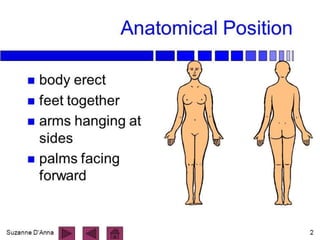
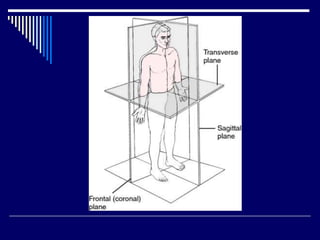
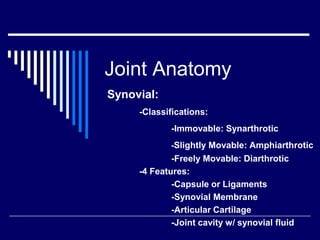
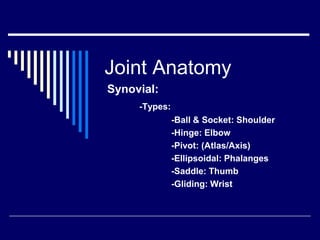
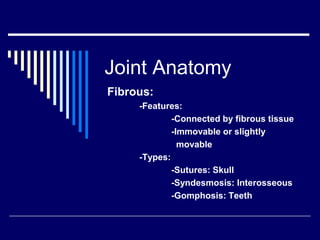
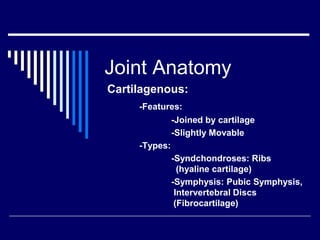
The document discusses anatomical terminology used to describe movement, directions, planes, and injuries in the body. It begins by defining the anatomical position and neutral body positioning. It then describes the three anatomical planes (sagittal, frontal, horizontal) used to view body structures. Key terms are introduced to describe directions in the body like superior, inferior, medial, lateral, anterior, and posterior. Fundamental movement terms like flexion, extension, abduction, adduction are also defined. Common injury terms and root words, prefixes, and suffixes used in anatomy are listed. Finally, the document discusses anatomy of the three main types of joints - synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous joints - and examples of each.