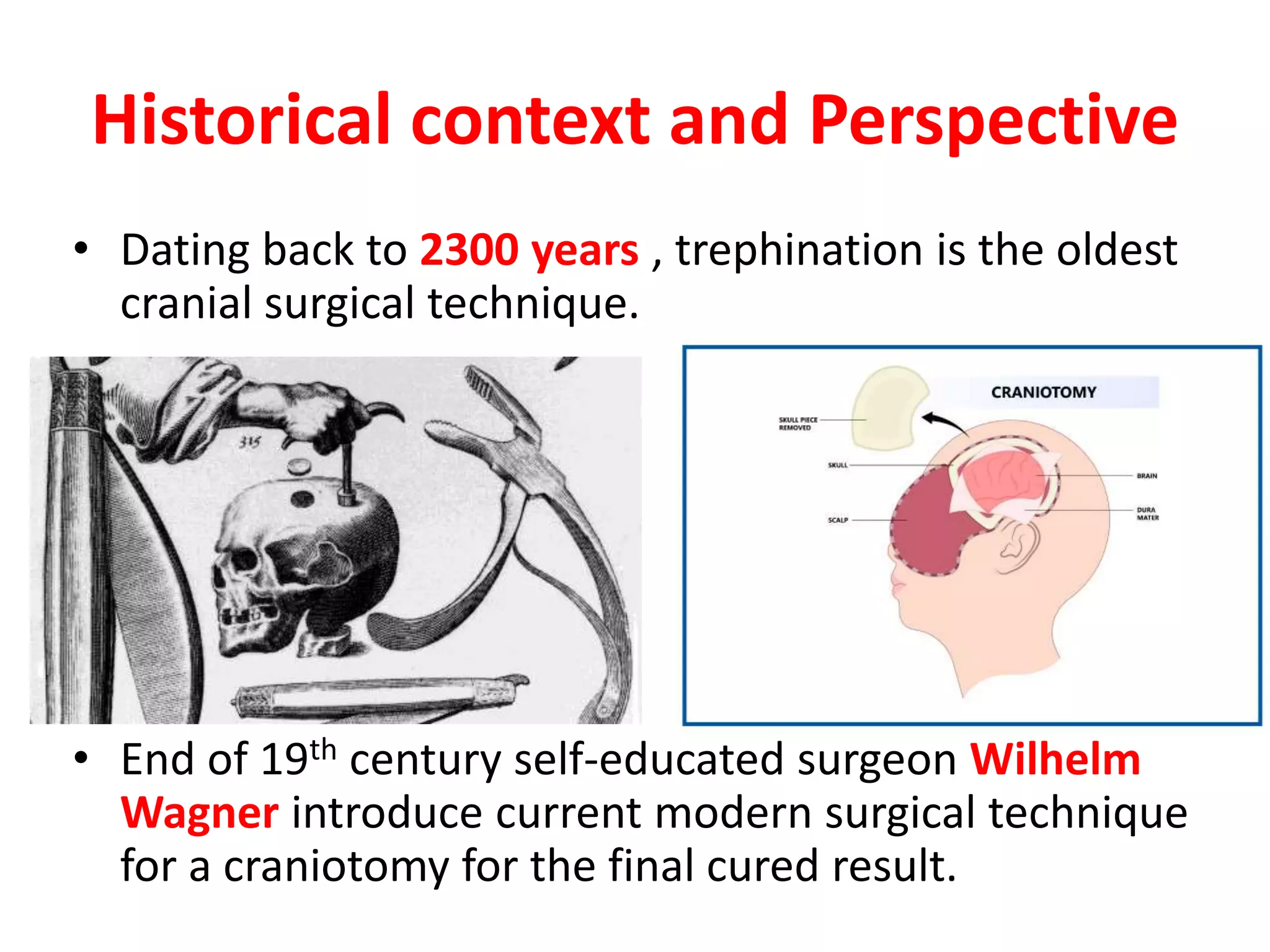
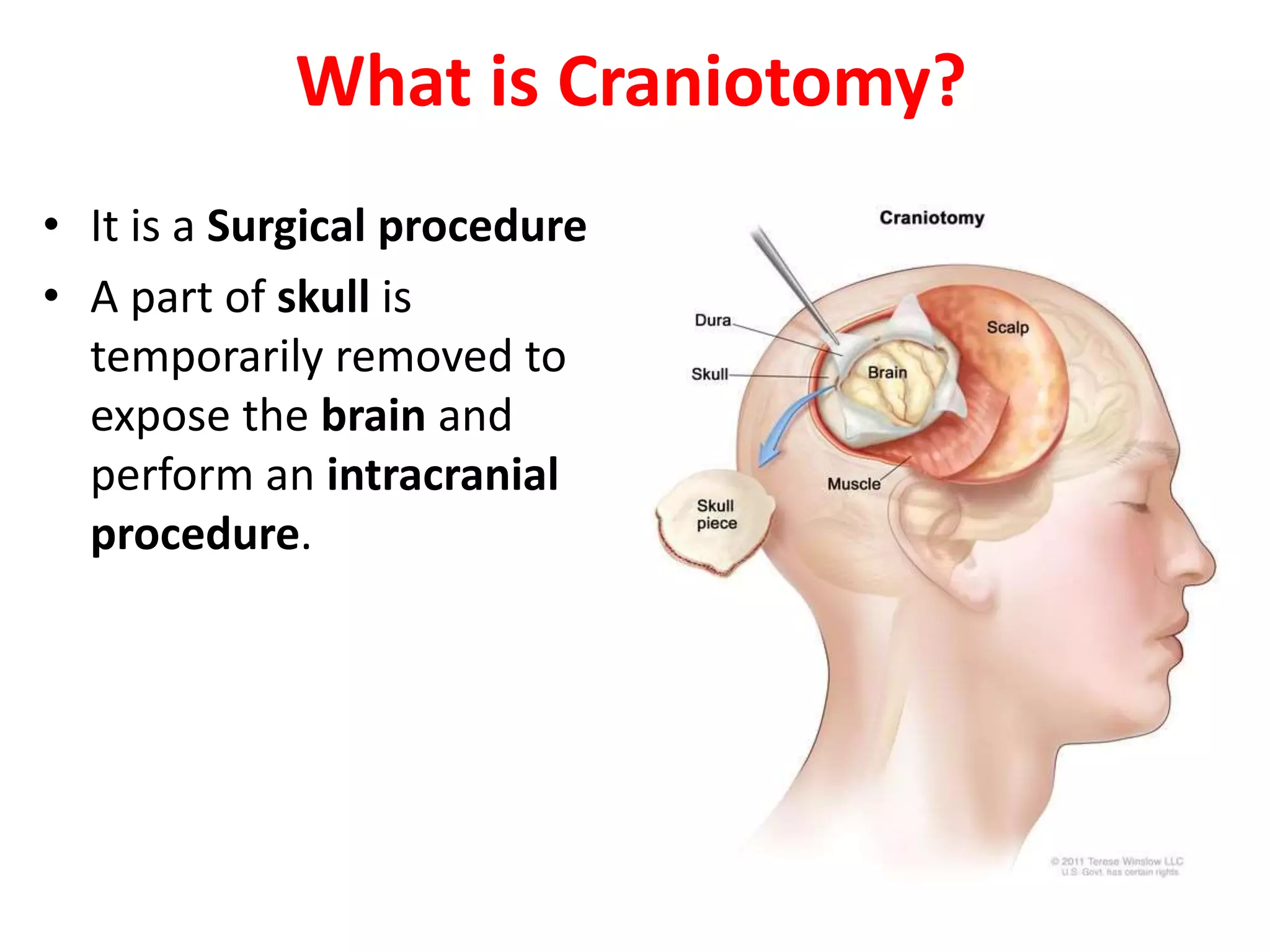
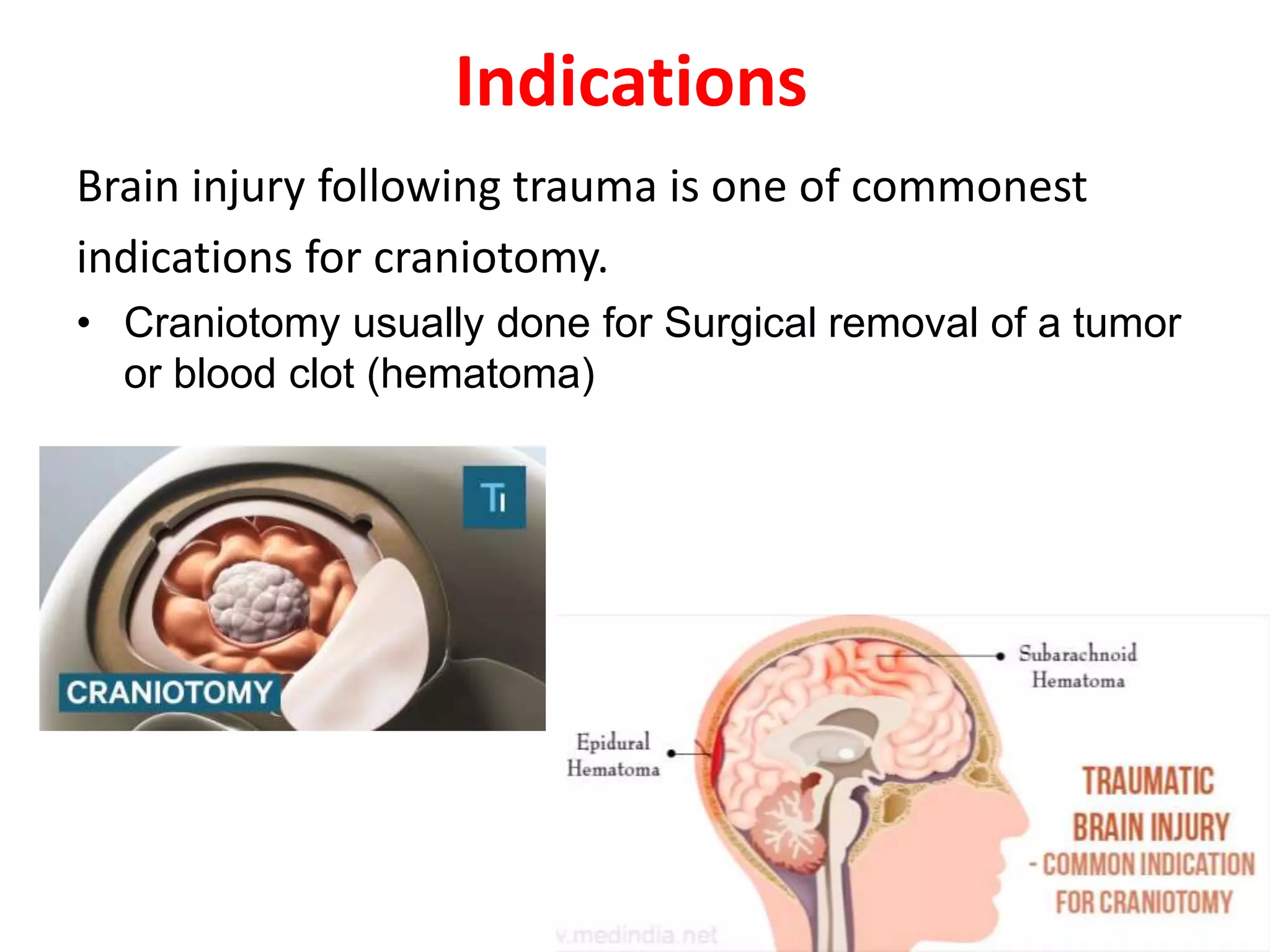
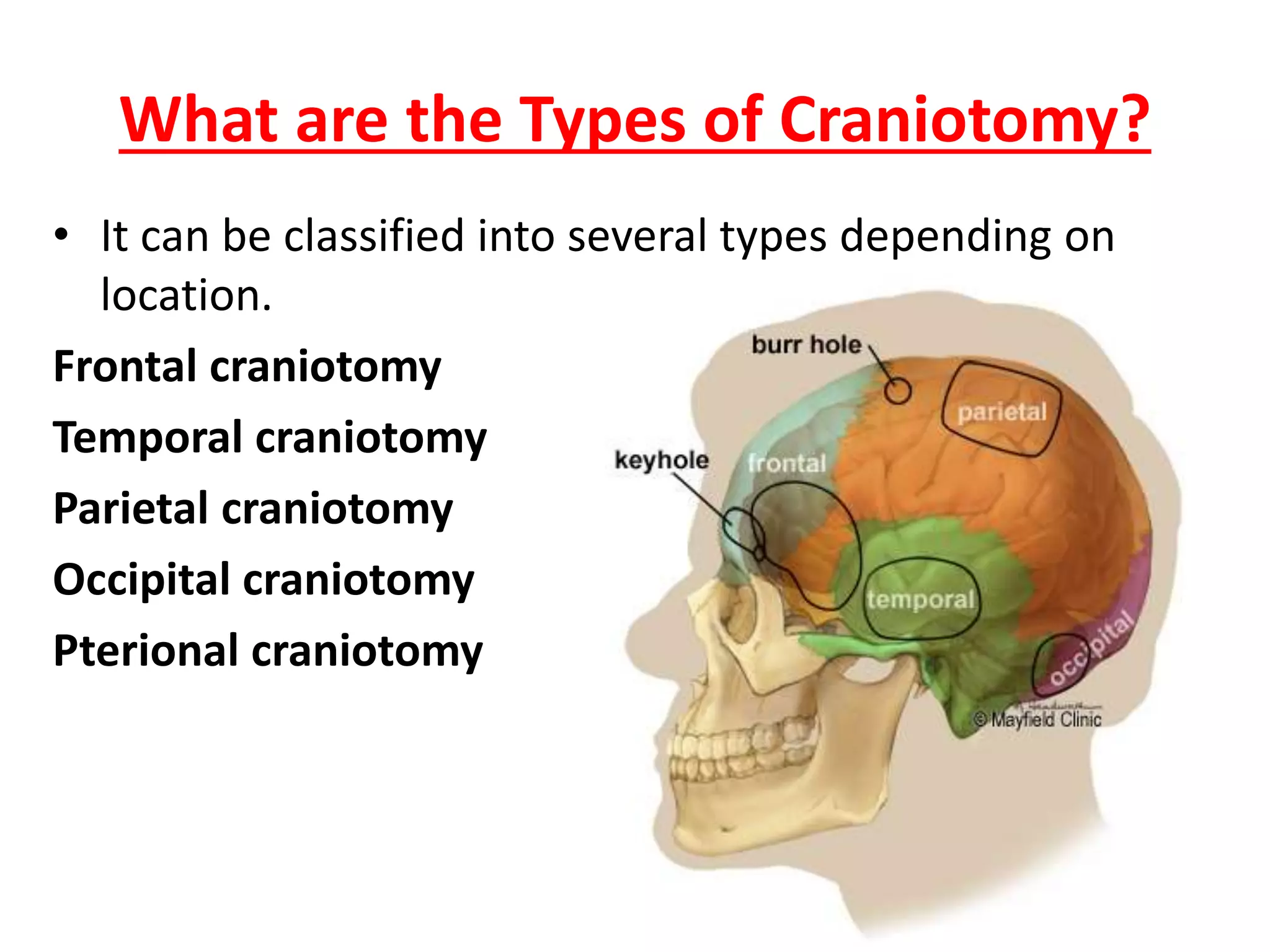
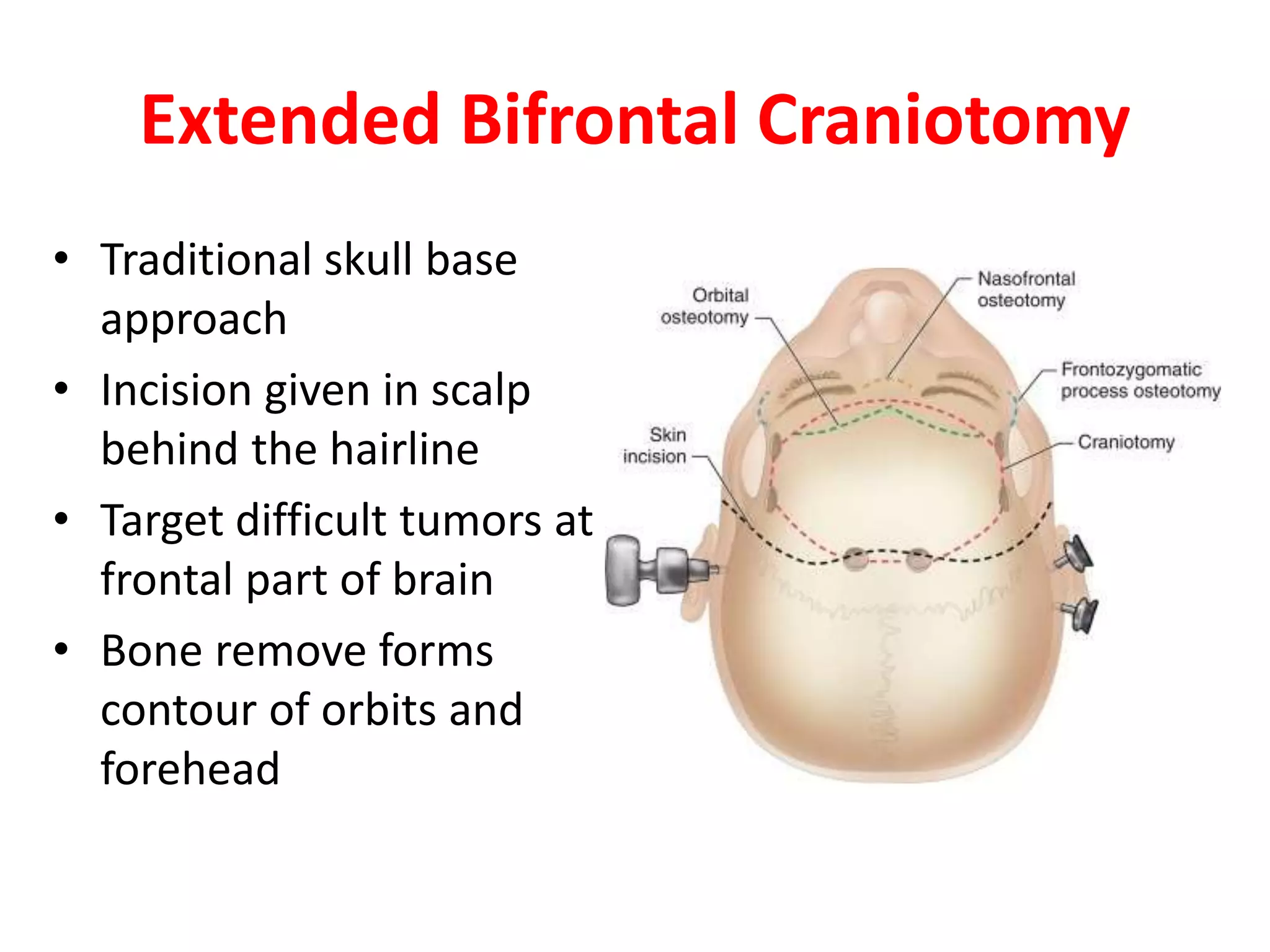
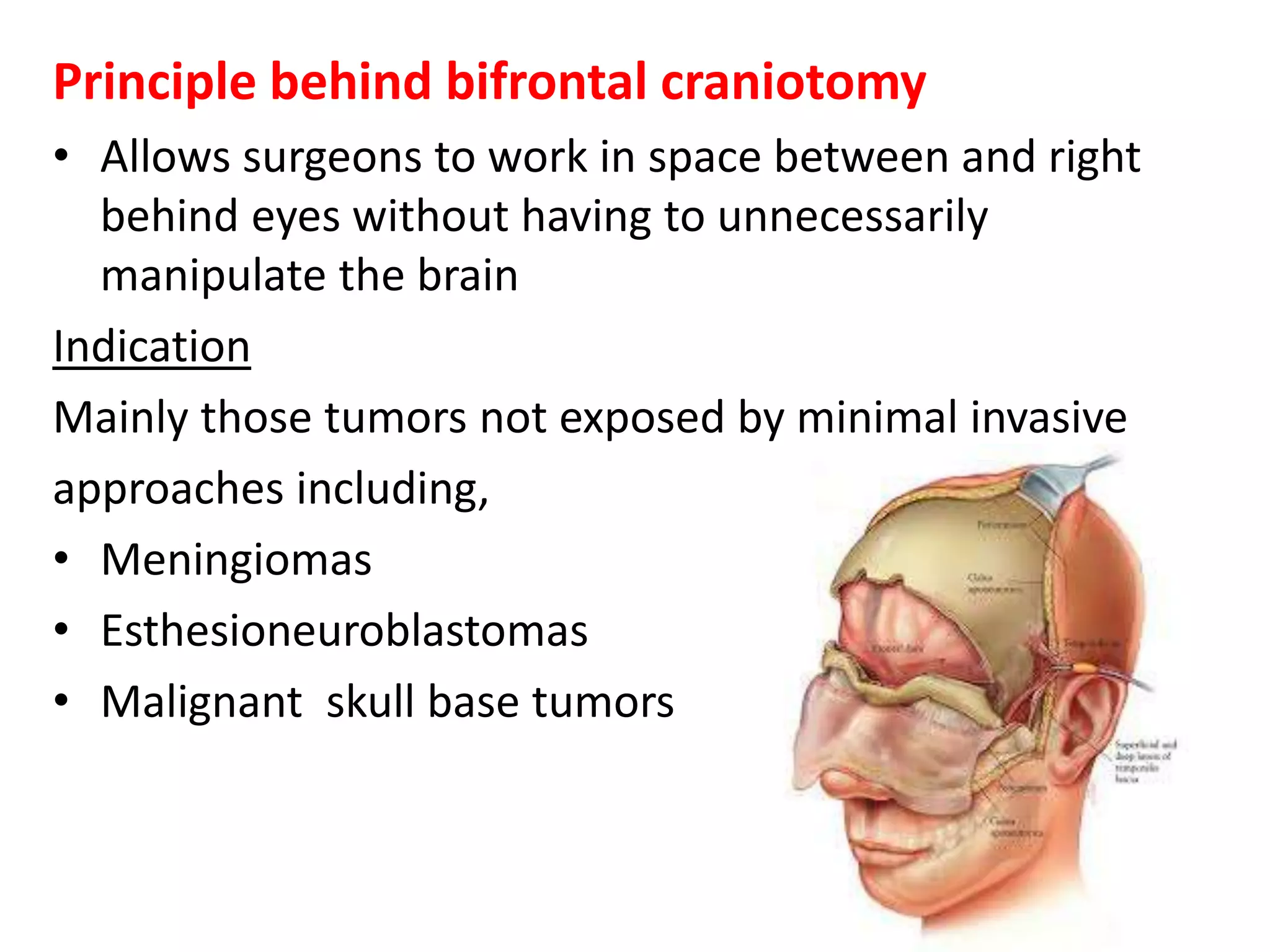
