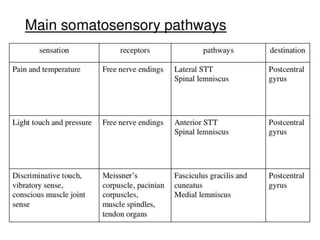
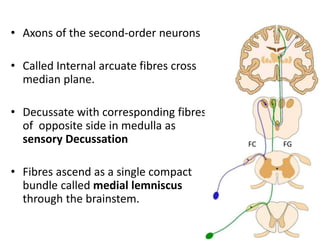
The document provides an overview of ascending tracts in the spinal cord, detailing the functions and pathways of various tracts such as the spinocerebellar, spinothalamic, and dorsal columns. It discusses clinical implications, sensory functions affected by injuries, and specific conditions like tabes dorsalis and posterior cord syndrome. Multiple-choice questions are included to assess knowledge of the spinal cord's sensory pathways and tracts.

































![• Posterior spinal artery supply the posterior funiculus
or the area in between the posterior horn.
Interruption of posterior spinal artery cause
condition posterior cord syndrome . What type of
sensation carried through posterior funinculus.
• Pain & temperature
• Crude touch & pressure
• Fine touch & two point discrimination
• No sensory tract
Fine touch & two point discrimination
Lindeire S, Hauser JM. Anatomy, Back, Artery Of Adamkiewicz. [Updated 2021 Aug 1].
In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ascendingtract1-230727140502-73c8dad0/85/ASCENDING-TRACT1-pptx-36-320.jpg)

![REFERENCES
• Snell clinical neuroanatomy 7th edition
• Khan YS, Lui F. Neuroanatomy, Spinal Cord. [Updated
2021 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island
(FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ascendingtract1-230727140502-73c8dad0/85/ASCENDING-TRACT1-pptx-38-320.jpg)
