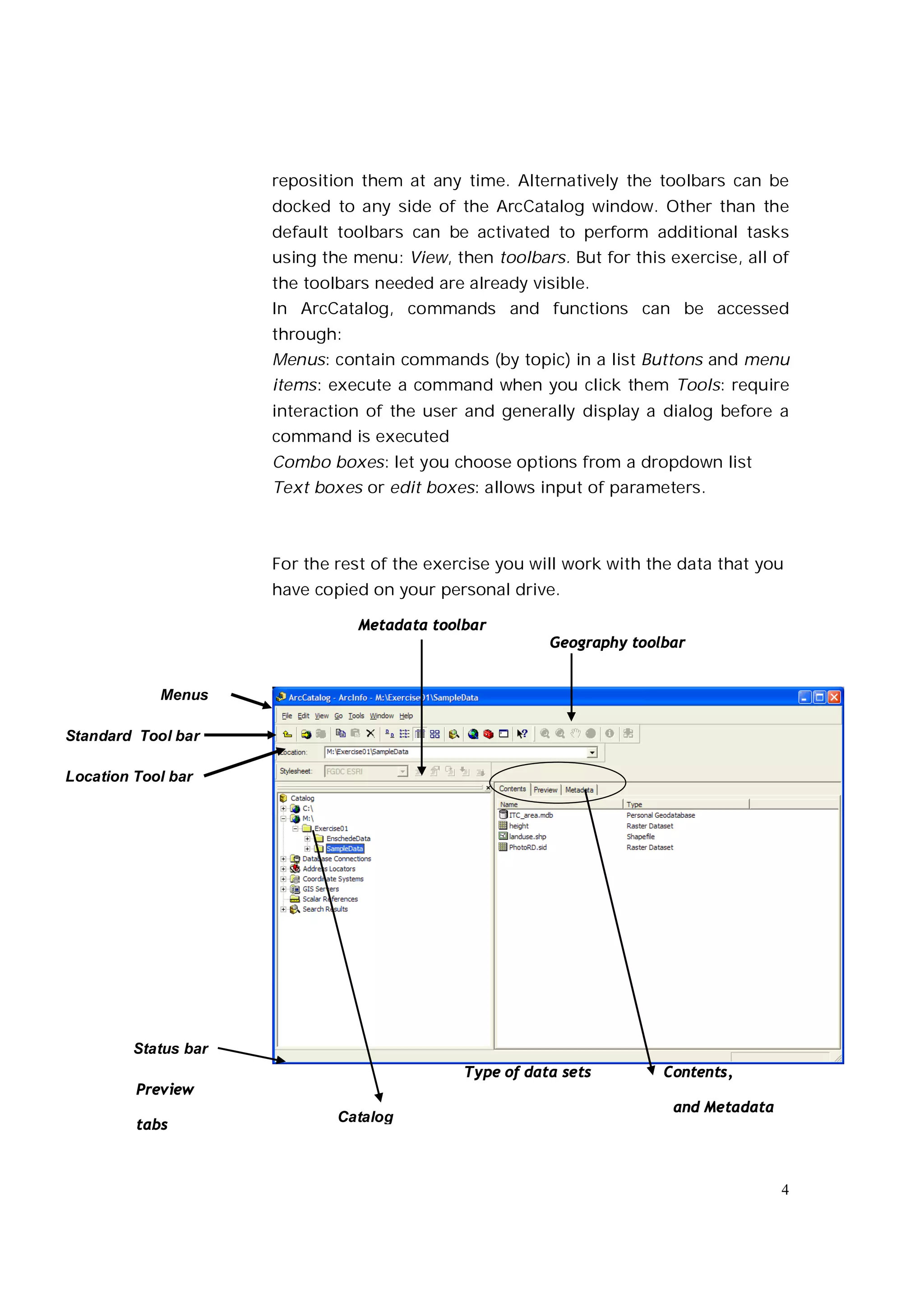
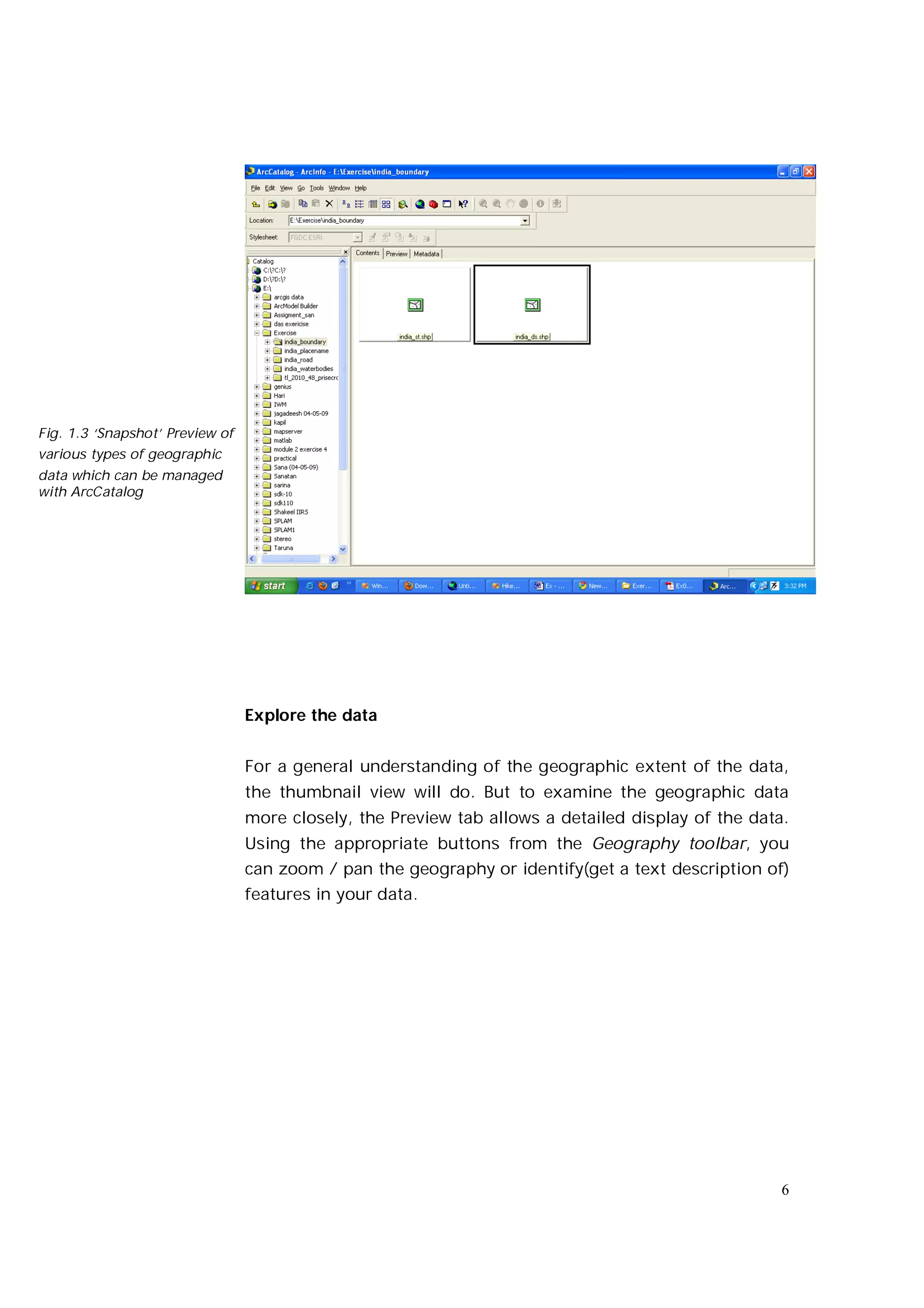
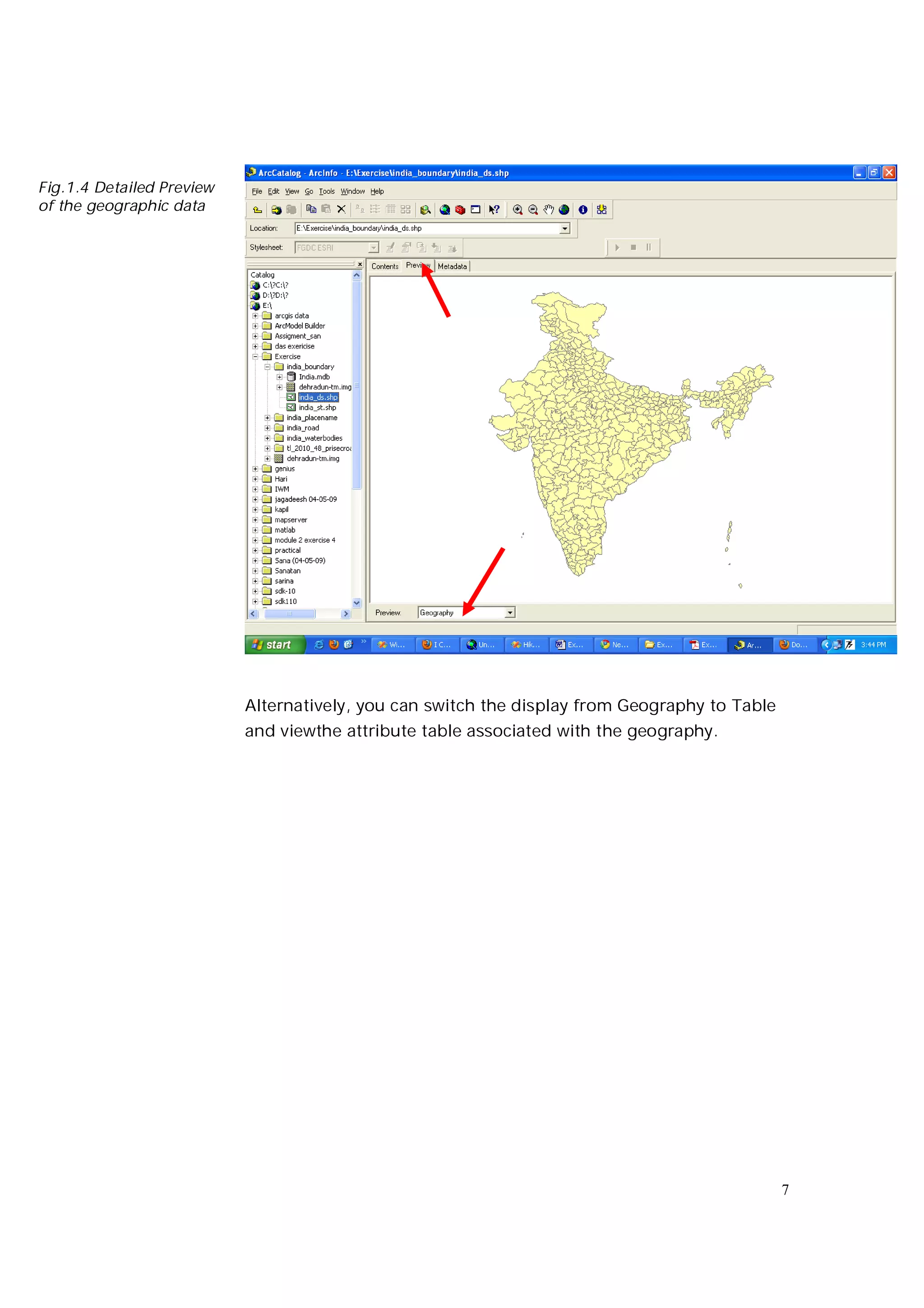
