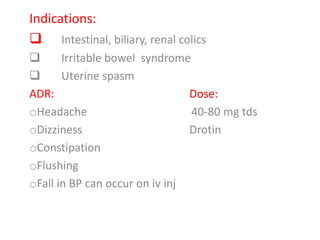
Anti-spasmodic drugs are used to treat symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome like pain and spasms. There are two main classes - antimuscarinic drugs which block cholinergic transmission and relax smooth muscle, and direct smooth muscle relaxants like mebeverine which directly affect colonic muscle activity. These drugs work by reducing contractions of the intestines which helps relieve IBS symptoms like pain and bloating. Common anti-spasmodics discussed include hyoscine butylbromide, dicyclomine, and drotaverine.