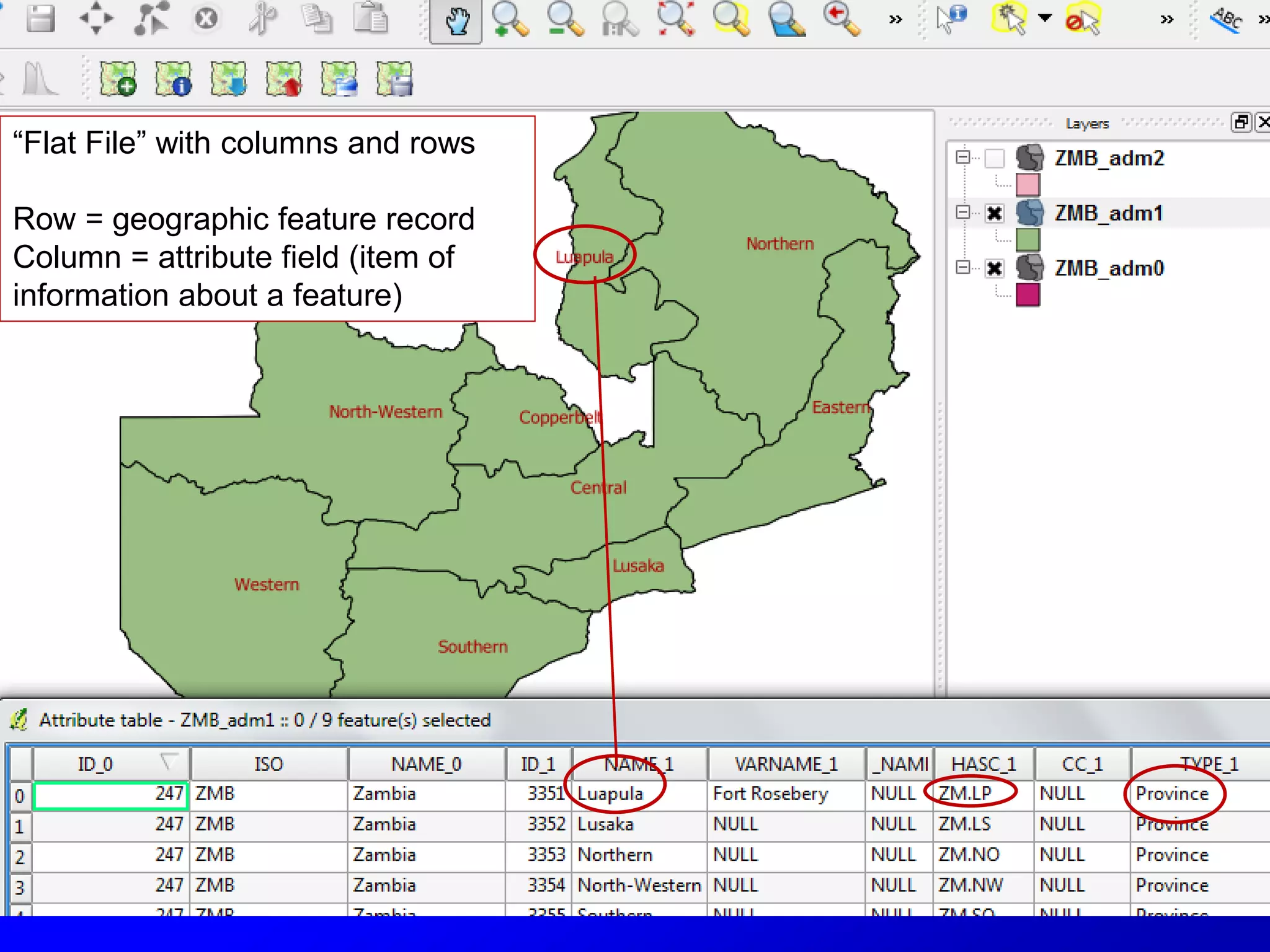
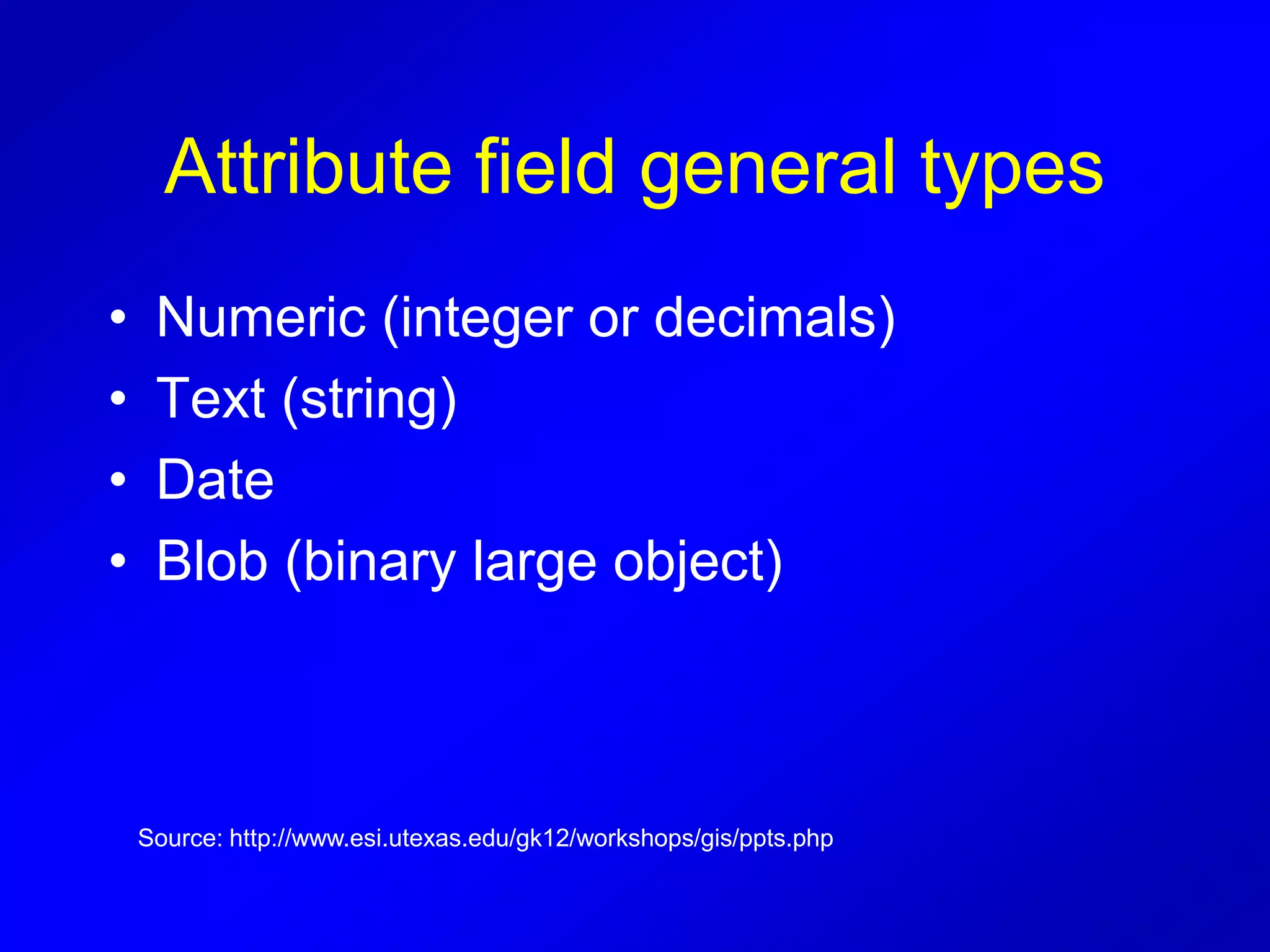
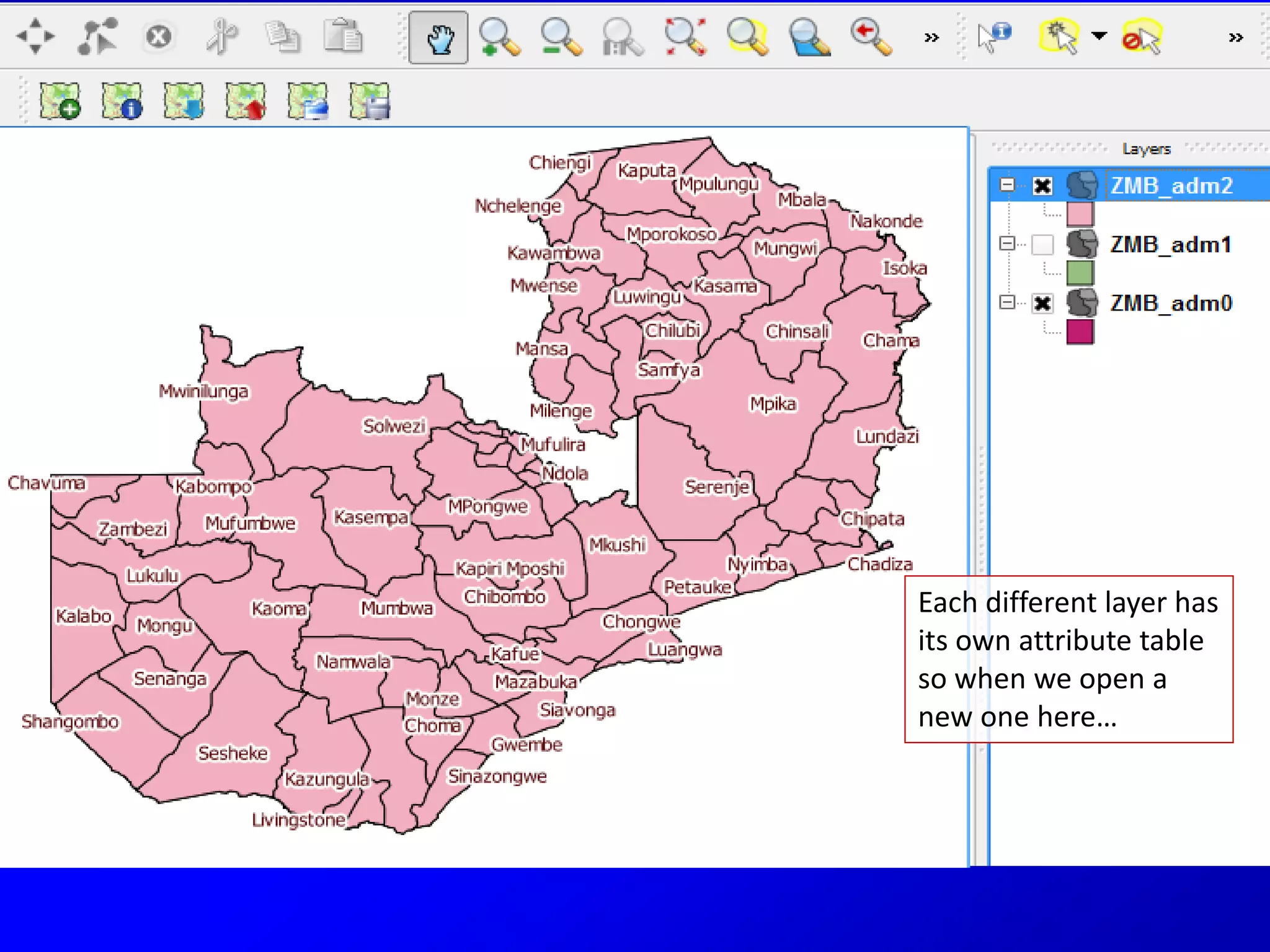
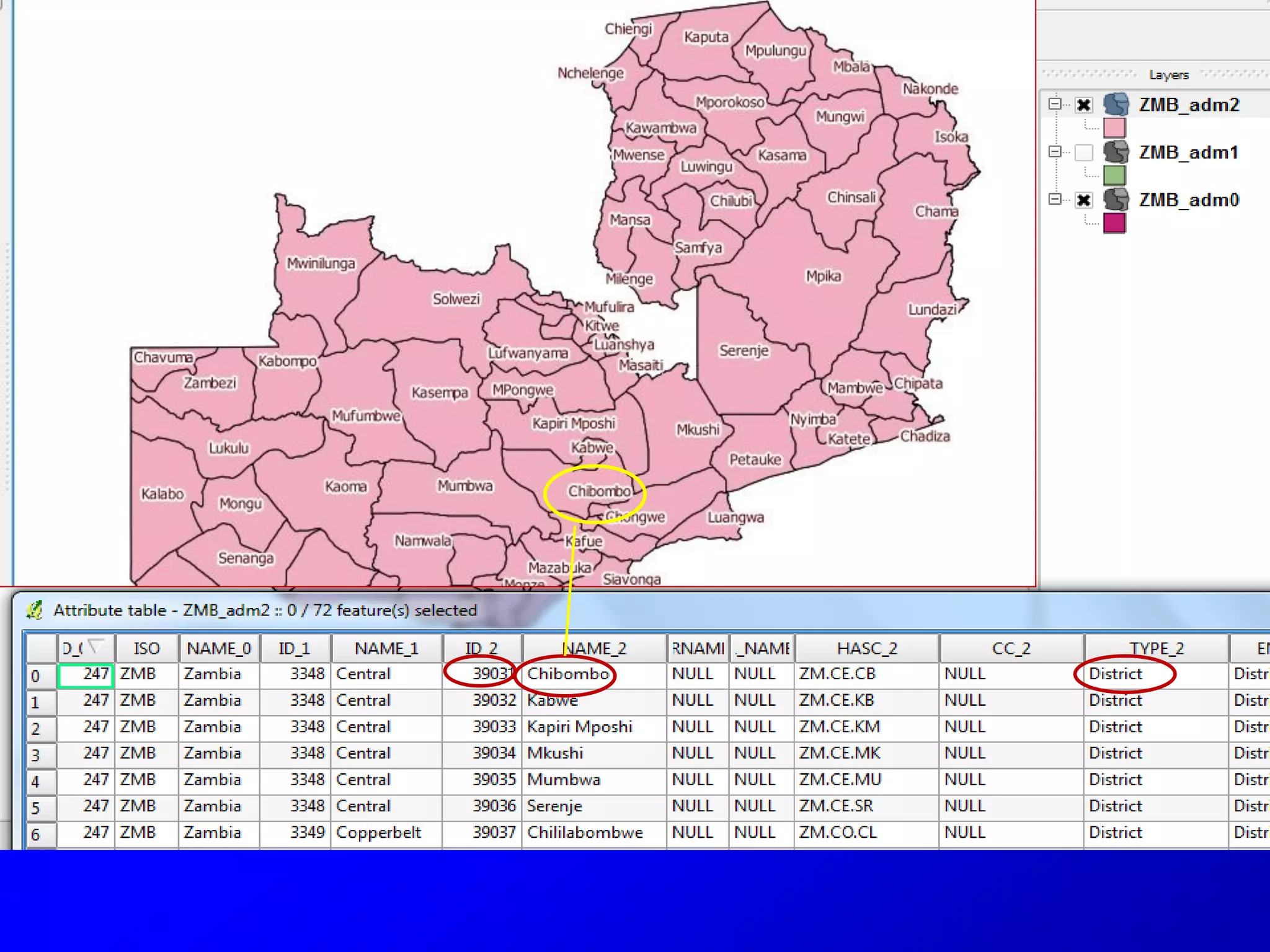
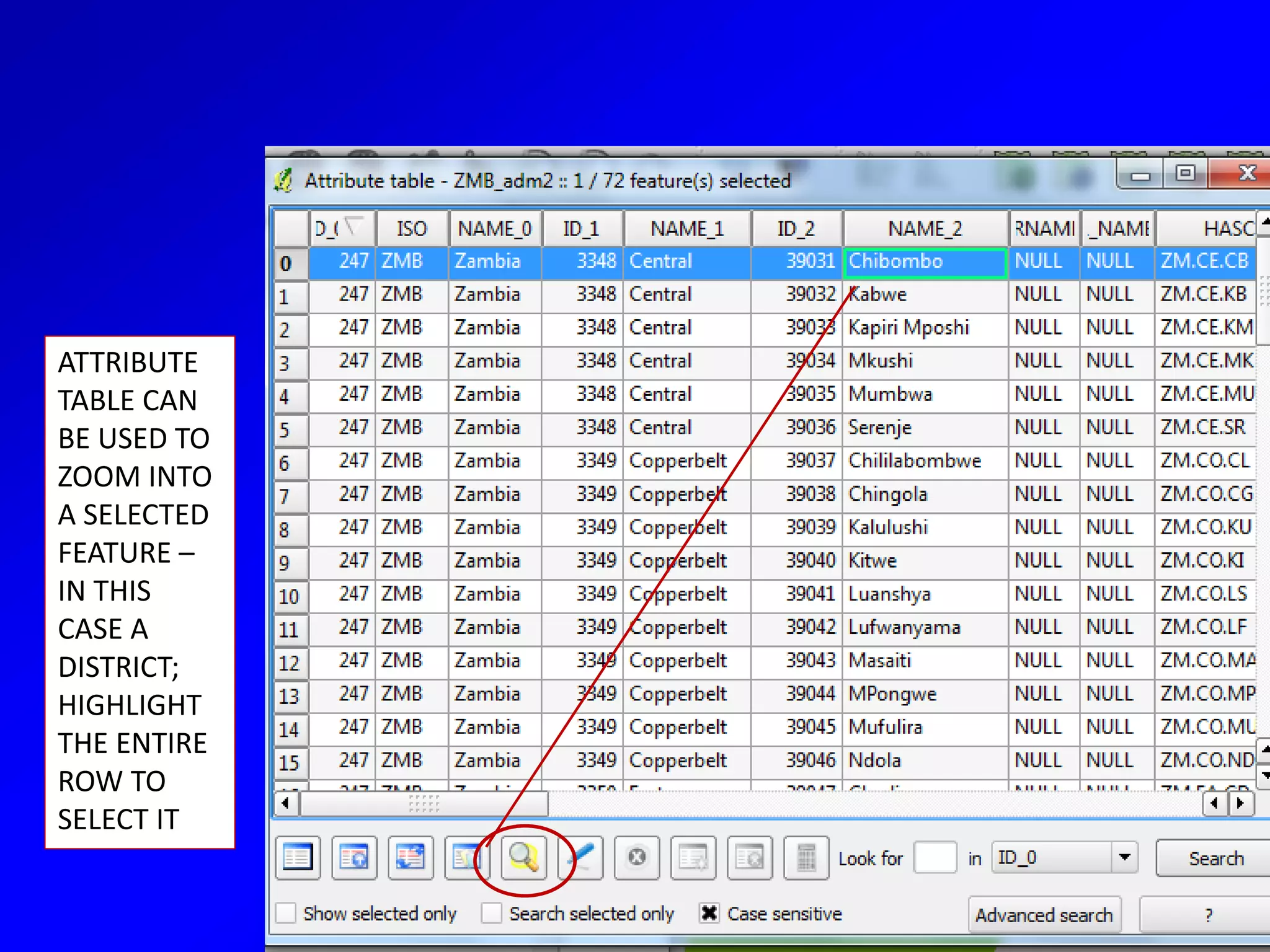
