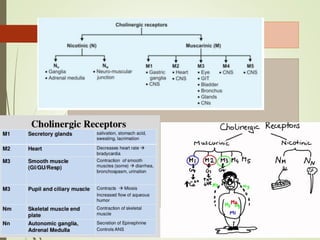
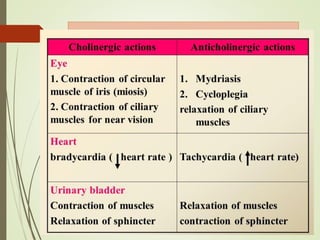
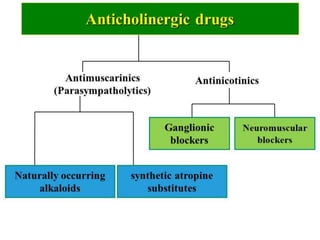
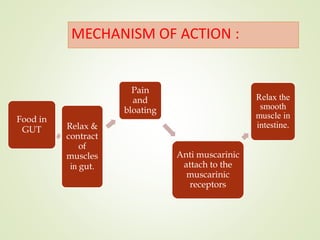
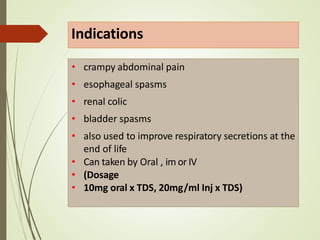
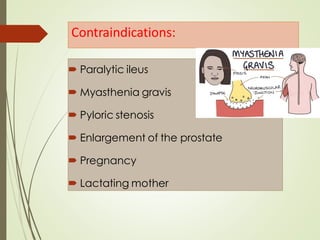
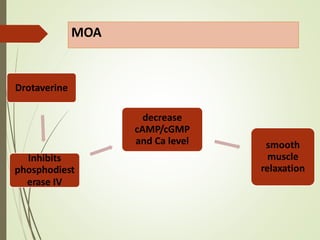
This document discusses anti-spasmodic drugs, which are smooth muscle relaxants used to prevent spasms in the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder. It describes two types - anticholinergics/antimuscarinics which block acetylcholine receptors, and non-anticholinergic smooth muscle relaxants. Specific drugs discussed include hyoscine butylbromide, dicyclomine, and drotaverine. These drugs are used to treat conditions involving smooth muscle spasms like irritable bowel syndrome, abdominal pain, and urinary incontinence. Their mechanisms of action and side effect profiles are also outlined.