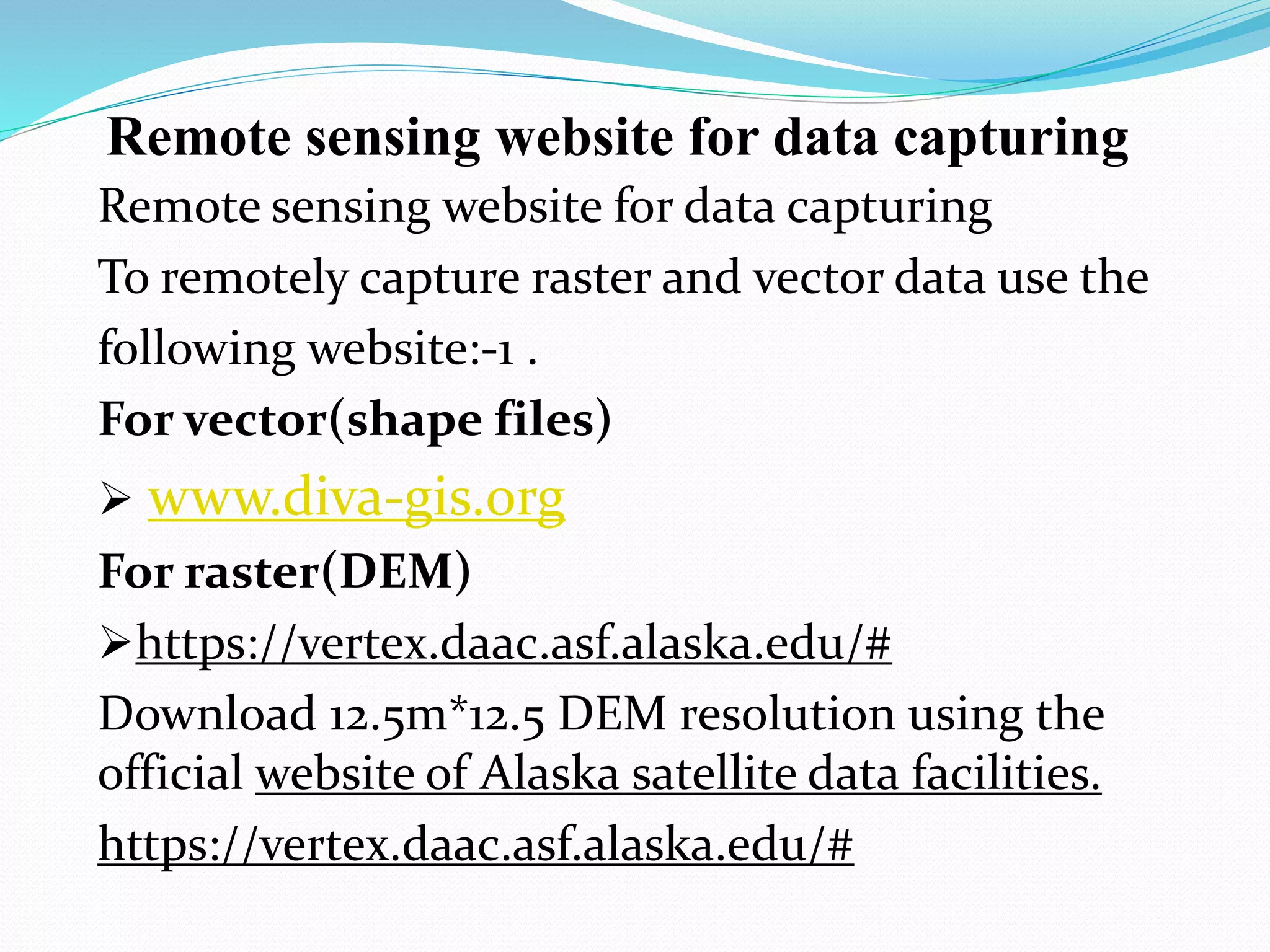
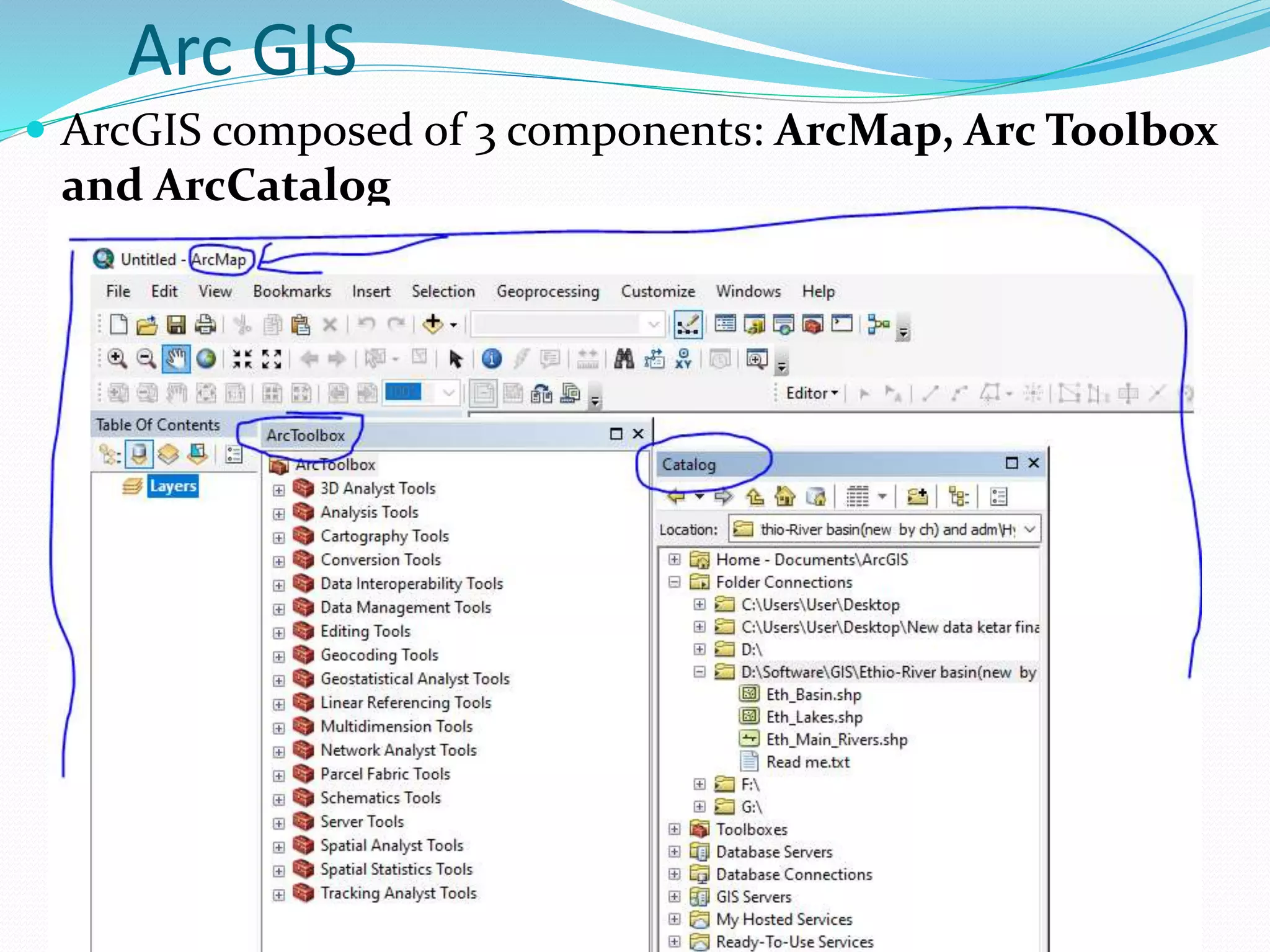
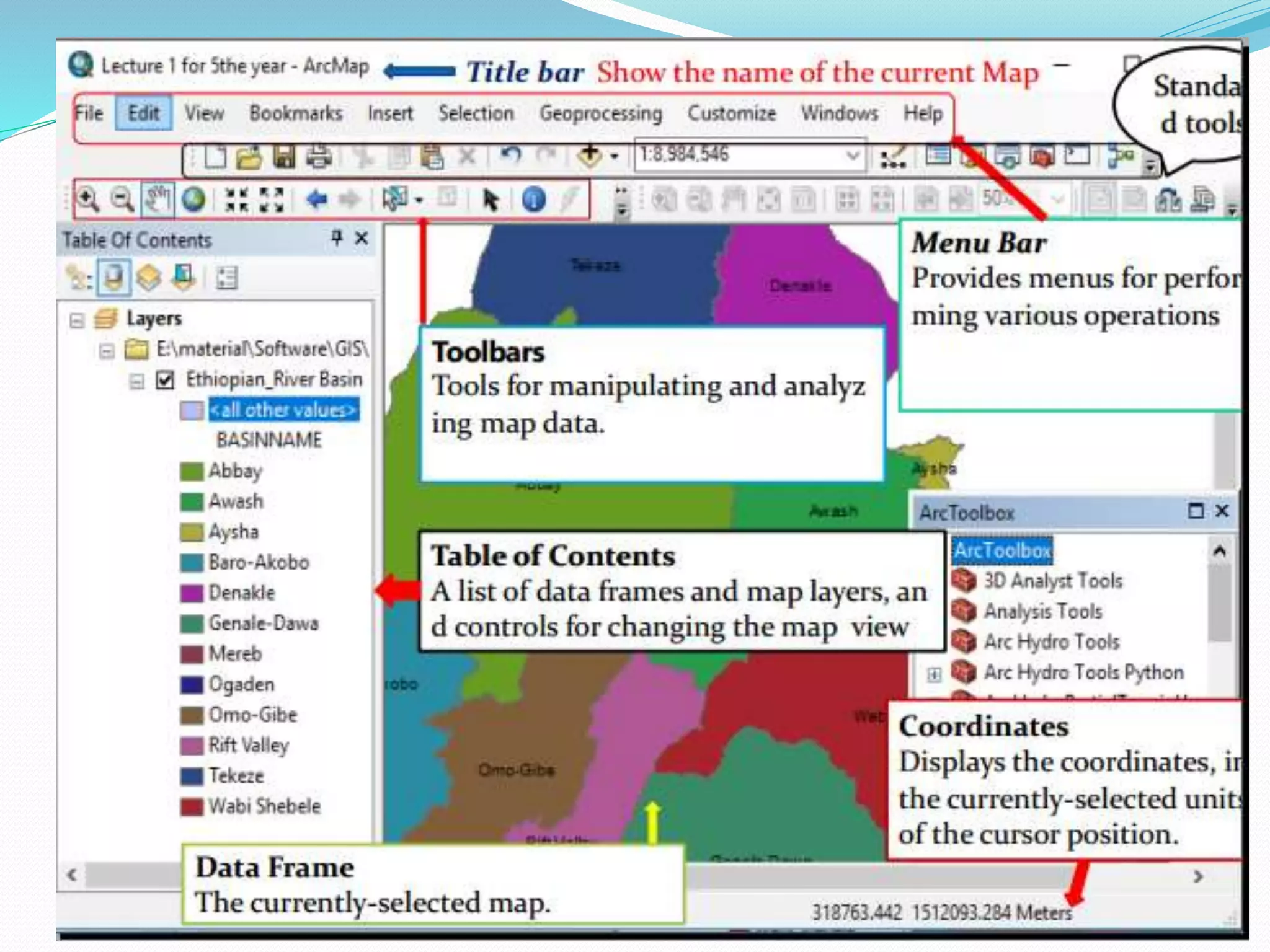