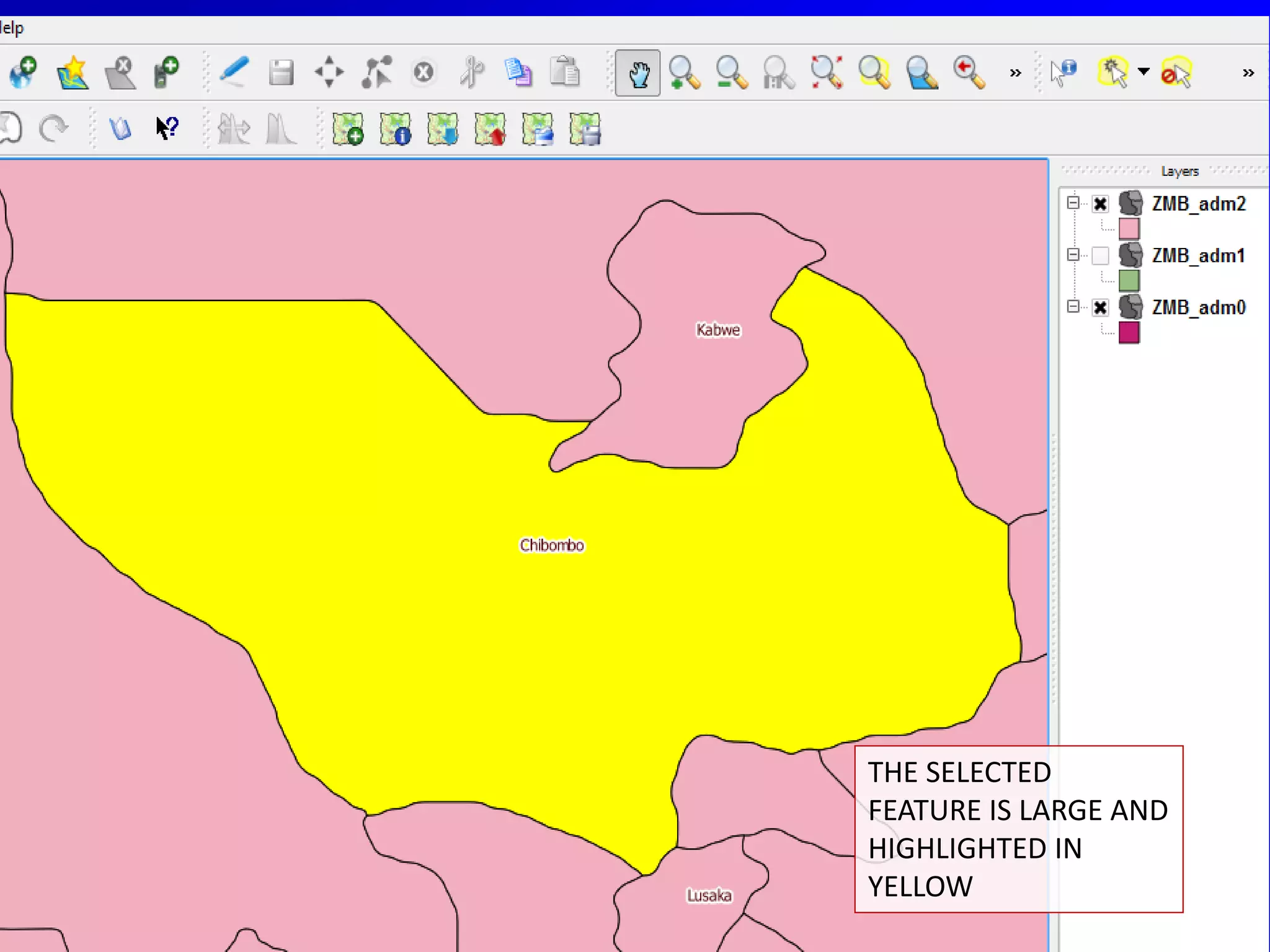
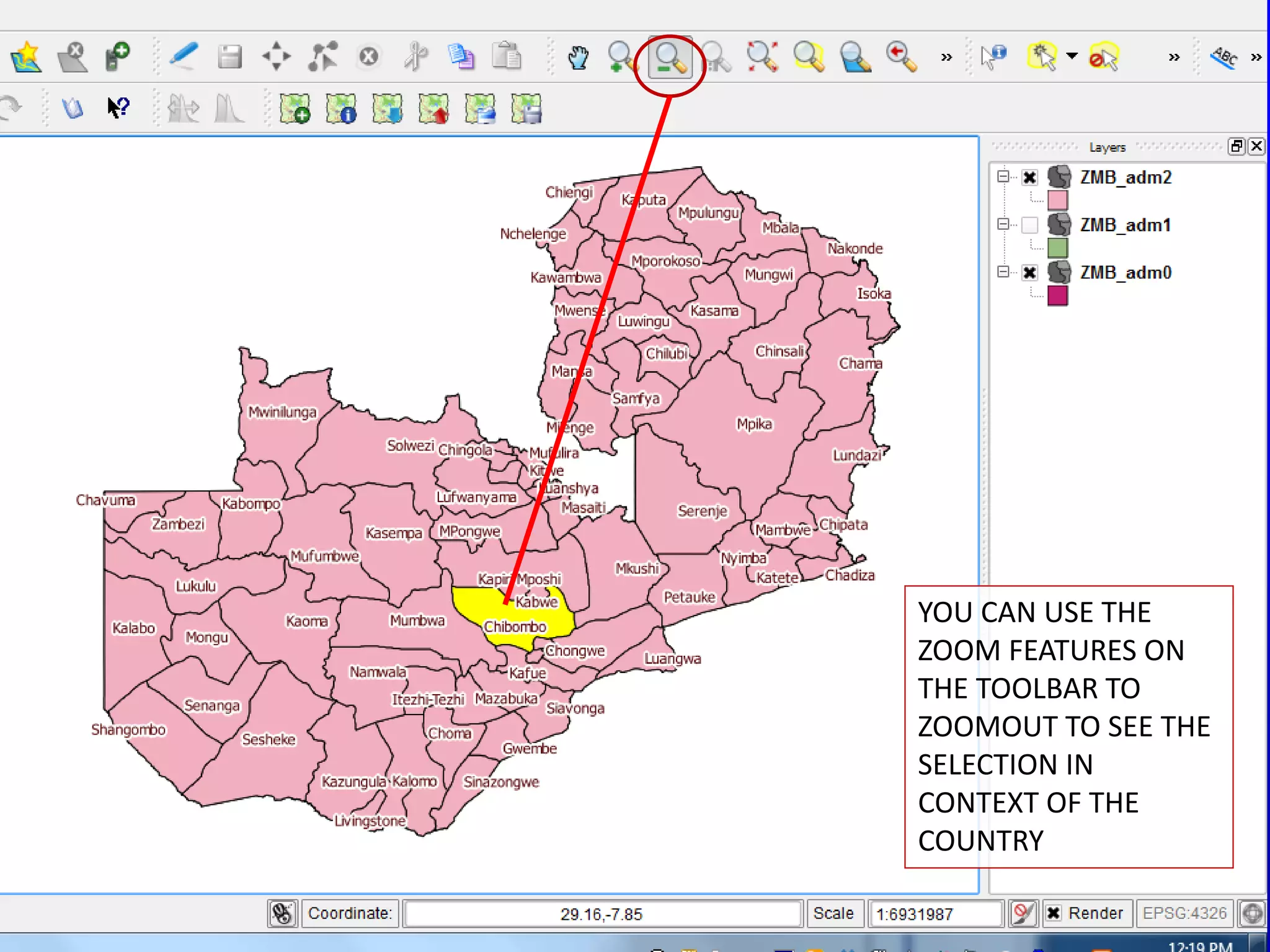
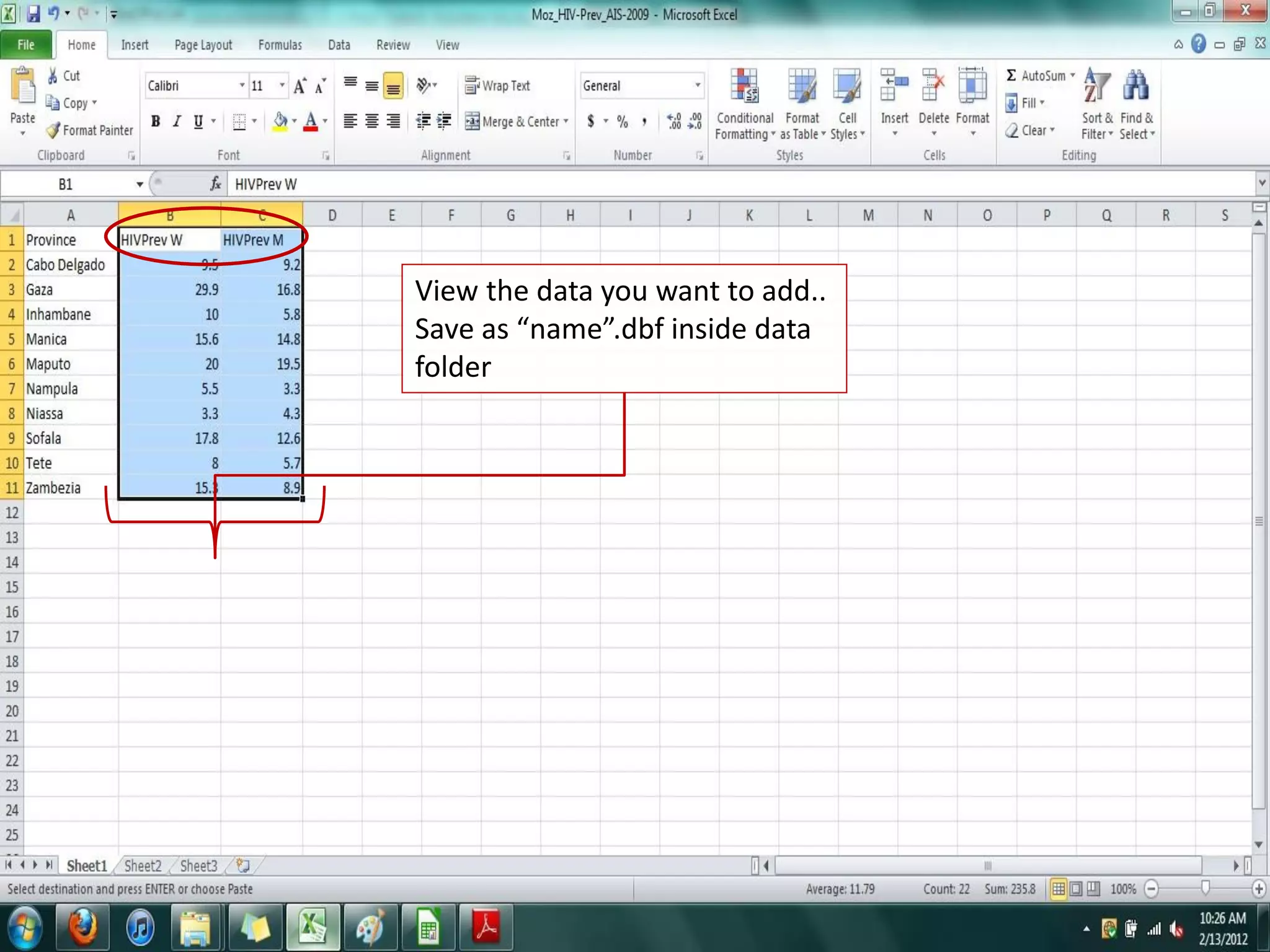
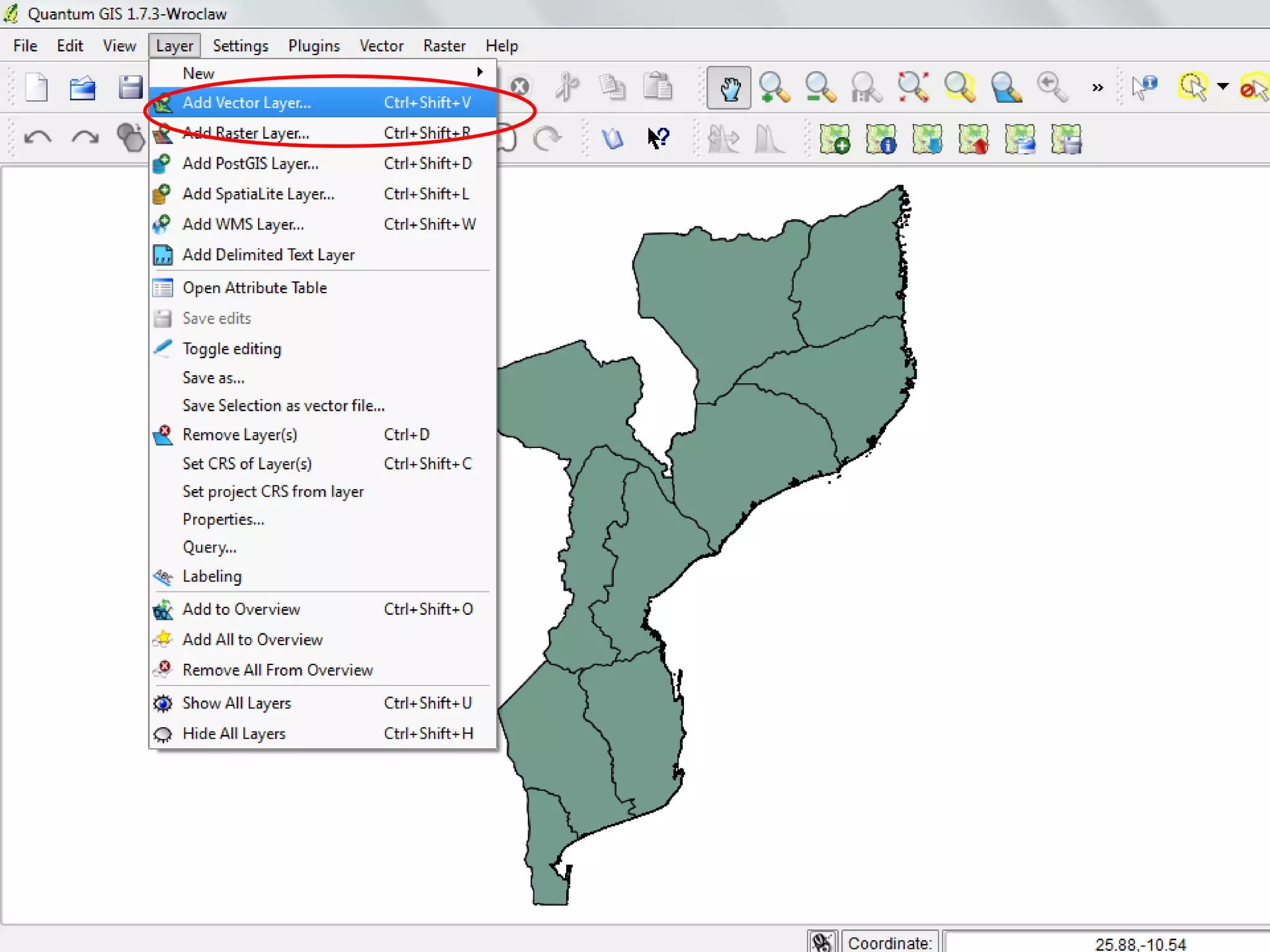
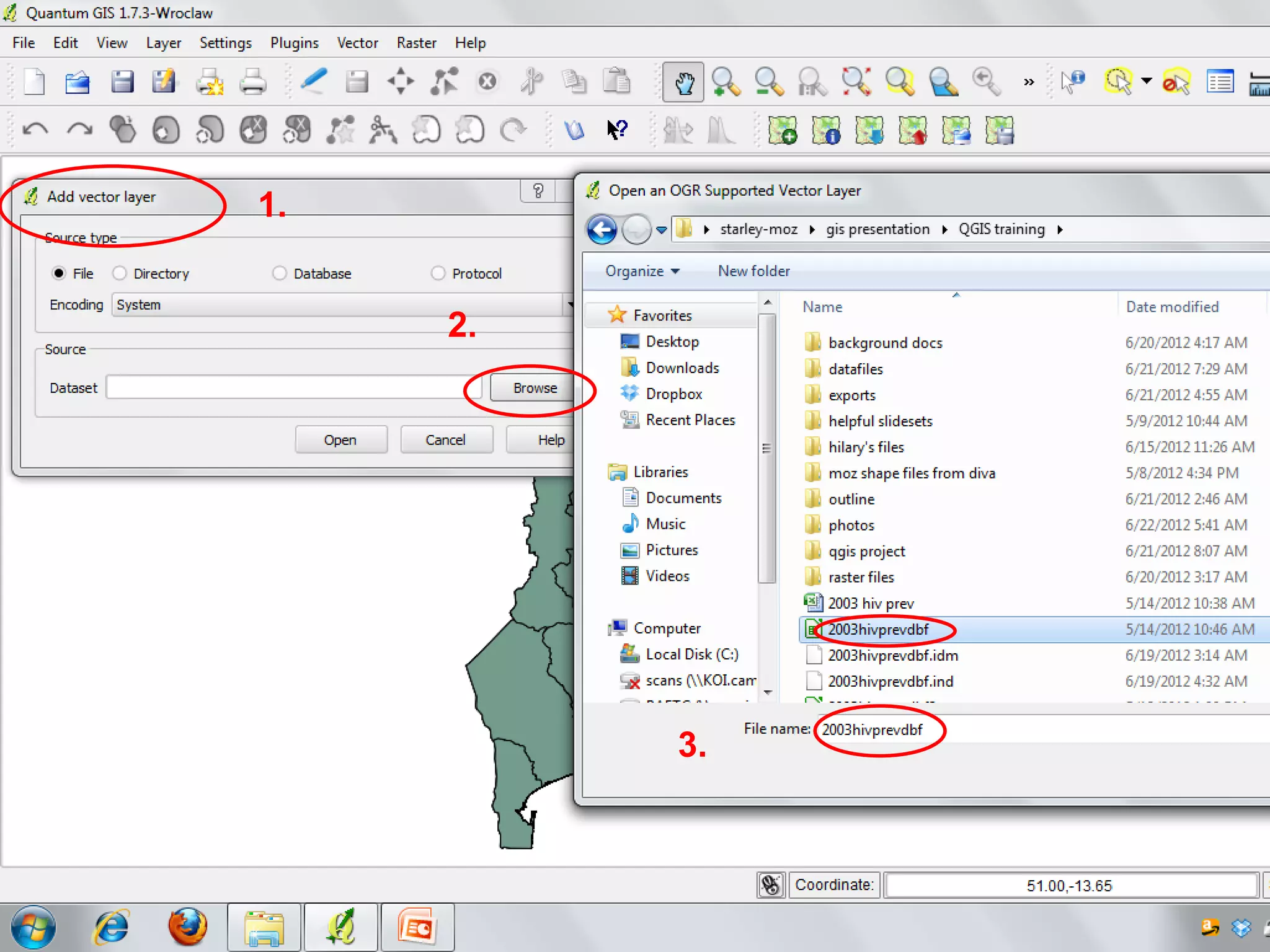
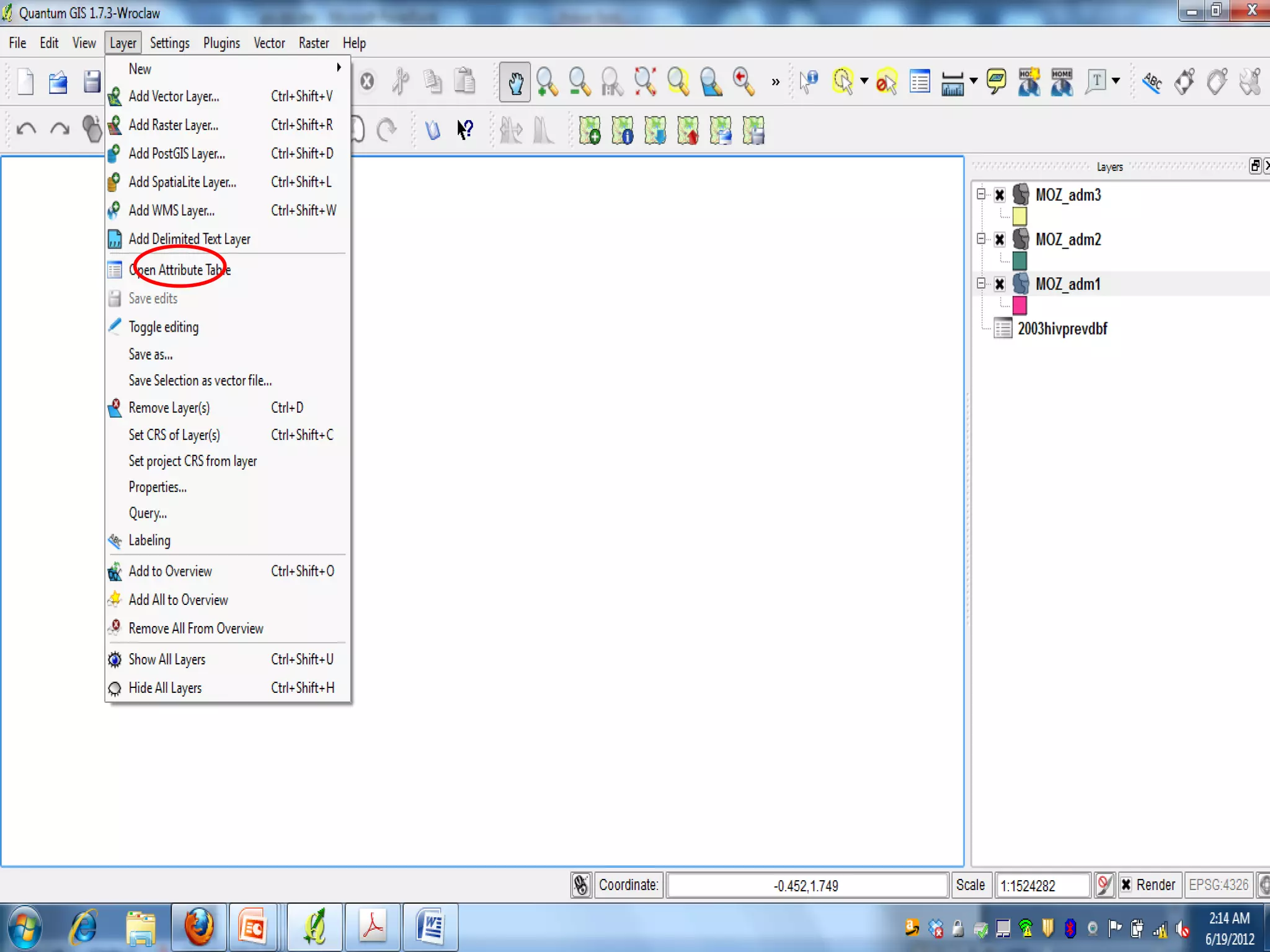