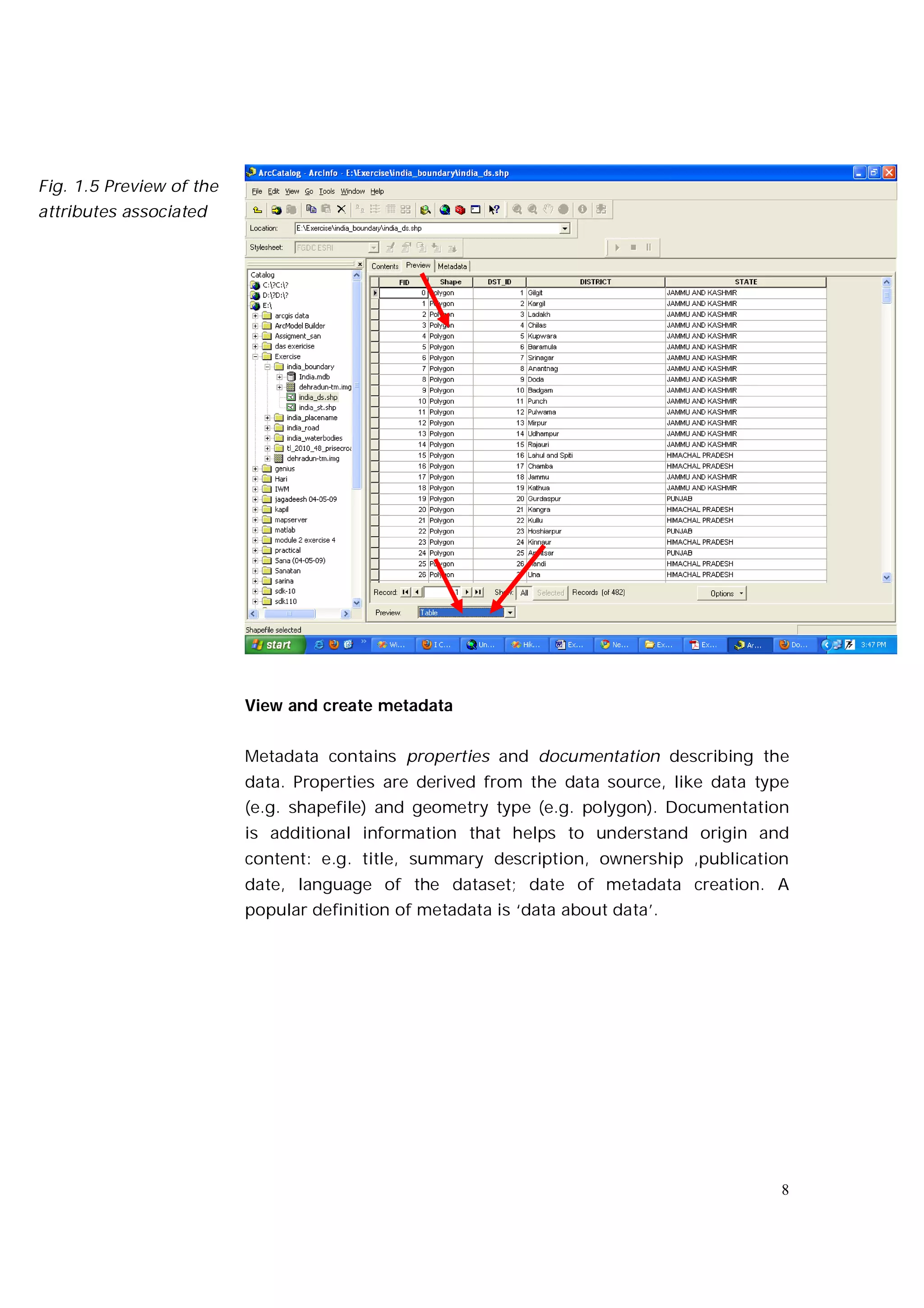
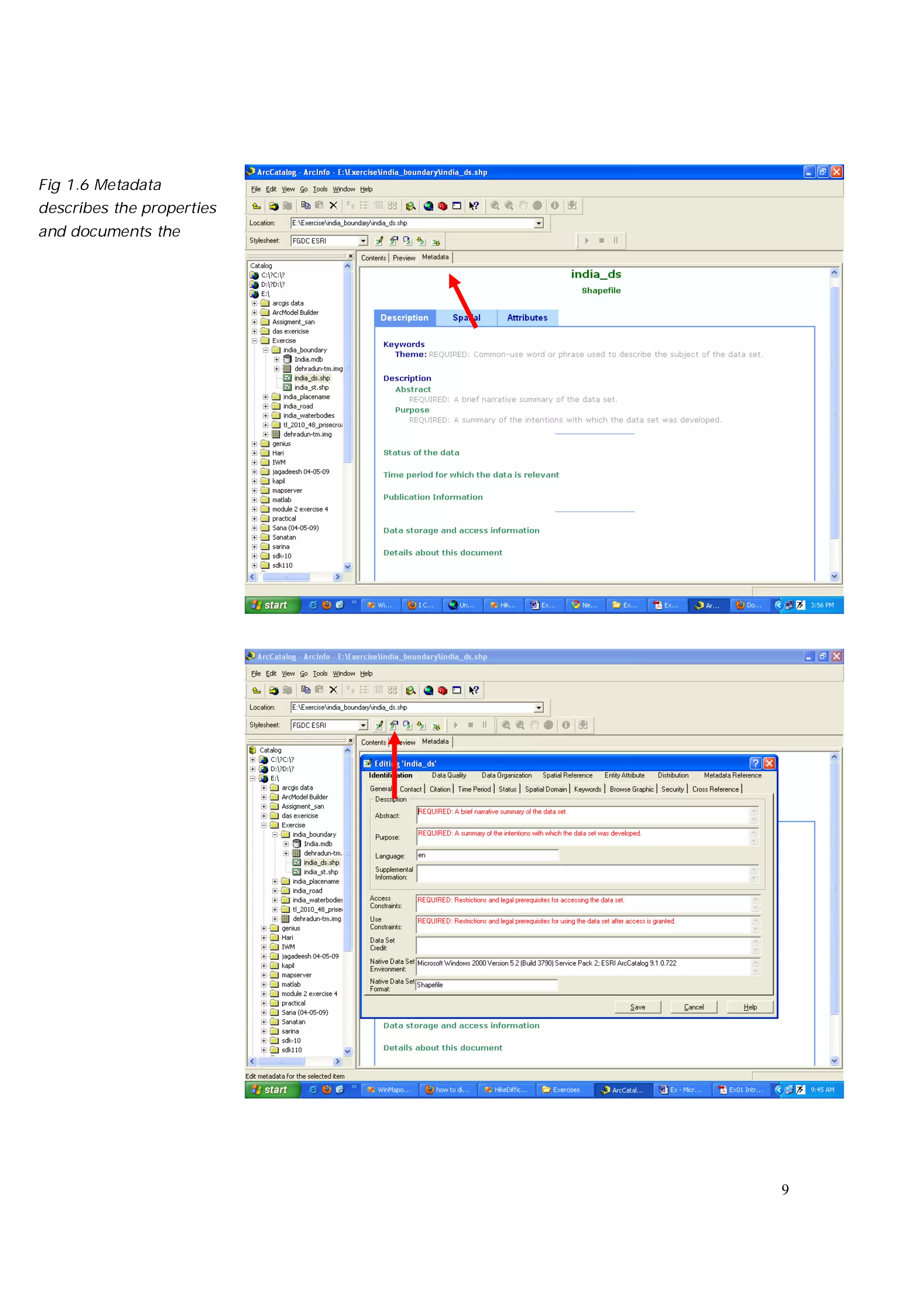
