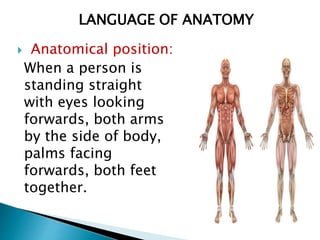
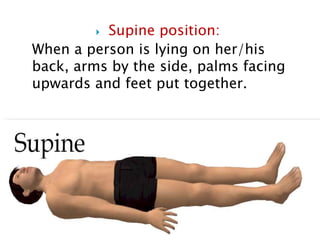
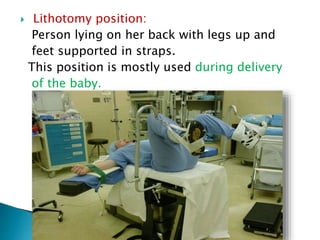
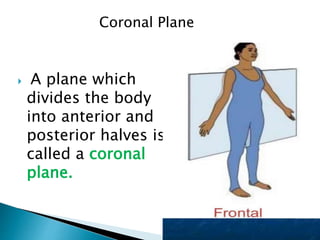
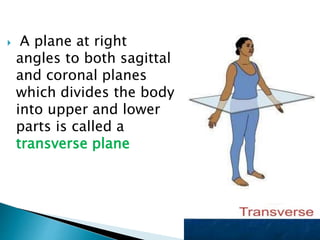
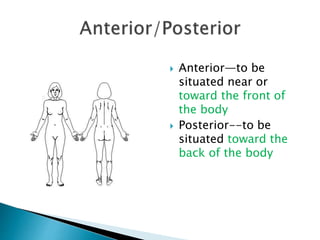
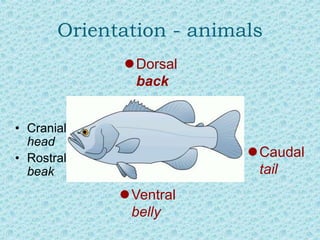
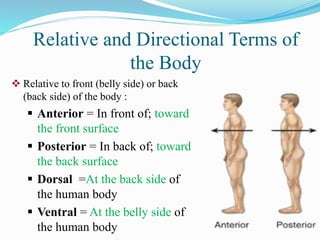
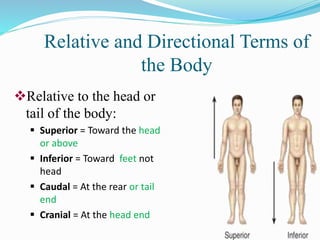
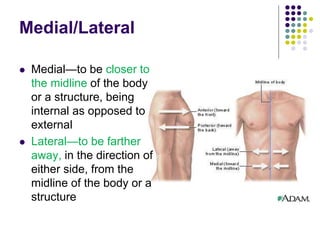
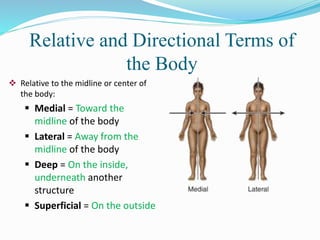
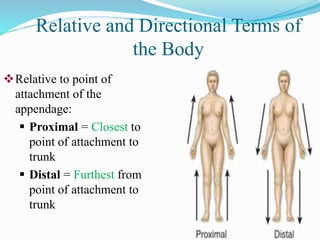
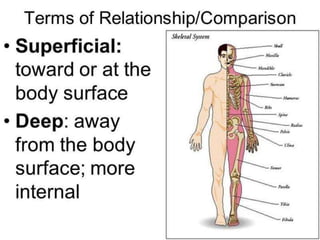
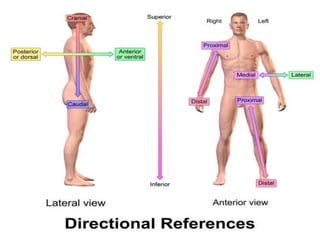
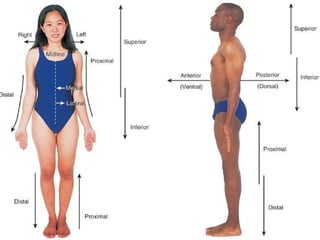
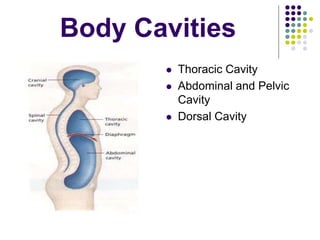
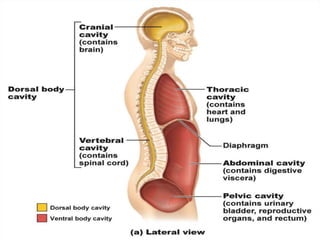
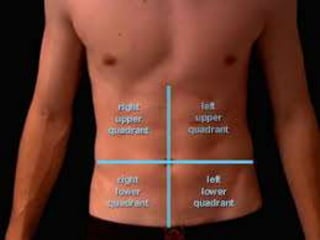
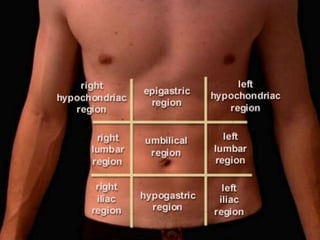
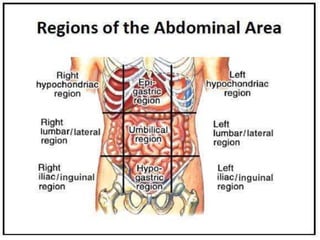
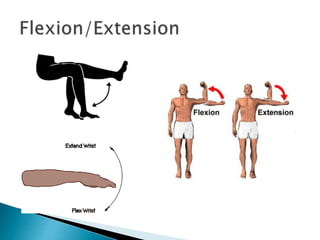
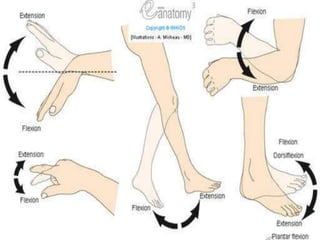
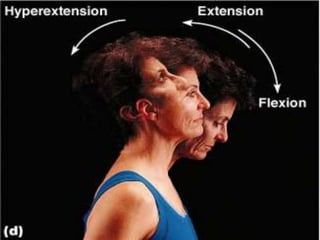
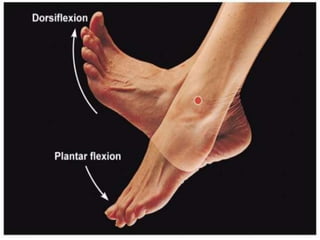
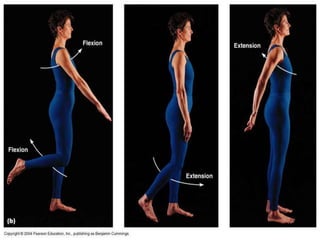
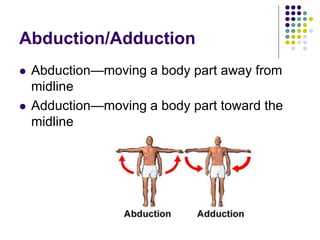
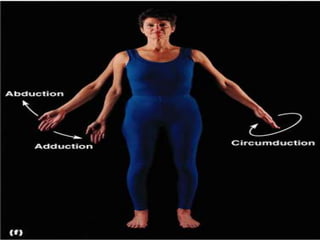