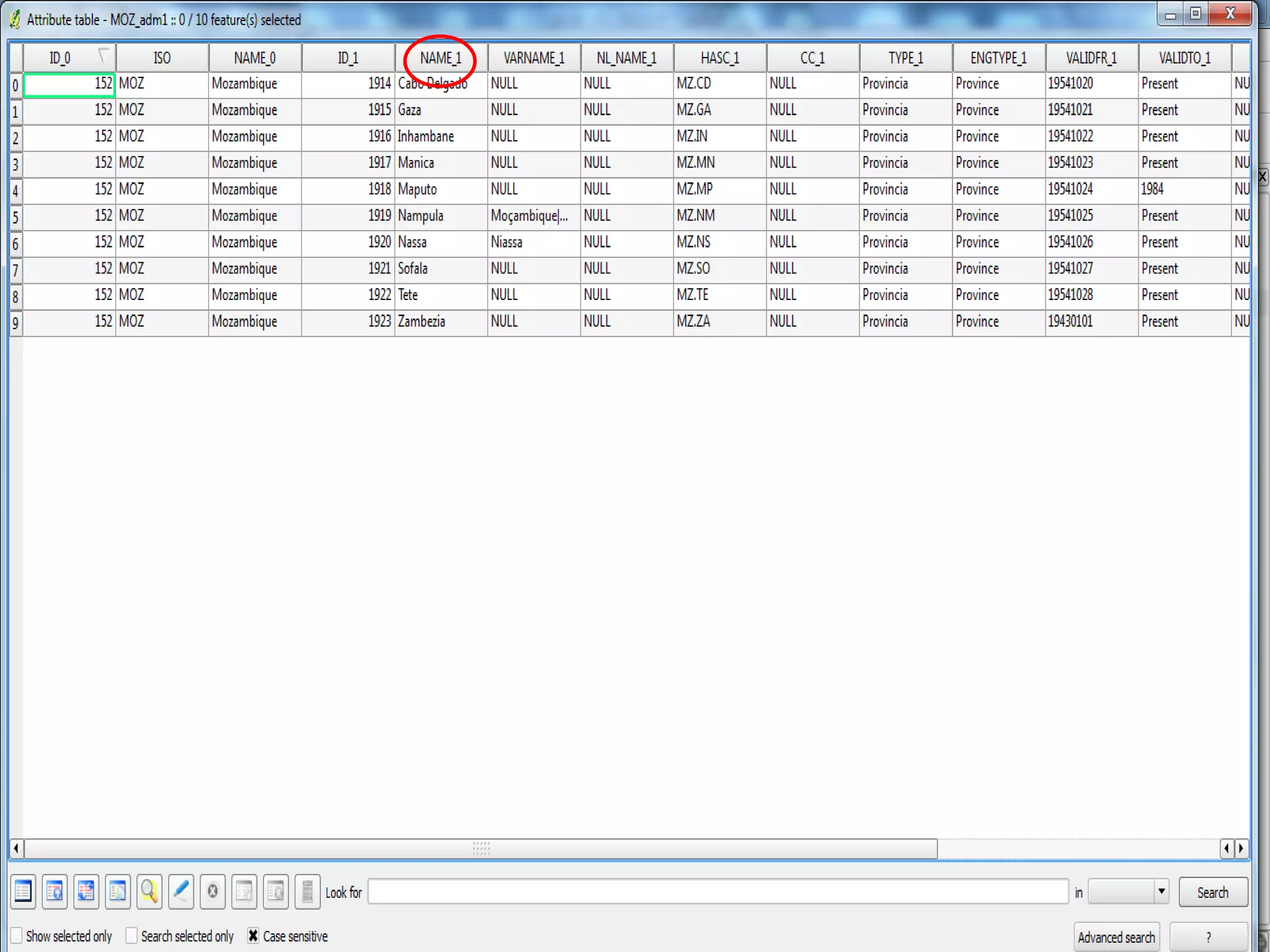
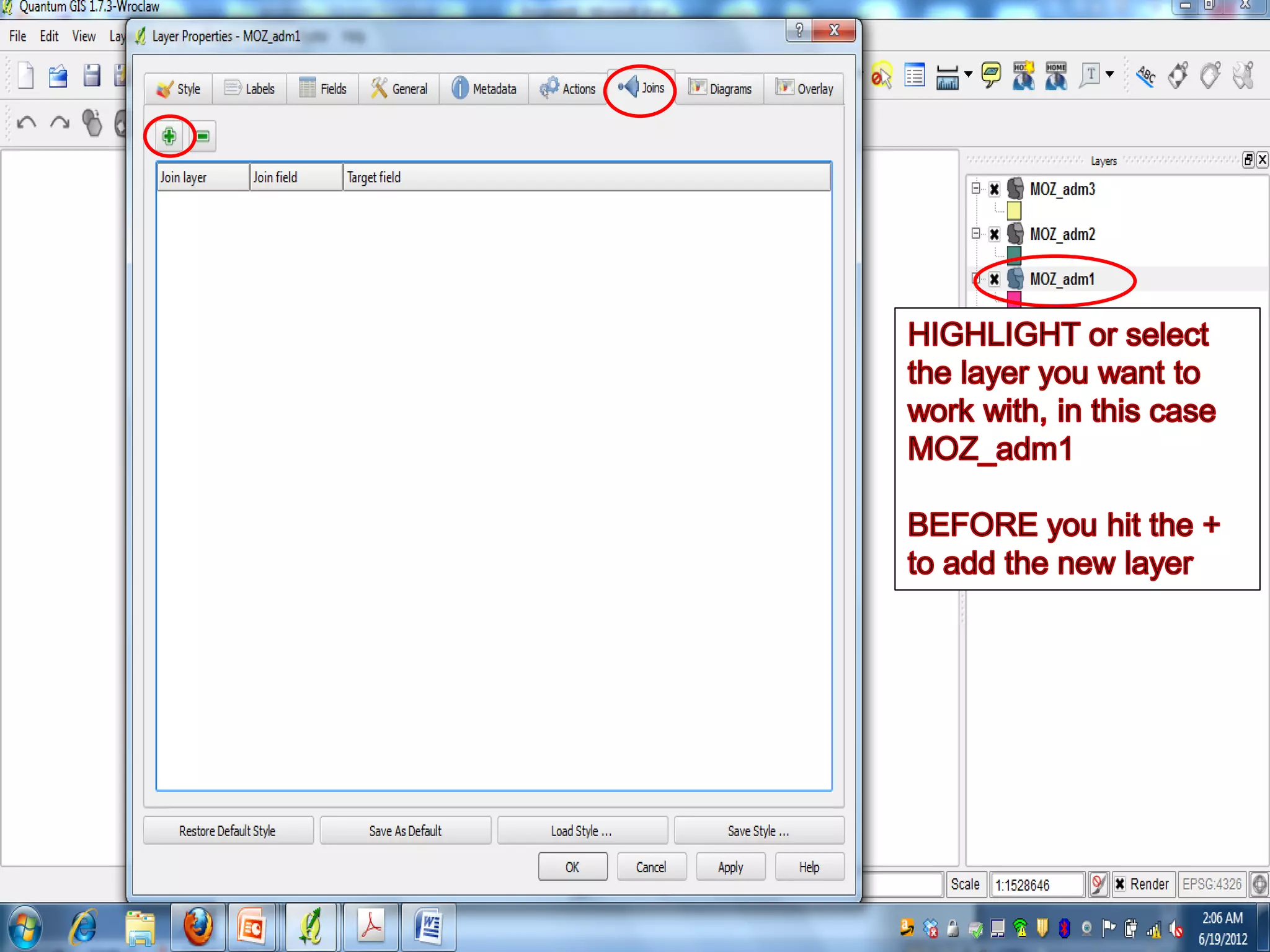
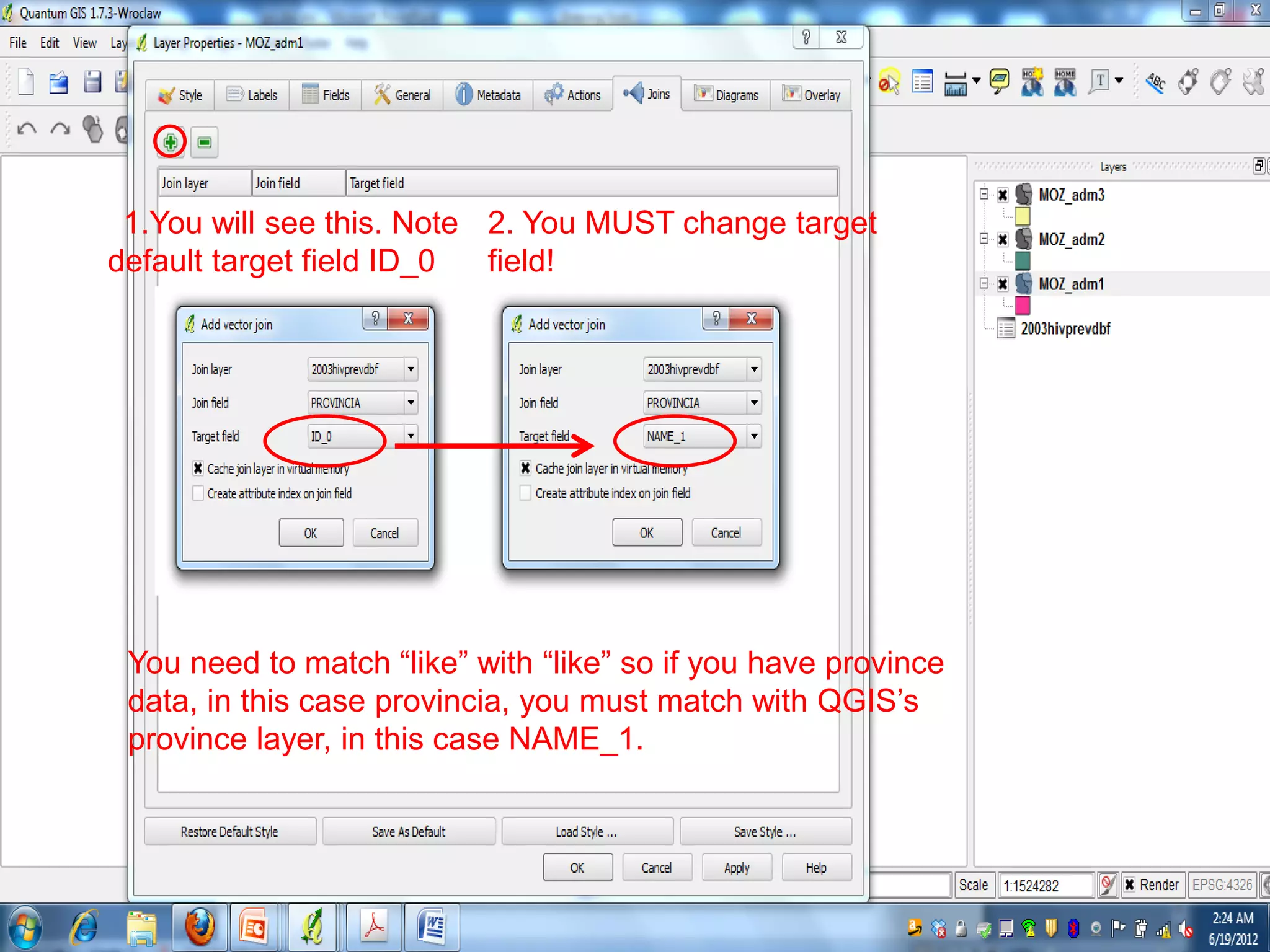
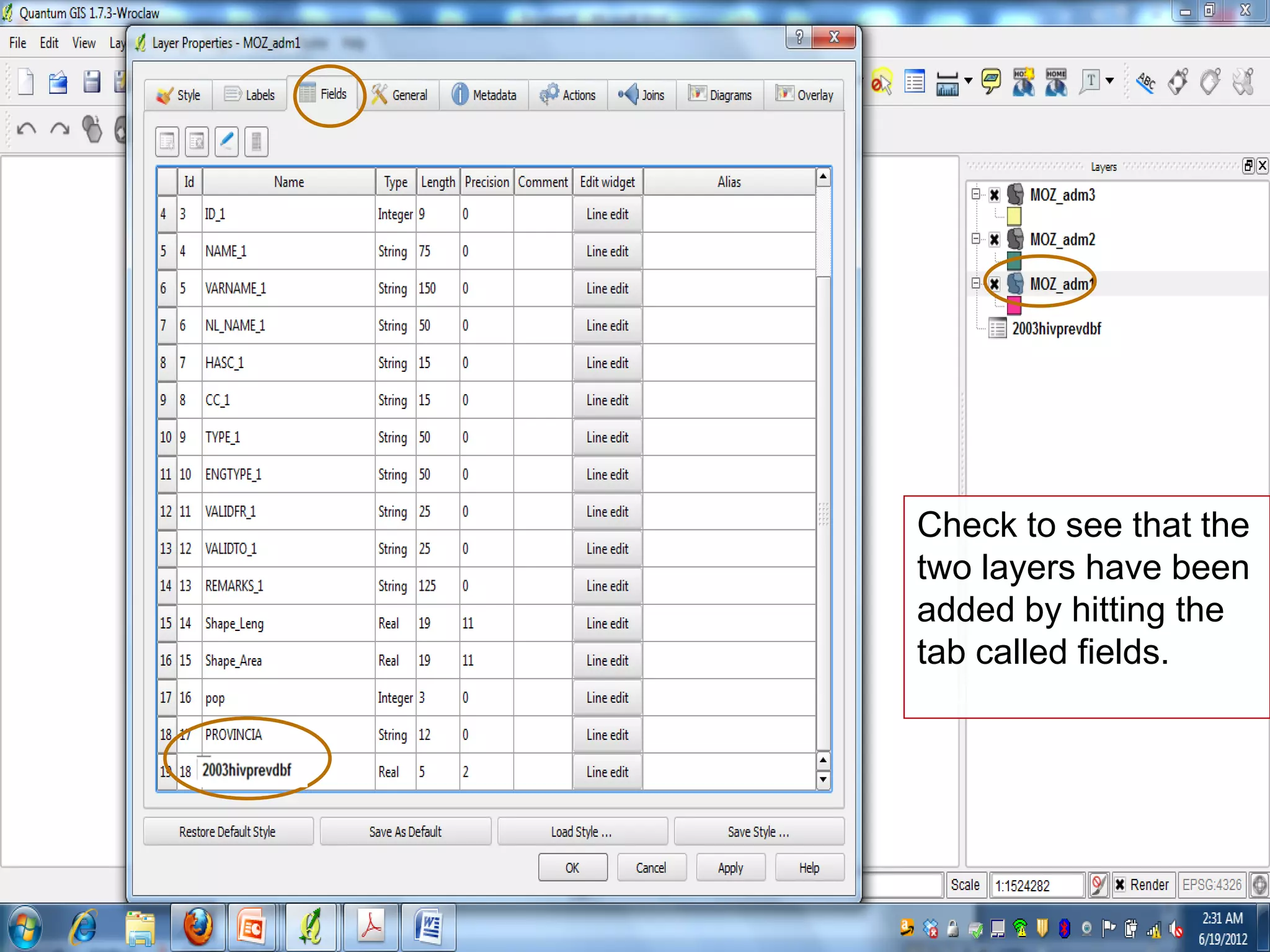
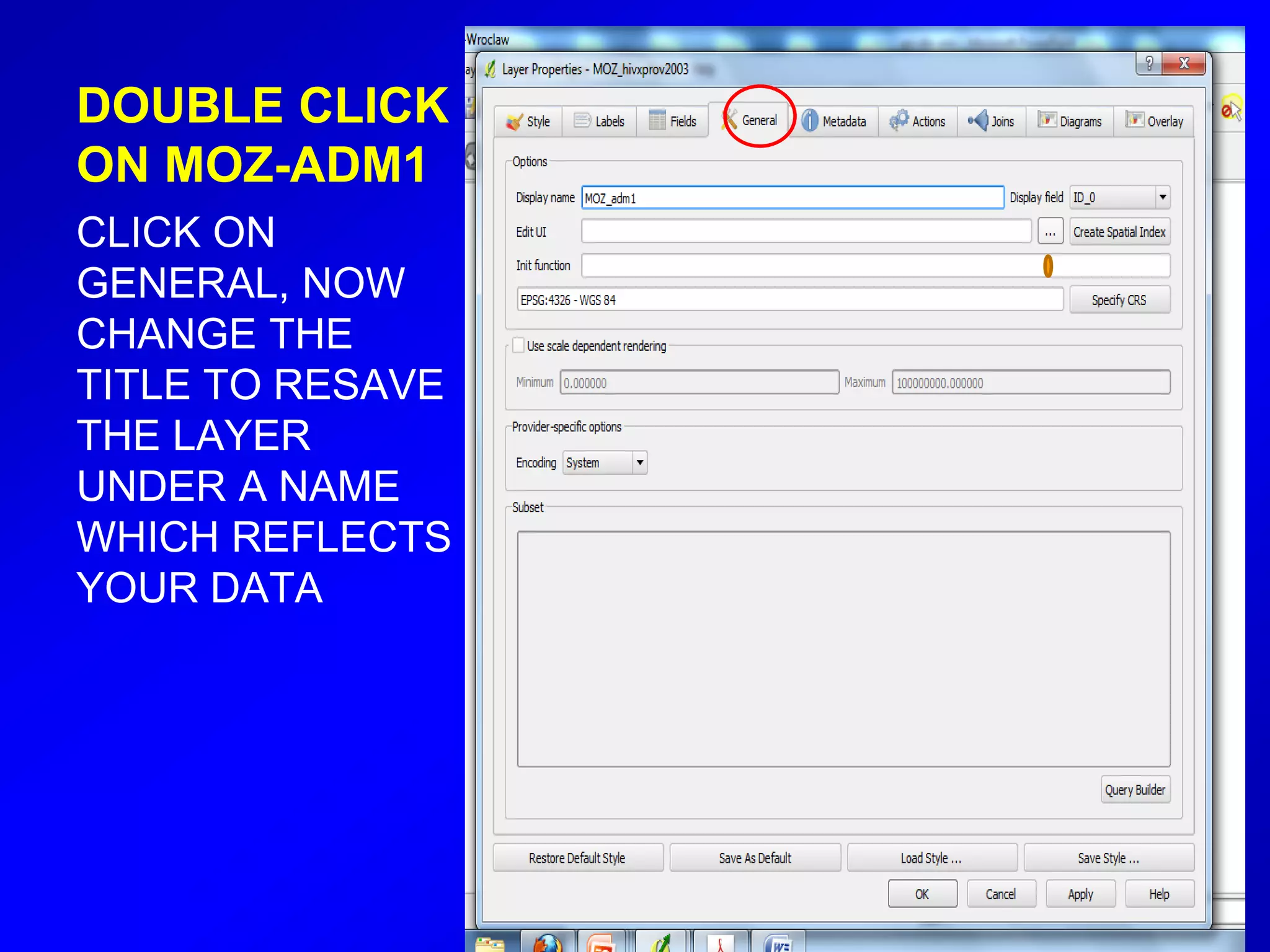
