Embed presentation
Downloaded 205 times

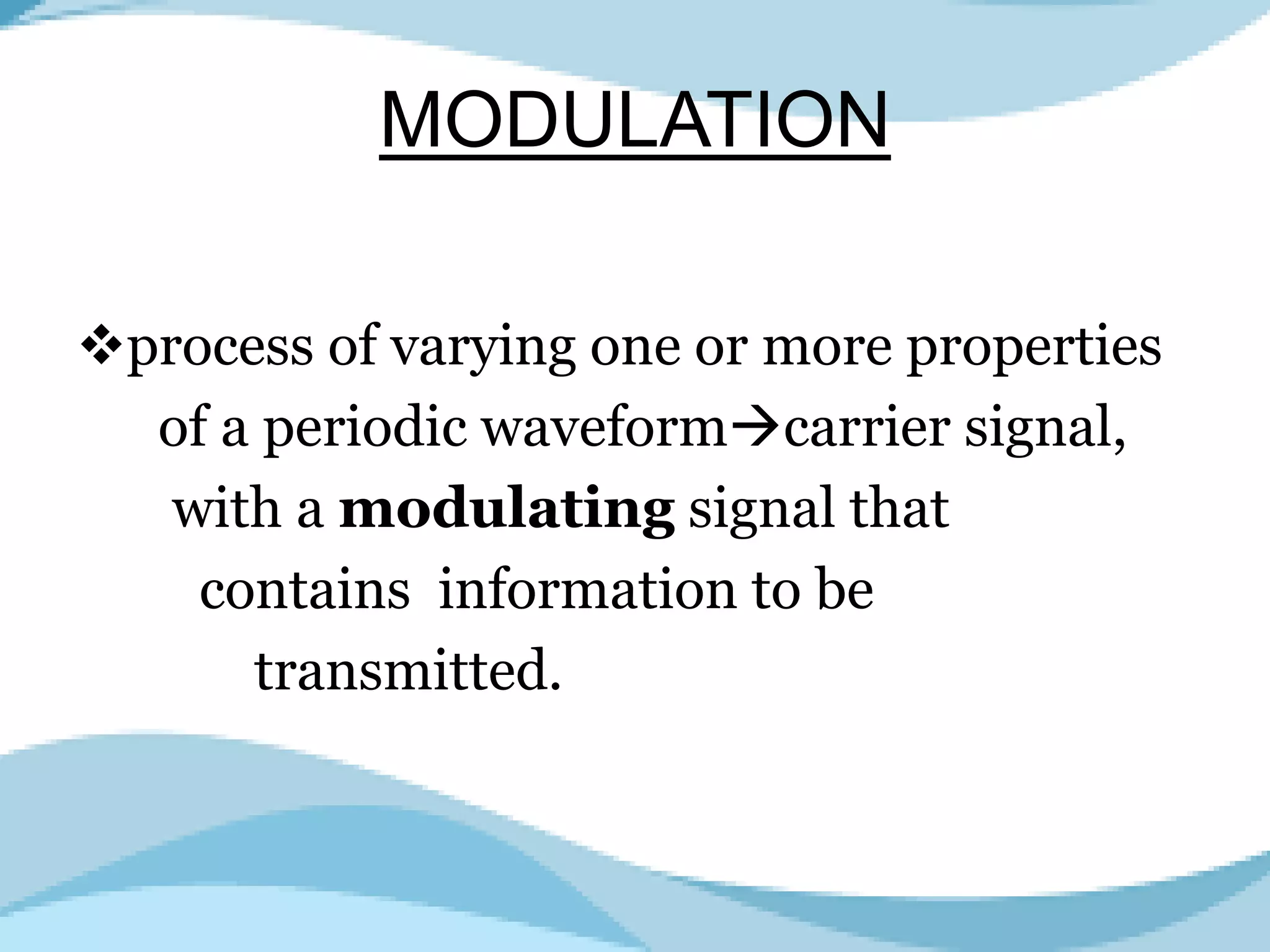
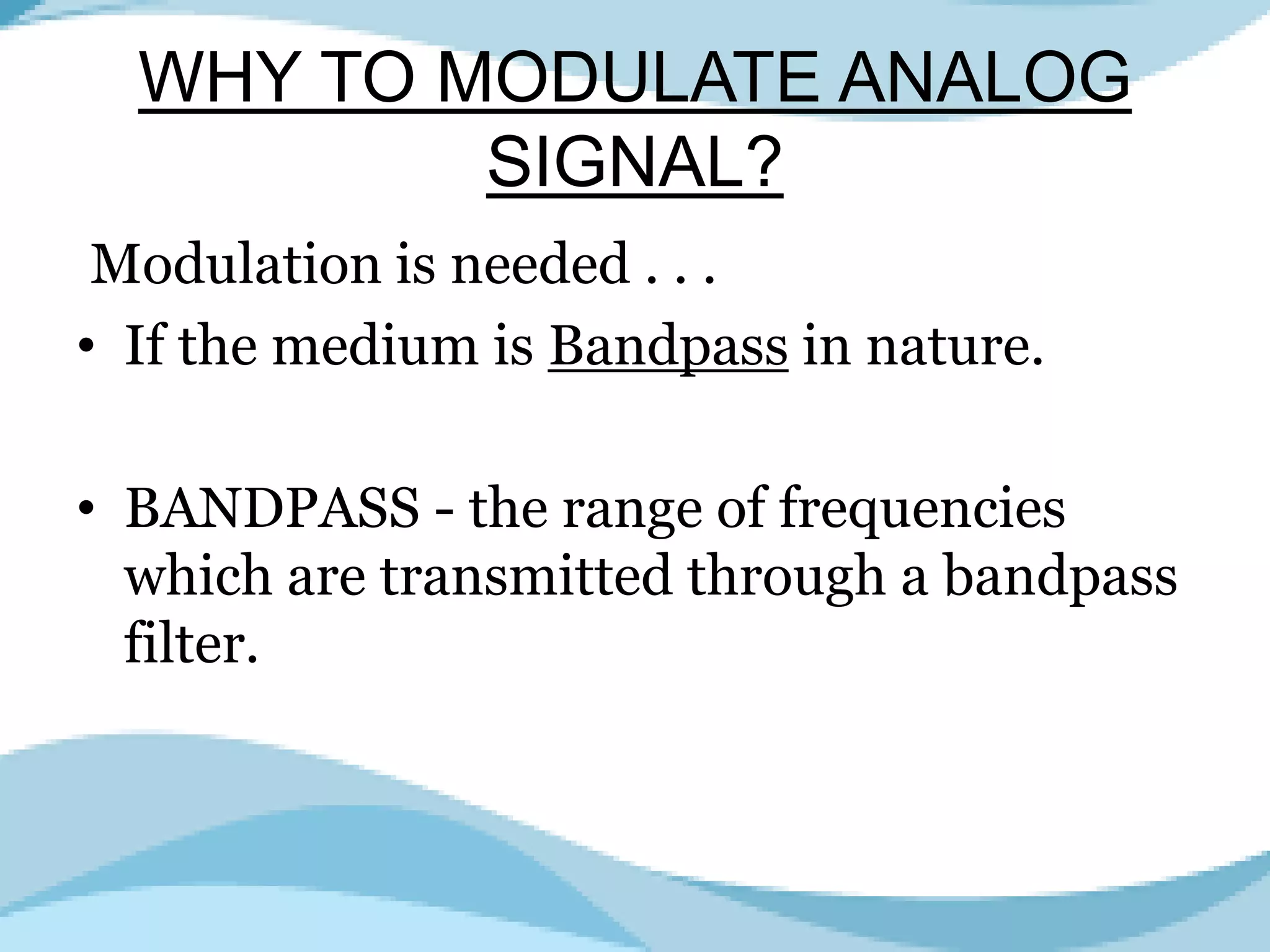


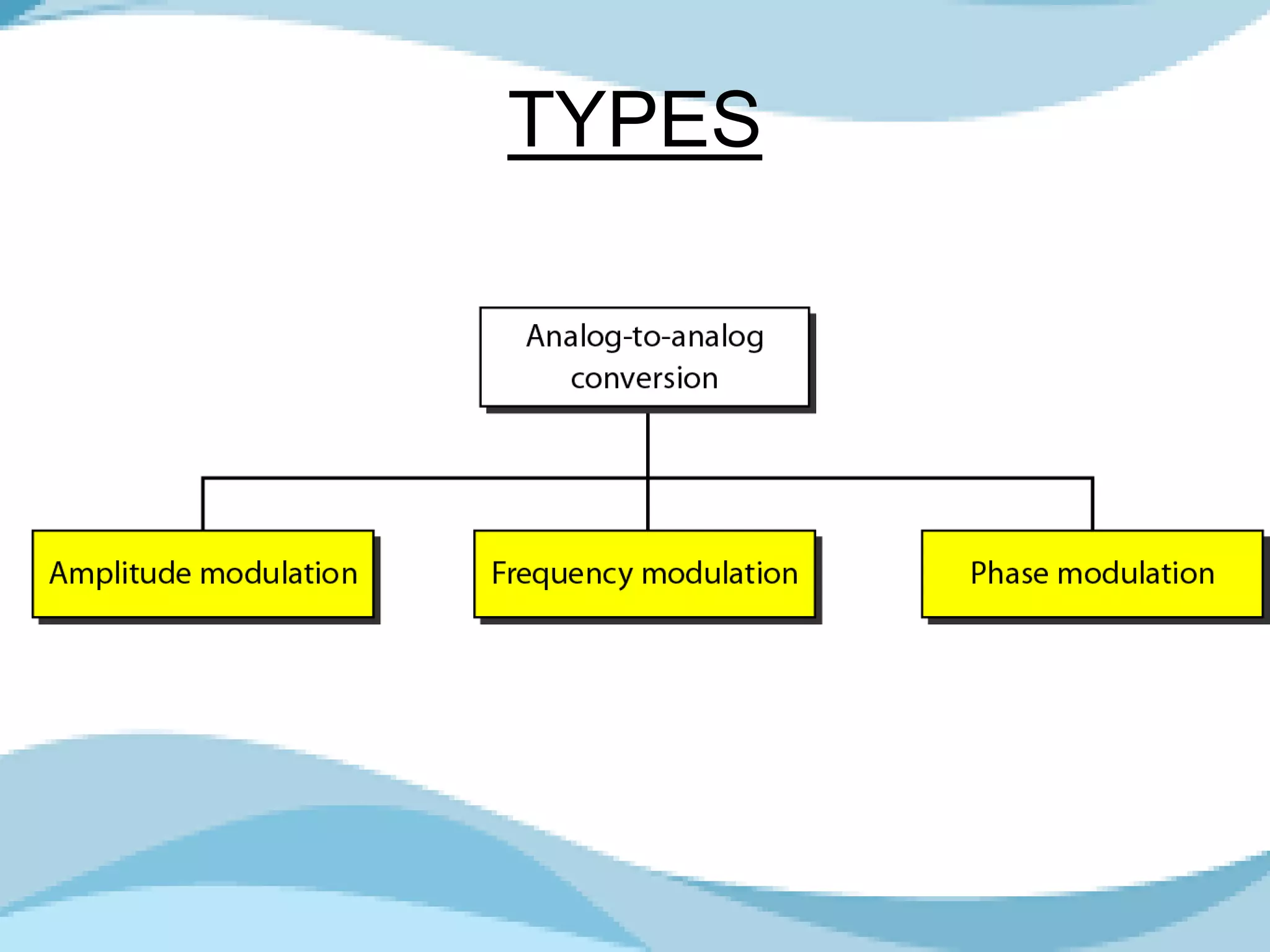