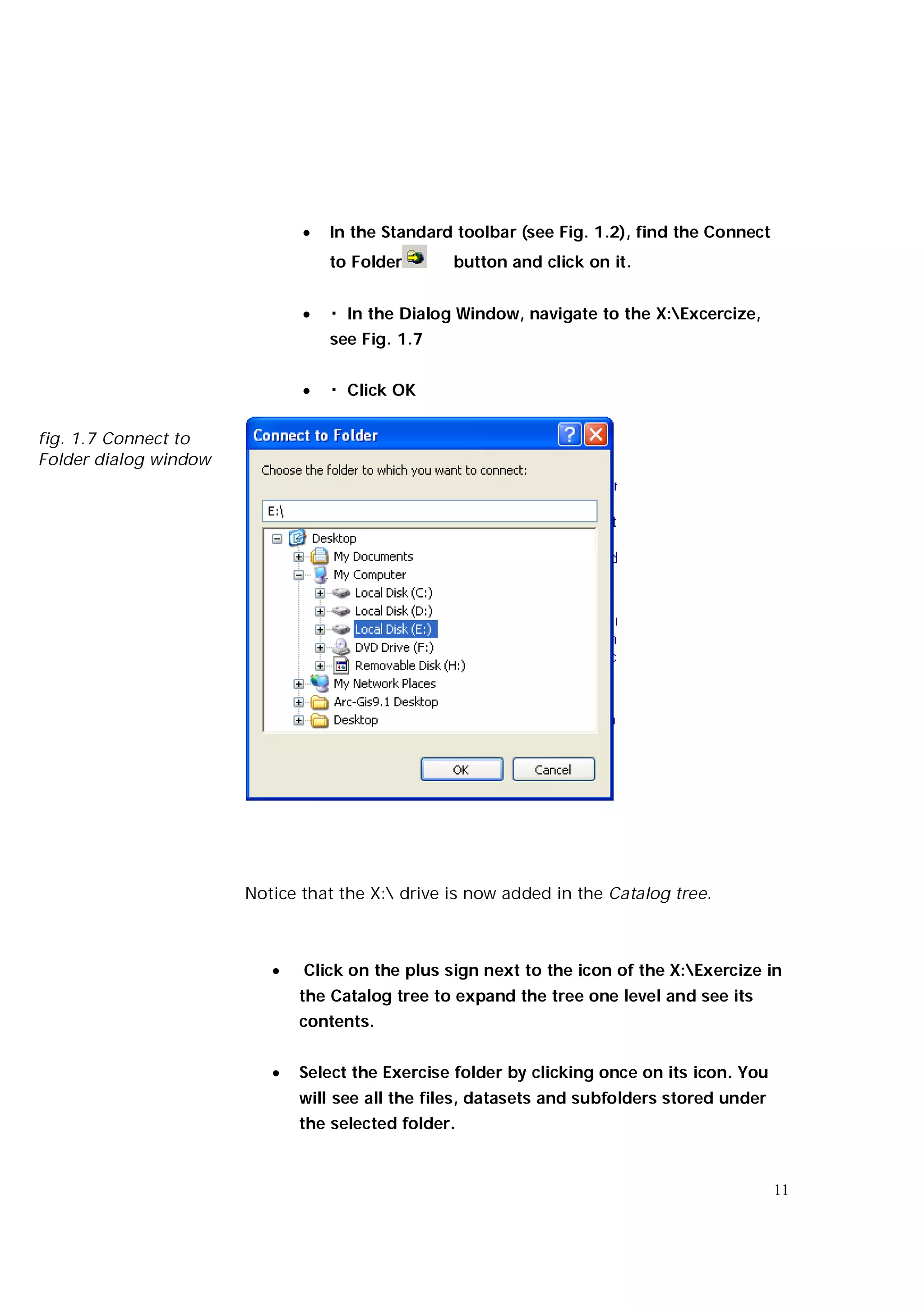
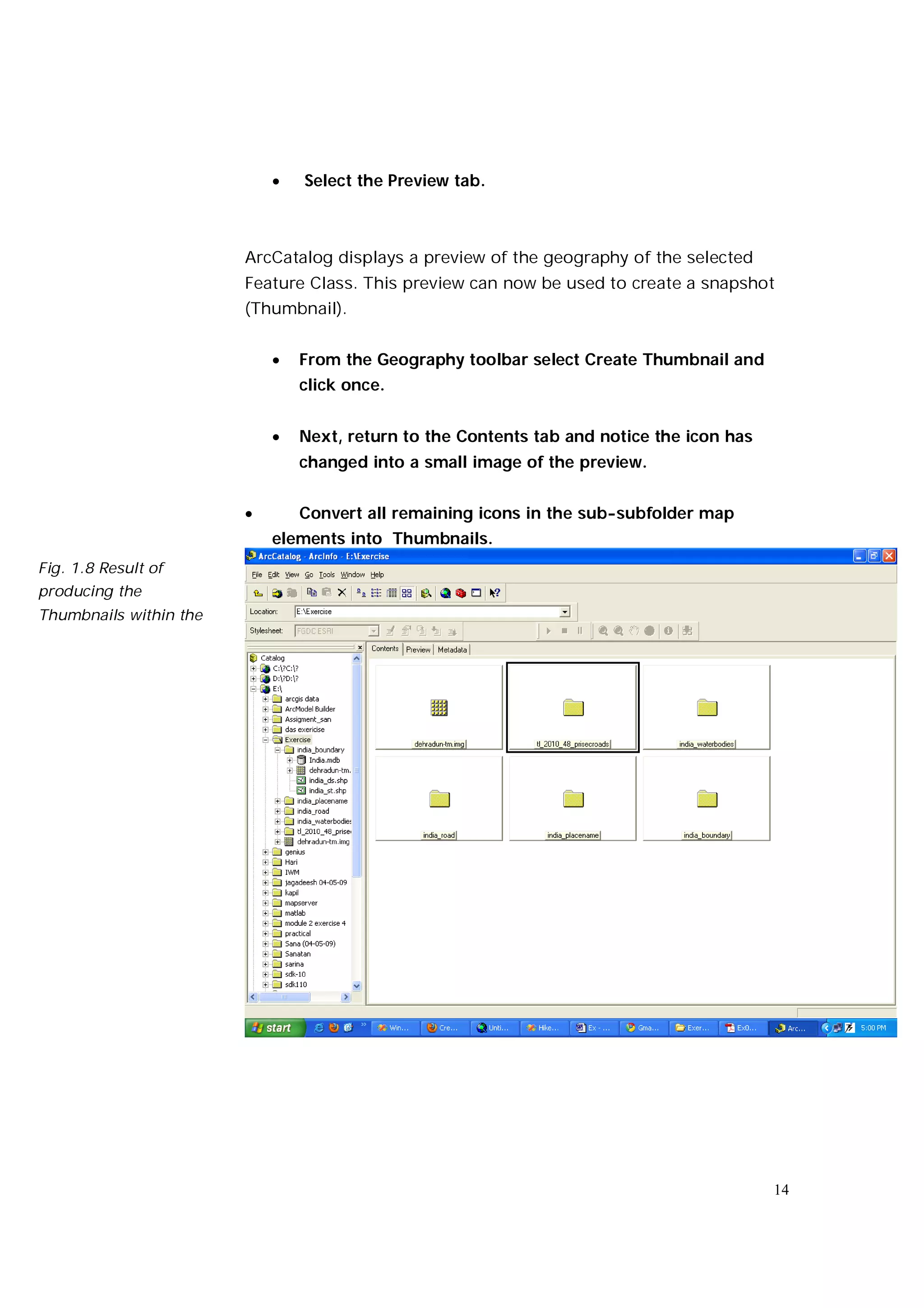
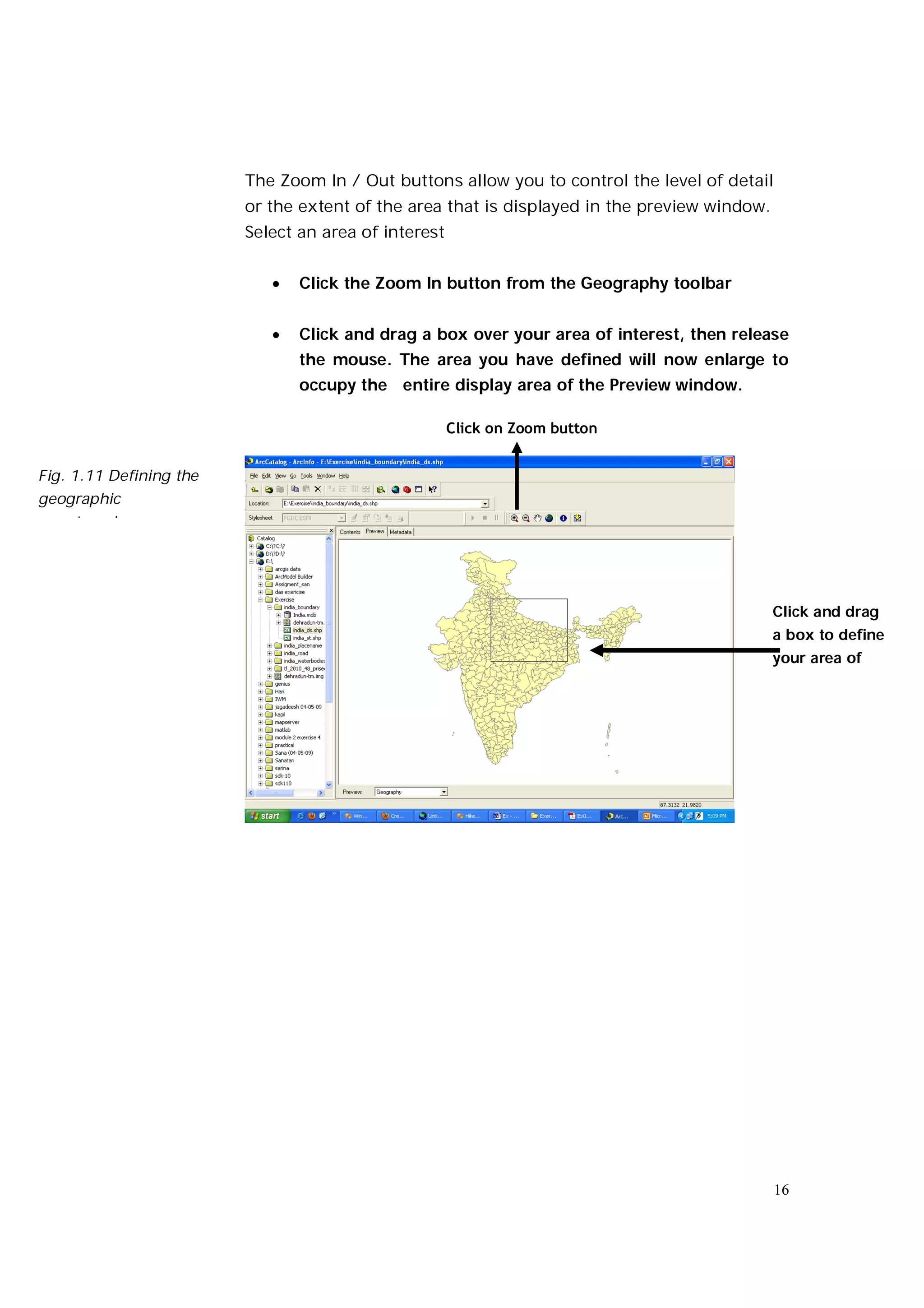