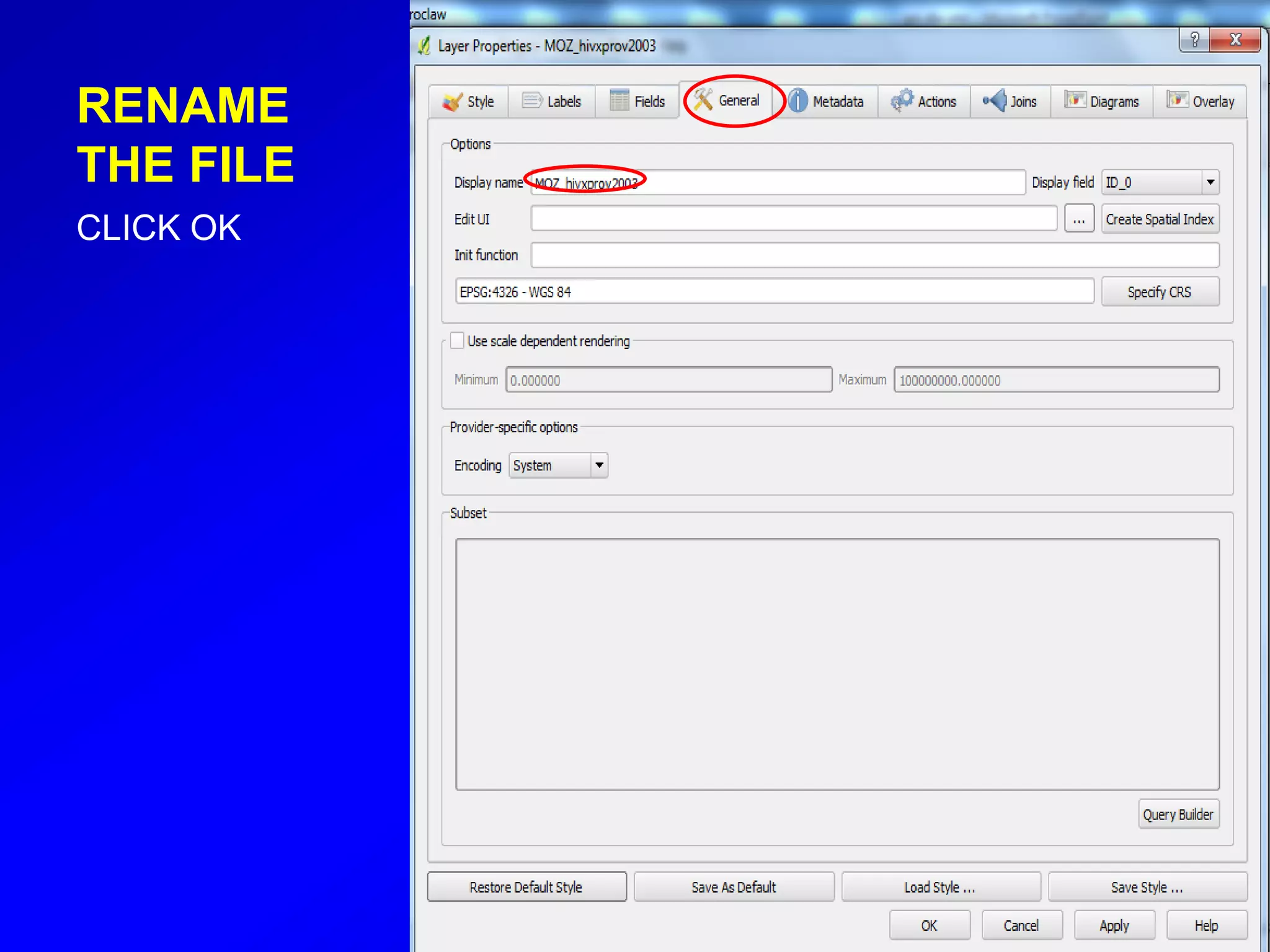
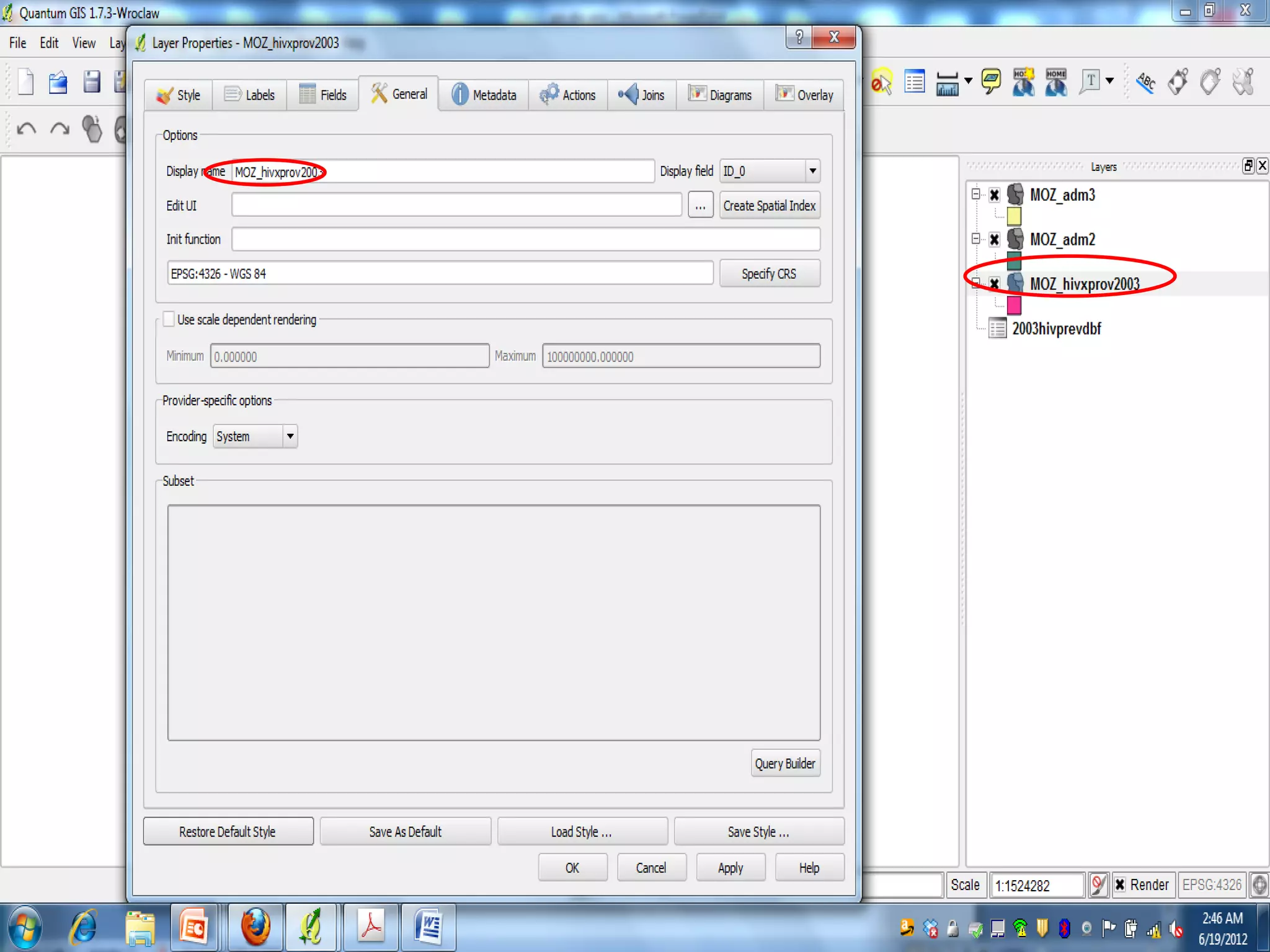
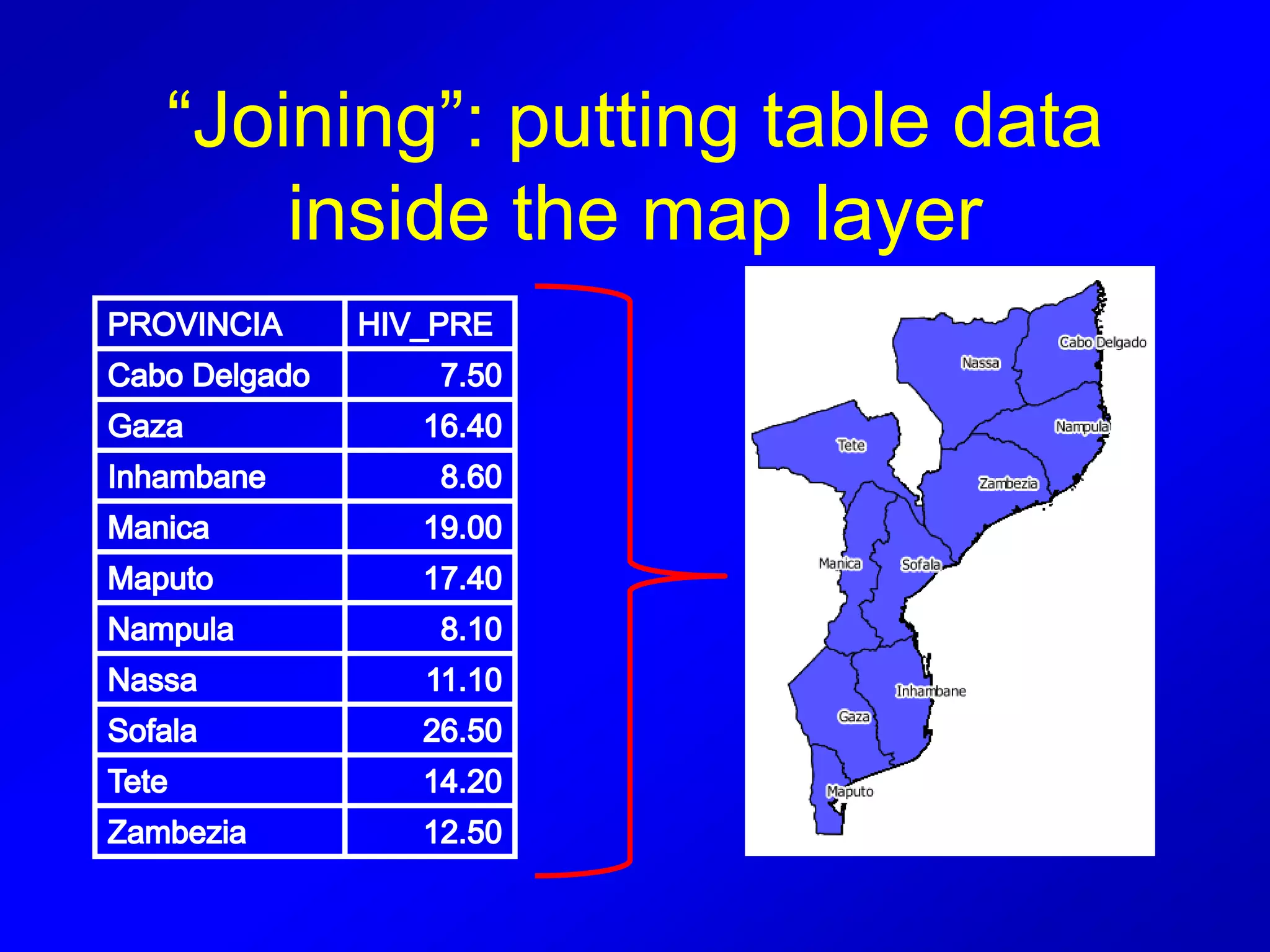
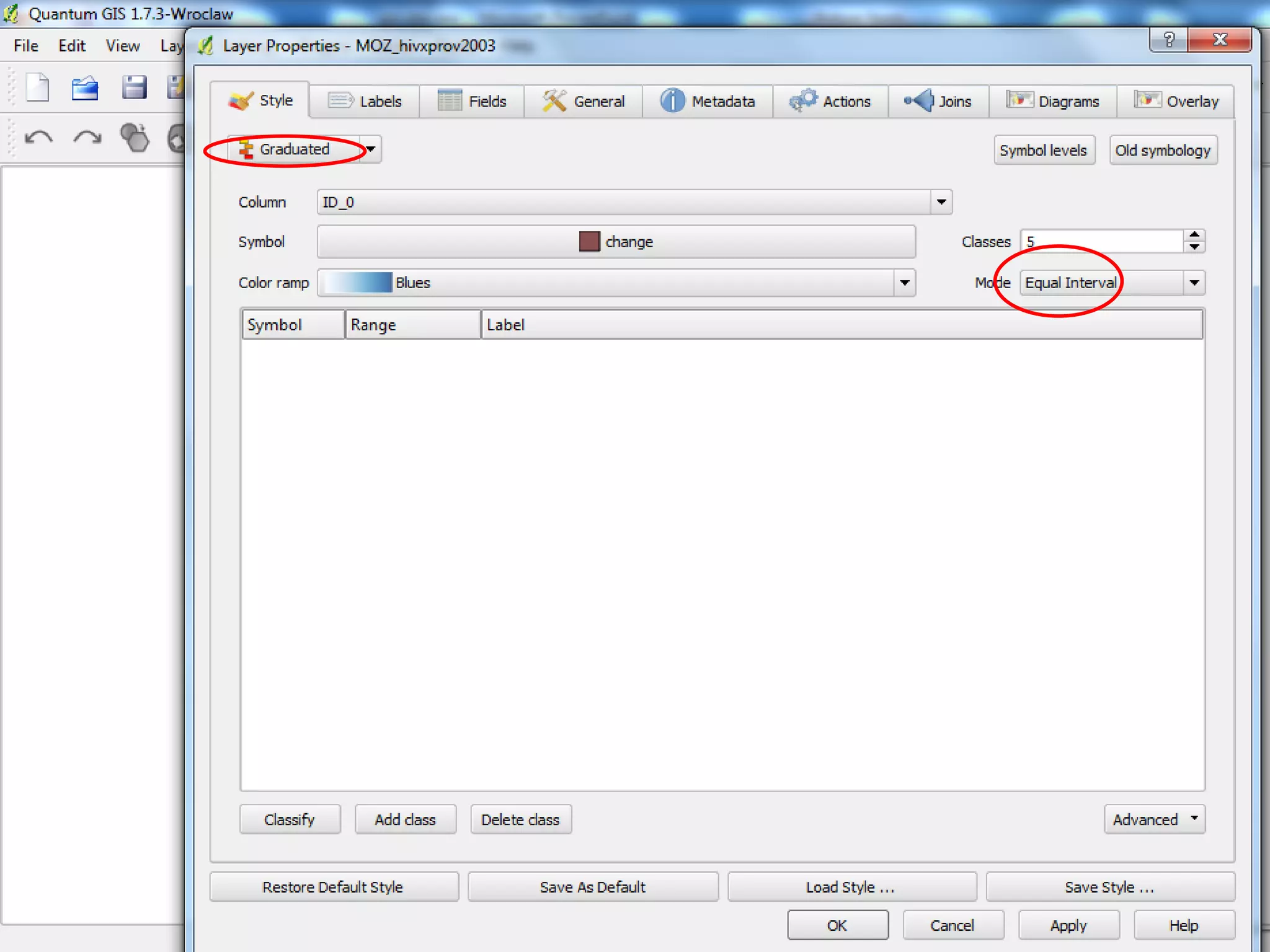
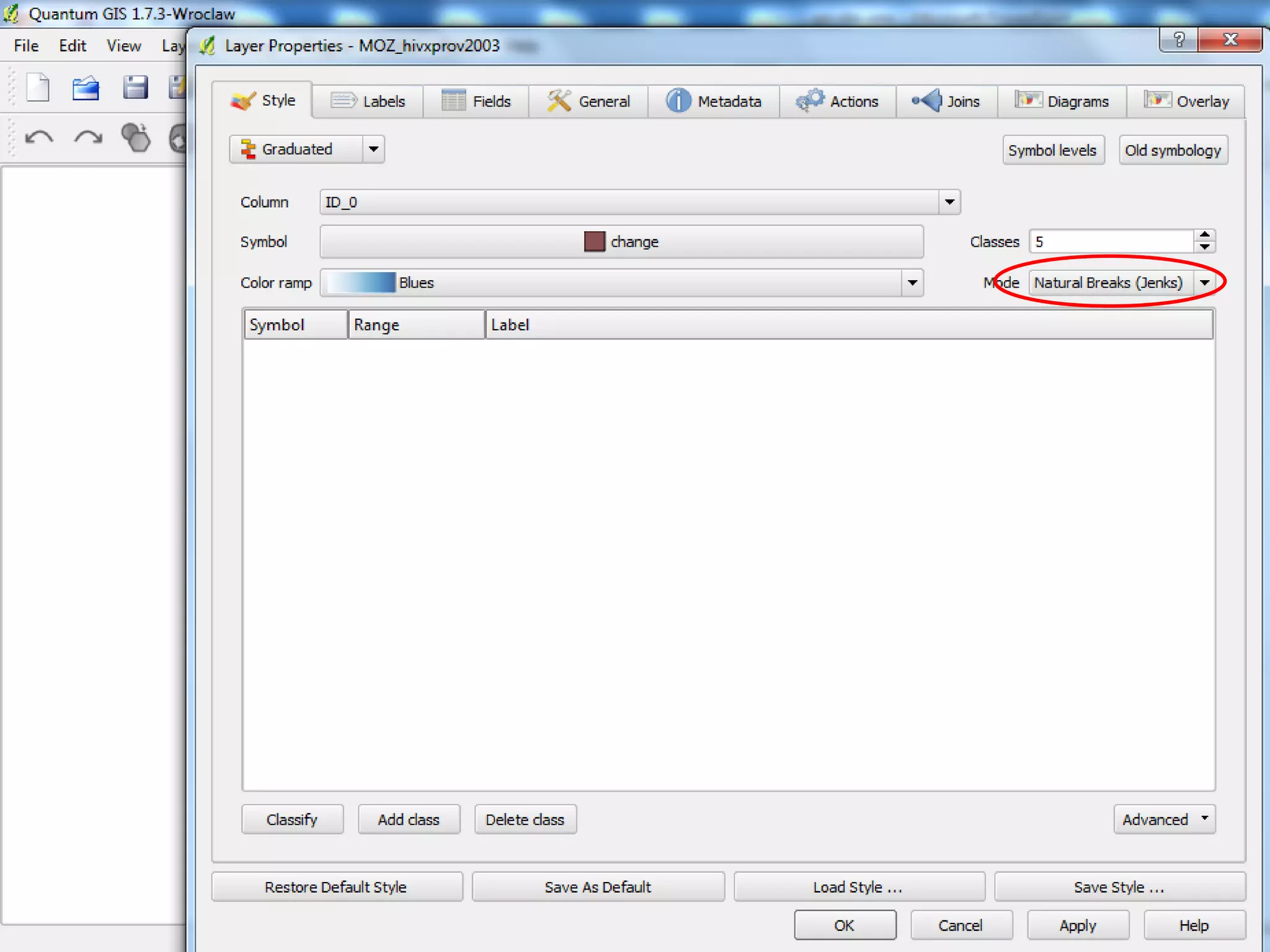
