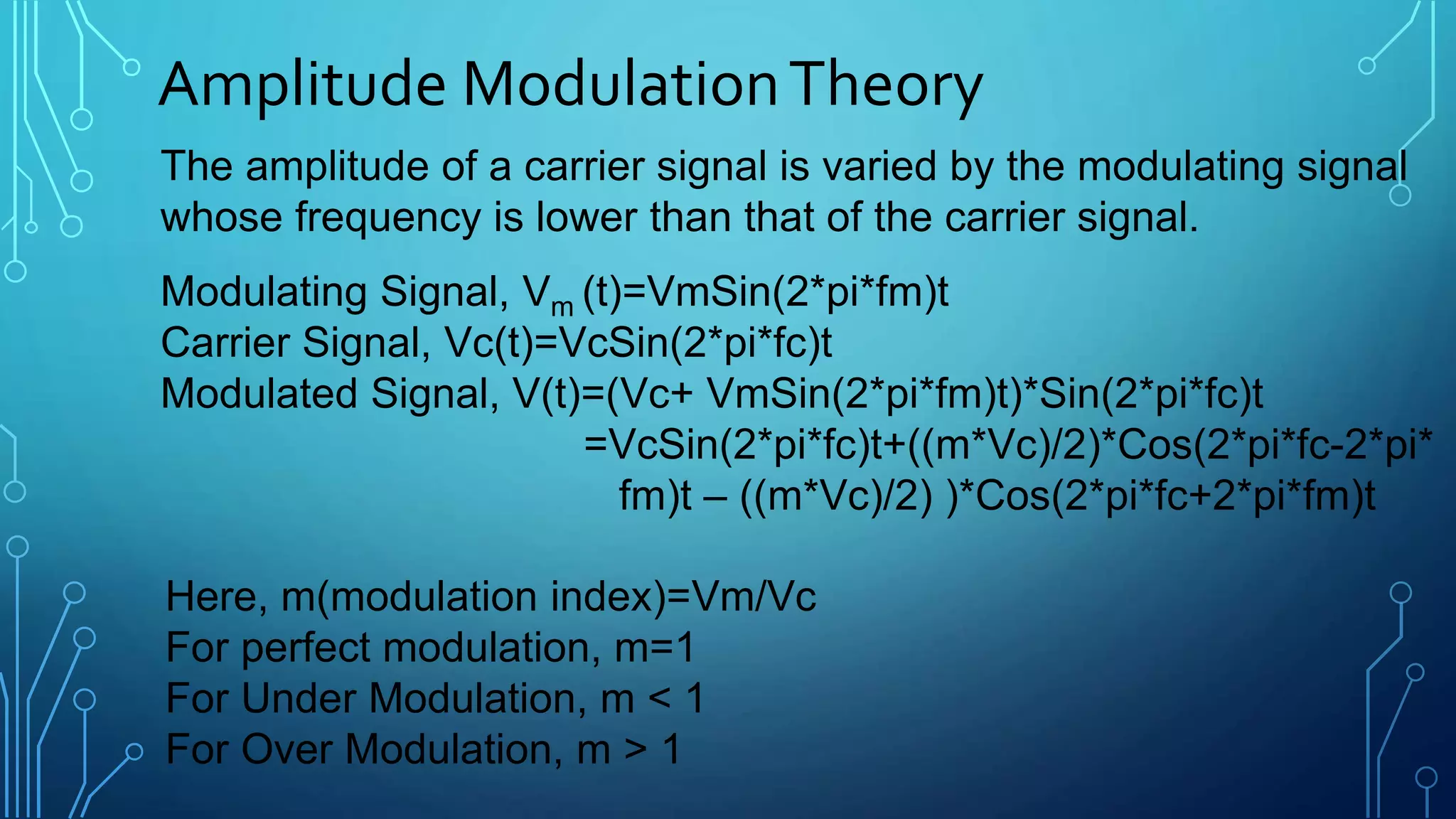
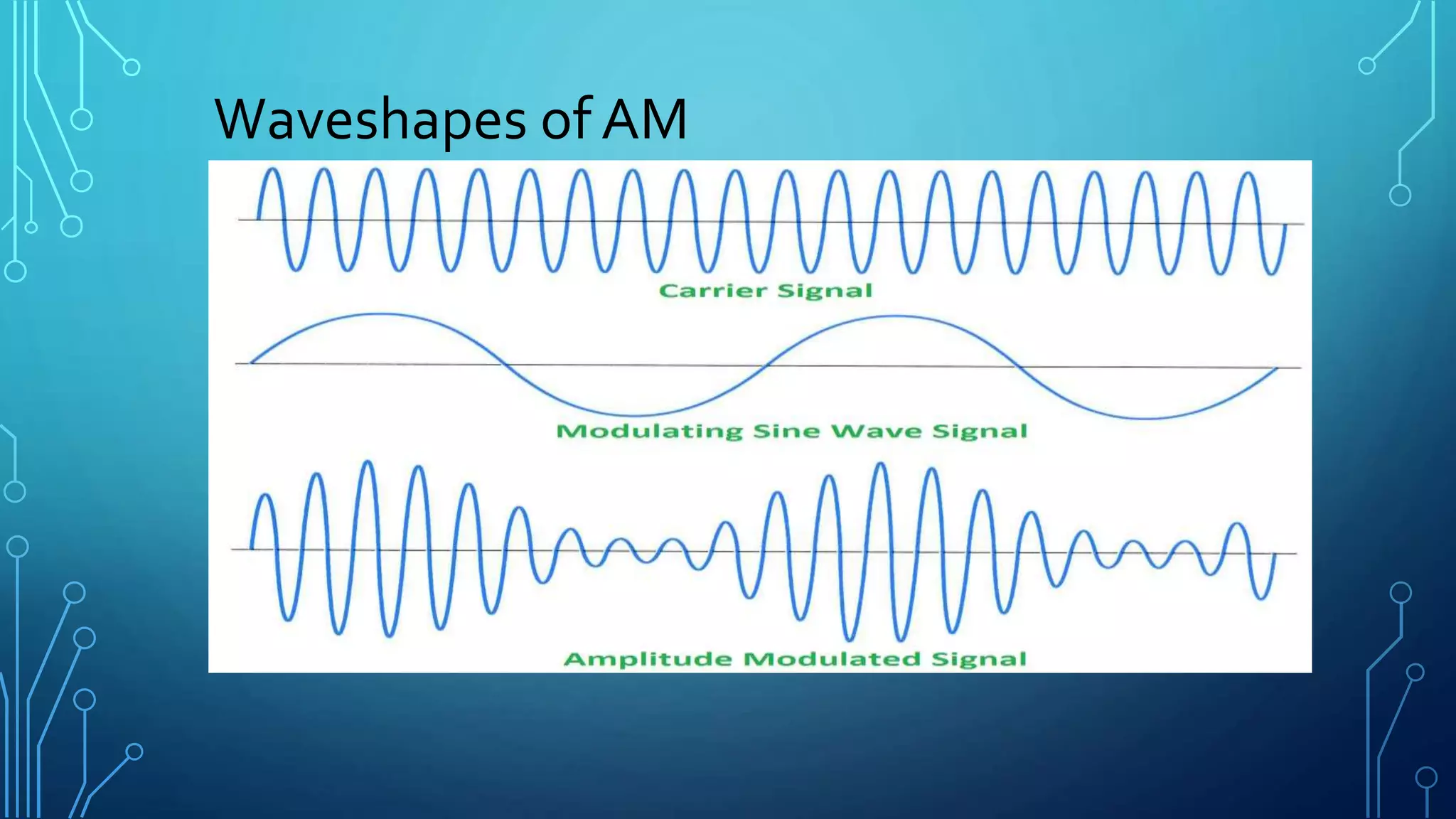
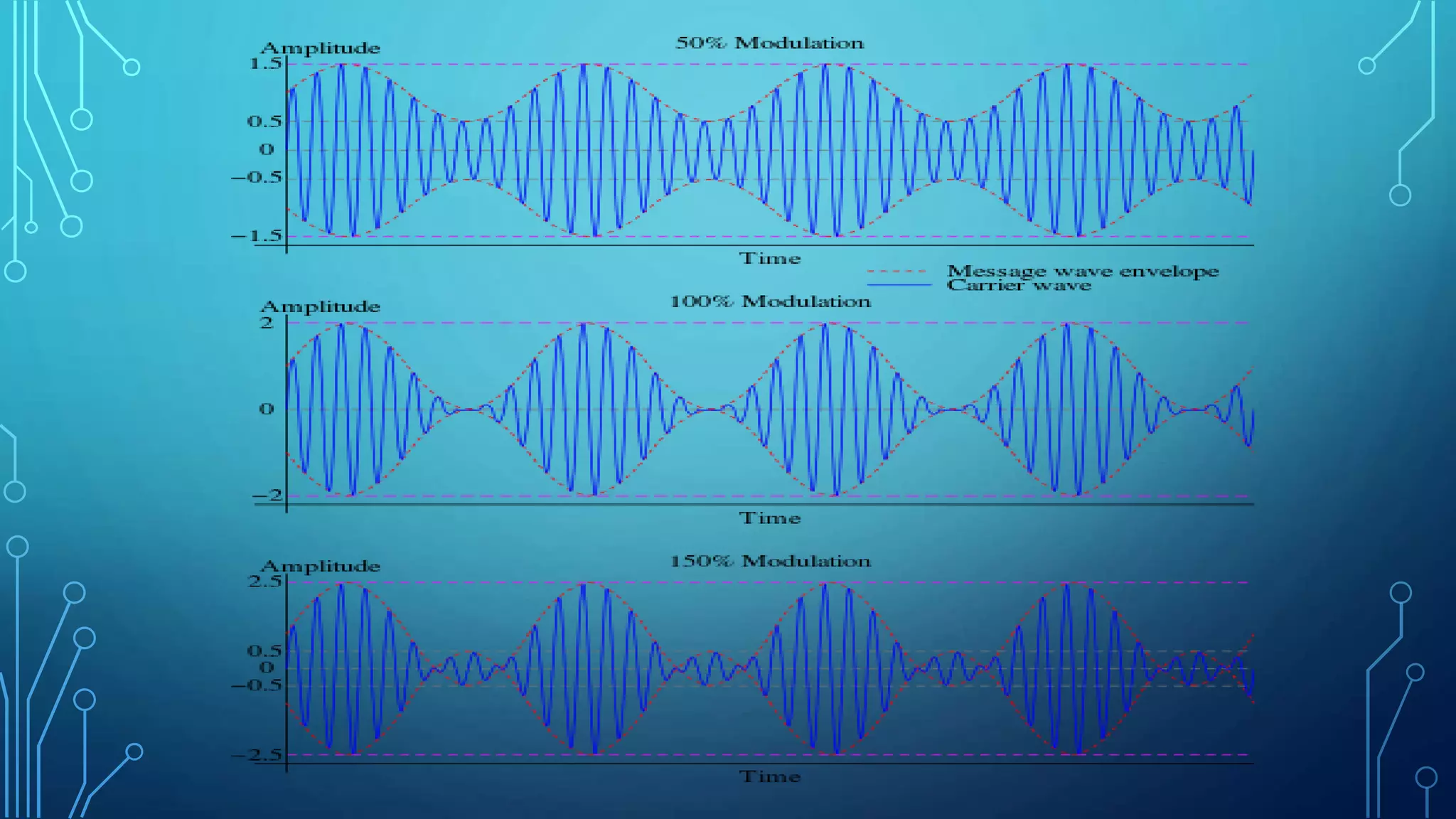
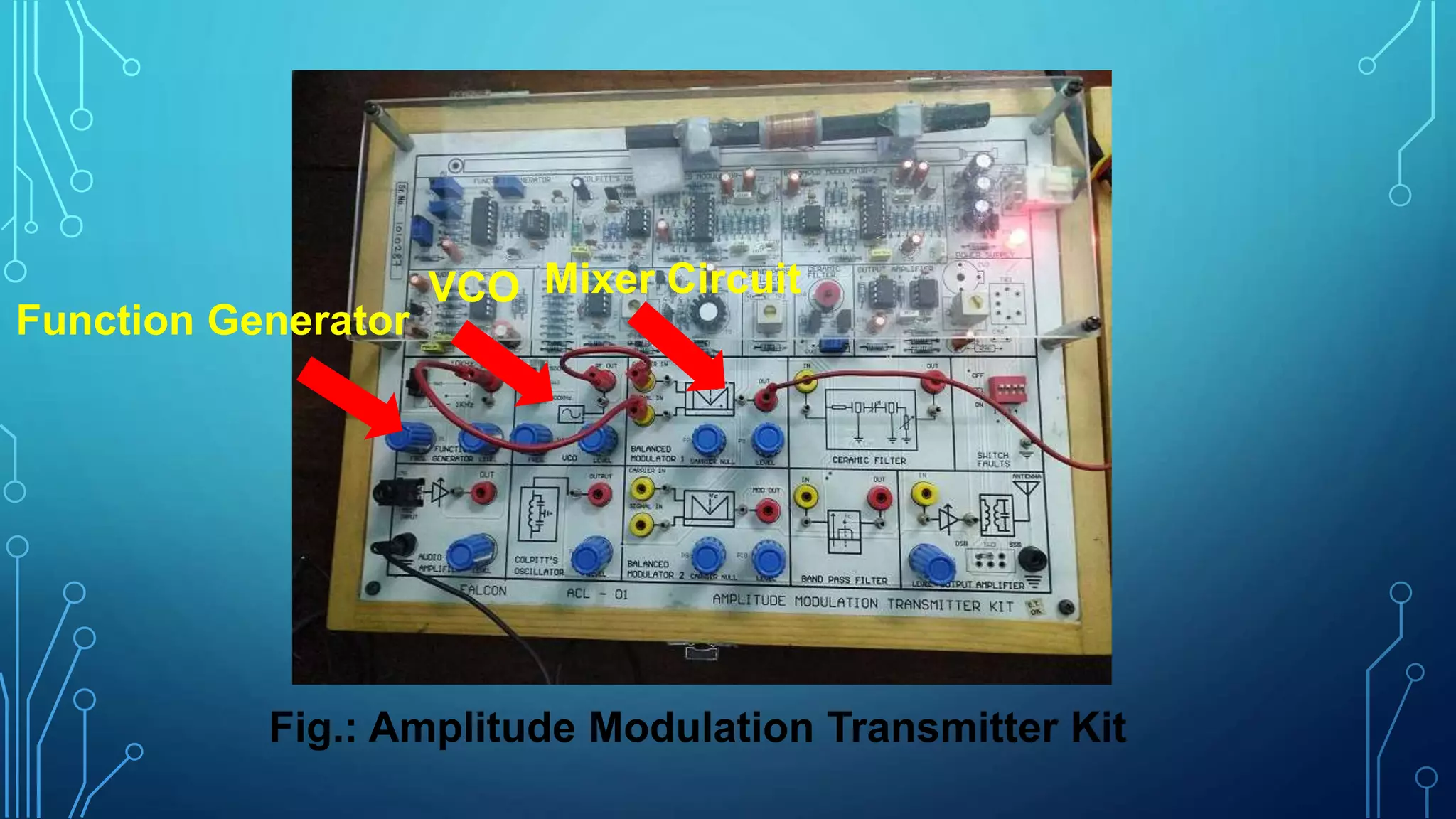
