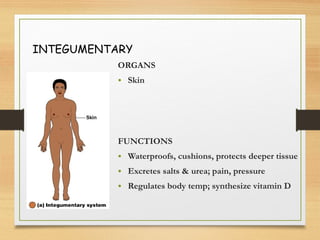
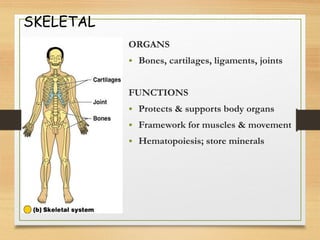
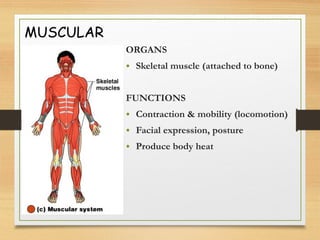
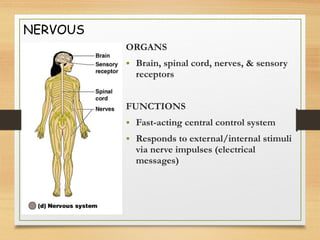
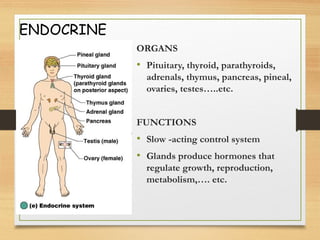
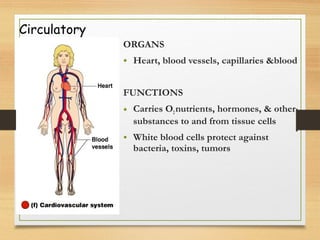
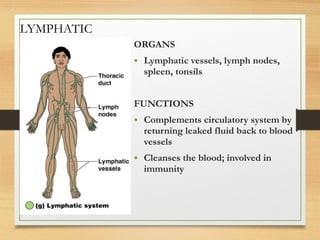
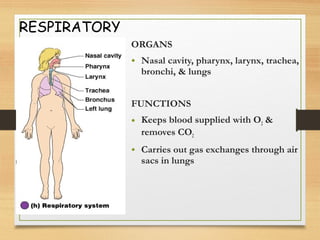
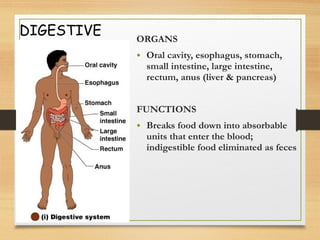
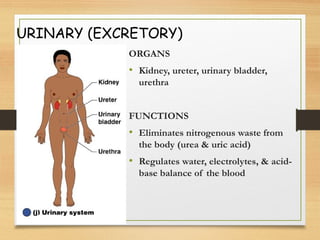
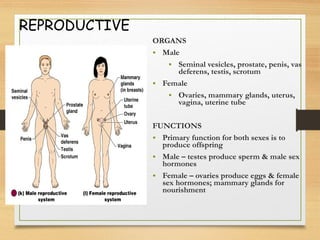
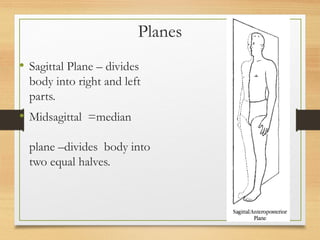
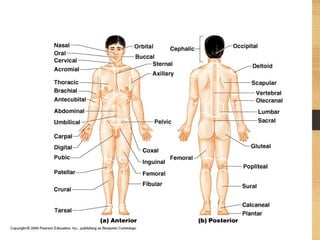
This document provides an overview of the major organ systems in the human body and their functions. It describes the integumentary system including the skin and its roles in temperature regulation, protection, and vitamin D synthesis. The skeletal system includes bones, cartilage, and joints which provide structure, protection, movement, and mineral storage. The muscular system contains skeletal muscles that allow locomotion, facial expressions, and heat production. The nervous system comprises the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and receptors which act as a control system responding to stimuli via electrical signals. The endocrine system consists of glands like the pituitary and thyroid that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction through hormone secretion.