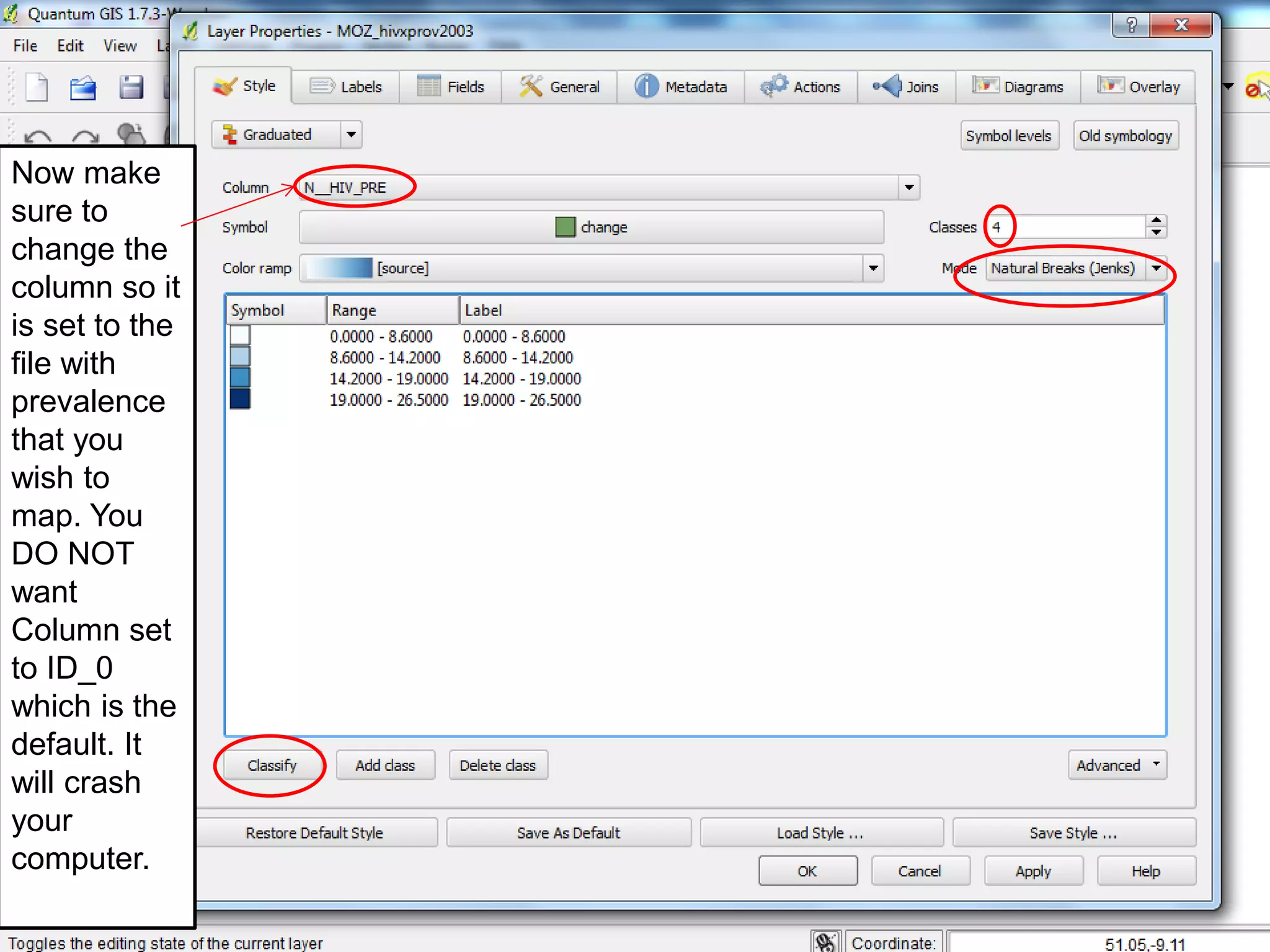
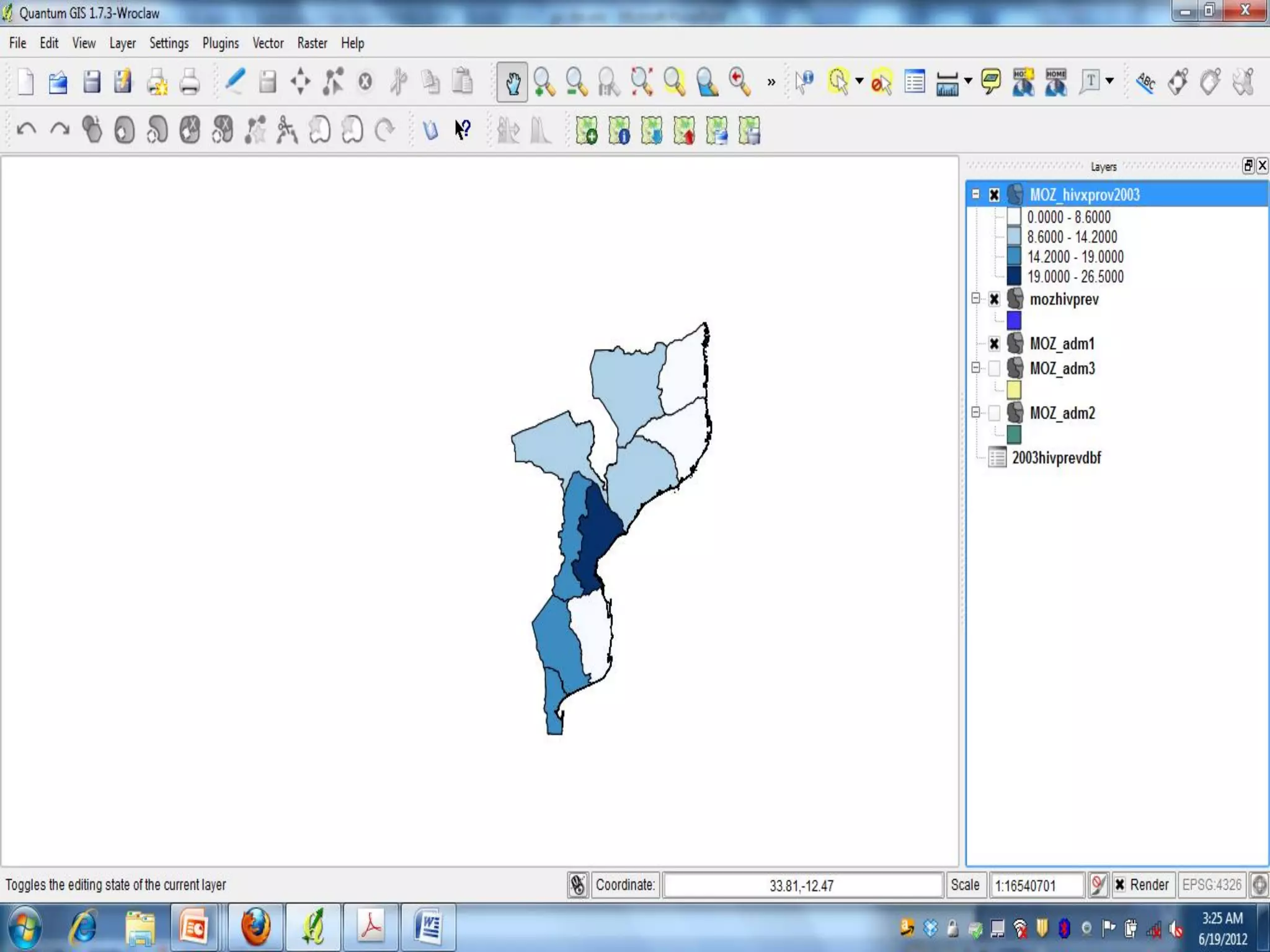
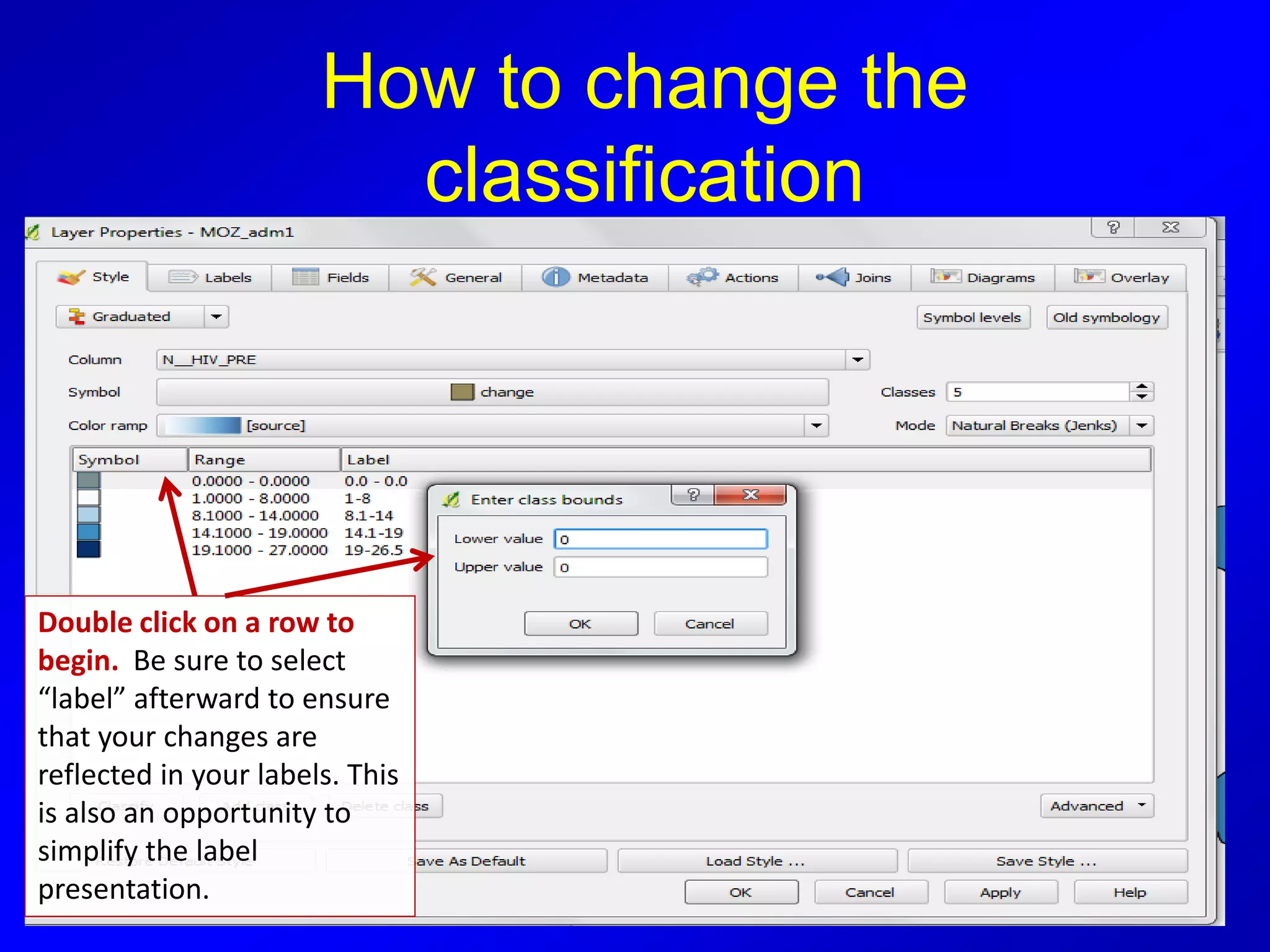
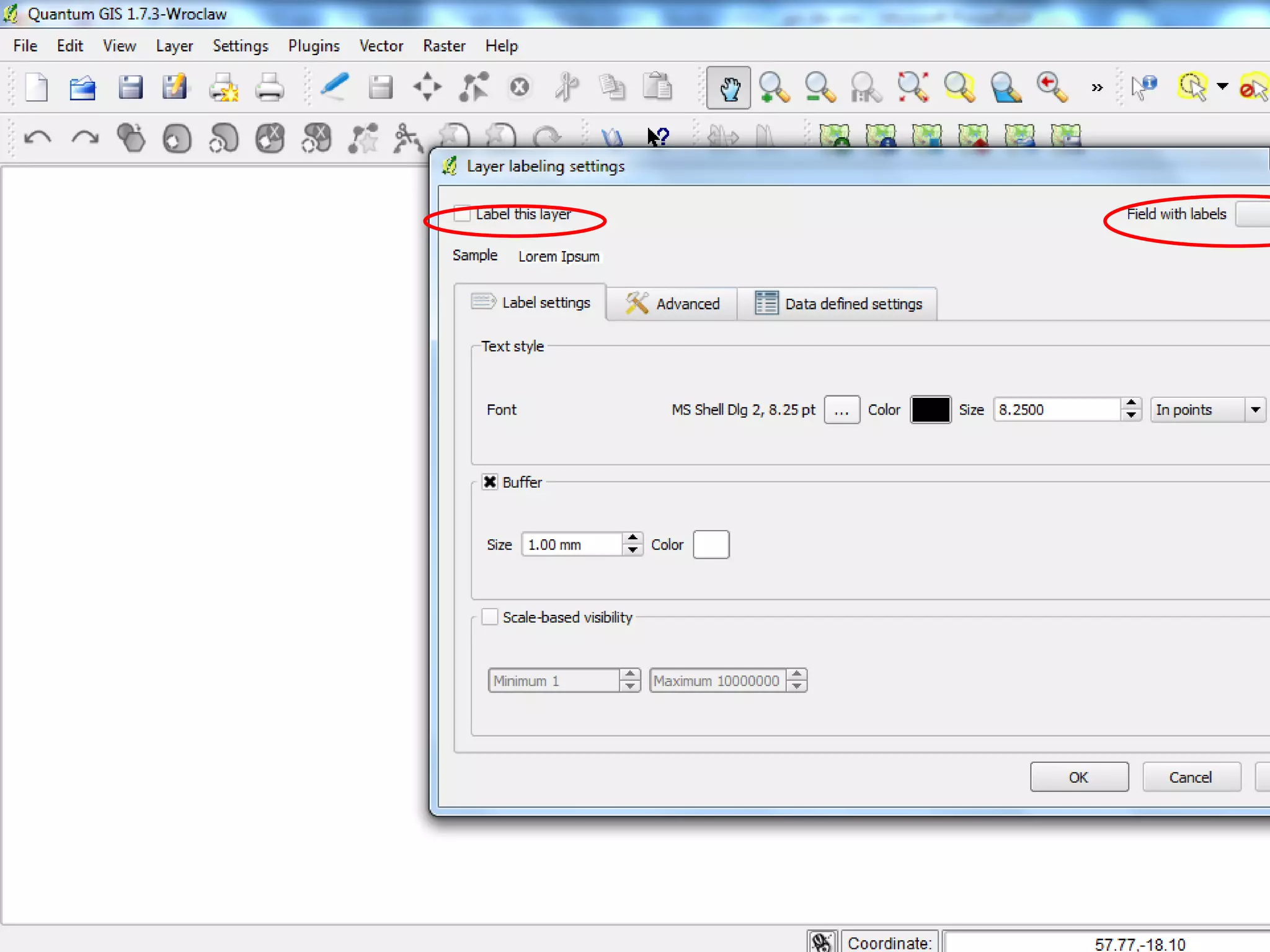
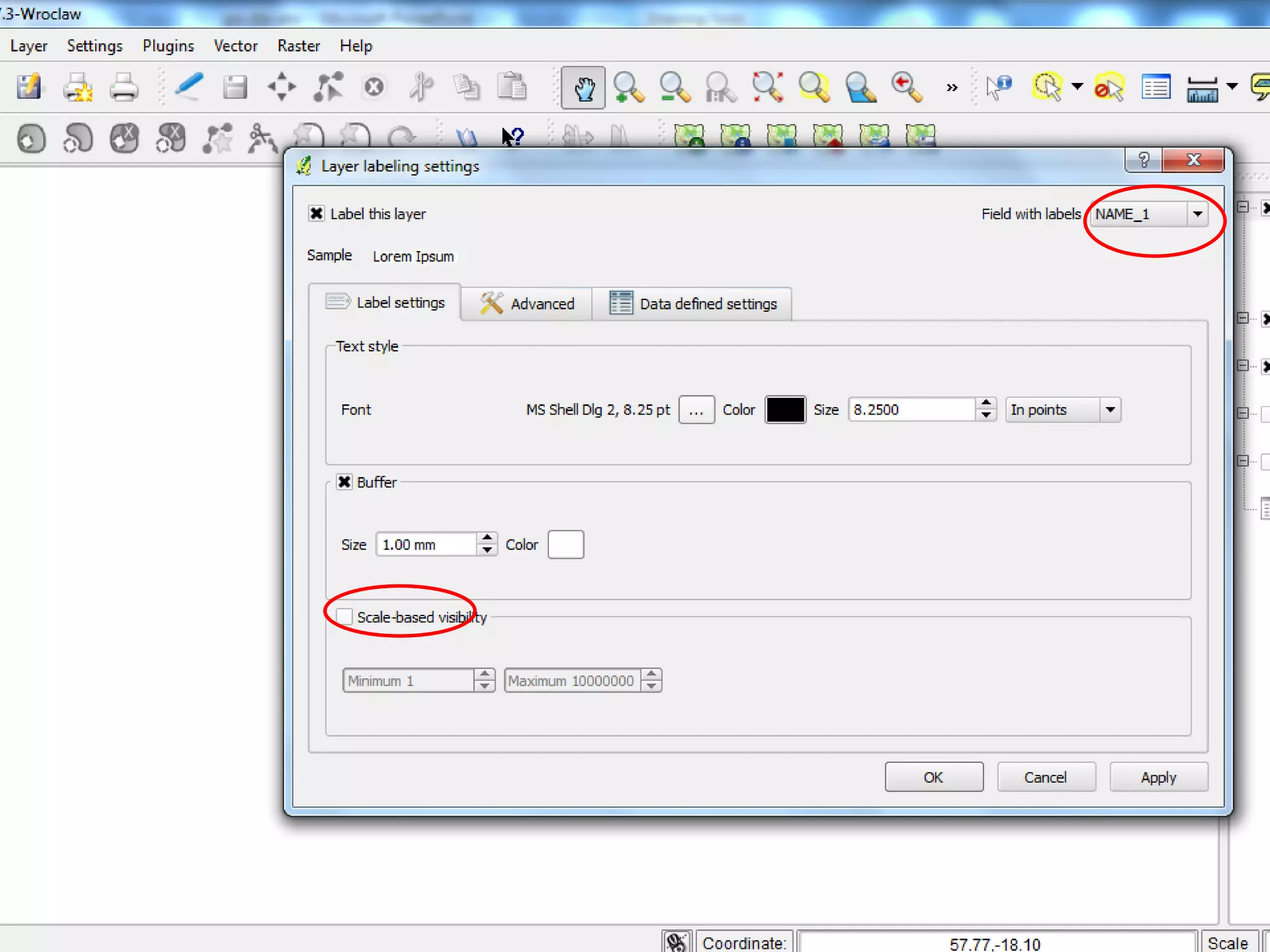
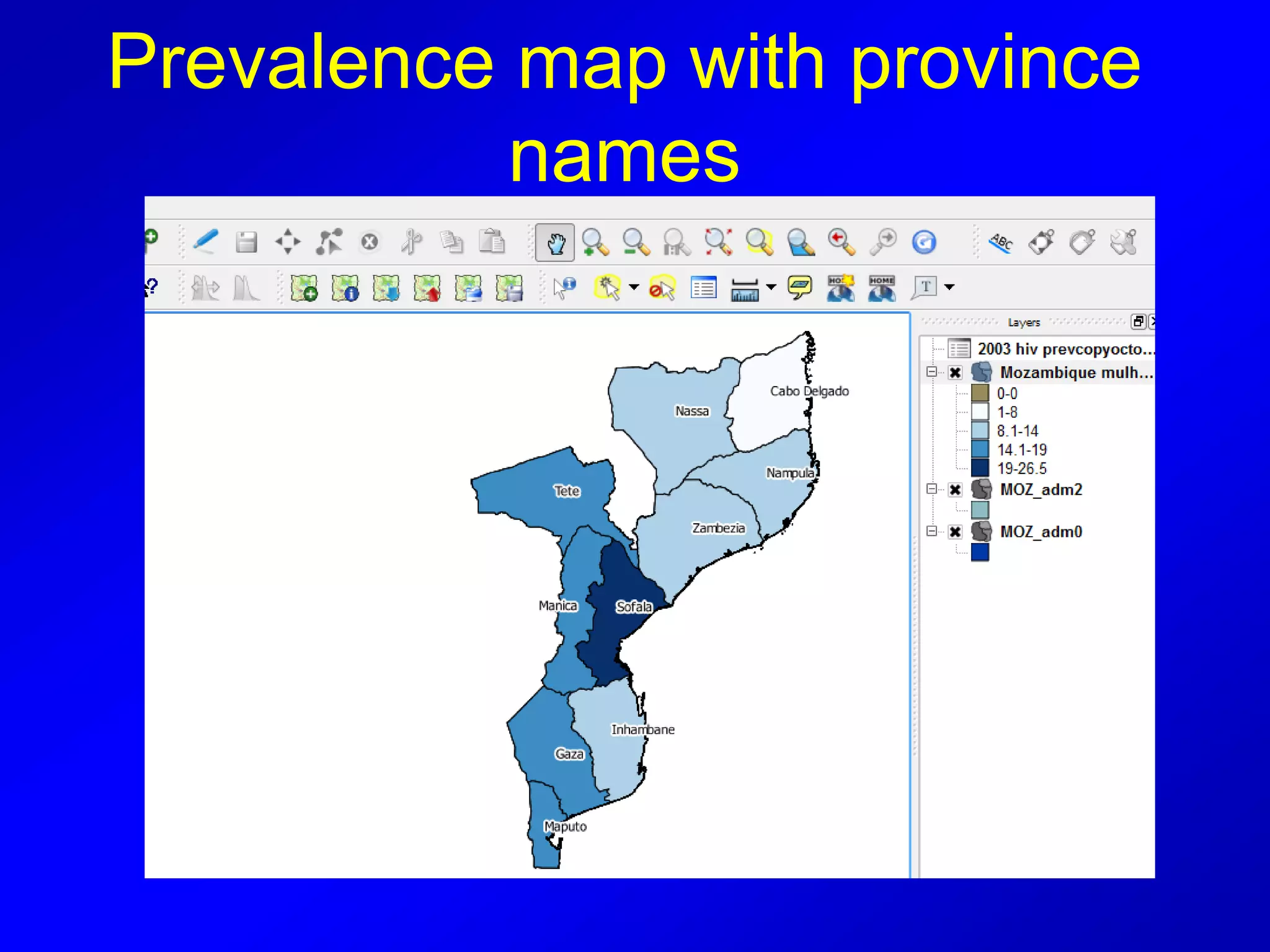
