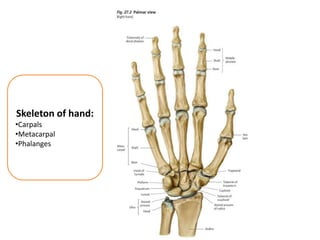
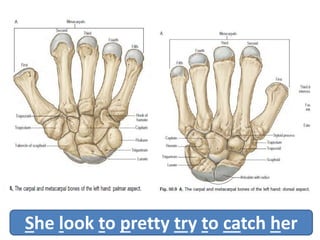
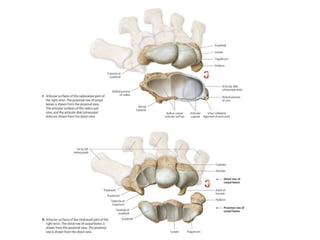
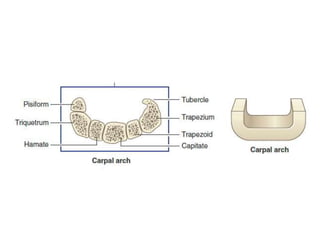
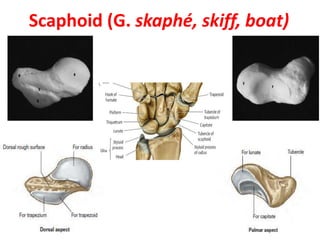
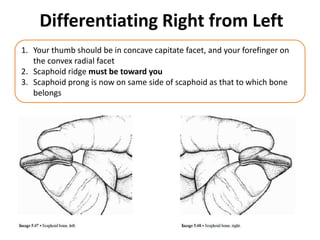
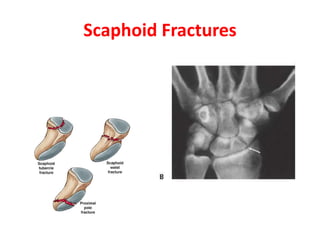
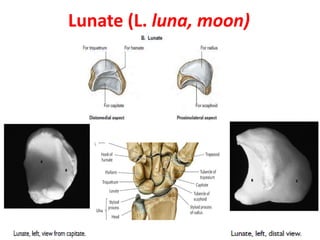
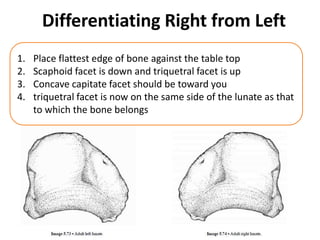
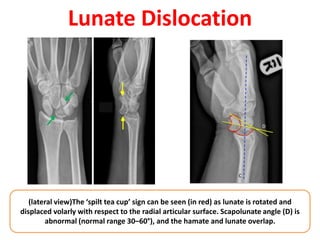
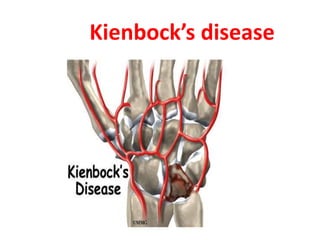
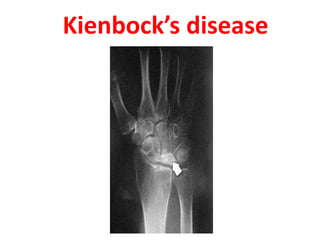
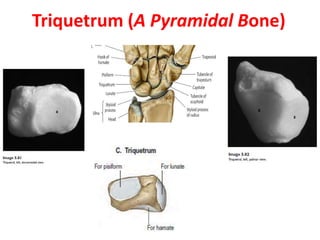
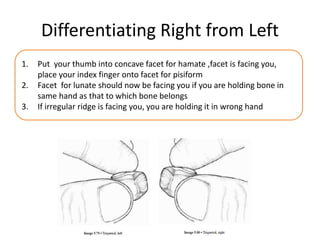
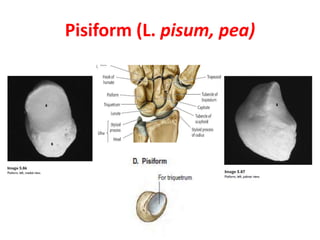
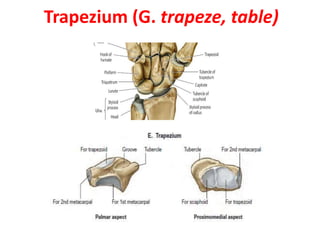
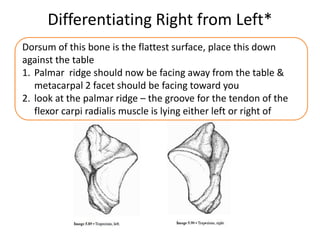
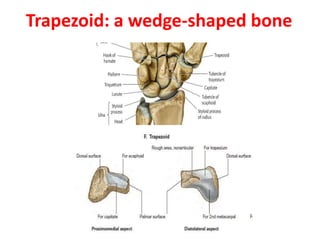
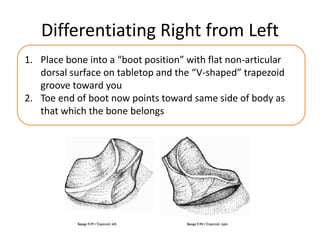