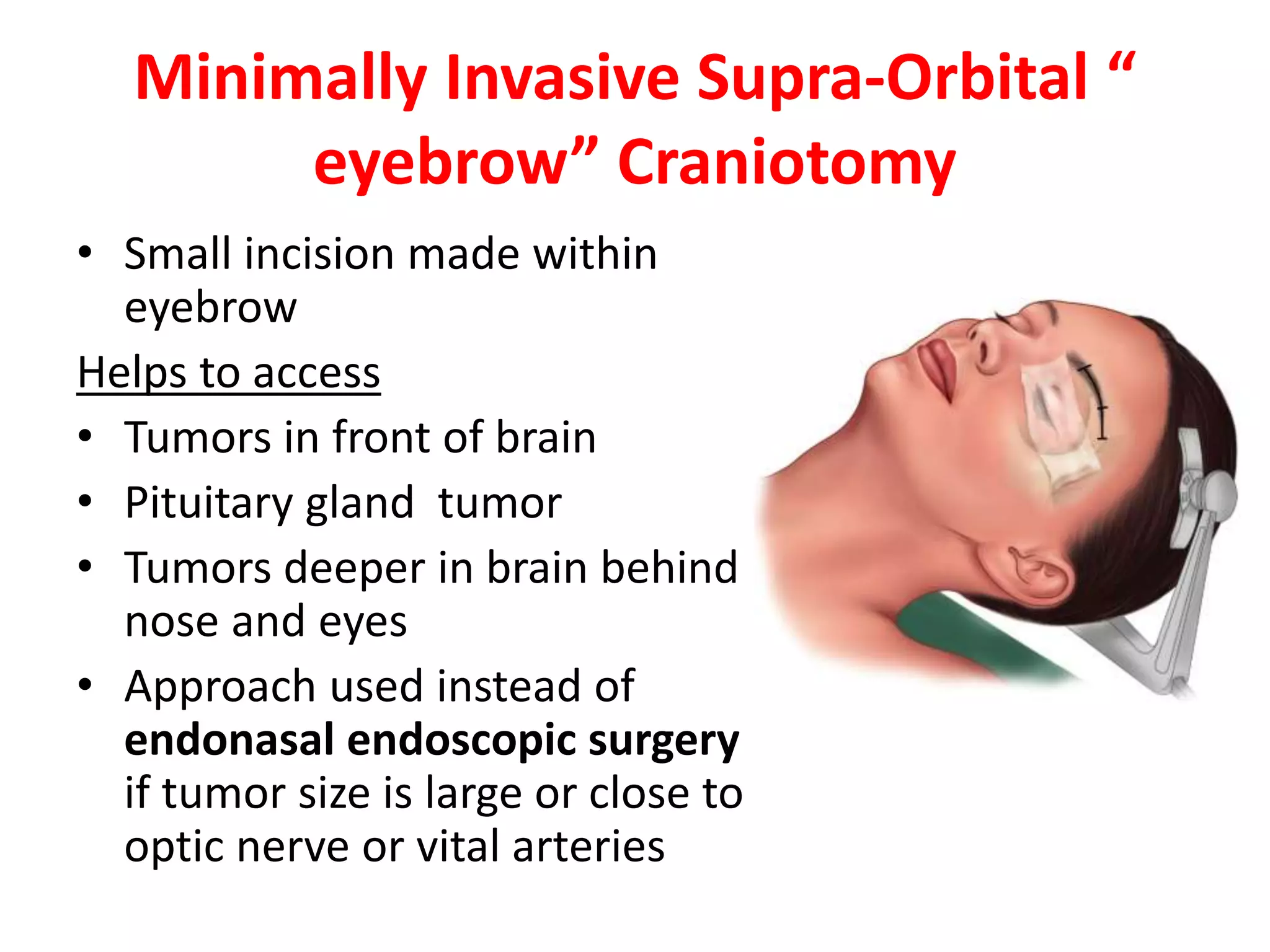
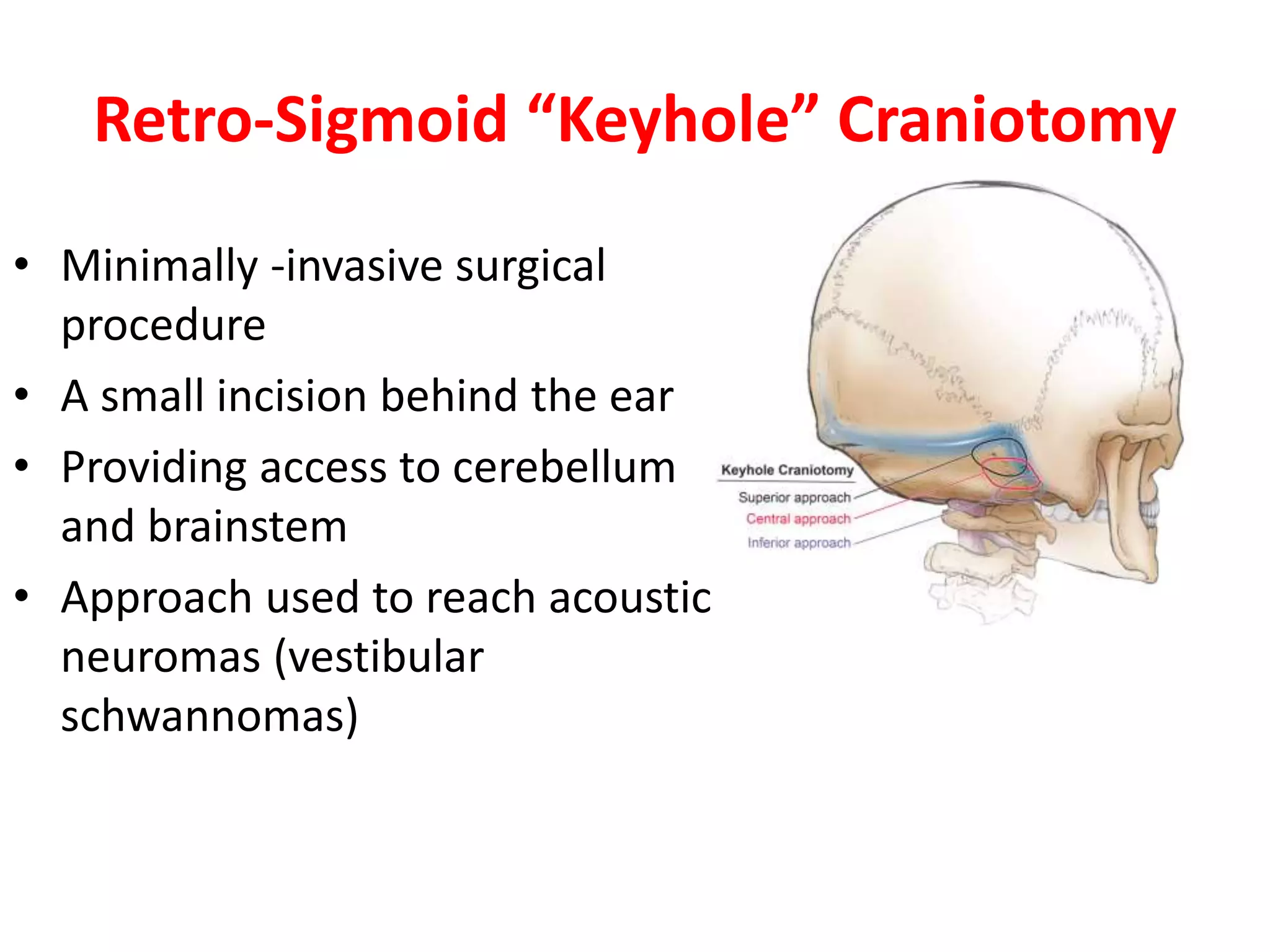
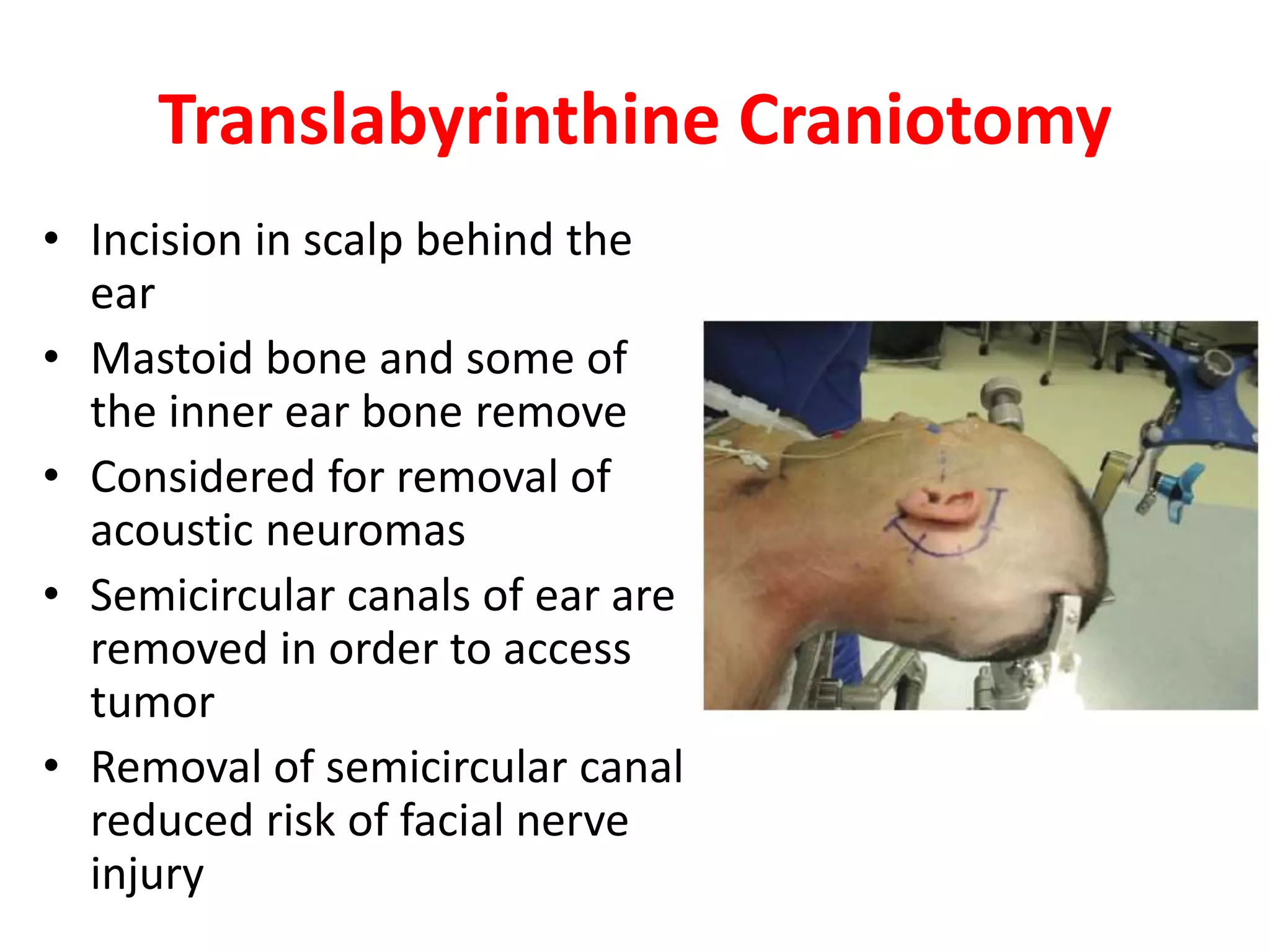
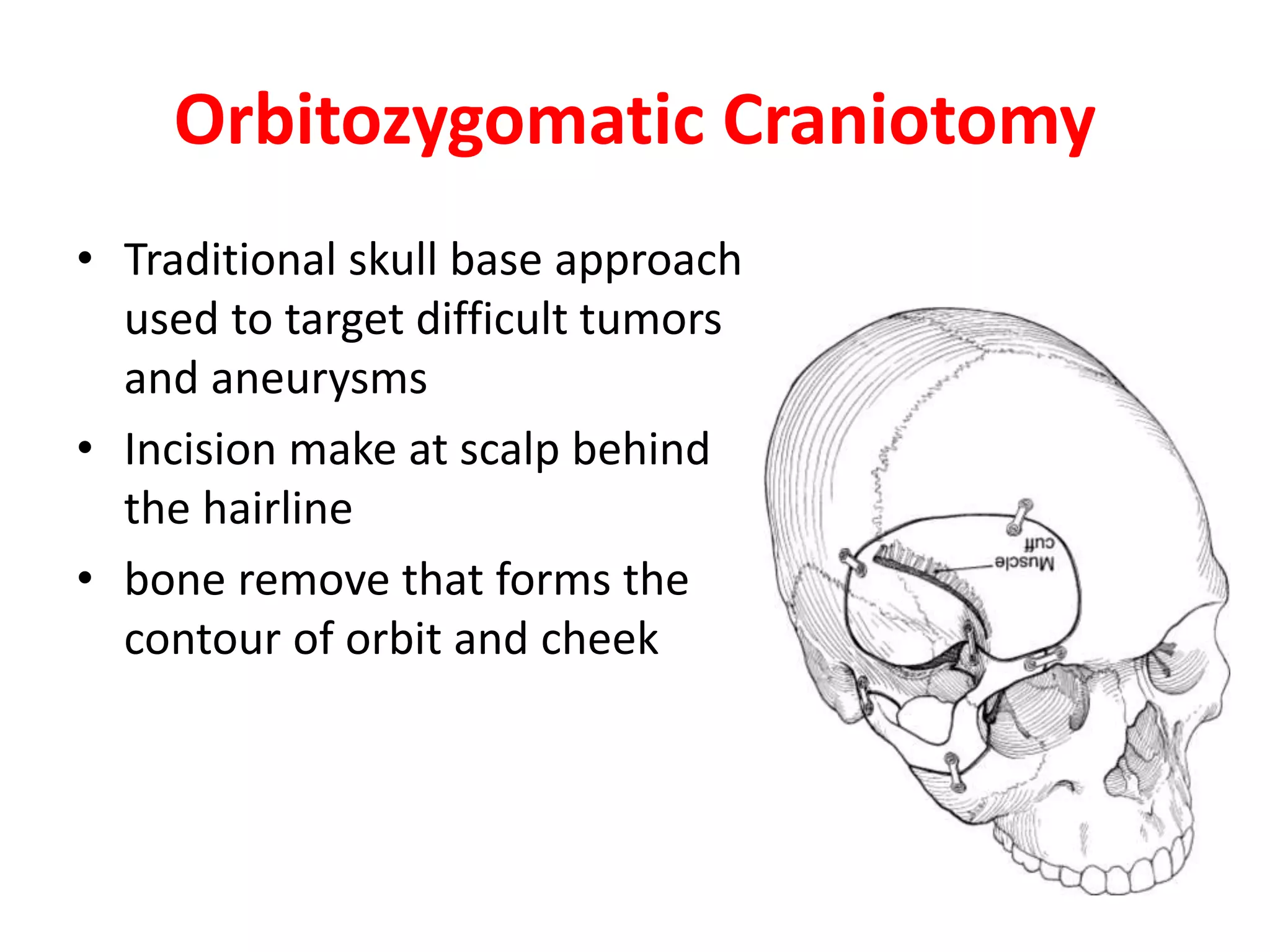
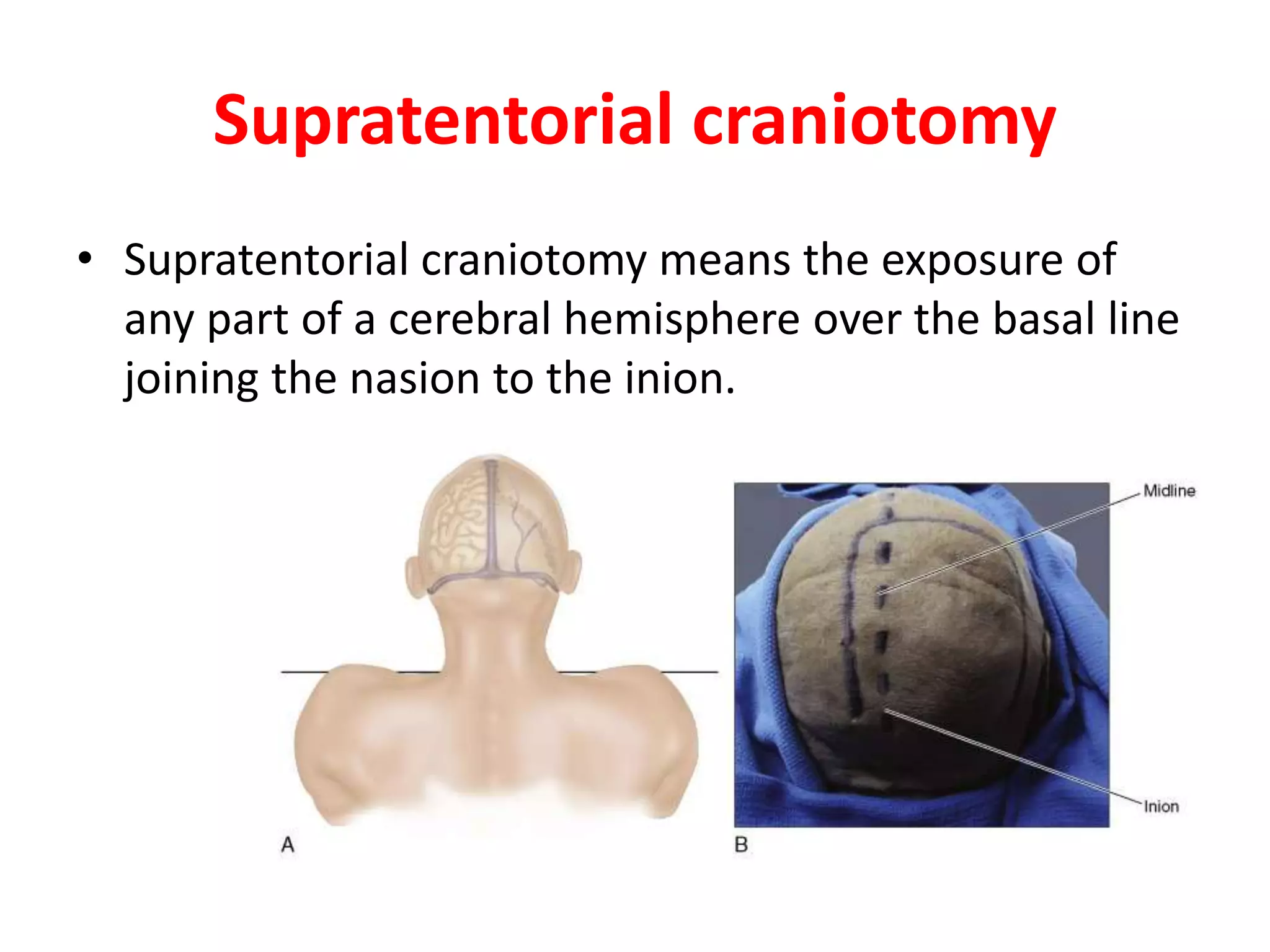
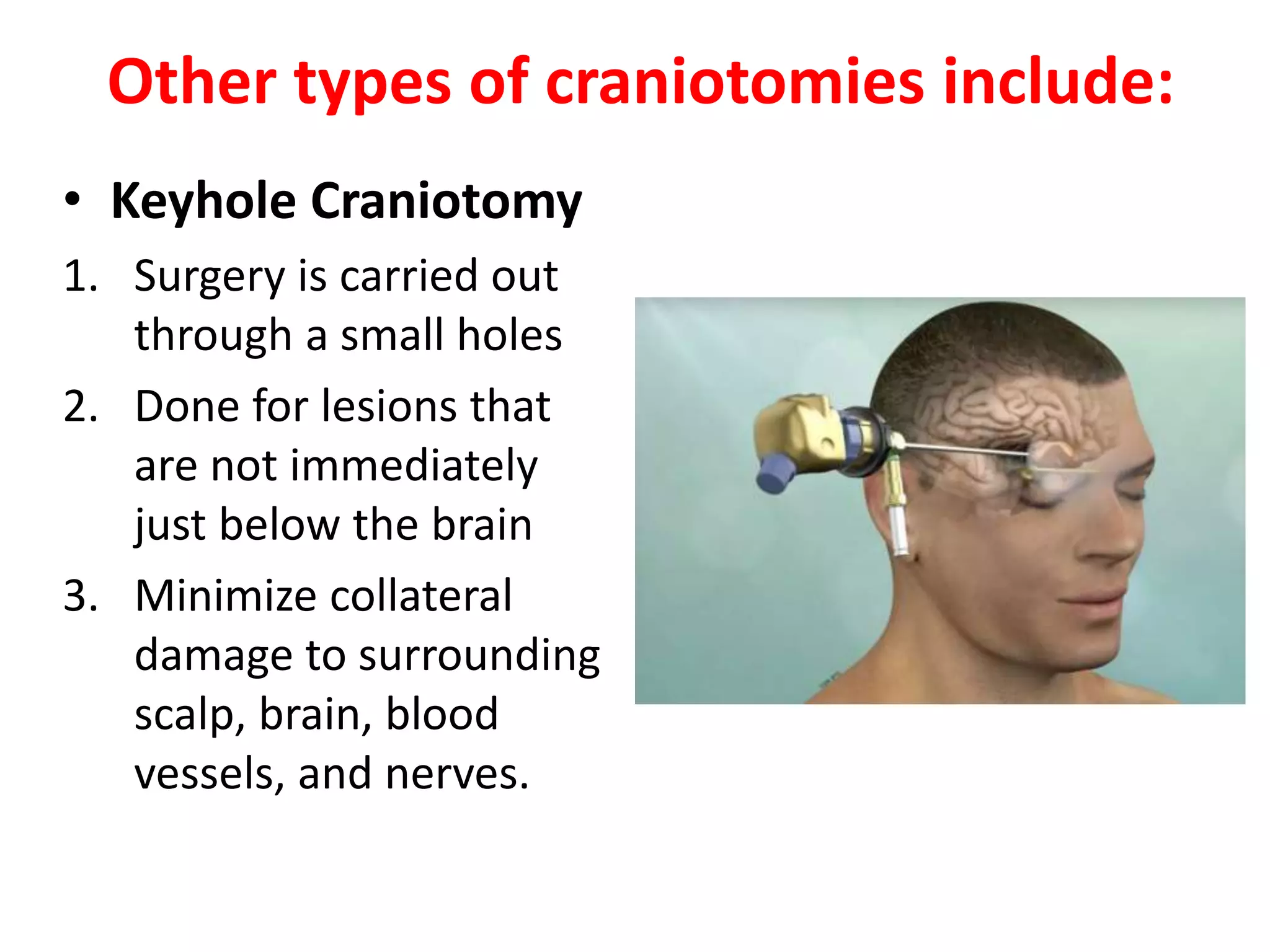