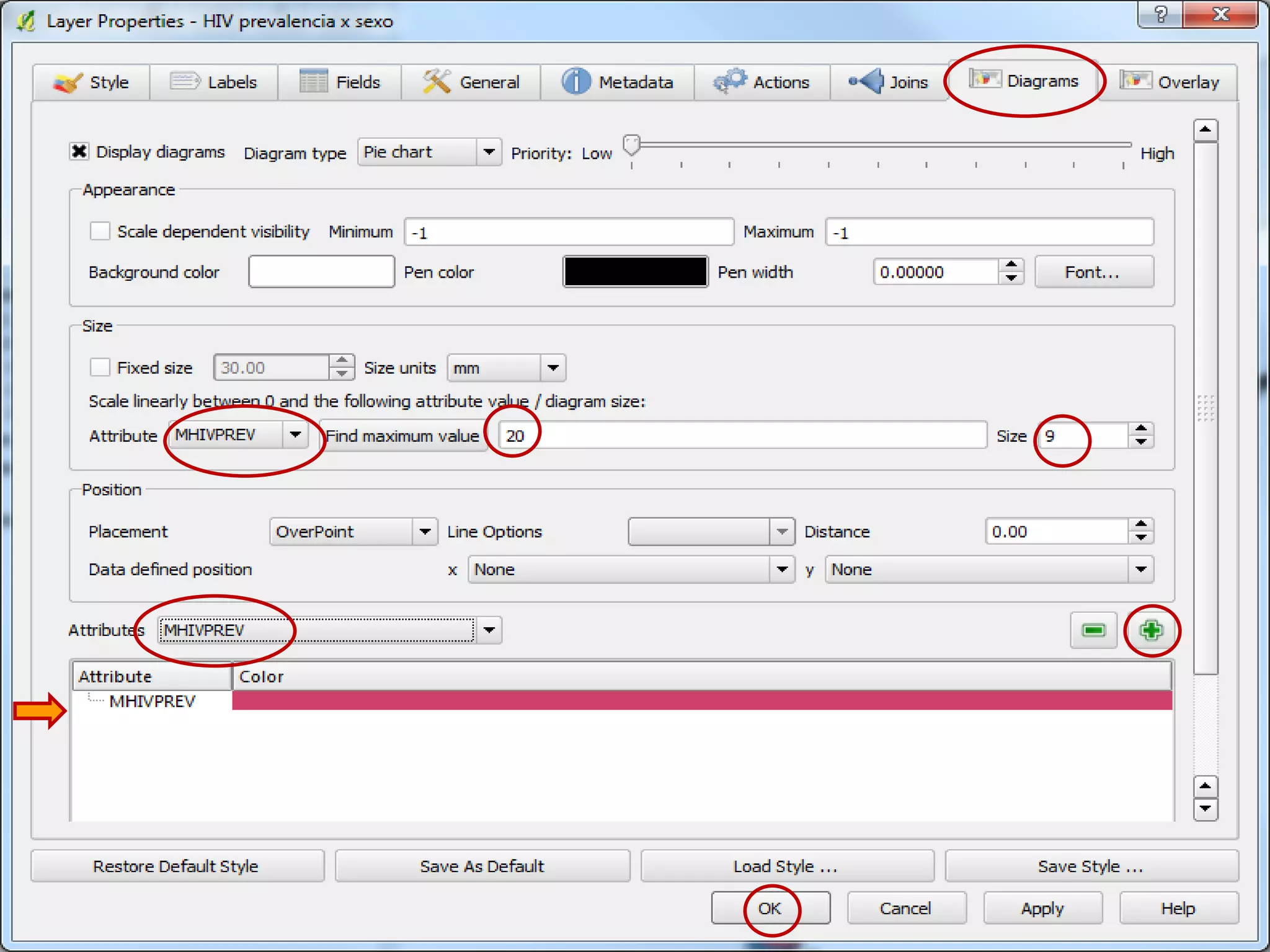
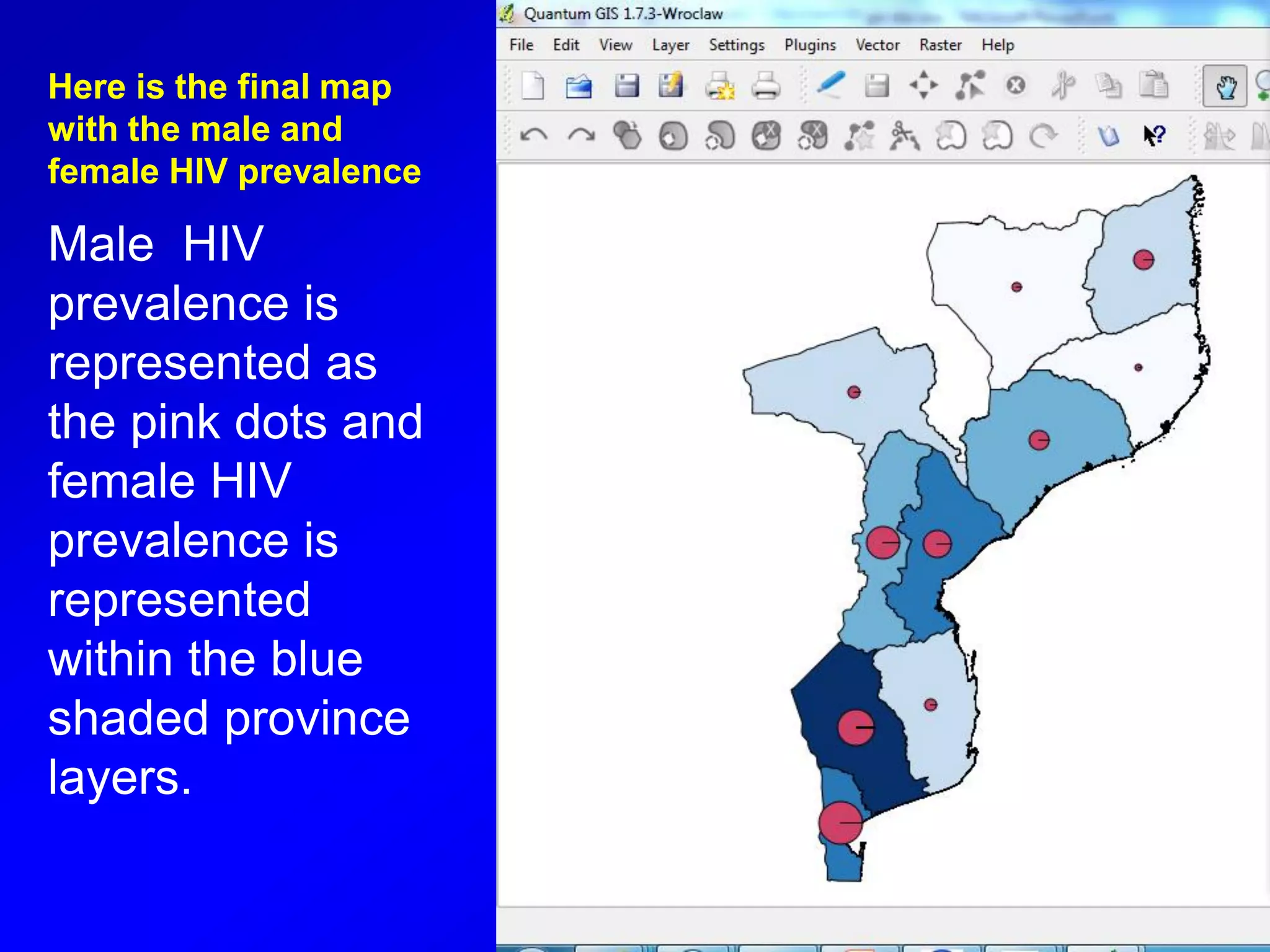
This document provides instructions for using attribute tables and joining data in QGIS. It discusses how attribute tables define the elements of a shapefile and allow users to view, select, and highlight geographic features. It then explains how to join external data stored in files like Excel and CSVs to shapefile layers in QGIS by converting the external files to DBF format and linking fields between the files and layers. The document demonstrates this process to map HIV prevalence data from a DBF file to administrative boundary layers in Mozambique.