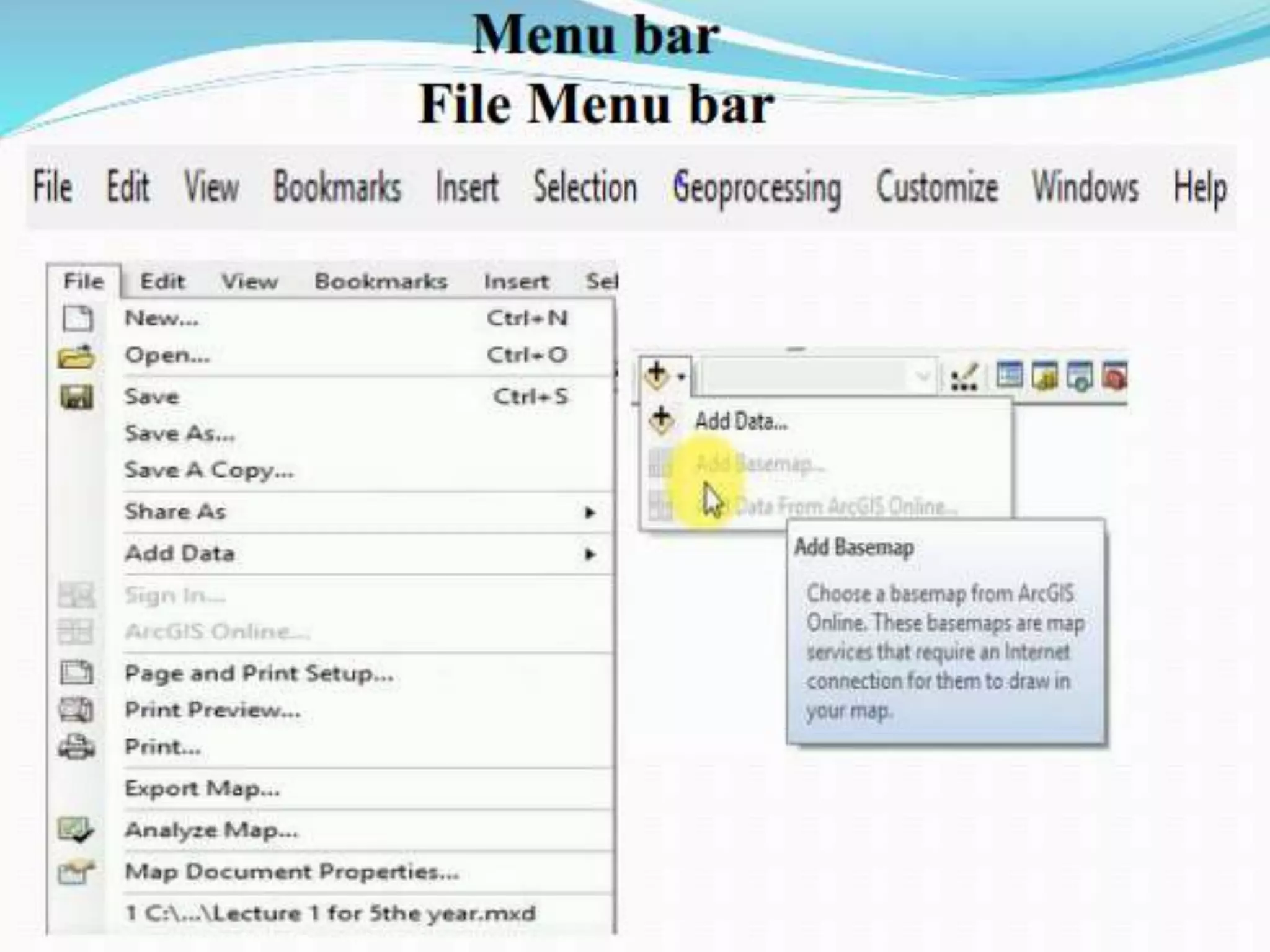
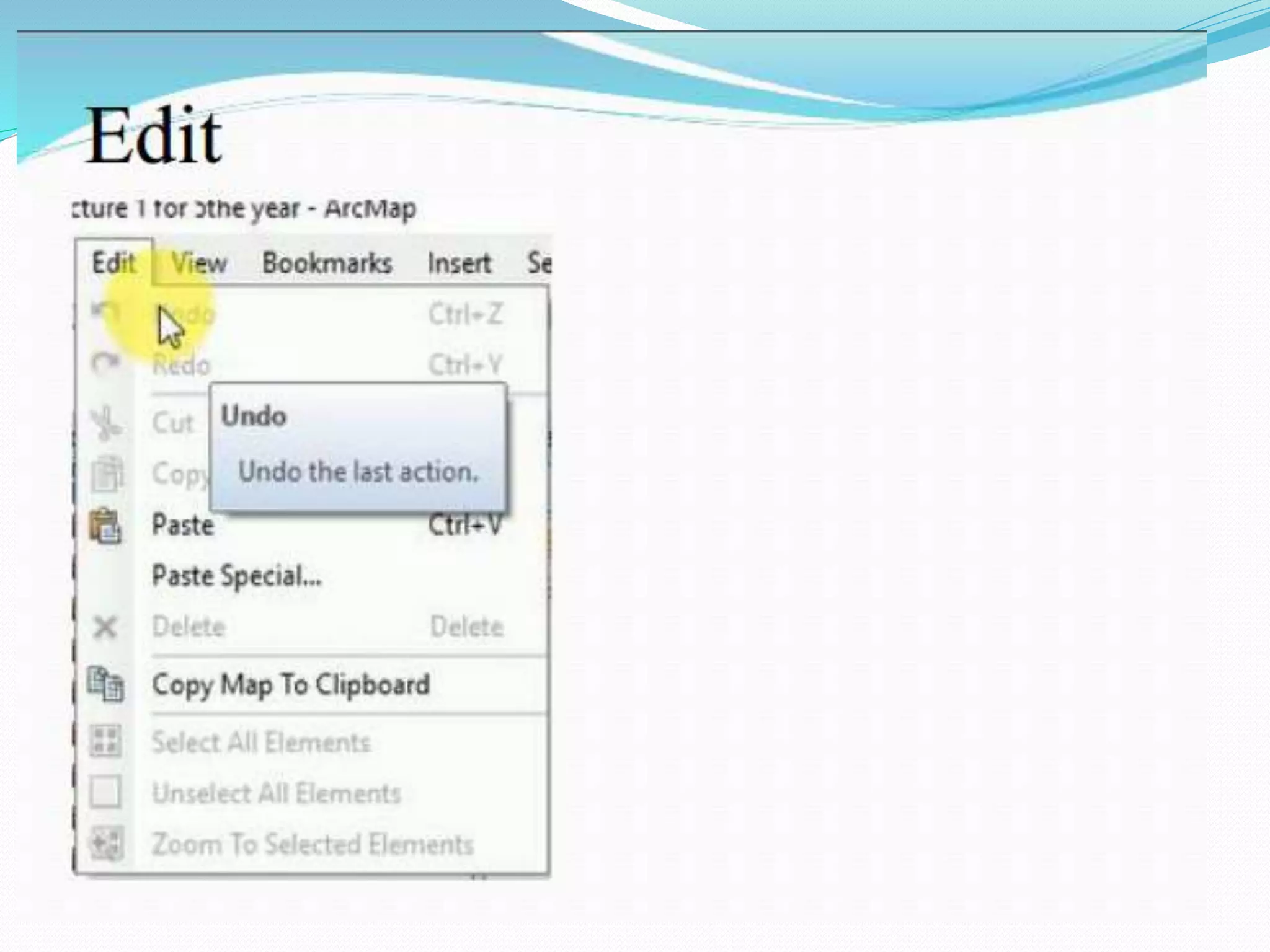
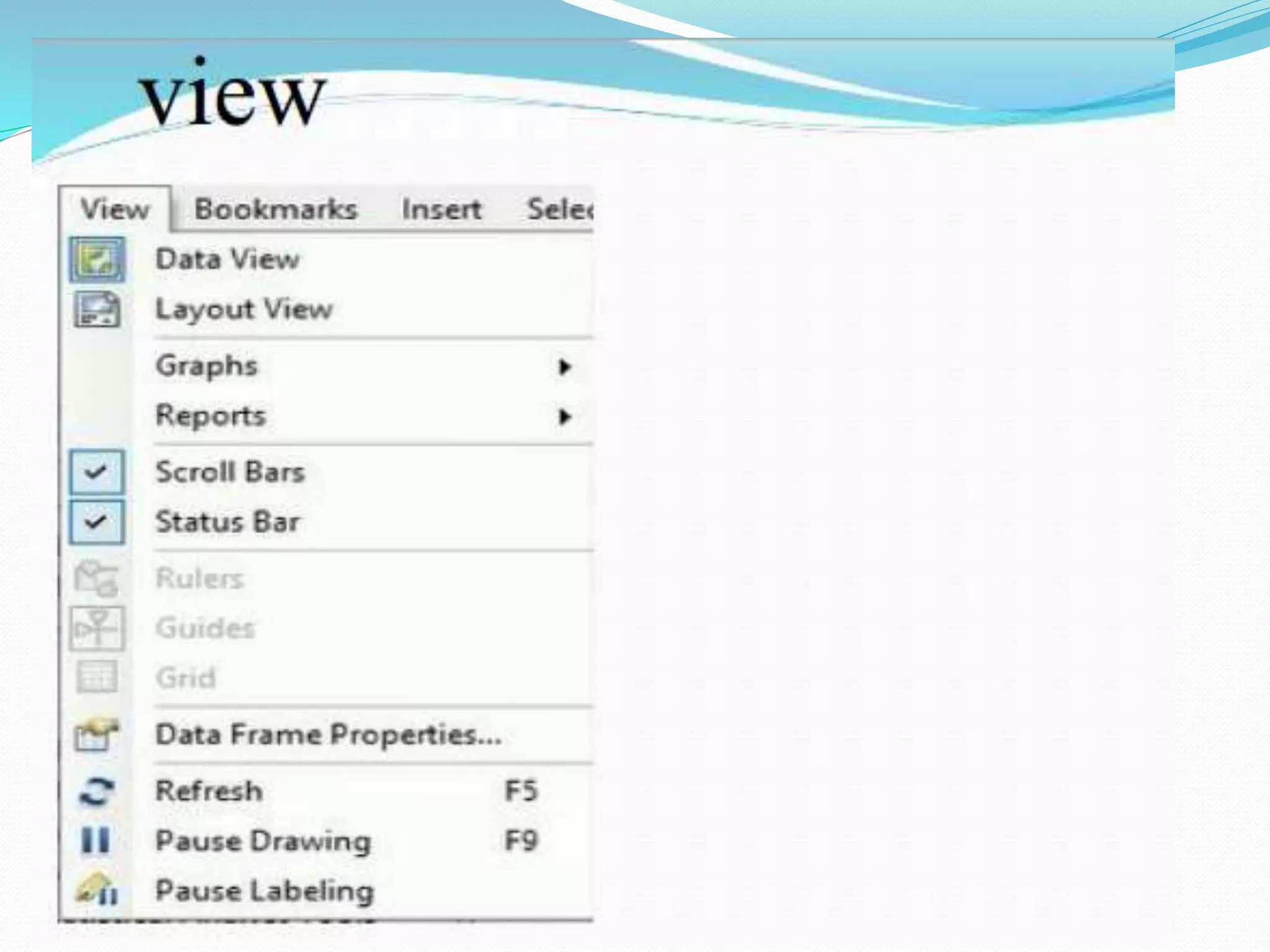
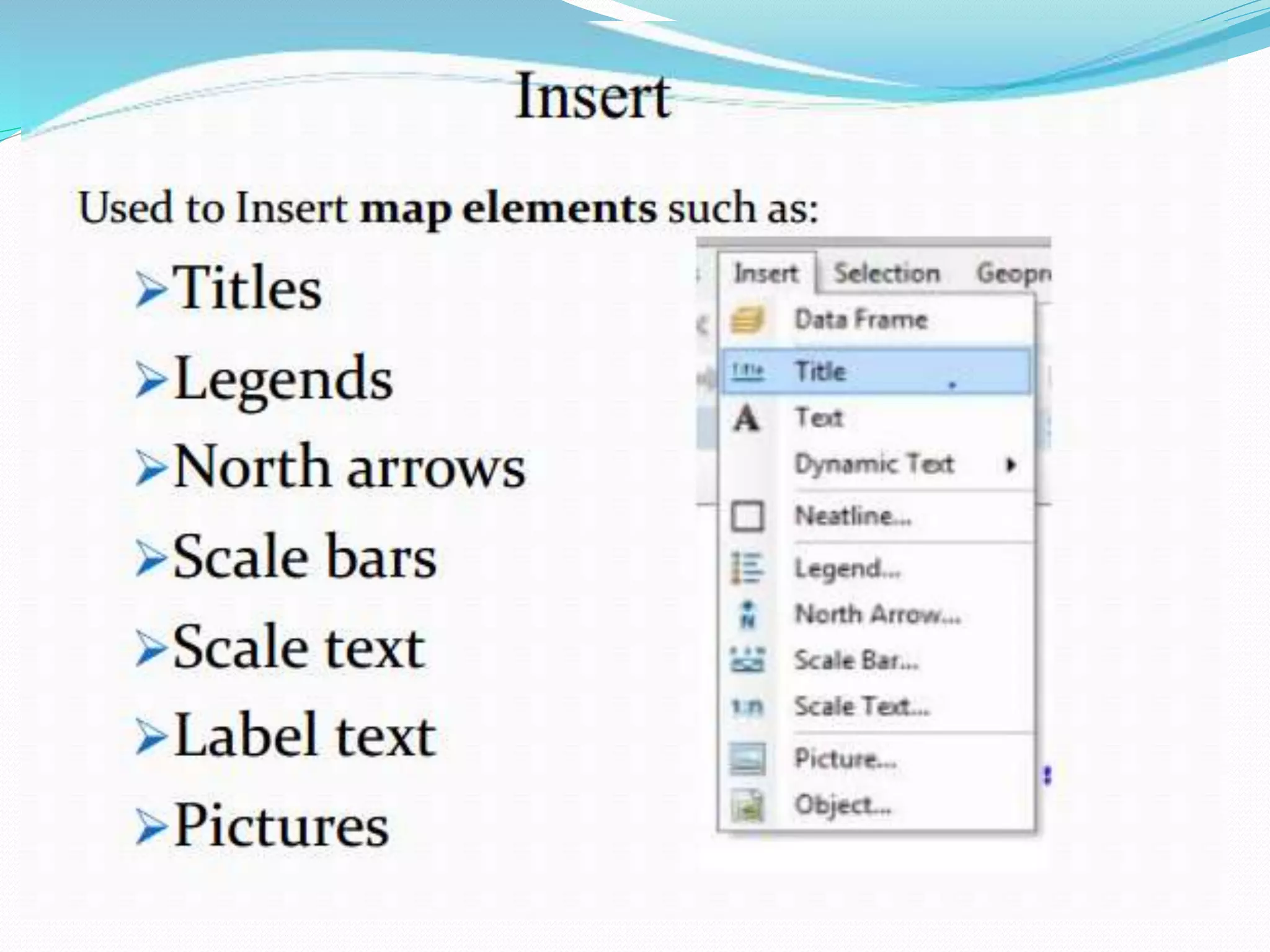