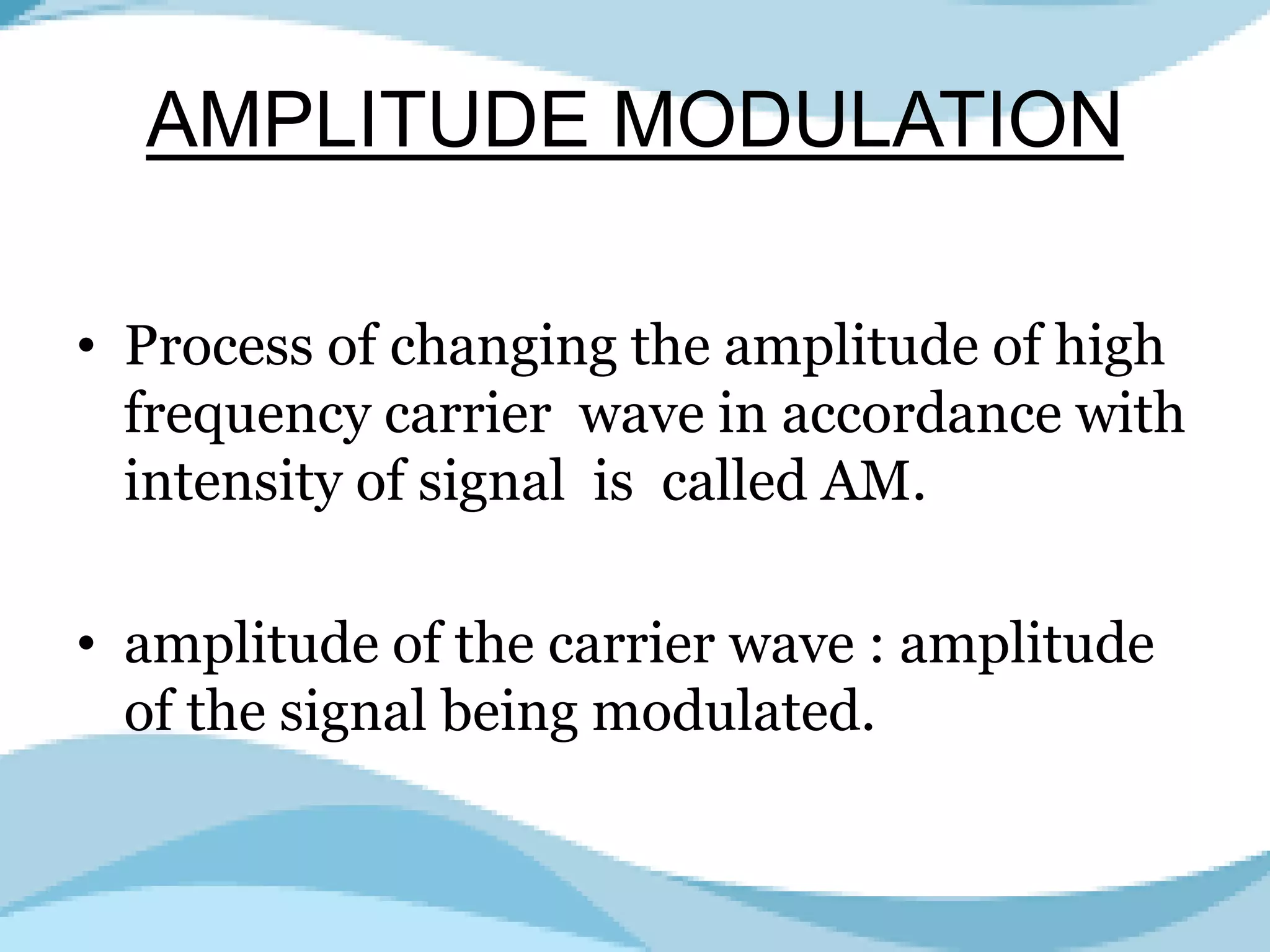
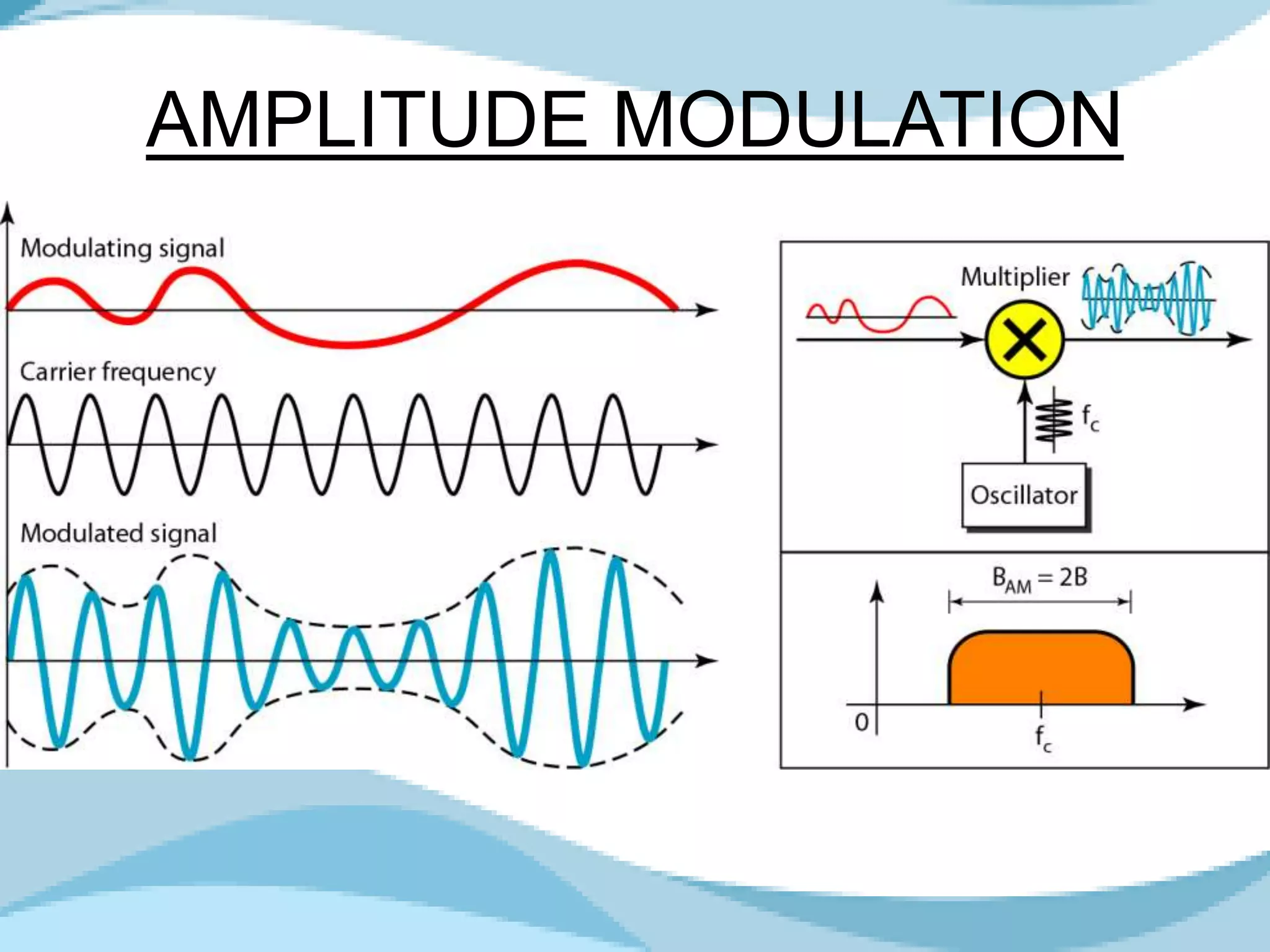



Analog to analog conversion modulation involves varying properties of a carrier signal with a modulating signal to transmit information. This is essential for bandpass mediums using filters that allow certain frequencies while blocking others. Amplitude modulation (AM) changes the amplitude of the carrier wave according to the modulating signal's intensity and is simple to implement, requiring minimal components for demodulation.
Explains analog to analog conversion, modulation process, and the need for bandpass filtering.
