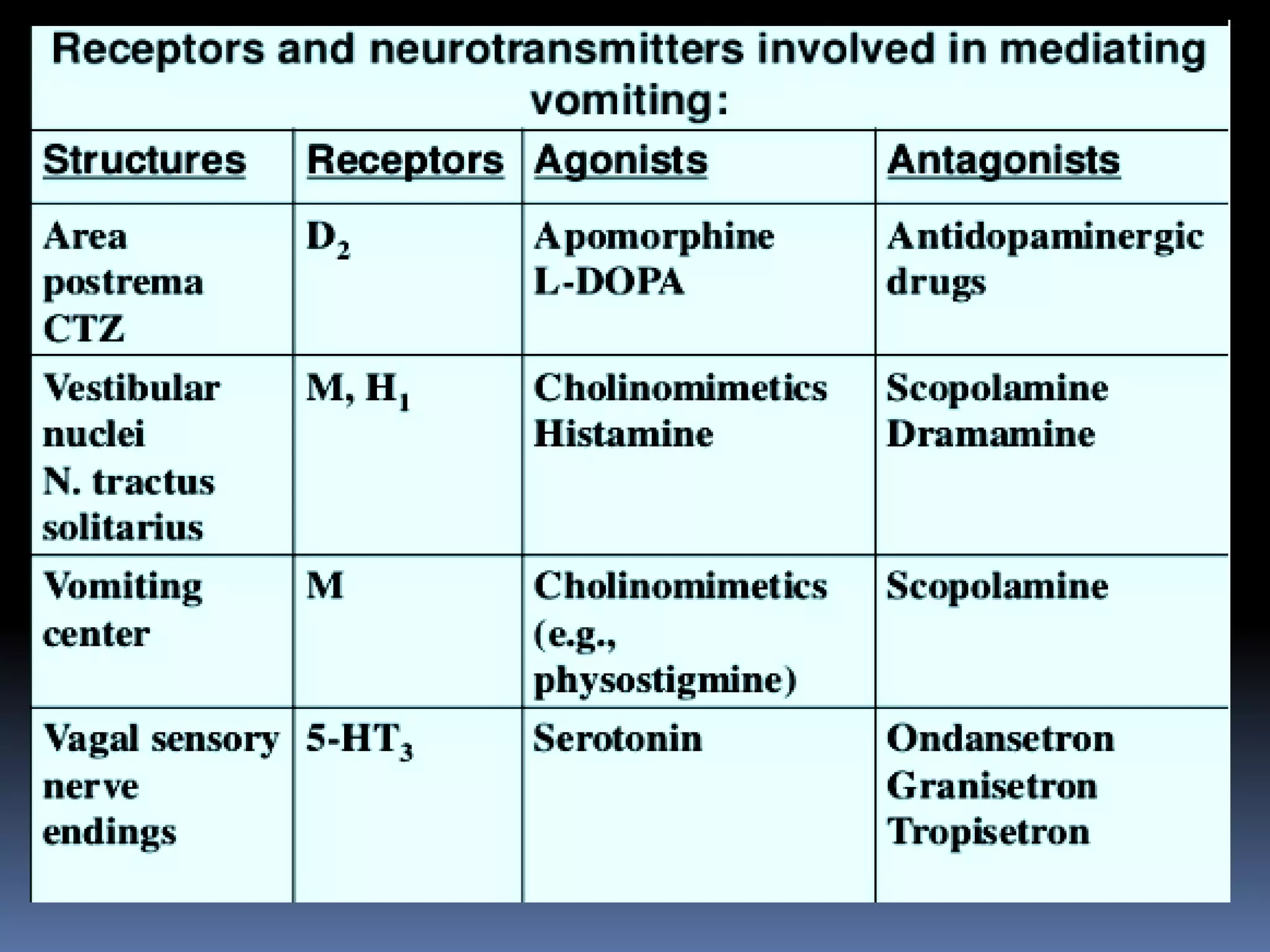
The document provides an extensive overview of emesis (vomiting), including its definition, causes, mechanisms, and various classes of antiemetic drugs used for treatment. It categorizes these drugs into anticholinergics, neuroleptics, antihistamines, prokinetic agents, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists, and adjuvant antiemetics, detailing their mechanisms of action, indications, and side effects. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding the pharmacological management of vomiting related to different conditions.