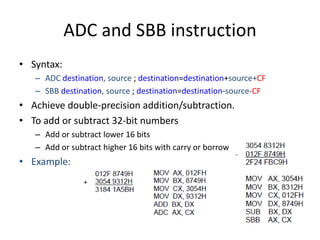
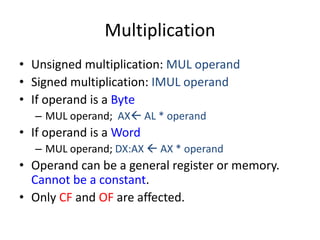
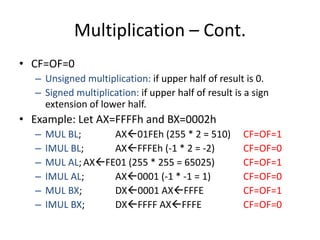
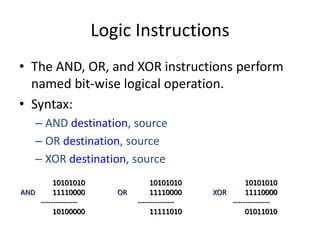
This document summarizes various arithmetic, logic, and shift instructions in x86 assembly language.
It describes increment, decrement, negation, comparison, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and logic instructions. It provides syntax examples and explains how they affect flags and can be used for tasks like inputting and outputting decimal numbers.
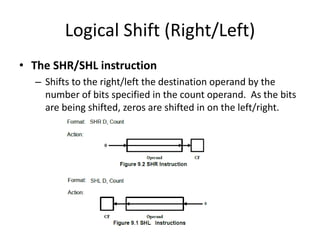
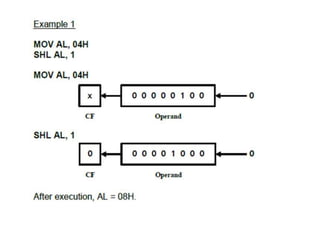
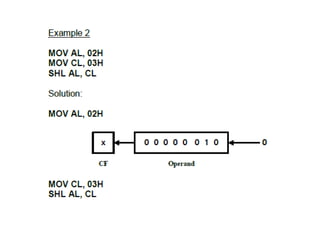
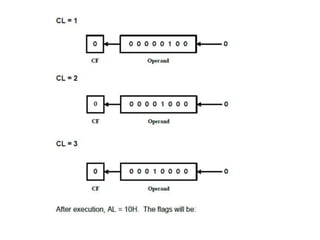
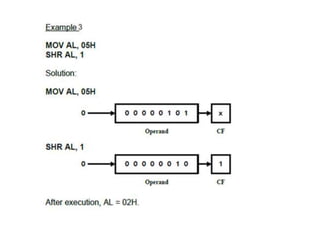
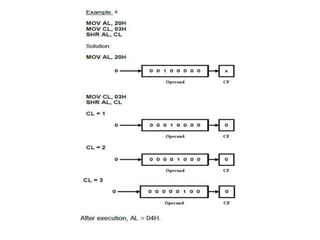
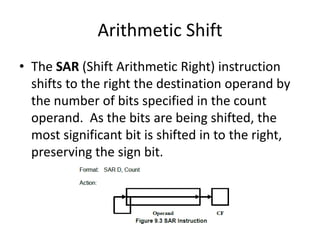
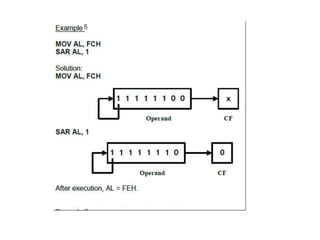
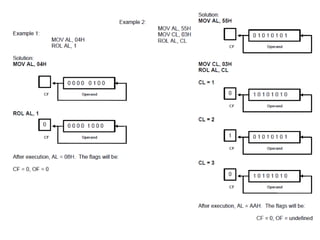
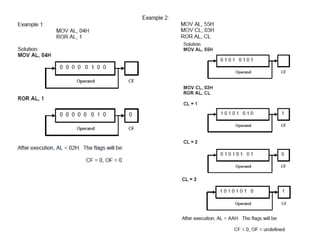
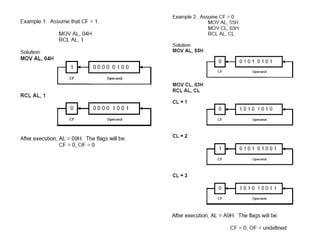
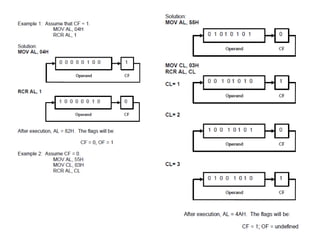
Shift instructions like logical and arithmetic shifts are covered, along with how they can perform multiplication and division via left and right shifts. Rotate instructions are also introduced. Application examples show how instructions can be combined to perform operations like converting between ASCII and binary representations.

![INC & DEC Instructions
• Syntax:
– INC operand ; operand=operand+1
– DEC operand ; operand=operand-1
• Operand can be a general register or memory.
• INC and DEC instructions affect all the flags.
• Examples:
– INC AX legal
– DEC BL legal
– INC [BX] illegal
– INC Byte PTR [BX] legal
– DEC I legal
– INC DS illegal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticinstructionspart2-150309201944-conversion-gate01/85/Arithmetic-instructions-2-320.jpg)