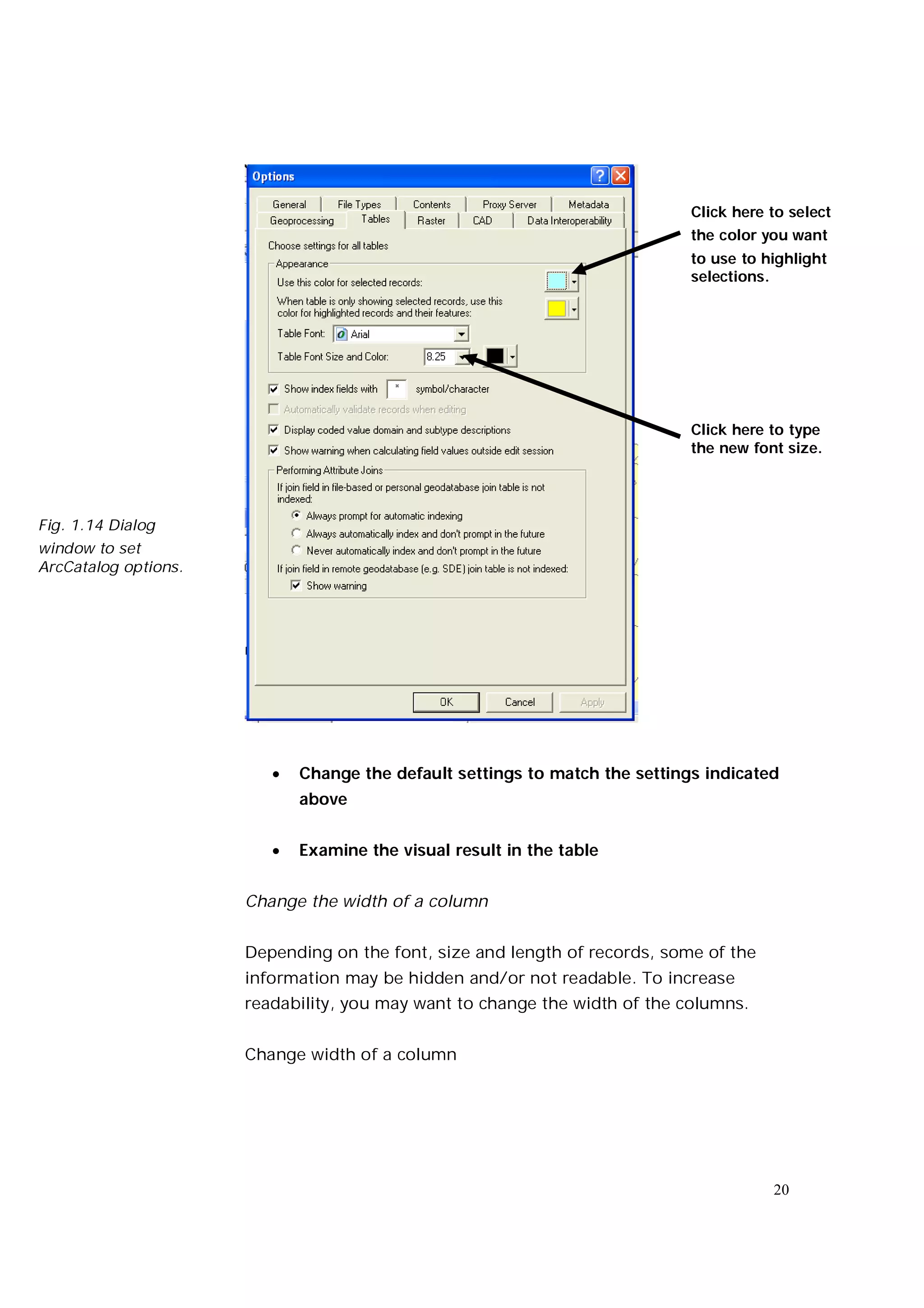
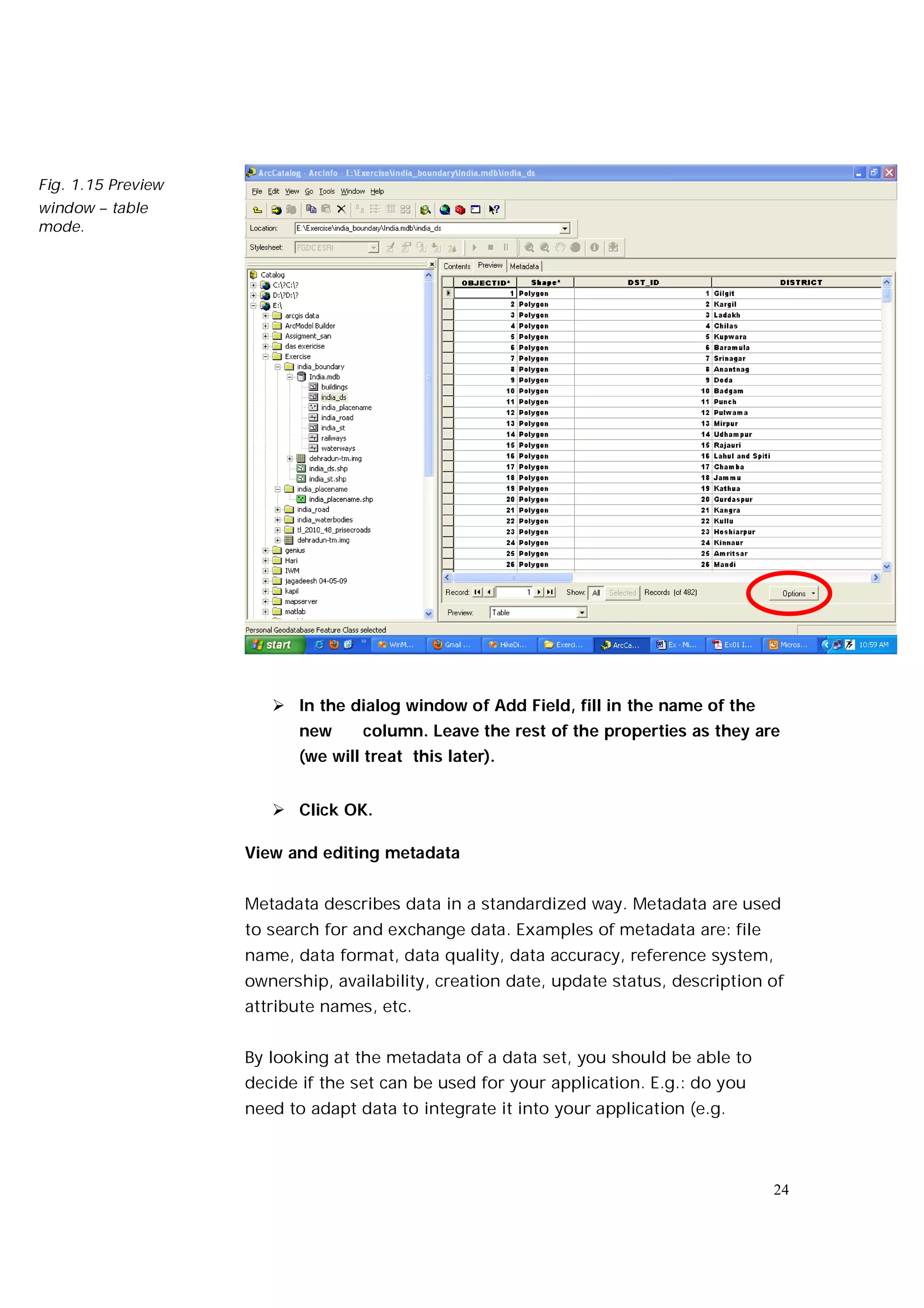
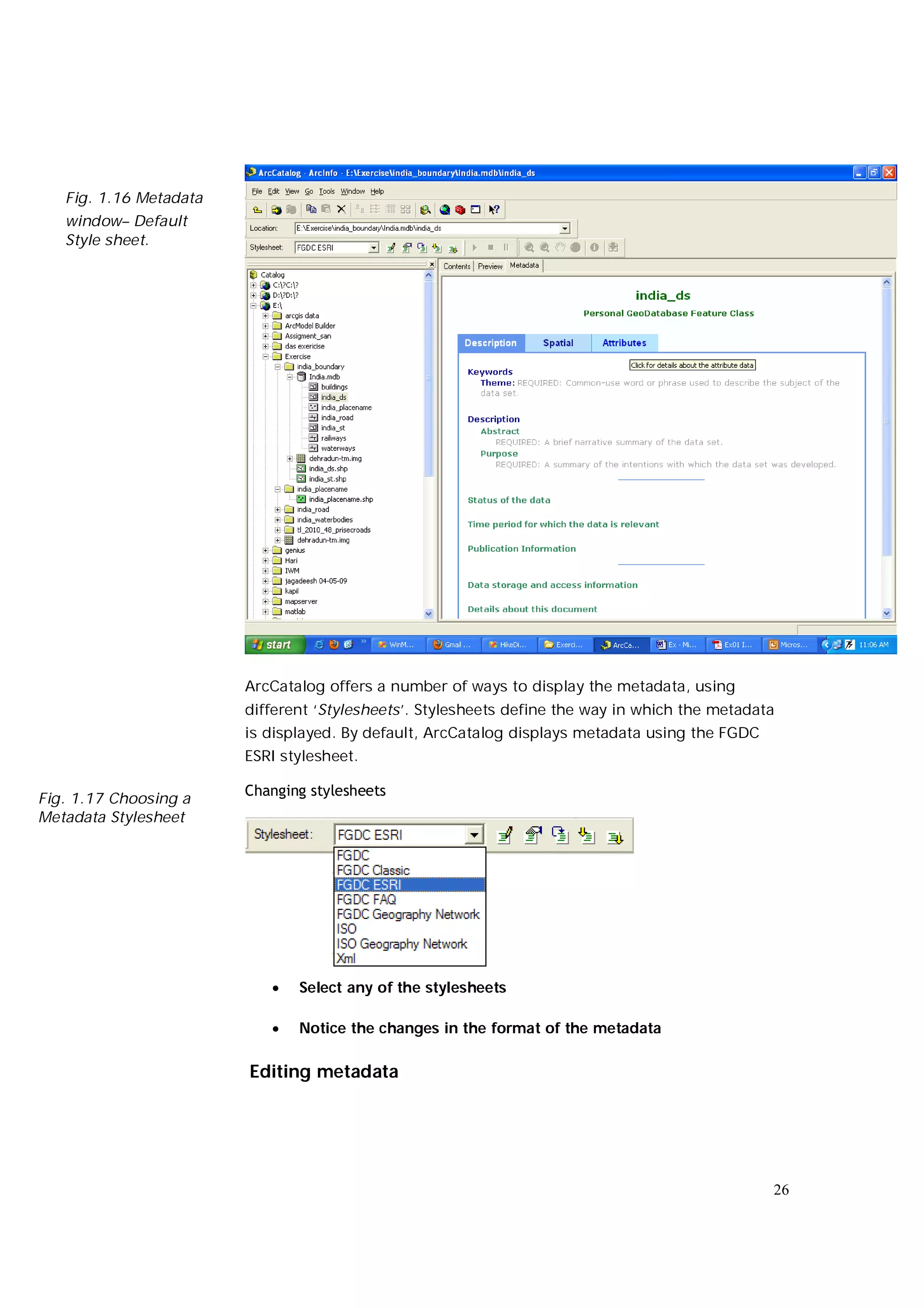