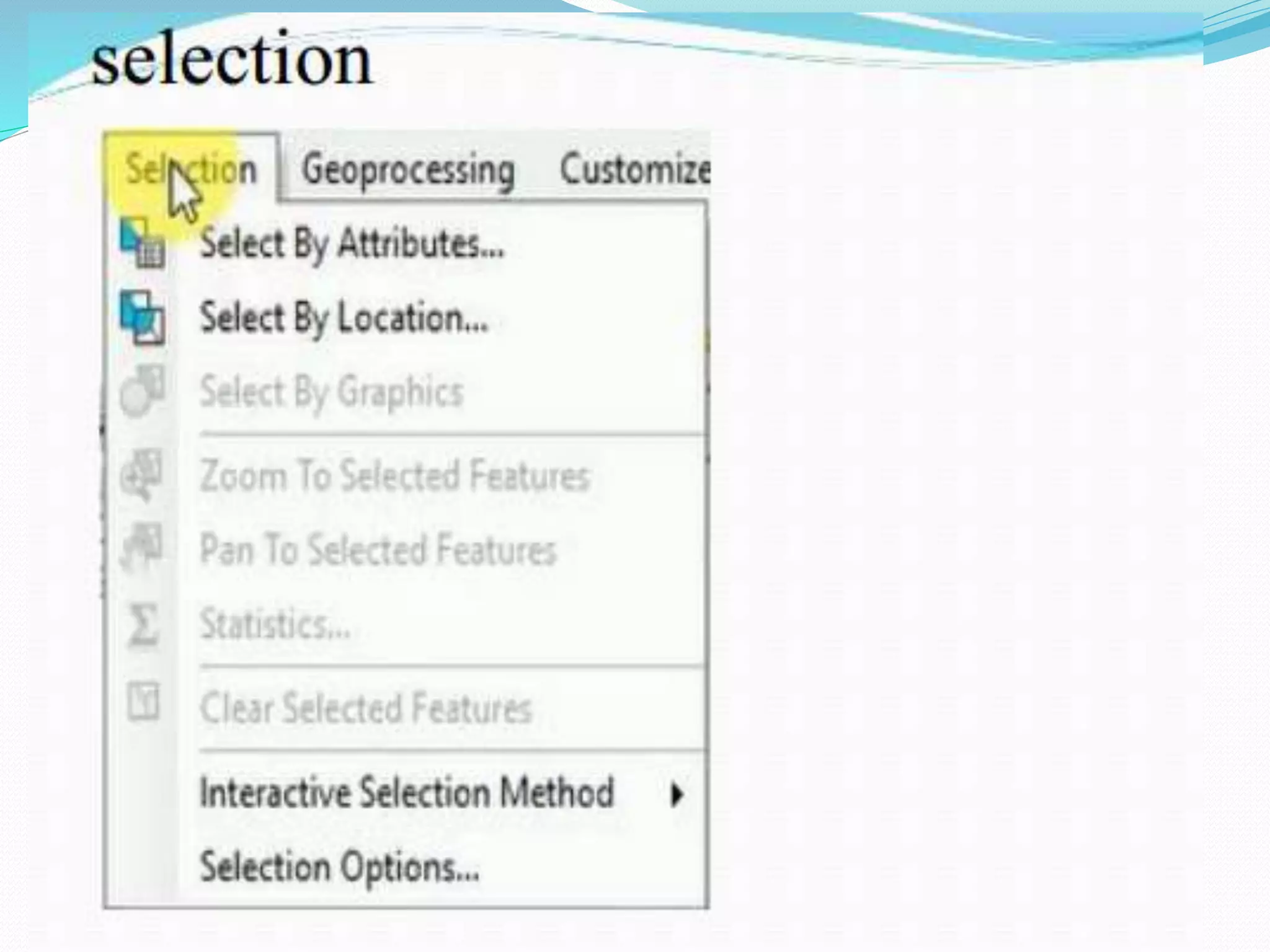
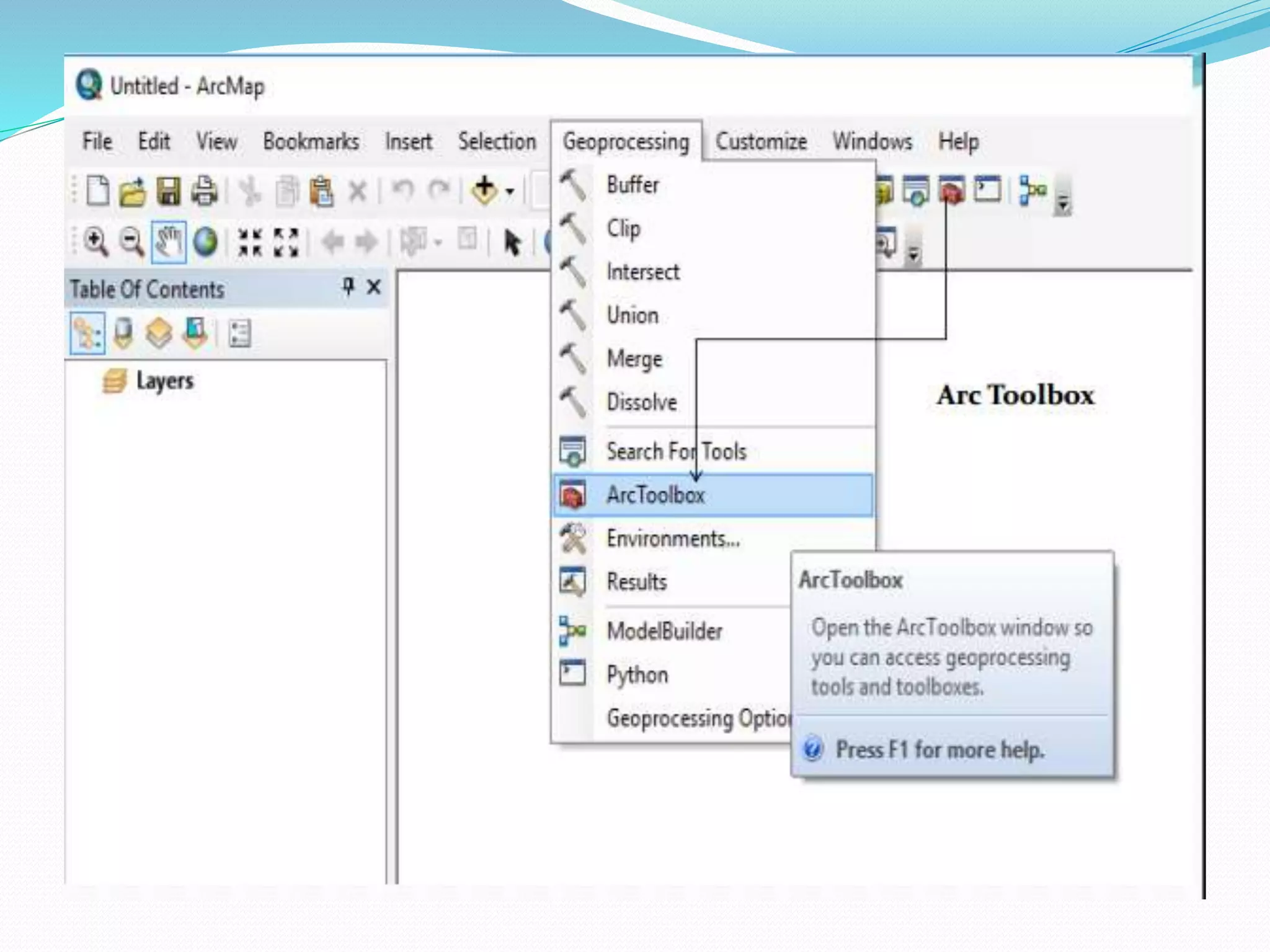
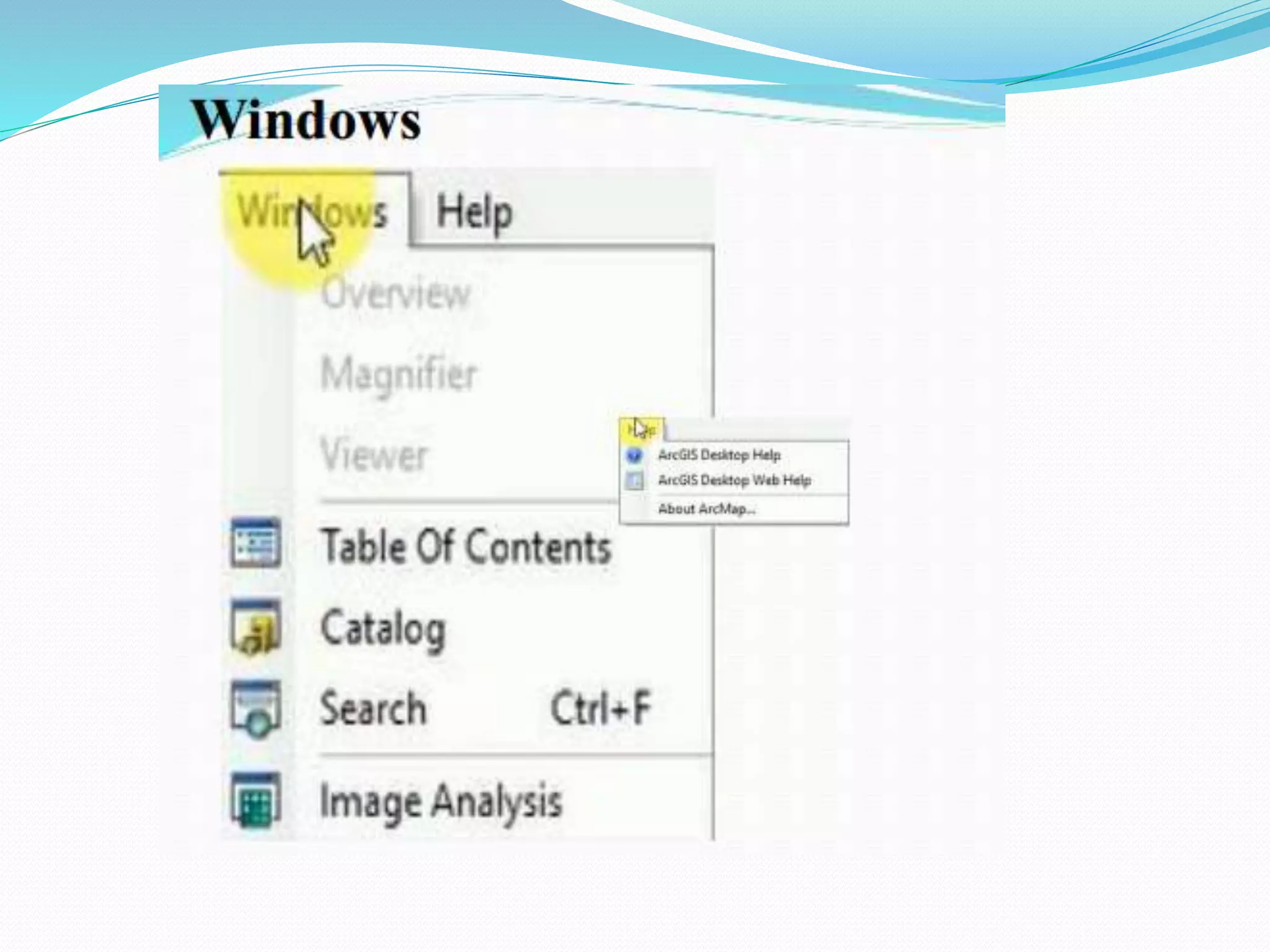
