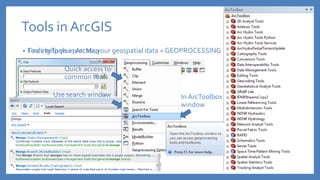
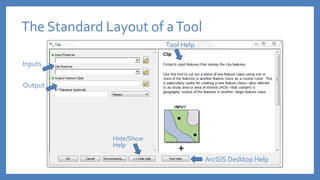
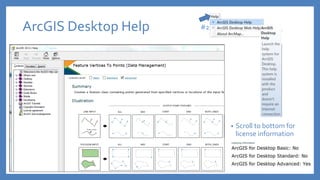
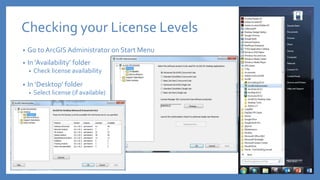
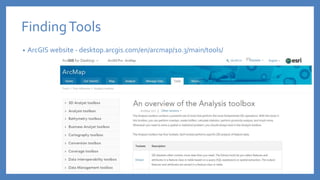
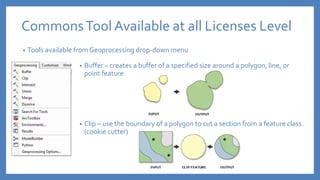
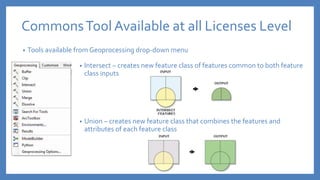
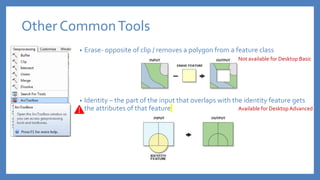
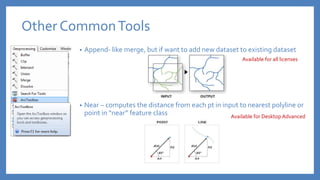
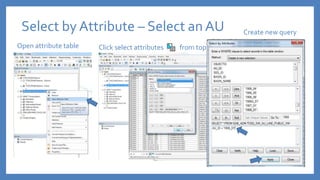
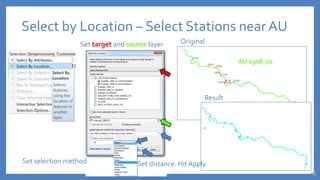
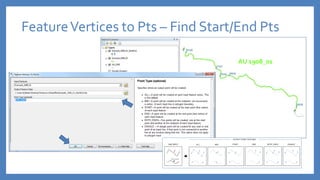
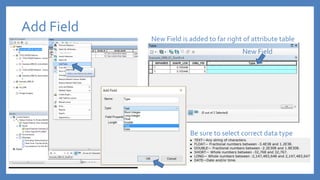
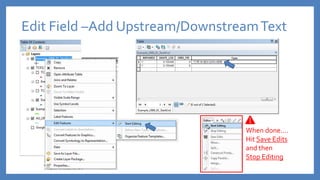
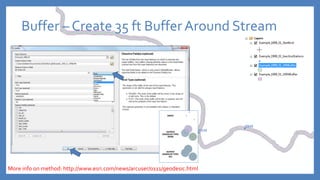
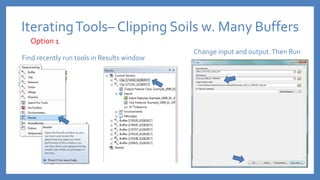
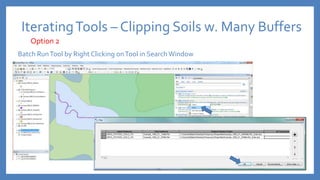
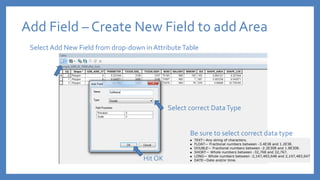
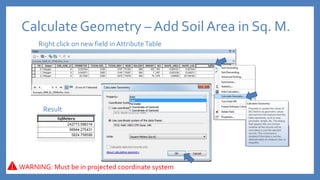
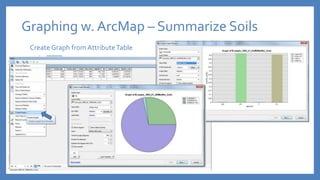
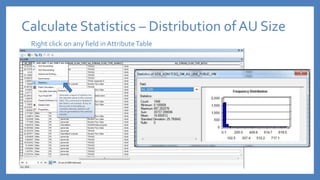
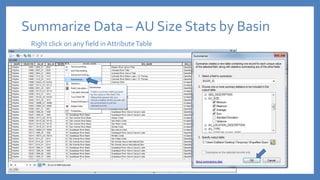
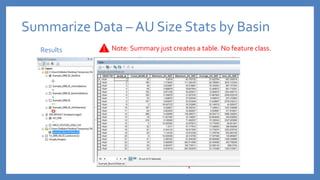
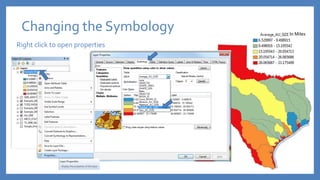
The document provides an introduction to tools in ArcGIS, highlighting the importance of geoprocessing for managing geospatial data and detailing how to access tools via the ArcToolbox and geoprocessing drop-down menu. It covers core tools available across different ArcGIS license levels, such as buffer, clip, intersect, and union, along with advanced options that require higher-level licenses. Additional resources for learning and support, as well as contact information for further inquiries, are also included.