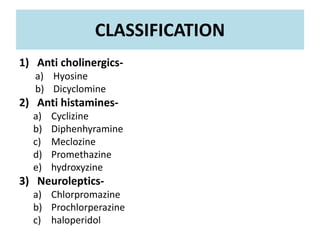
1) Anti-emetic drugs are used to prevent or suppress vomiting. They are classified into different categories including anti-cholinergics, anti-histamines, neuroleptics, prokinetic drugs, 5HT antagonists, and adjuvent anti-emetics.
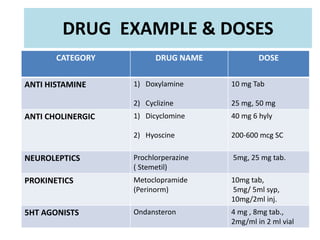
2) Common anti-emetic drugs include cyclizine, dicyclomine, prochlorperazine, metoclopramide, and ondansetron. They work through different mechanisms such as blocking neurotransmitters or receptors.
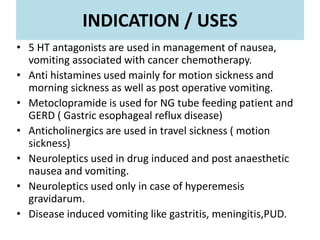
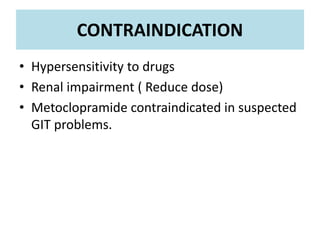
3) Anti-emetics are used to treat nausea and vomiting from conditions like cancer chemotherapy, motion sickness, and post-operative vomiting. Adverse effects can include