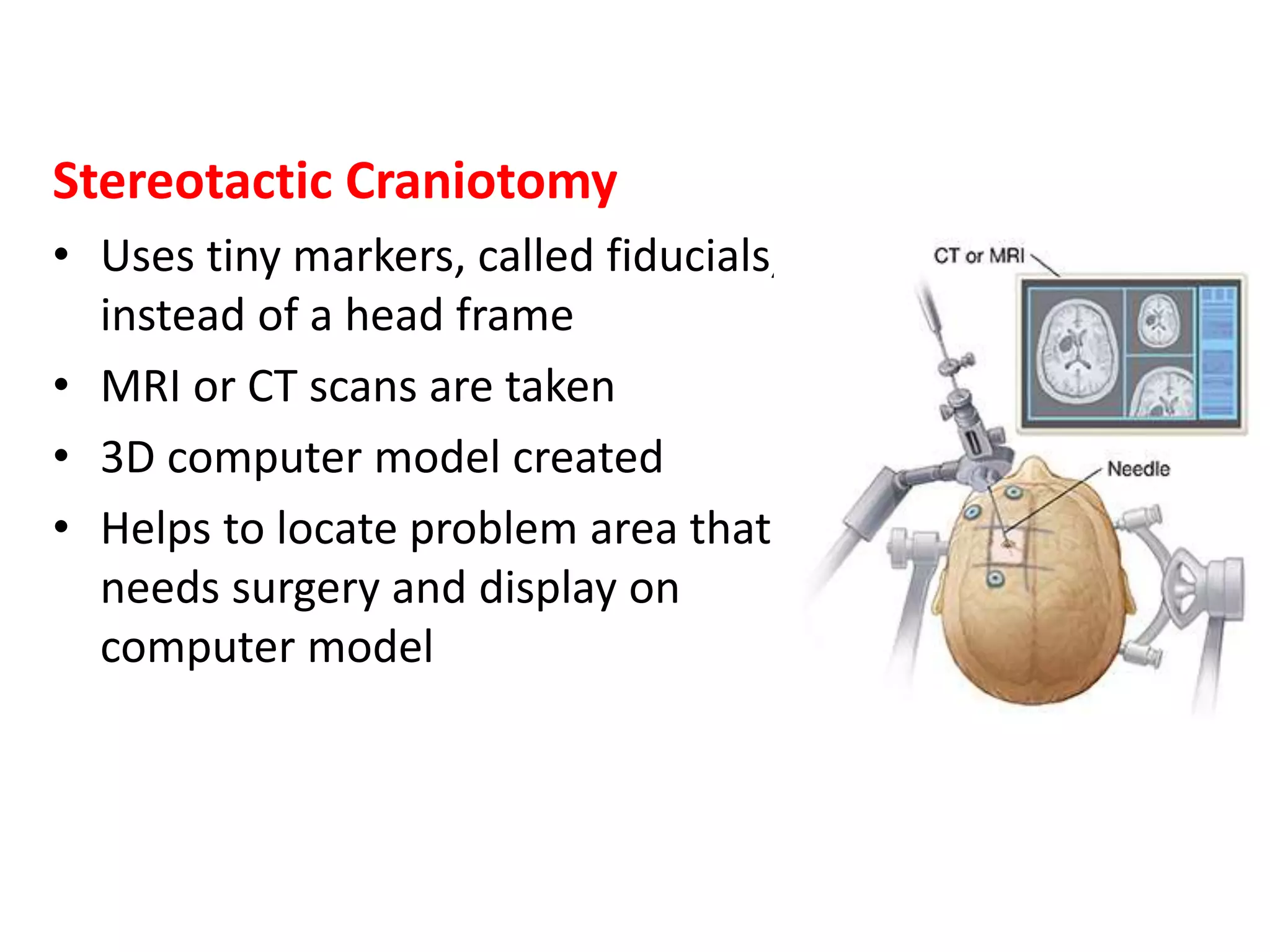
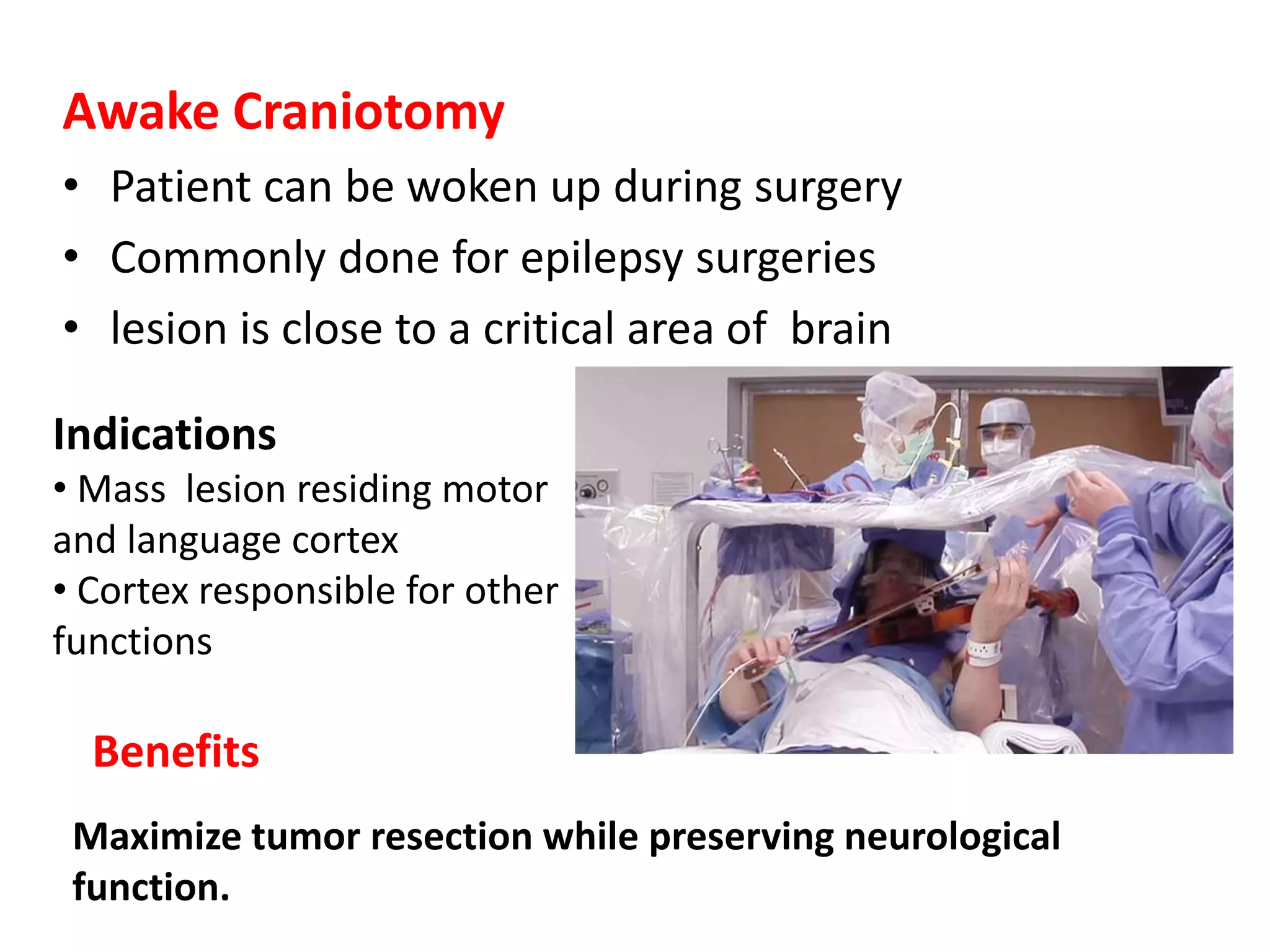
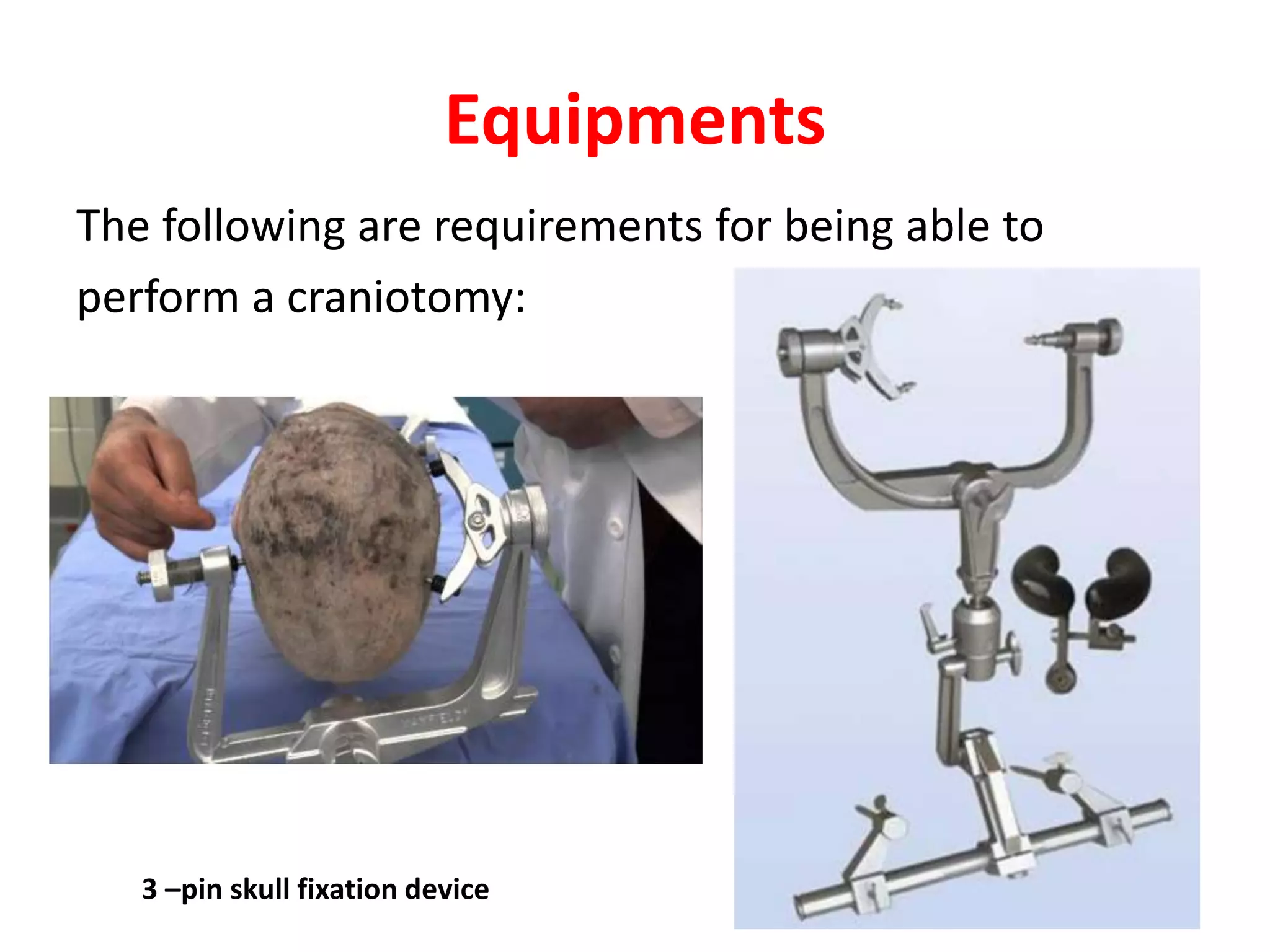
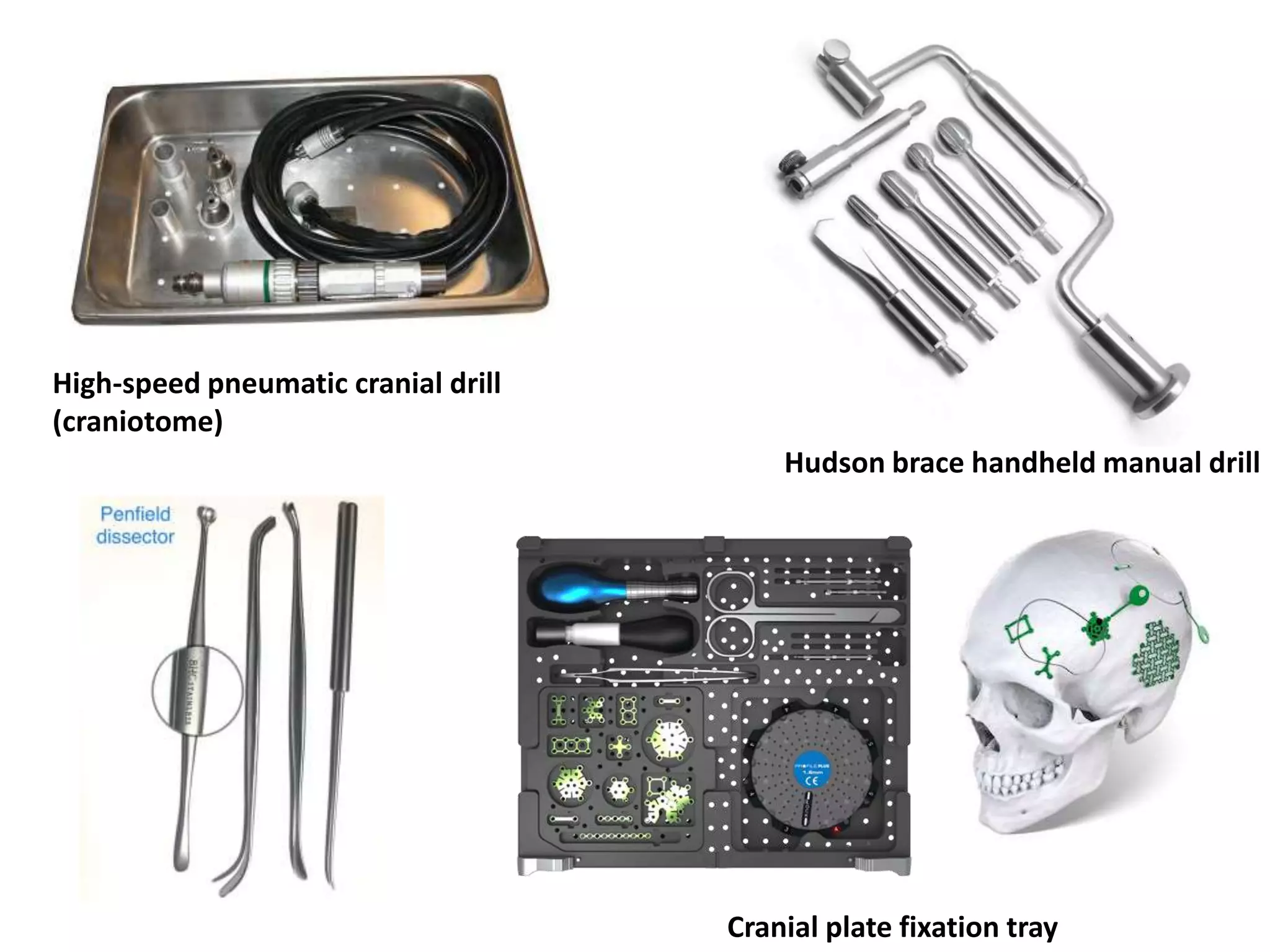
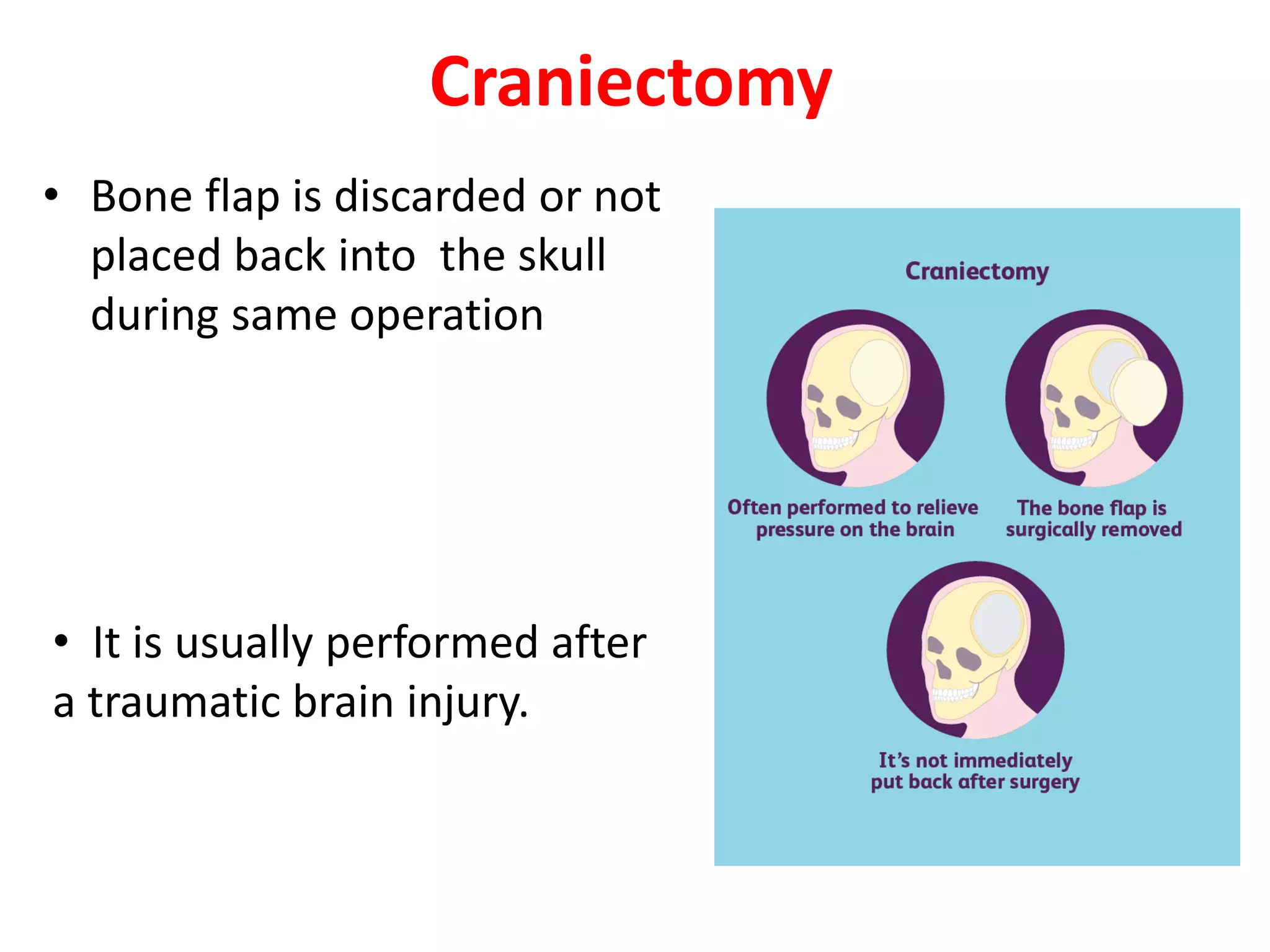
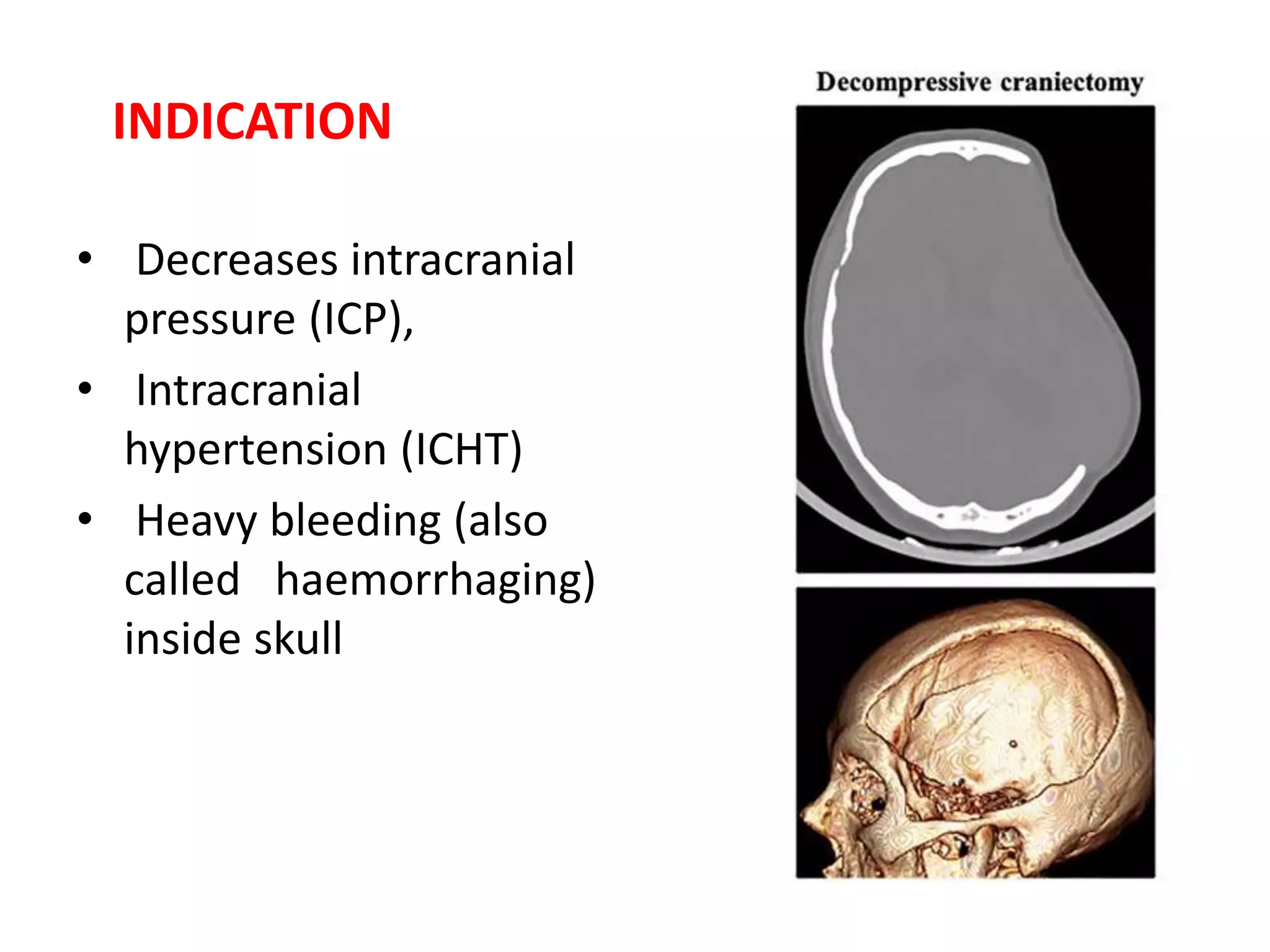