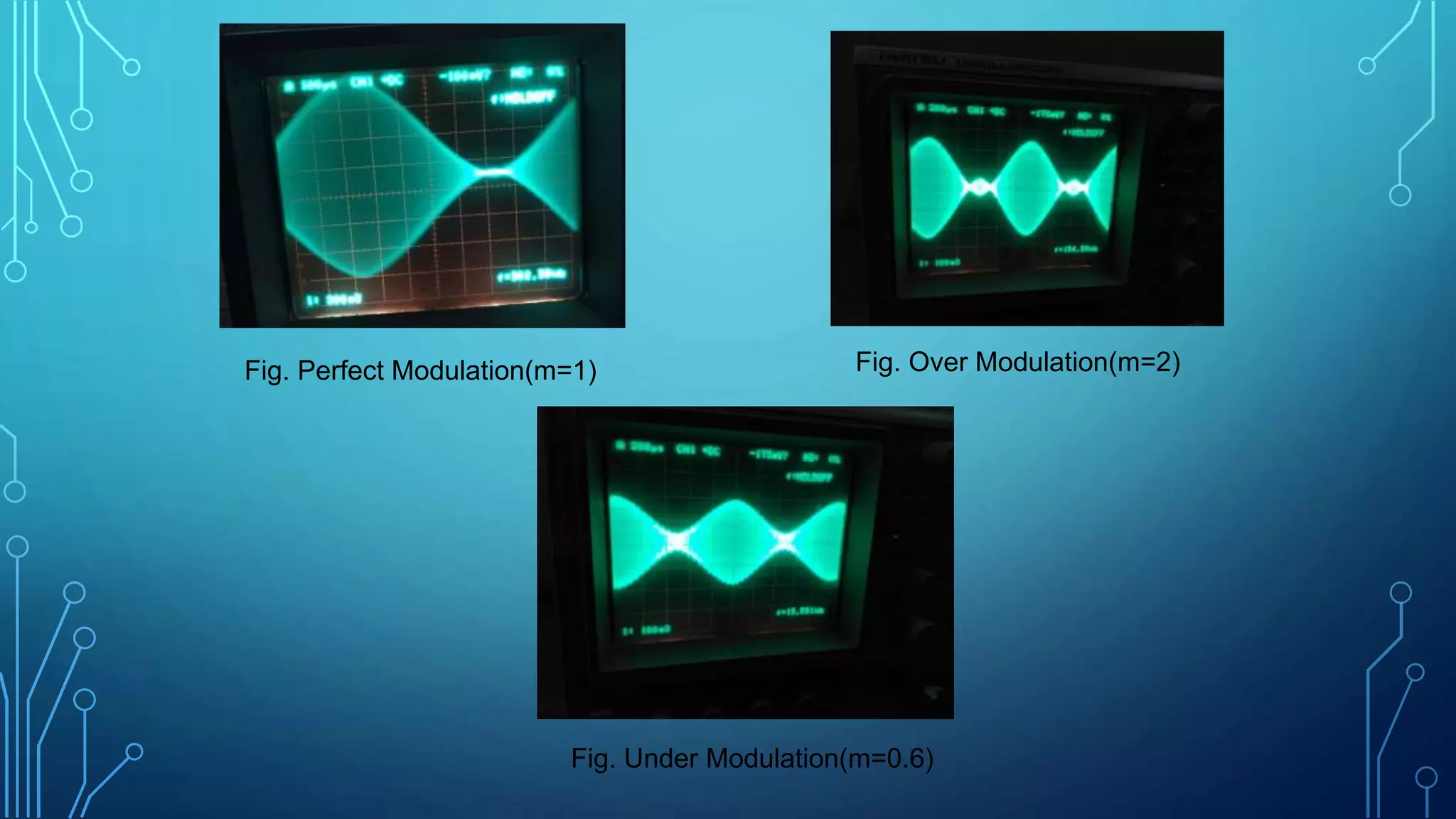
This document discusses amplitude modulation (AM). It defines AM as a modulation technique where the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied in accordance with a message signal. It describes the theory behind AM mathematically and discusses generating AM signals in a lab using a function generator, voltage controlled oscillator, and mixer circuit. It also lists the components used, shows waveshapes of AM, and discusses advantages/disadvantages and applications of AM including broadcasting, mobile communications, and aircraft communications.