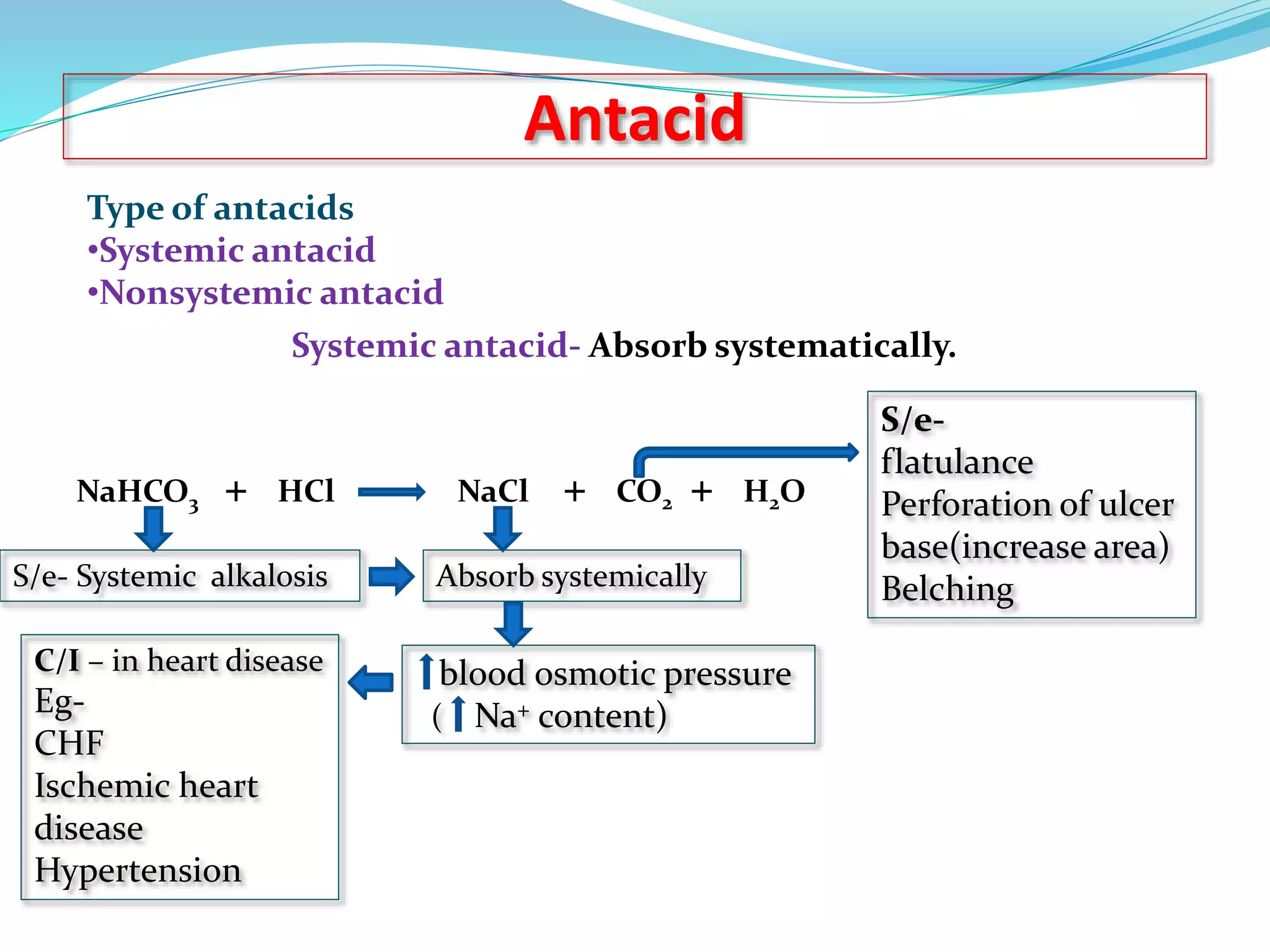
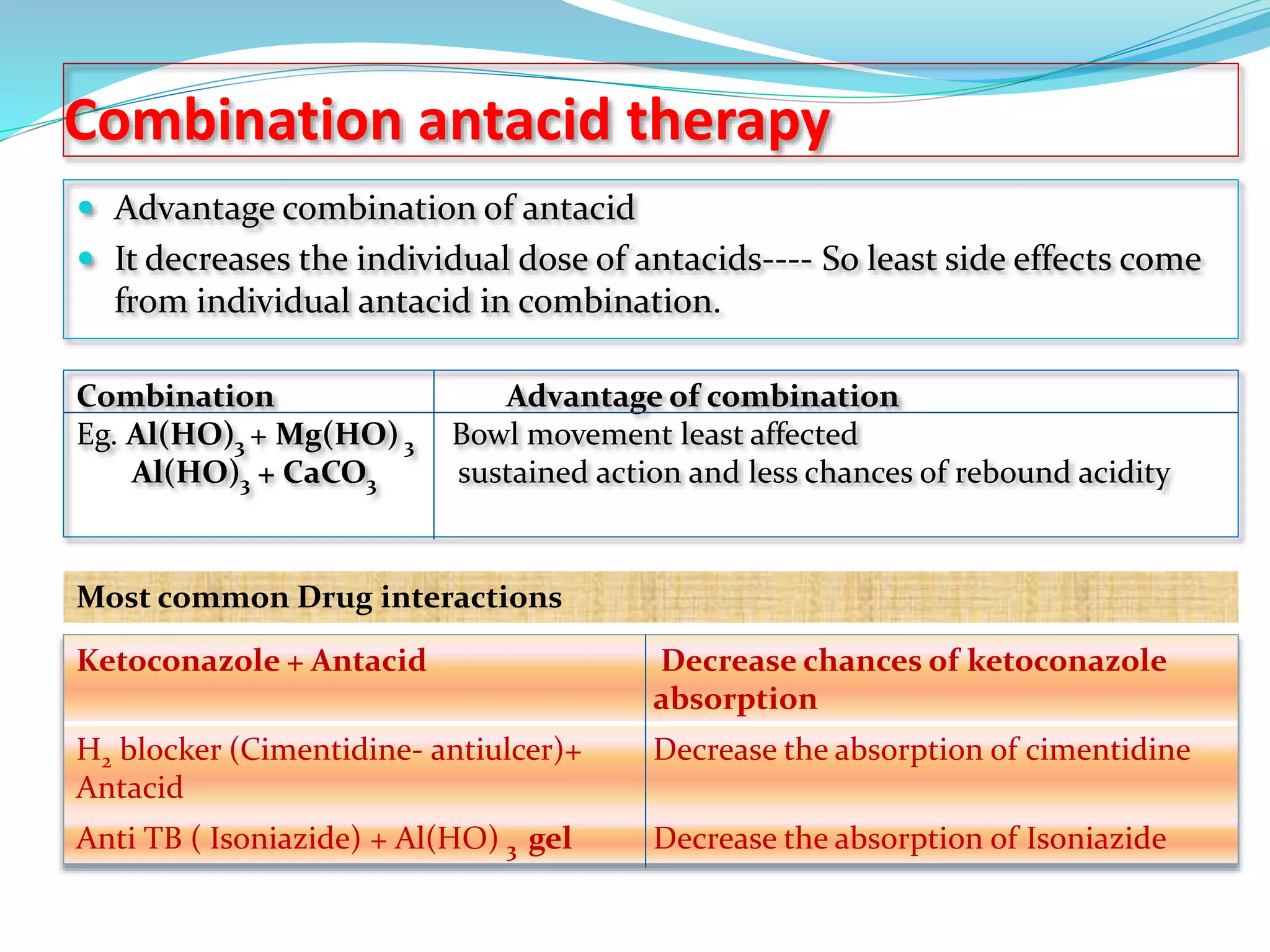
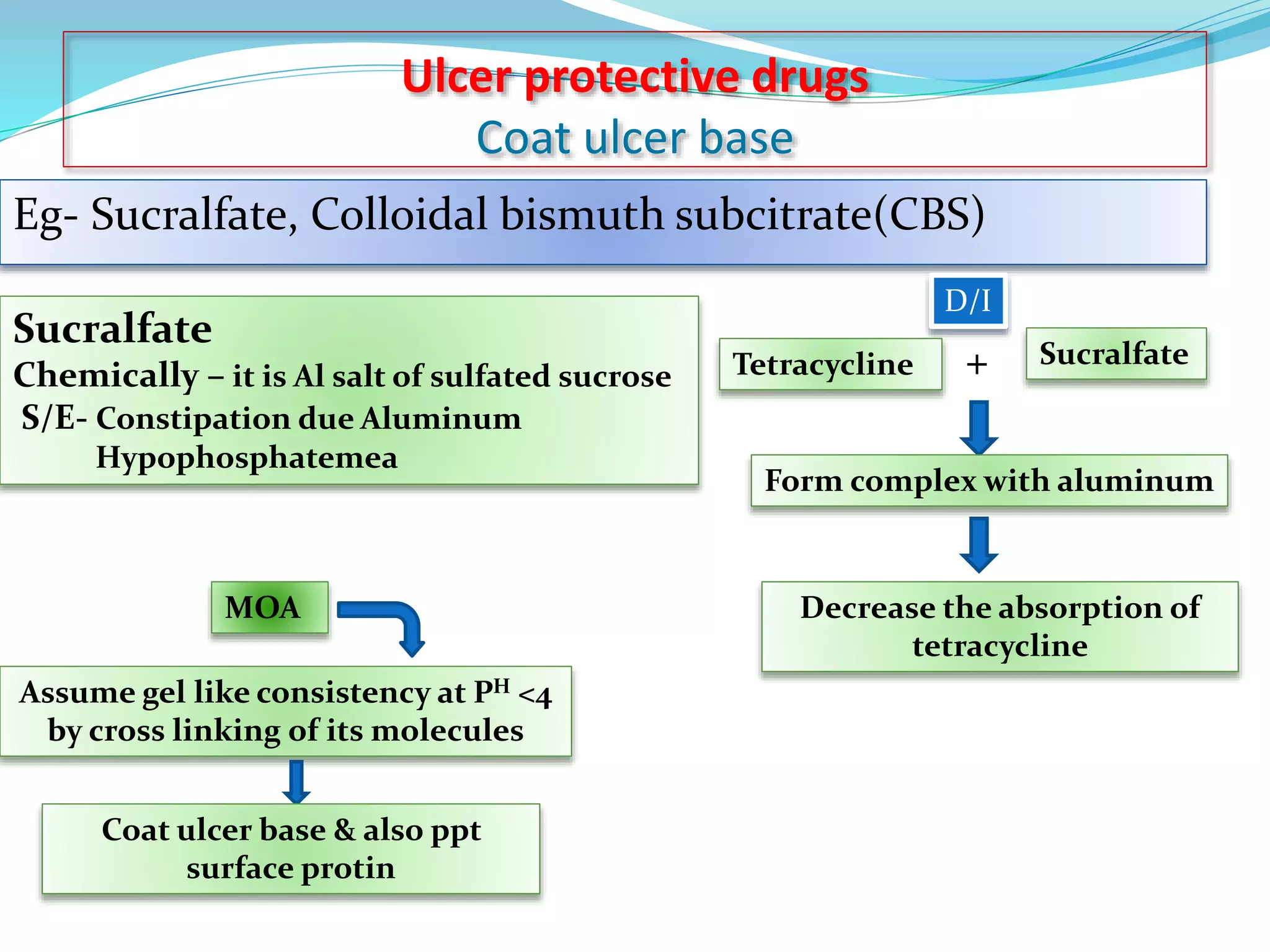
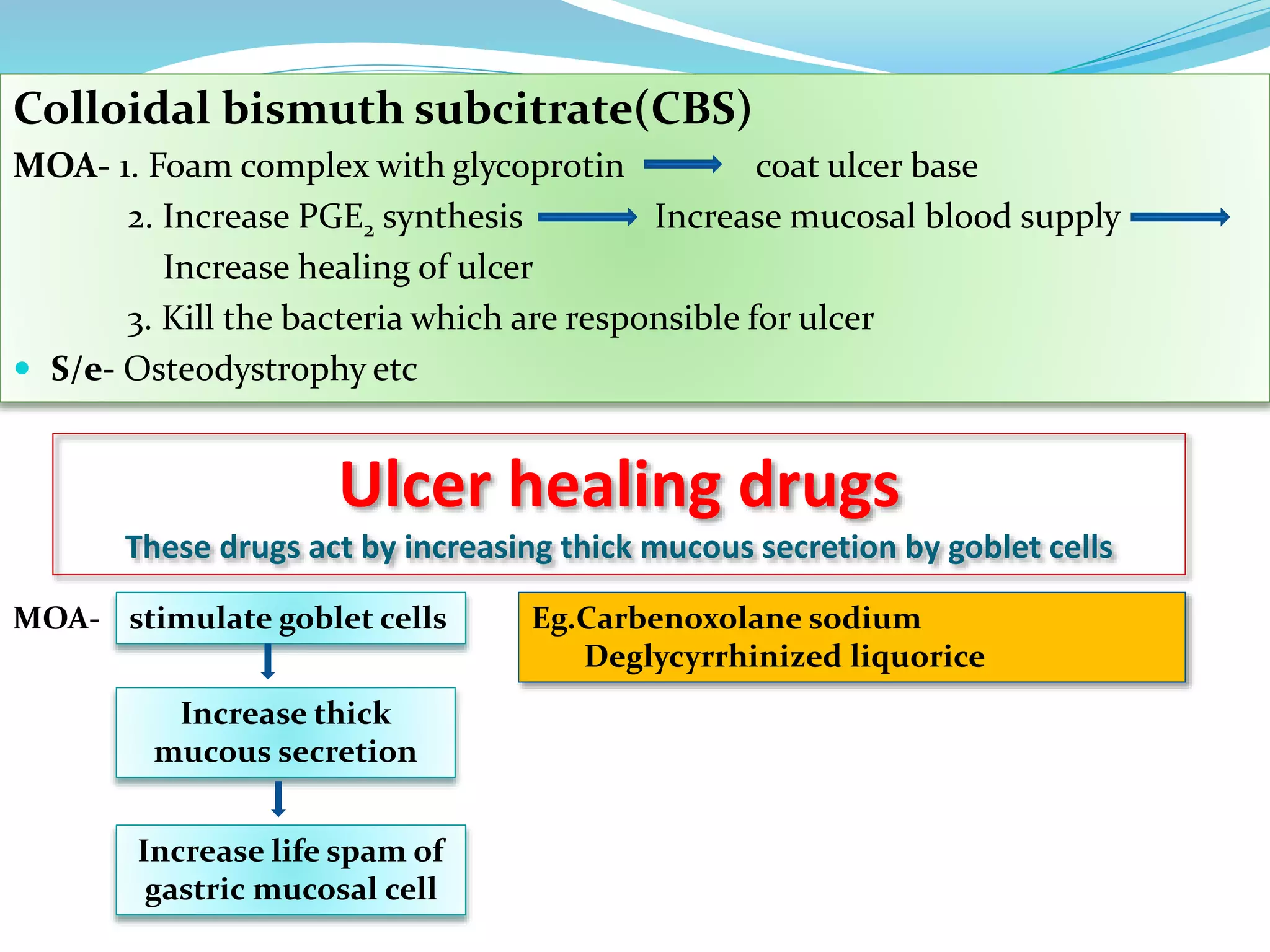
This document discusses peptic ulcers, including their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It notes that peptic ulcers are open sores in the upper digestive tract that can form in the stomach (gastric ulcer) or small intestine (duodenal ulcer). Common causes include H. pylori infection, NSAIDs, and stress. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, black stools, or weight loss. Treatments discussed include antibiotics to kill H. pylori, antacids to neutralize stomach acid, drugs that decrease acid secretion, ulcer protective drugs to coat the ulcer, and ulcer healing drugs.