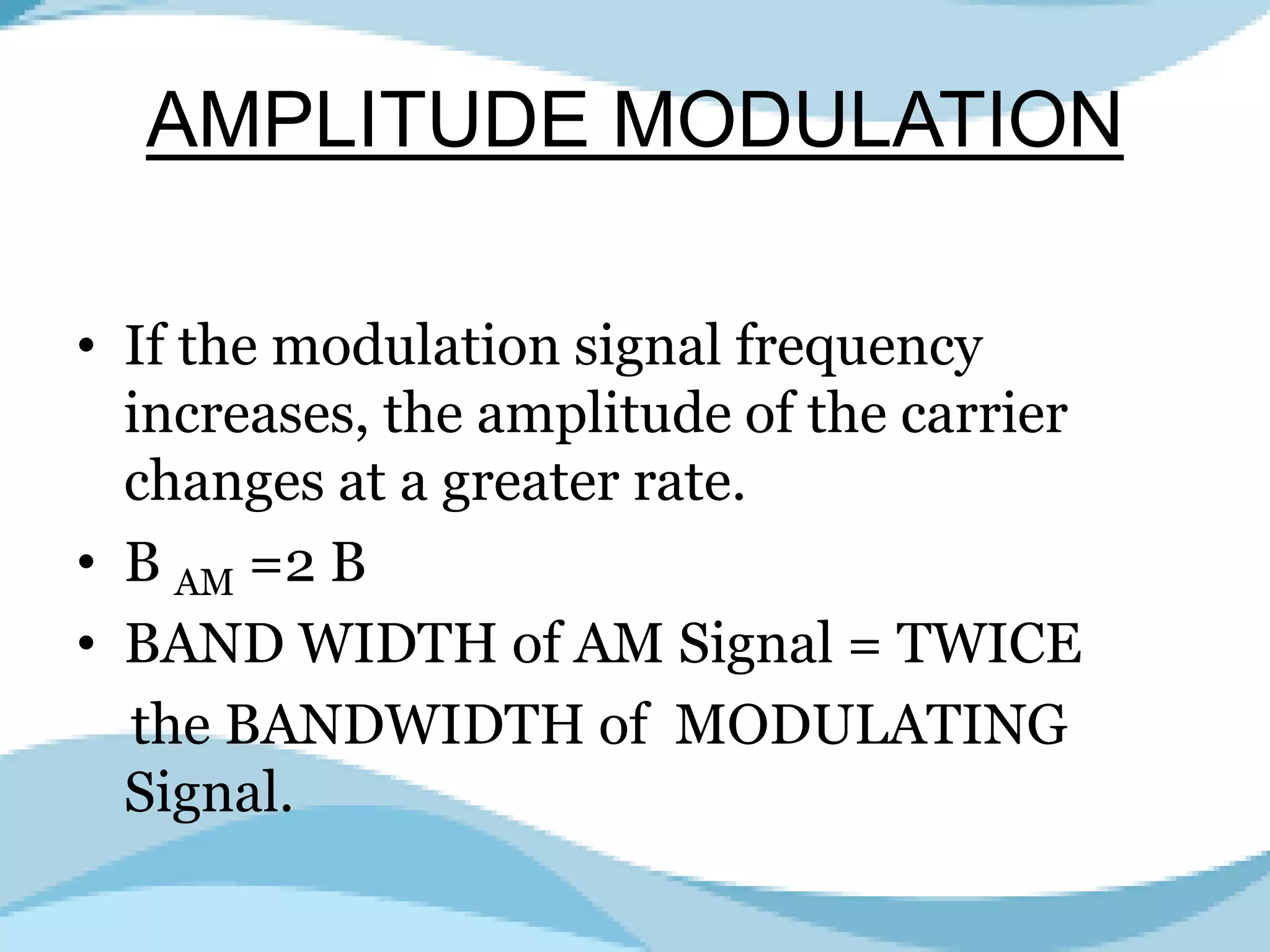
Describes Amplitude Modulation, its necessity, impact on signals, and bandwidth characteristics.