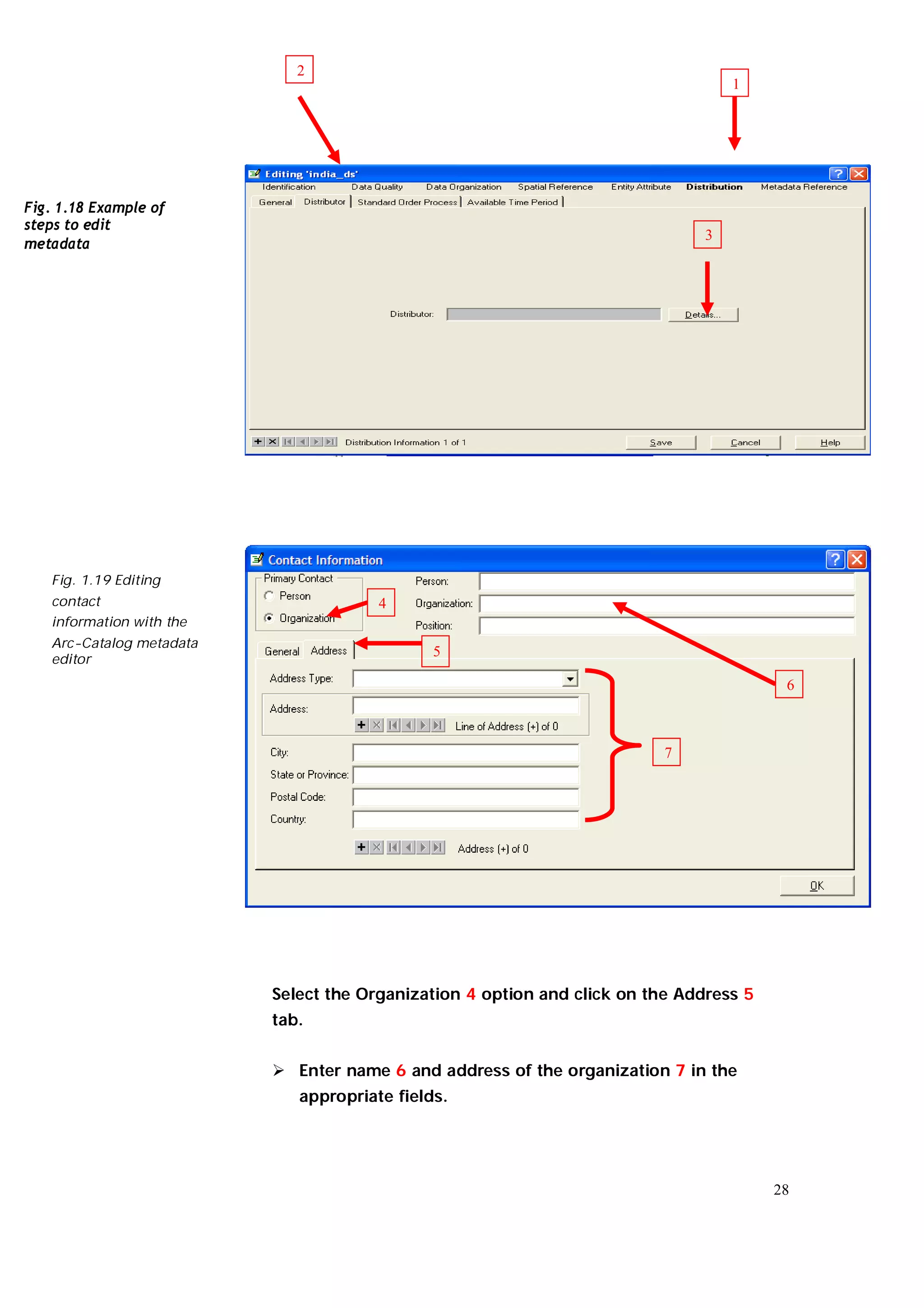
This document is an introductory guide to ArcCatalog 2, part of the ArcGIS environment, focusing on its interface, basic functions, and data management capabilities. Users will learn to browse, explore, and manage geographic data within ArcCatalog, as well as create and edit metadata. Additionally, it highlights how ArcCatalog serves as a gateway to ArcMap for further data analysis and map creation.