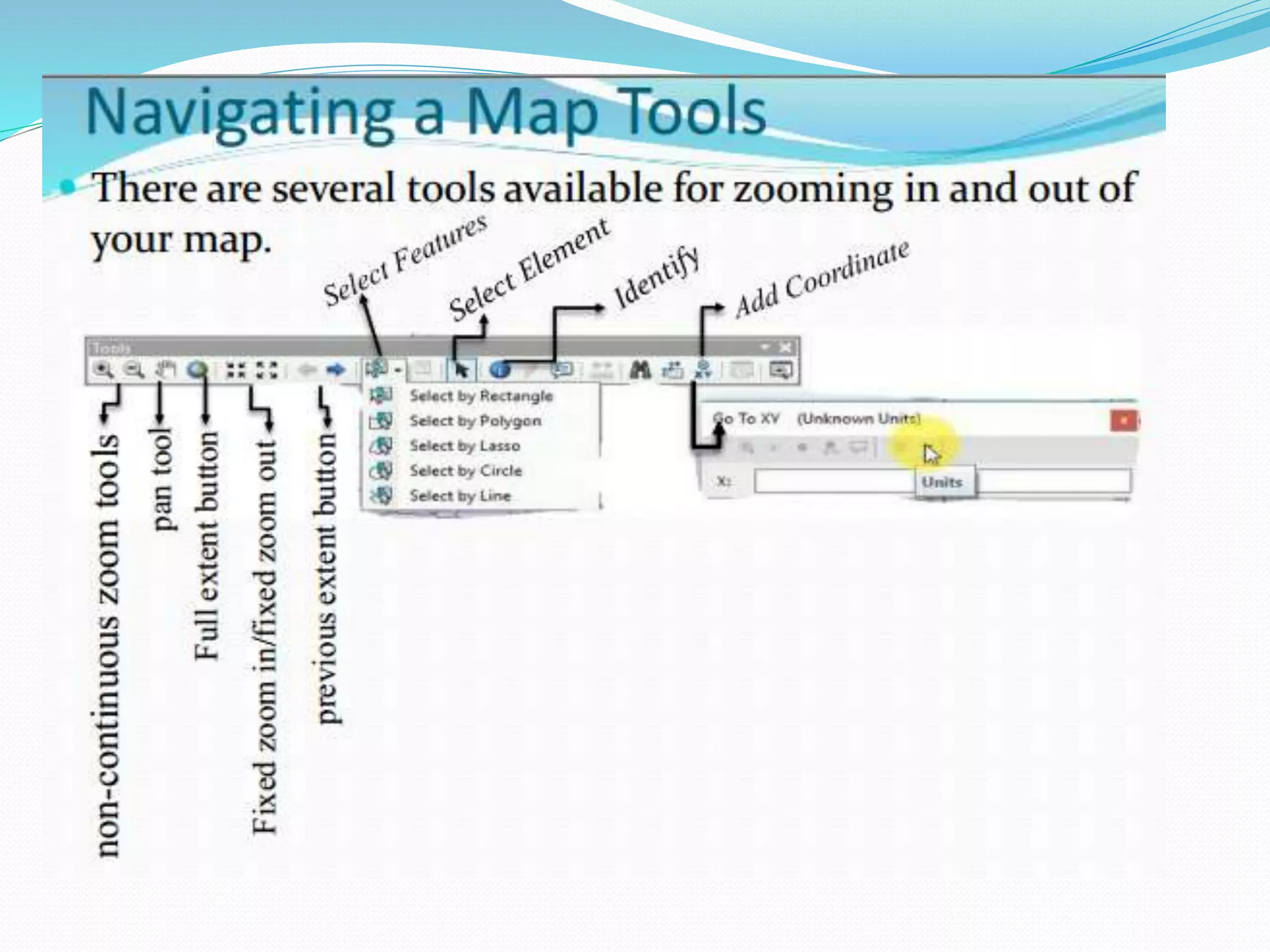
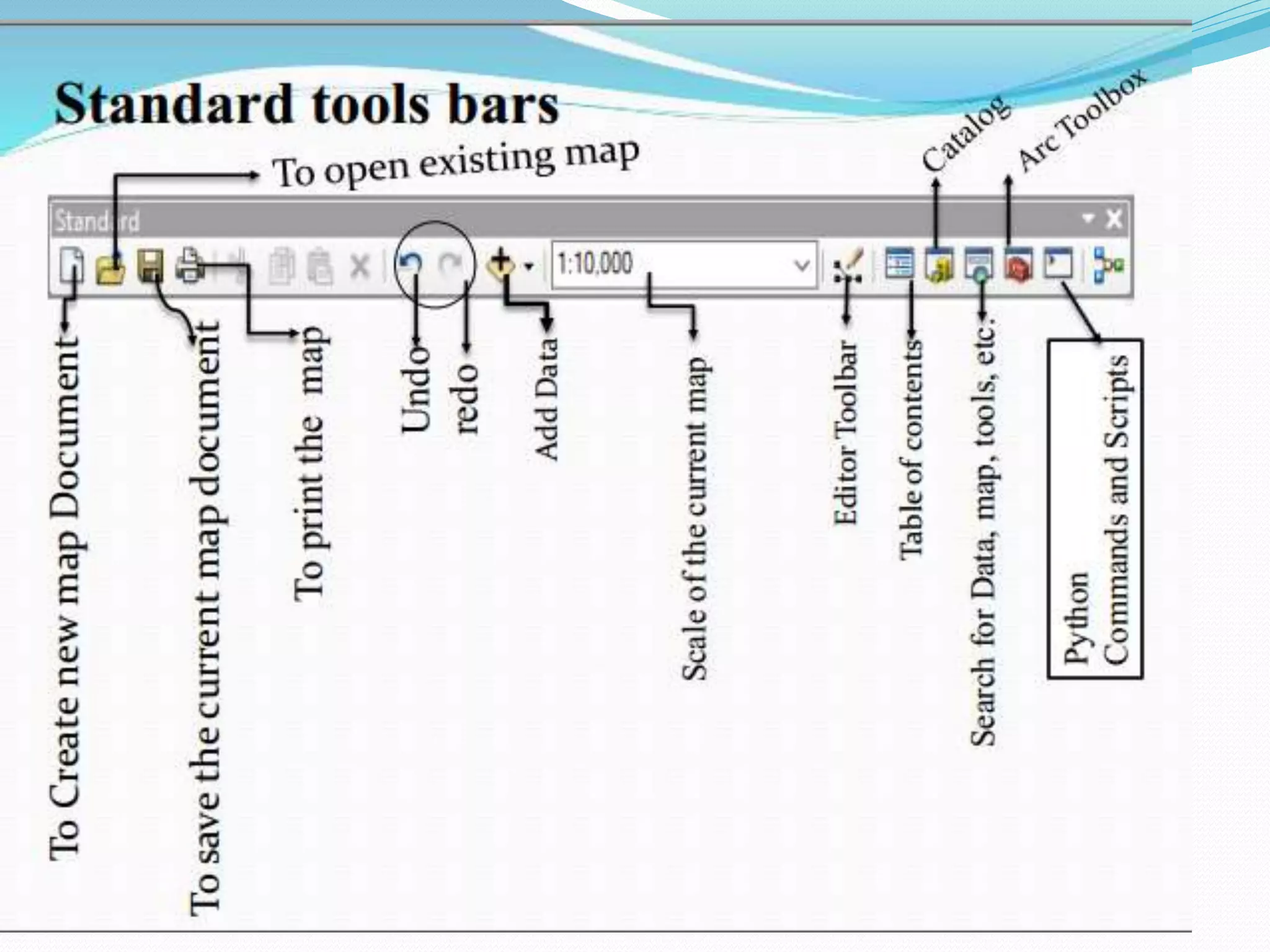
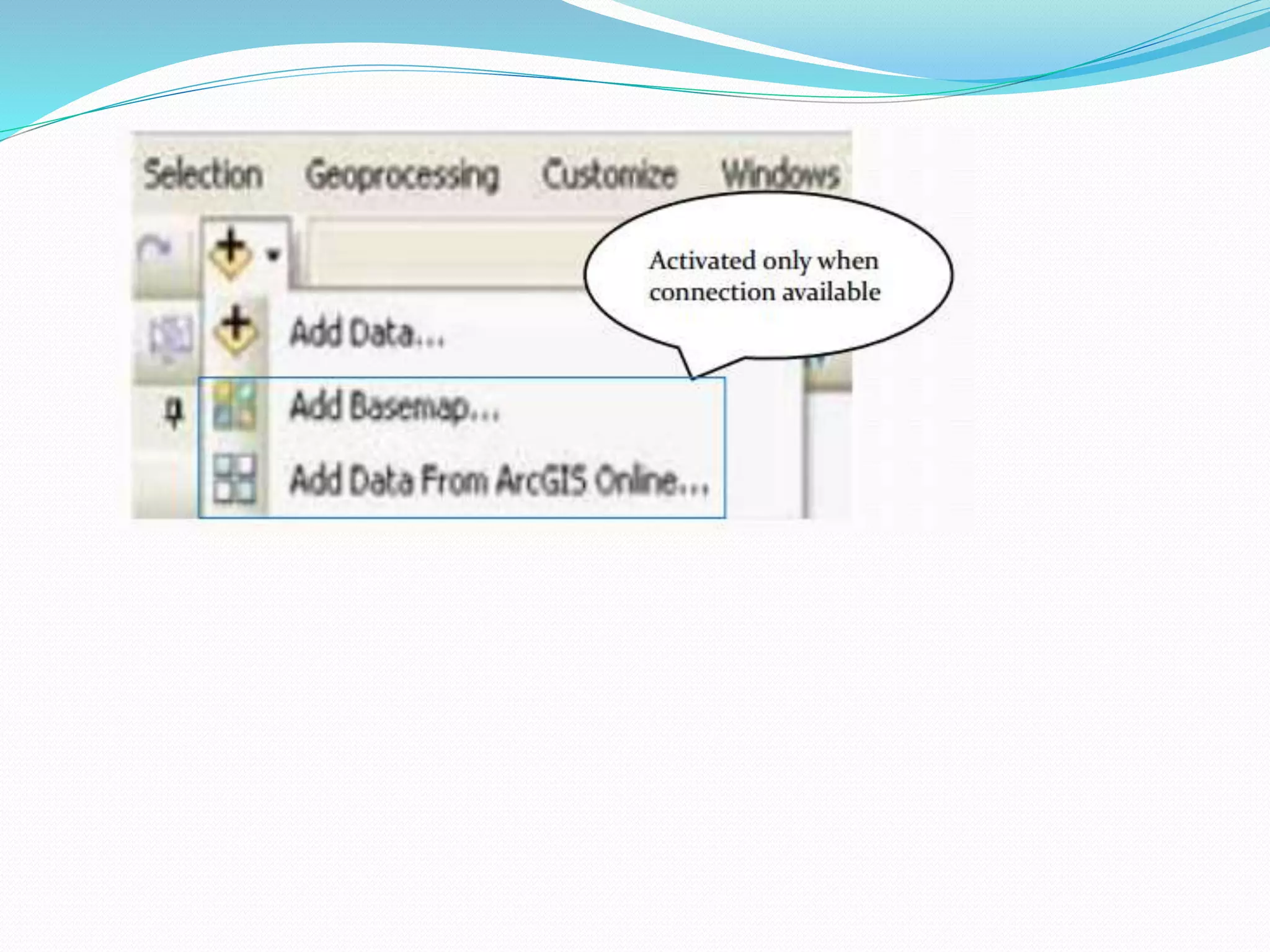
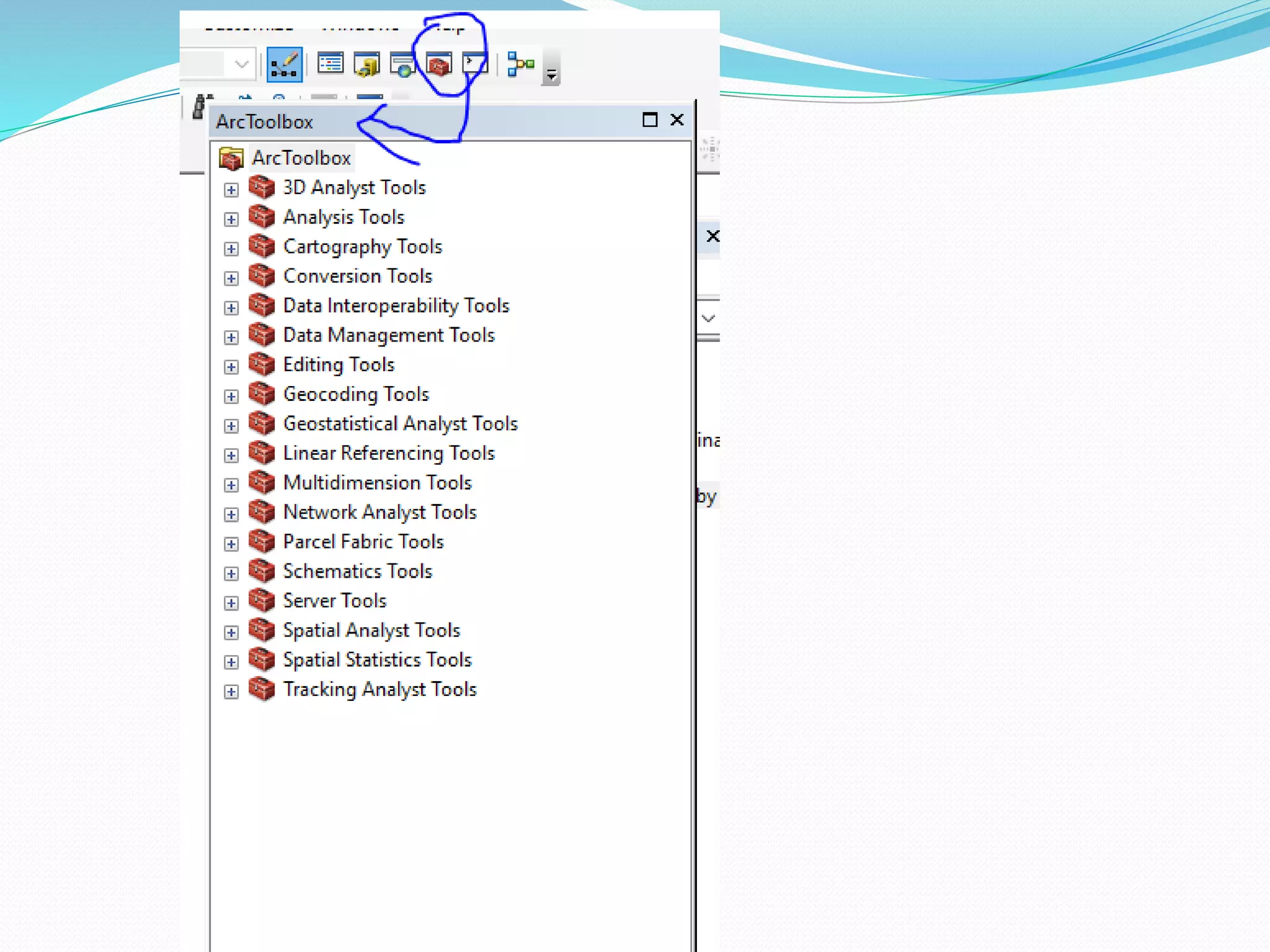