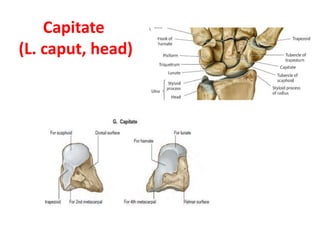
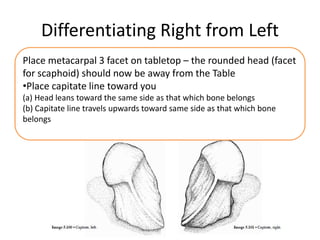
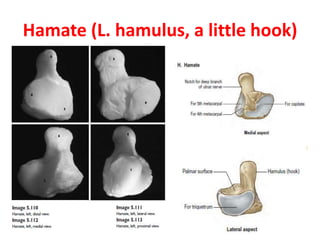
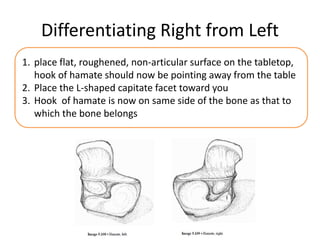
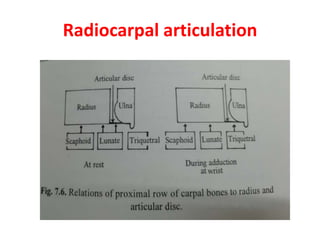
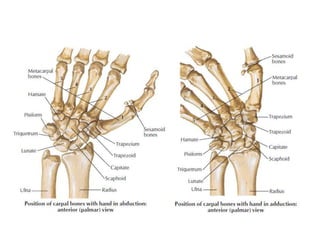
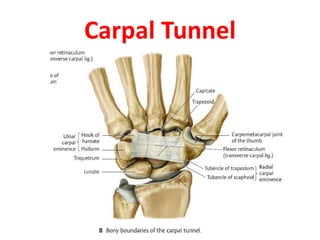
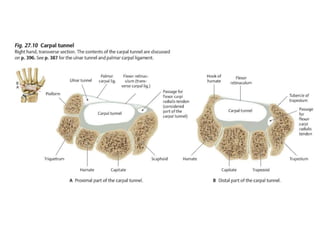
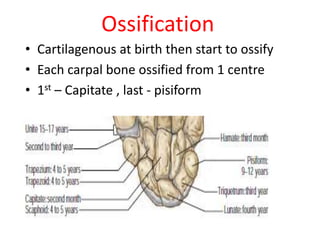
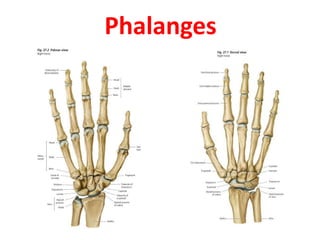
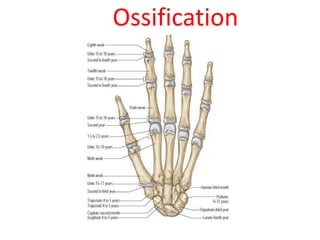
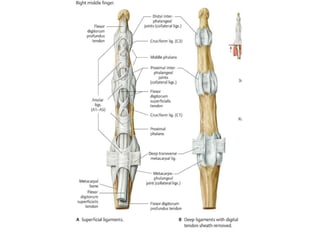
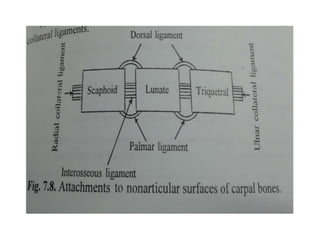
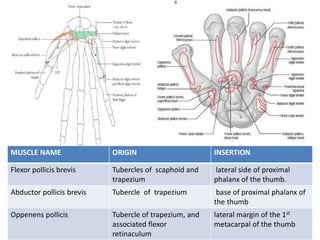
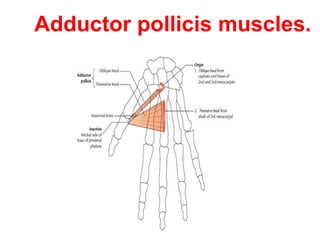
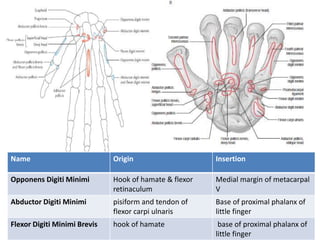
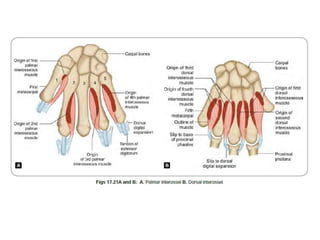
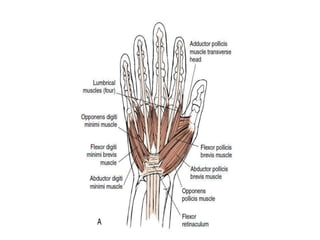
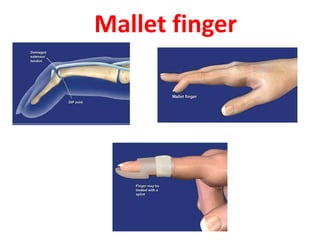