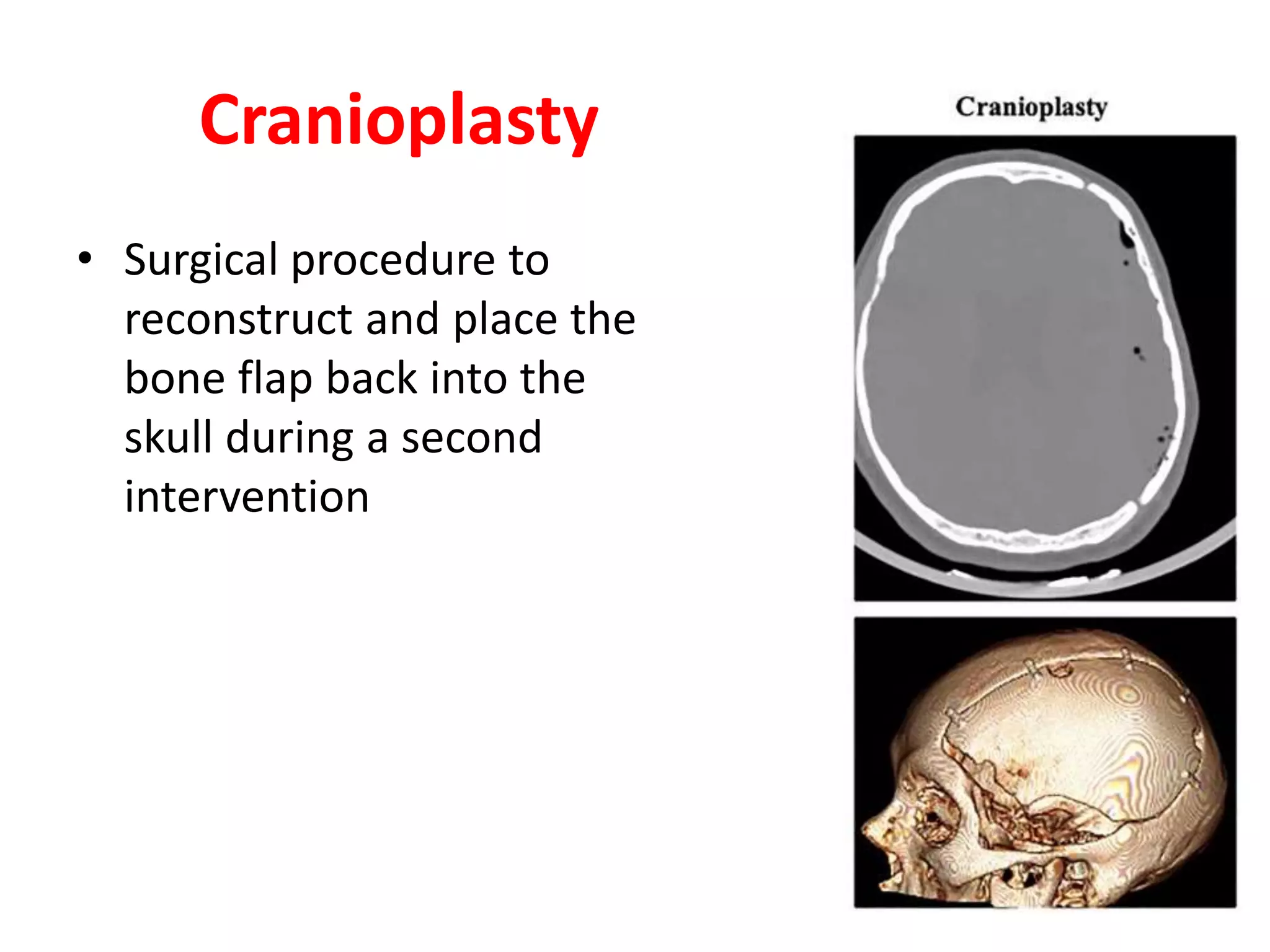
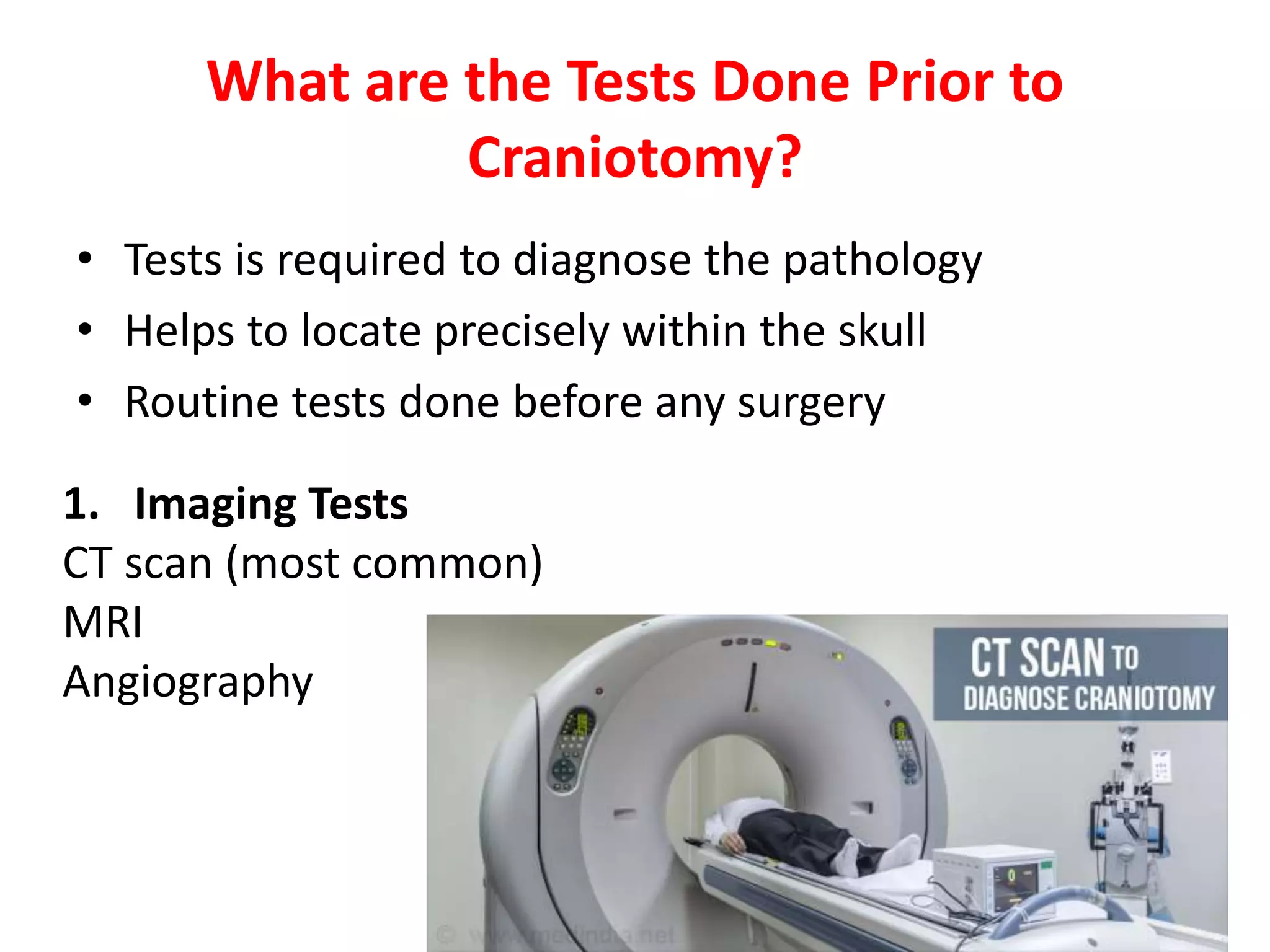
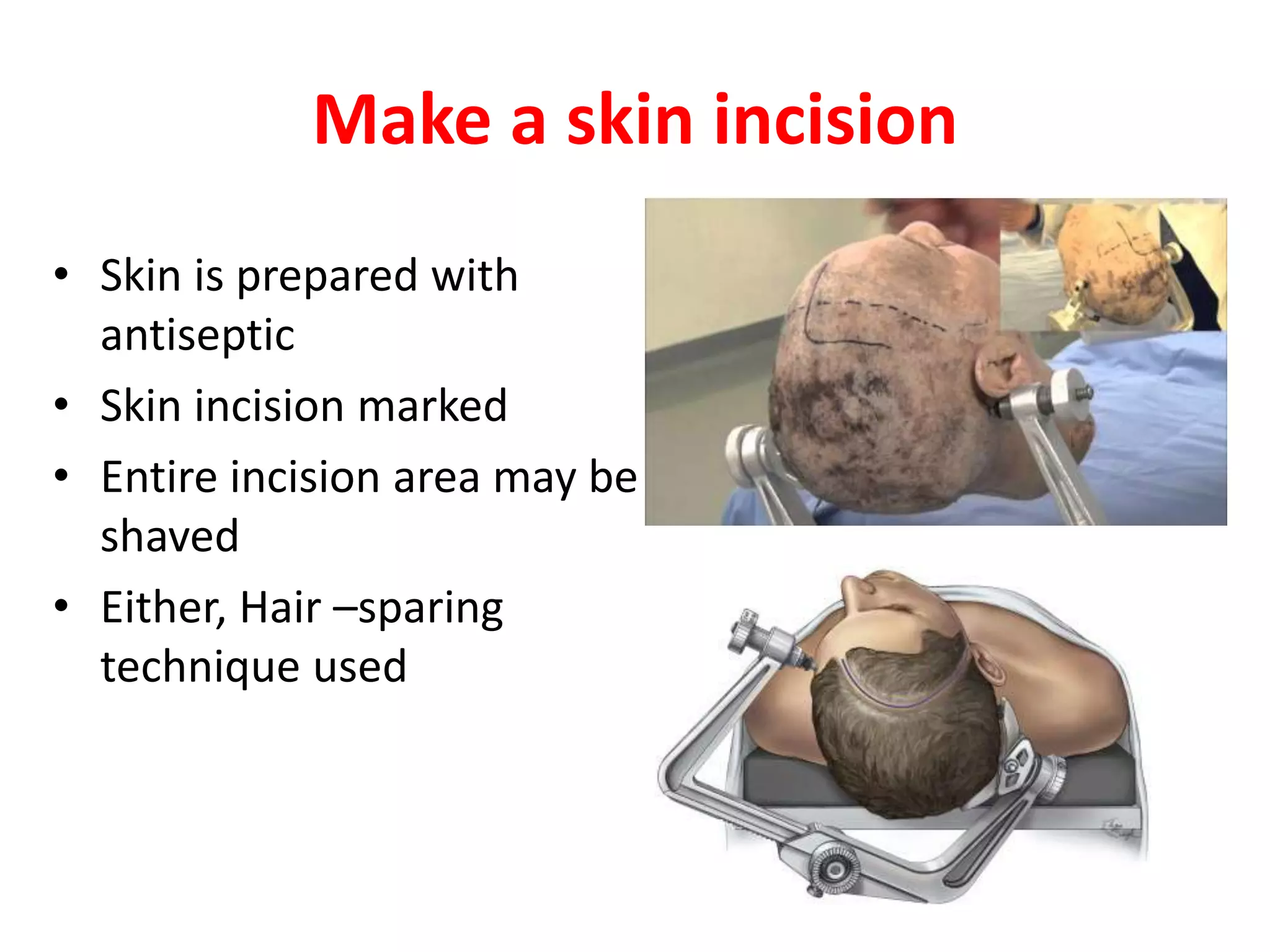
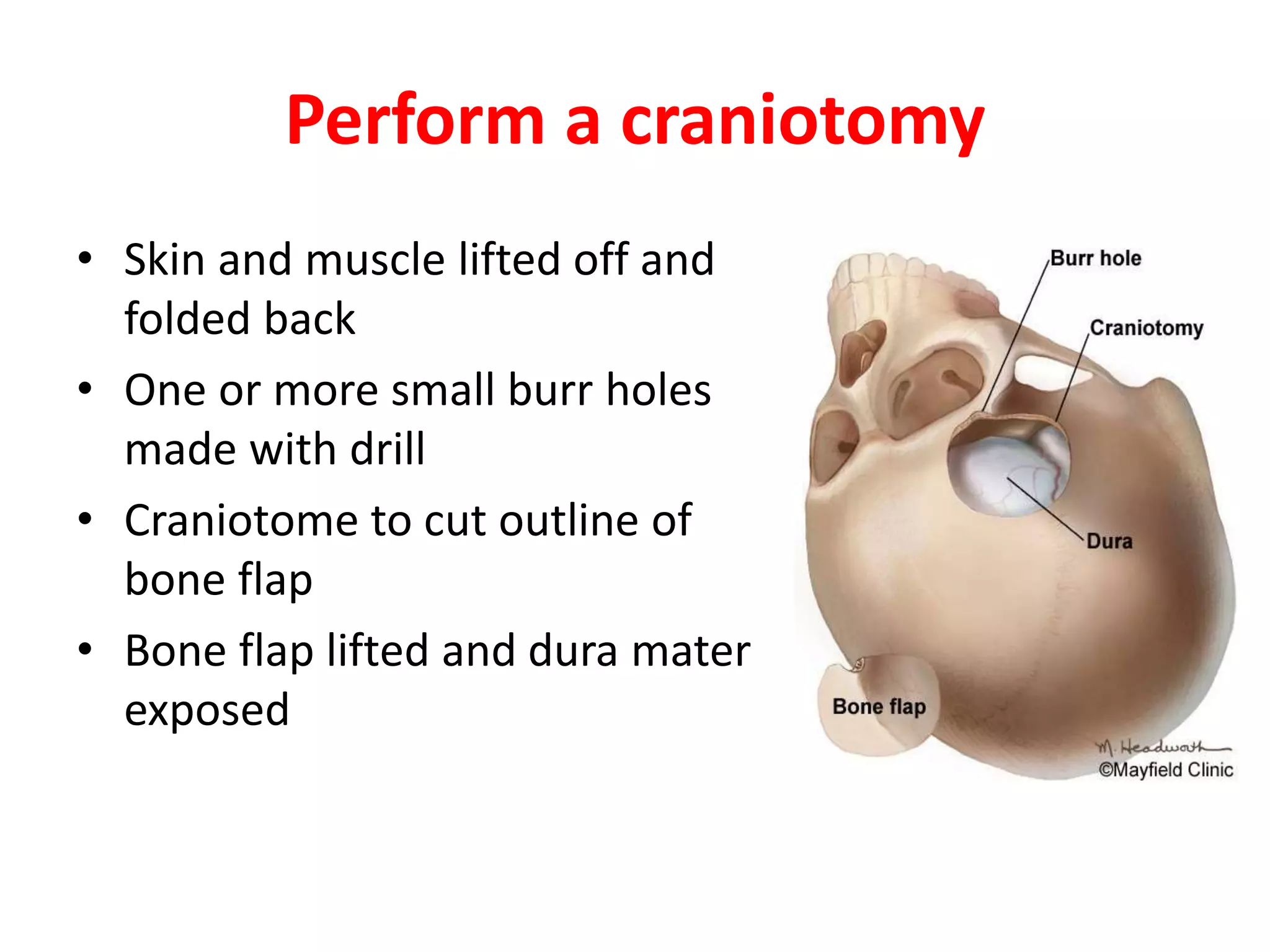
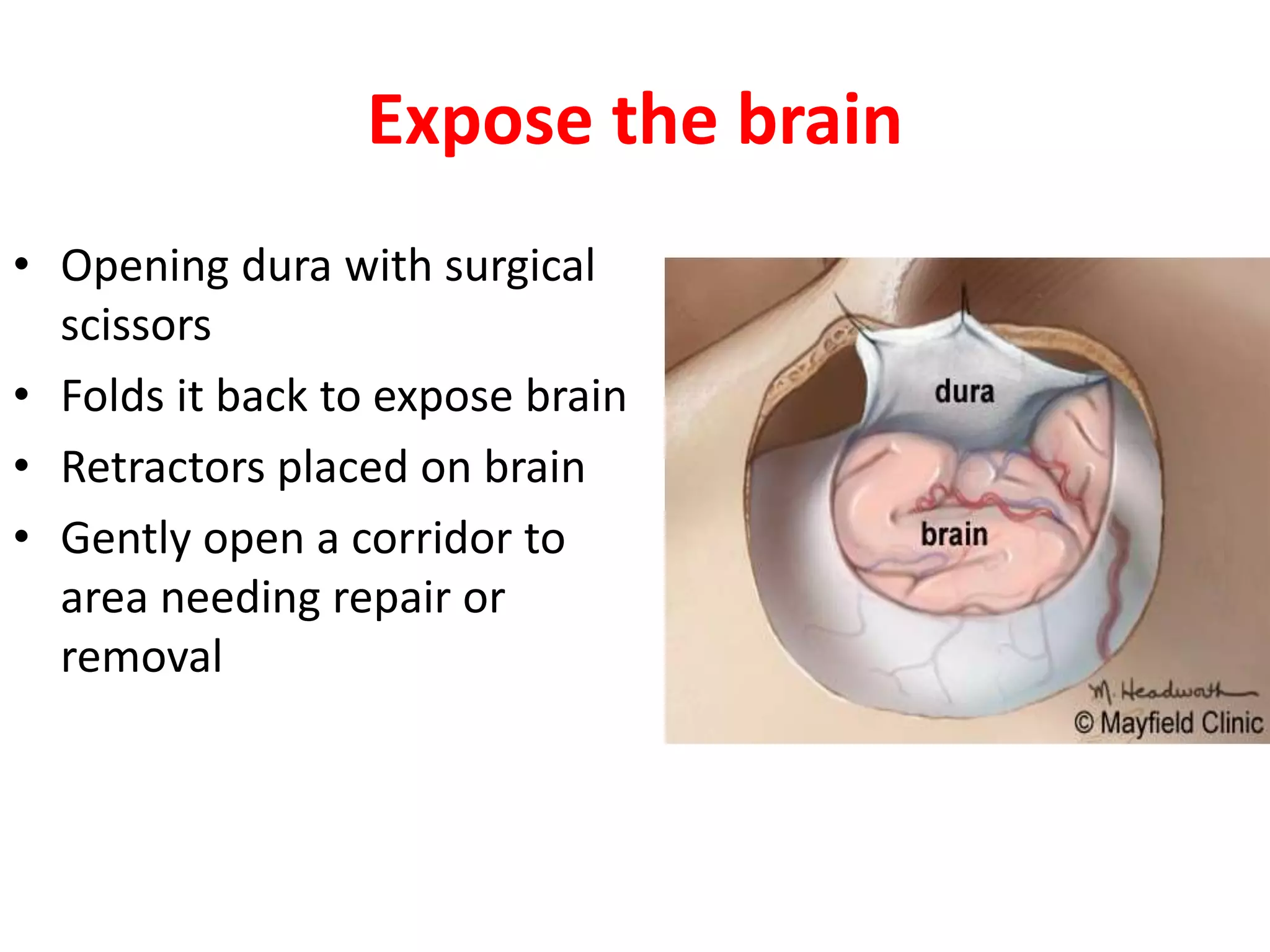
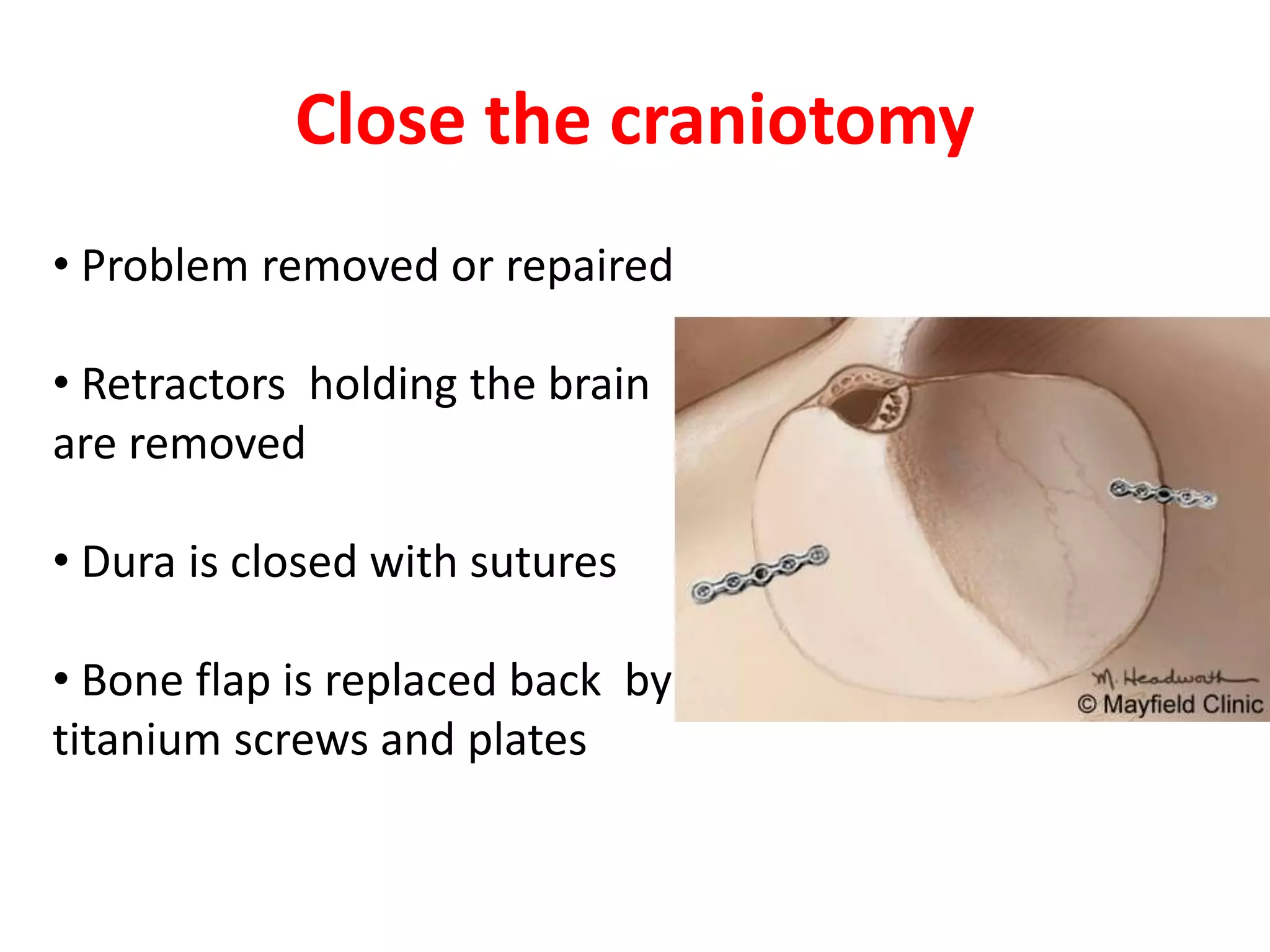
Craniotomy is a surgical procedure involving the temporary removal of a portion of the skull to access the brain for various intracranial operations, primarily indicated for brain injuries, tumors, hemorrhages, and vascular malformations. Different types of craniotomy exist based on location and technique, including minimally invasive approaches to reduce recovery time and complications. The procedure involves several critical steps and carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and neurological deficits.

















![References
• https://www.iowaclinic.com/webres/File/cran
iotomy.pdf
• Fernández-de Thomas RJ, De Jesus O. Craniotomy.
[Updated 2022 Apr 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet].
Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-
• https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-craniotomy.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/craniotomy-221121101039-c480c407/75/Craniotomy-pptx-42-2048.jpg)