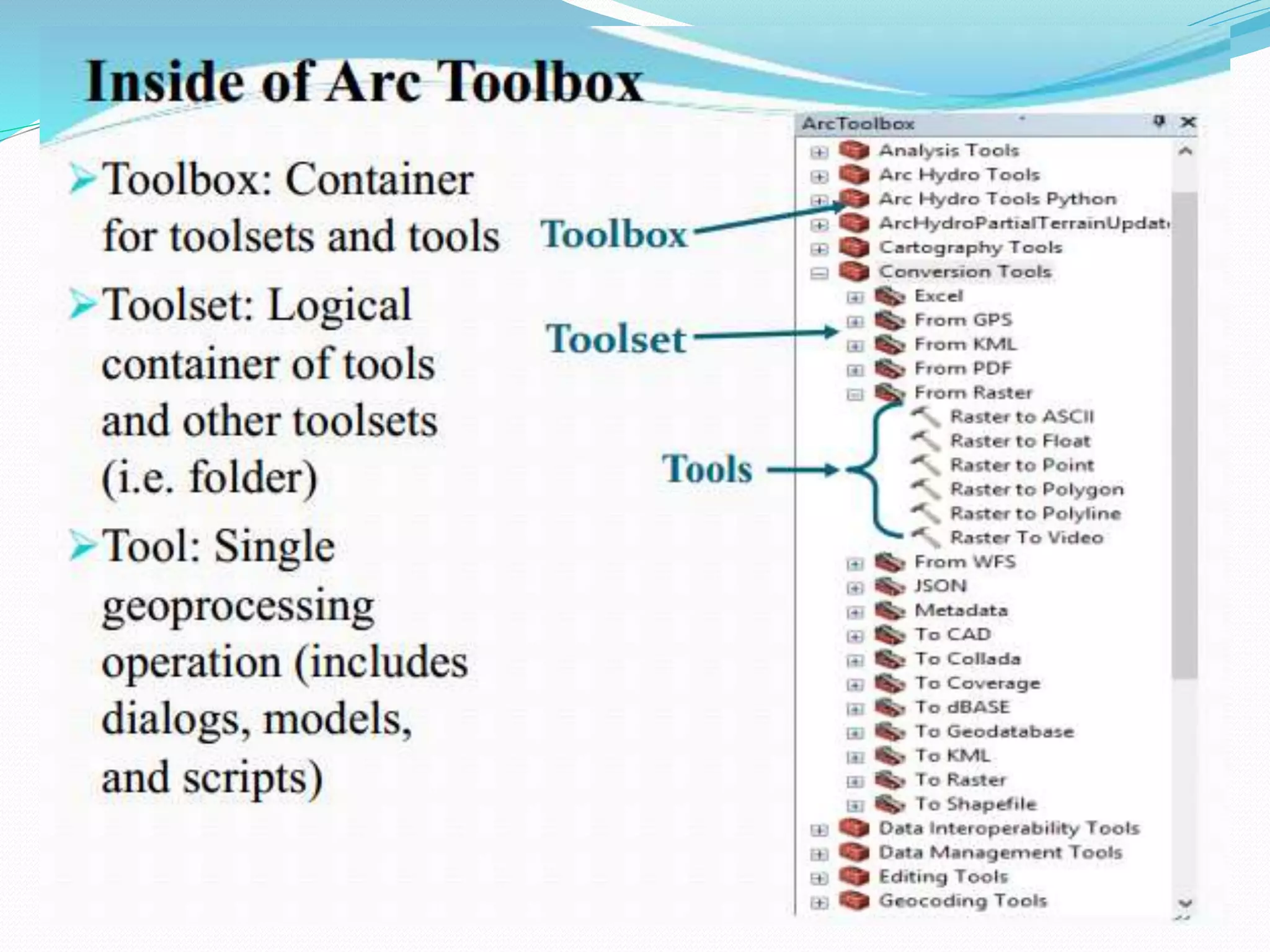
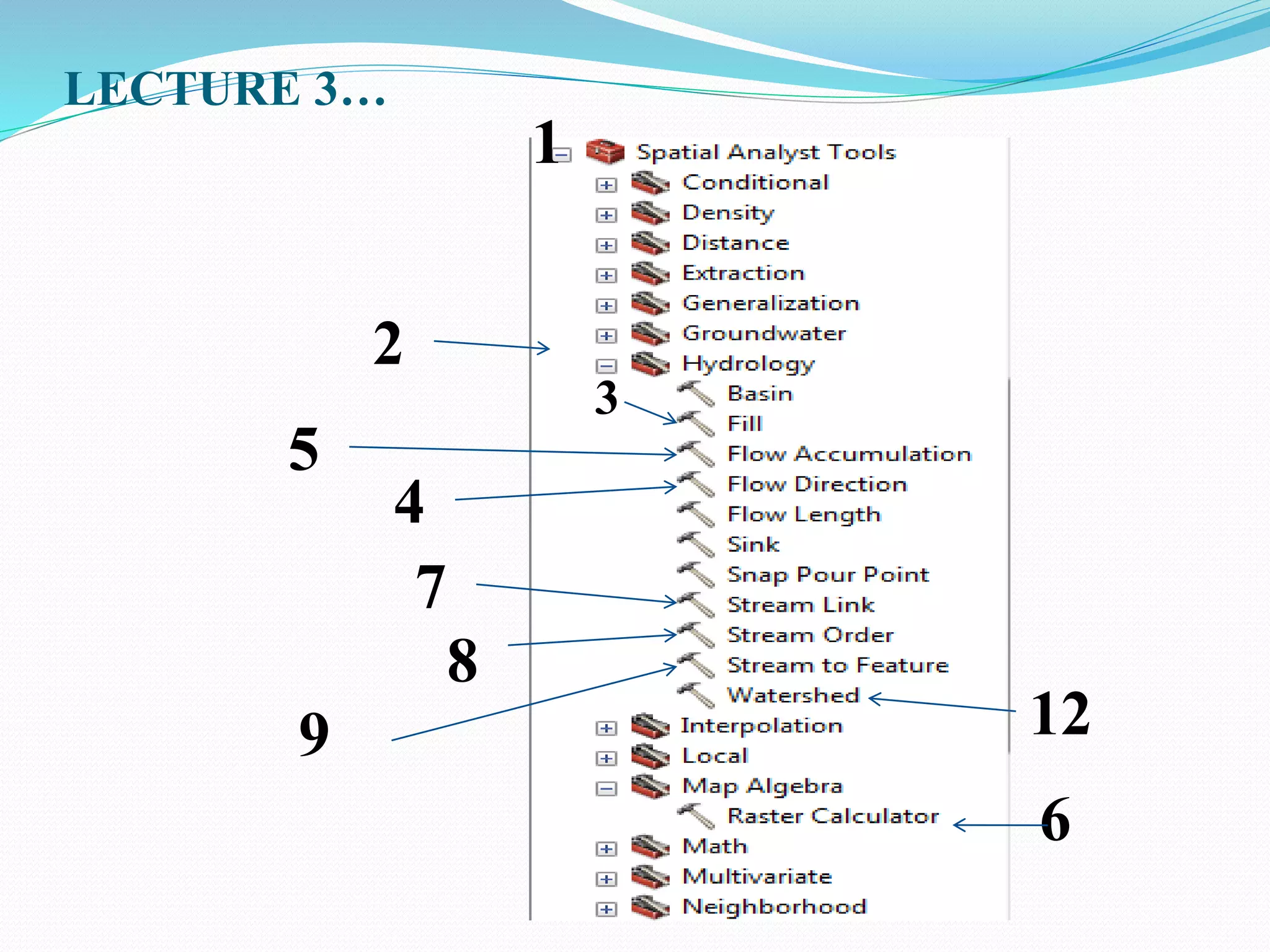
The document provides an overview of remote sensing and GIS tools used in mapping and spatial analysis, focusing on ArcGIS software functionalities such as ArcMap, ArcToolbox, and ArcCatalog. It covers essential operations including data integration, map layer editing, watershed delineation, and cartographic principles necessary for effective map-making. Furthermore, it includes links to tutorials and resources for further learning and practical applications in GIS.