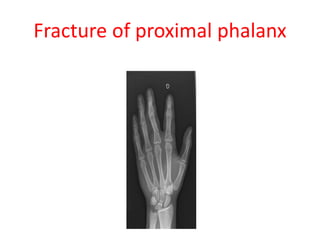
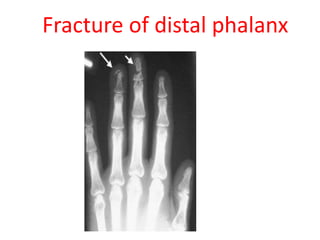
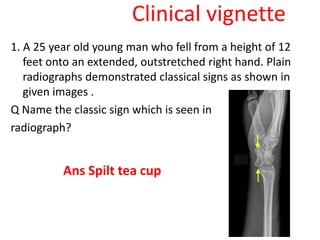
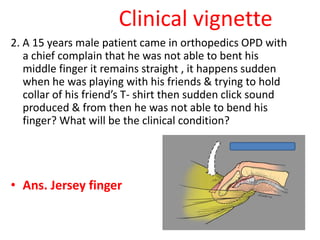
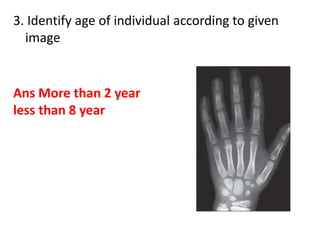
This document provides an overview of the carpals and phalanges bones in the hand. It discusses the characteristic features, muscular attachments, ossification, and clinical aspects of the carpals (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate) and phalanges. Methods for differentiating right and left carpals are presented. Common injuries and conditions like scaphoid fractures, Kienbock's disease, mallet finger, and Jersey finger are described. MCQs are provided to test understanding. Radiographic images demonstrate examples like the "spilt tea cup" sign of lunate dislocation.