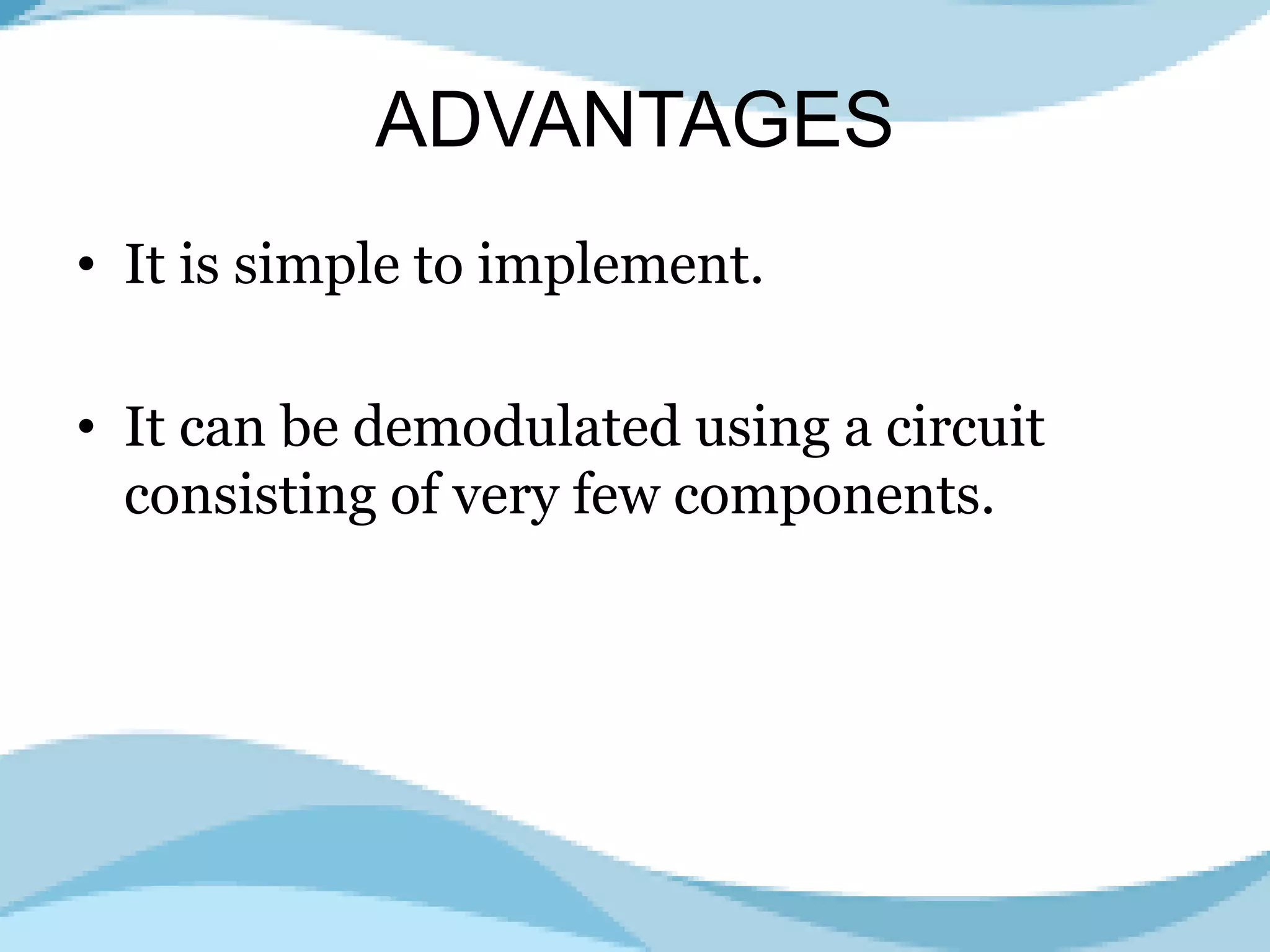
Highlights the advantages of Amplitude Modulation including simplicity and ease of demodulation.