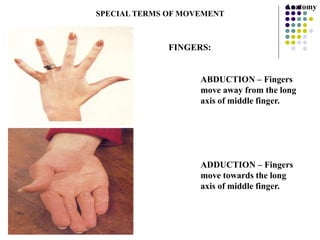
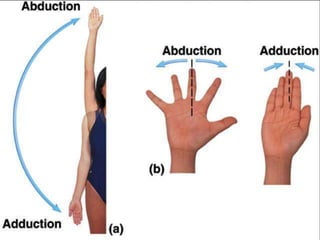
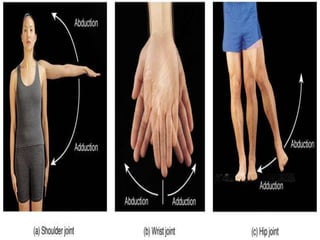
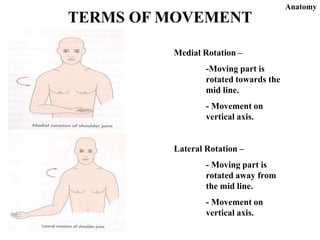
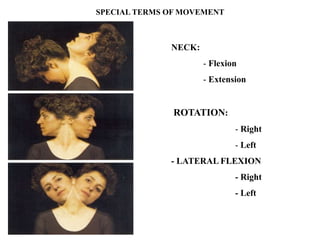
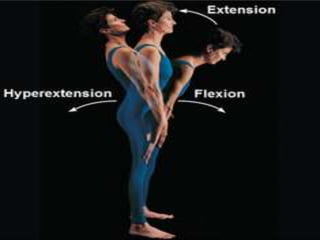
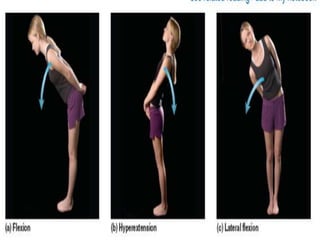
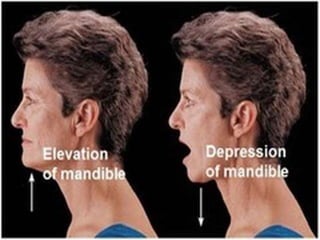
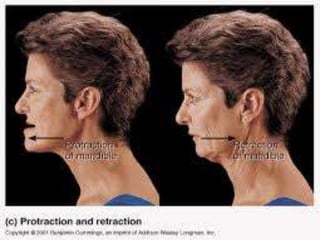
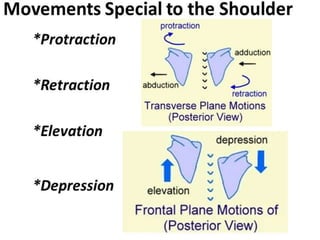
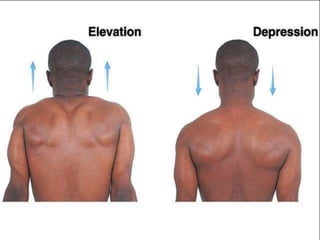
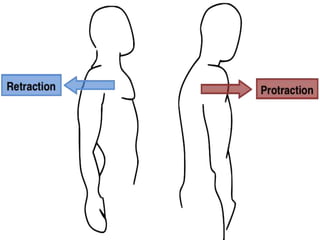
The document discusses various topics in human anatomy. It defines anatomy as the study of the structure of the human body and describes its main subdivisions. These include cadaveric anatomy, regional anatomy, systemic anatomy, and living anatomy which can be studied through inspection, palpation, and various medical imaging techniques. It also discusses embryology, histology, surface anatomy, radiographic anatomy, comparative anatomy, and applied anatomy. Finally, it outlines some key anatomical terminology, body positions, planes, and directions as well as movements like abduction, adduction, and rotation.