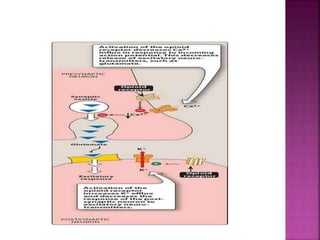
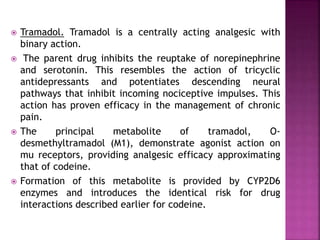
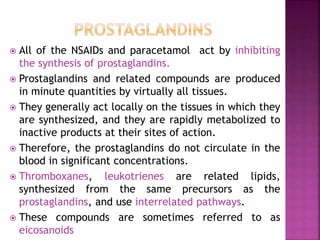
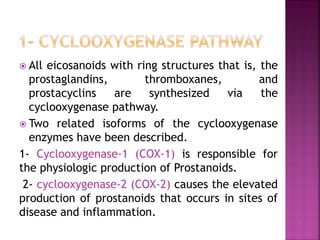
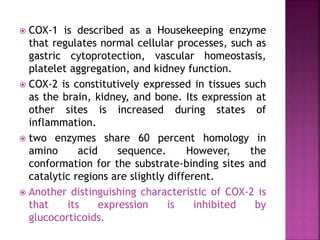
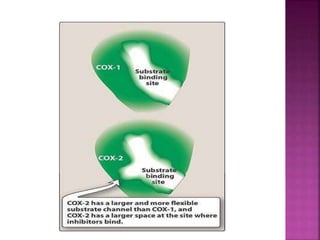
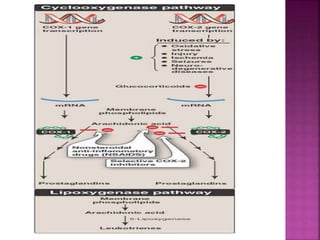
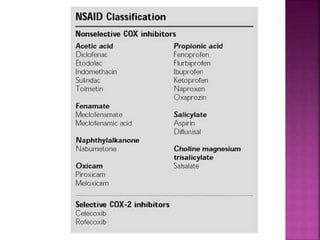
This document discusses the mechanisms of action and pharmacological properties of nonopioid analgesics, including acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It explains that these drugs inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes involved in prostaglandin synthesis, thereby reducing pain and inflammation. The document outlines the pathways involved in prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid. It also describes the therapeutic effects and potential gastrointestinal, renal, platelet, and allergy-related side effects that can result from COX inhibition.



































![ Ibuprofen [eye-byoo-PROE-fen] was the first in
this class of agents to become available.
It has been joined by naproxen [nah-PROX-en],
fenoprofen [fen-oh-PROE-fen], ketoprofen [key-
toe-PROE-fen], flurbiprofen [flur-bye-PROE-
fen], and oxaprozin [ox-ah-PROE-zin].
All these drugs possess anti-inflammatory,
analgesic, and antipyretic activity; additionally,
they can can alter platelet function and prolong
bleeding time.
their GI effects are generally less intense than
those of aspirin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-42-320.jpg)

![ This group of drugs includes indomethacin [in-doe-METH-
a-sin], sulindac [sul-IN-dak], and etodolac [eh-TOEdoh-
lak].
All have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic
activity.
They are generally not used to lower fever.
Despite its potency as an anti-inflammatory agent, the
toxicity of indomethacin limits its use to the treatment of
acute gouty arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and
osteoarthritis of the hip.
Sulindac is an inactive prodrug that is closely related to
indomethacin. The adverse reactions caused by sulindac
are similar to, but less severe than, those of the other
NSAIDs, including indomethacin.
Etodolac has effects similar to those of the other NSAIDs.
GI problems are less common.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-44-320.jpg)
![ Piroxicam [peer-OX-i-kam] and meloxicam [mel-
OX-i-kam] are used to treat RA, ankylosing
spondylitis, and osteoarthritis.
They have long half-lives, which permit once-
daily administration.
Meloxicam inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2, with
preferential binding for COX-2, and at low to
moderate doses shows less GI irritation than
piroxicam.
However, at high doses, meloxicam is a
nonselective NSAID, inhibiting both COX-1 and
COX-2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-45-320.jpg)
![ Diclofenac [dye-KLO-feh-nak] and tolmetin
[tole-MEN-tin] are approved for long-term
use in the treatment of RA, osteoarthritis,
and ankylosing spondylitis.
Diclofenac is more potent than indomethacin
or naproxen.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-46-320.jpg)
![ Ketorolac [key-toe-ROLE-ak] is a potent analgesic but
has moderate anti-inflammatory effects.
It is available for oral administration, for
intramuscular use in the treatment of postoperative
pain.
Ketorolac undergoes hepatic metabolism, and the
drug and its metabolites are eliminated via the urine.
Ketorolac is indicated for short-term relief of
moderate to severe pain for up to 5 days after the
first dose is administered via IV or intramuscular
dosing at the doctor's office or in a hospital.
This agent is to be avoided in pediatric patients;
patients with mild pain, and those with chronic
conditions, the dose should not exceed 40 mg/day.
Ketorolac can cause fatal peptic ulcers as well as GI
bleeding and/or perforation of the stomach or
intestines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-47-320.jpg)
![ Celecoxib [sel-eh-COCKS-ib] is significantly more
selective for inhibition of COX-2 than of COX-1.
Unlike aspirin, celecoxib does not inhibit platelet
aggregation and does not increase bleeding time.
Celecoxib has similar efficacy to NSAIDs in the
treatment of pain.
Celecoxib, when used without concomitant
aspirin therapy, has been shown to be associated
with less GI bleeding and dyspepsia; however, this
benefit is lost when aspirin is added to celecoxib
therapy.
In patients at high risk for ulcers (that is, history
of peptic ulcer disease), use of PPIs with
celecoxib and aspirin may be necessary to avoid
gastric ulcers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-48-320.jpg)


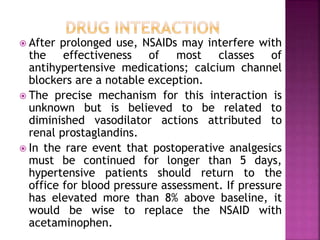





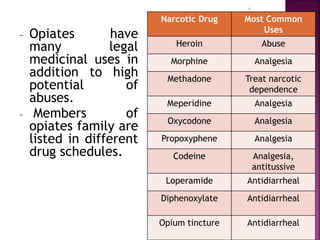
![ Opioids are natural or synthetic compounds that produce
morphine-like effects. [The term opiate is reserved for
drugs, such as morphine and codeine, obtained from the
juice of the opium poppy.]
All drugs in this category act by binding to specific opioid
receptors in the CNS to produce effects that mimic the
action of endogenous peptide neurotransmitters (for
example, endorphins, enkephalins, and dynorphins).
Although the opioids have a broad range of effects, their
primary use is to relieve intense pain and the anxiety that
accompanies it, whether that pain is from surgery or a
result of injury or disease, such as cancer.
However, their widespread availability has led to abuse of
those opioids with euphoric properties. [Dependence is
seldom a problem in patients being treated for severe
pain with these agents, as in cancer or acute pain in
terminally ill patients.]
Antagonists that can reverse the actions of opioids are
also very important clinically for use in cases of overdose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingacuteandpain-201106224602/85/Analgesics-59-320.jpg)