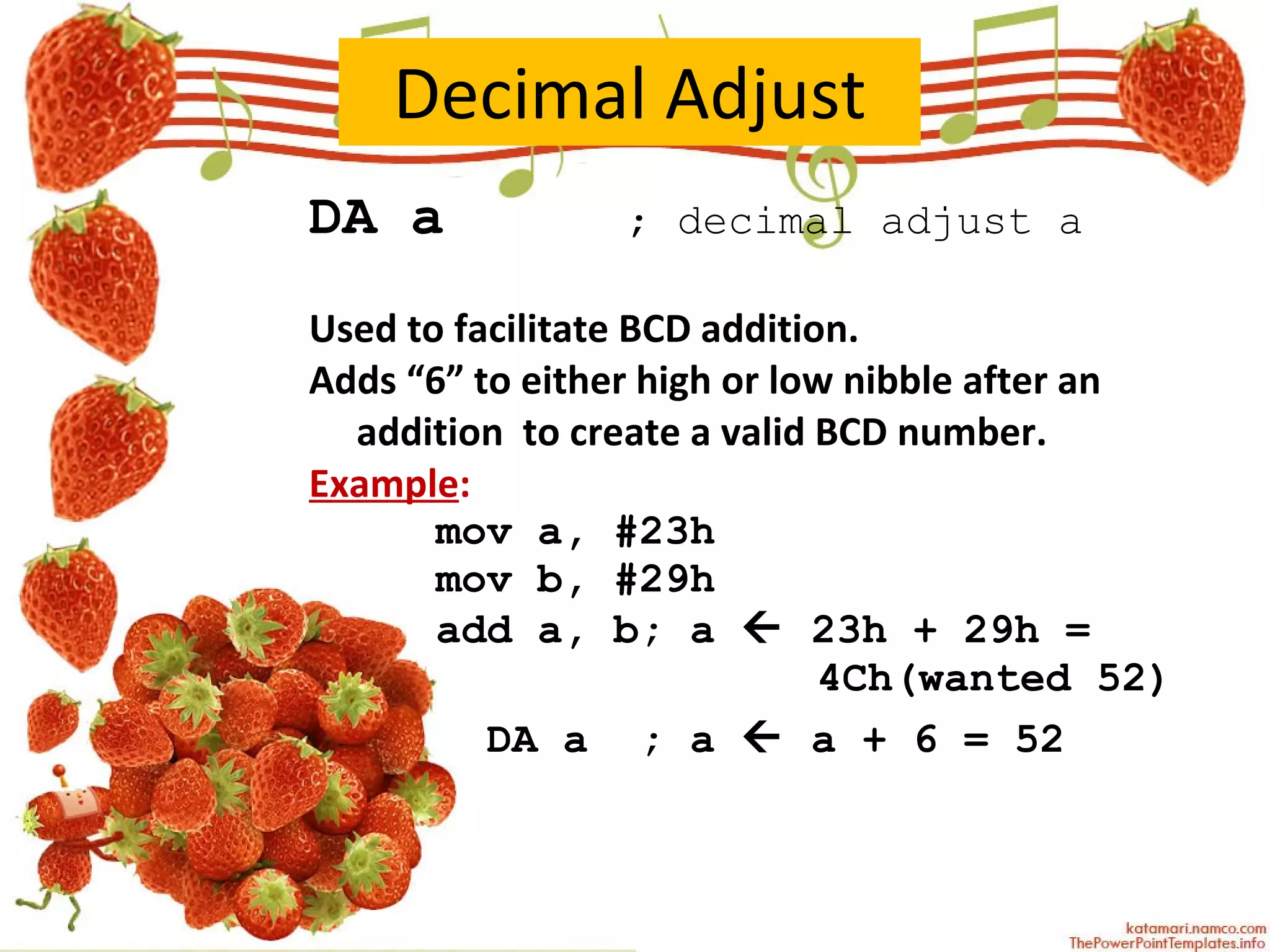
The document describes various arithmetic instructions for an 8-bit microcontroller including ADD, SUB, INC, DEC, MUL, and DIV. It explains how these instructions affect the flags in the Program Status Word register. Addition and subtraction instructions can set flags for carry, auxiliary carry, and overflow. Increment and decrement only affect the accumulator and do not change flags. Multiplication stores the high byte in B and low byte in A. Division stores the quotient in A and remainder in B, setting the overflow flag if there is a divide by zero.