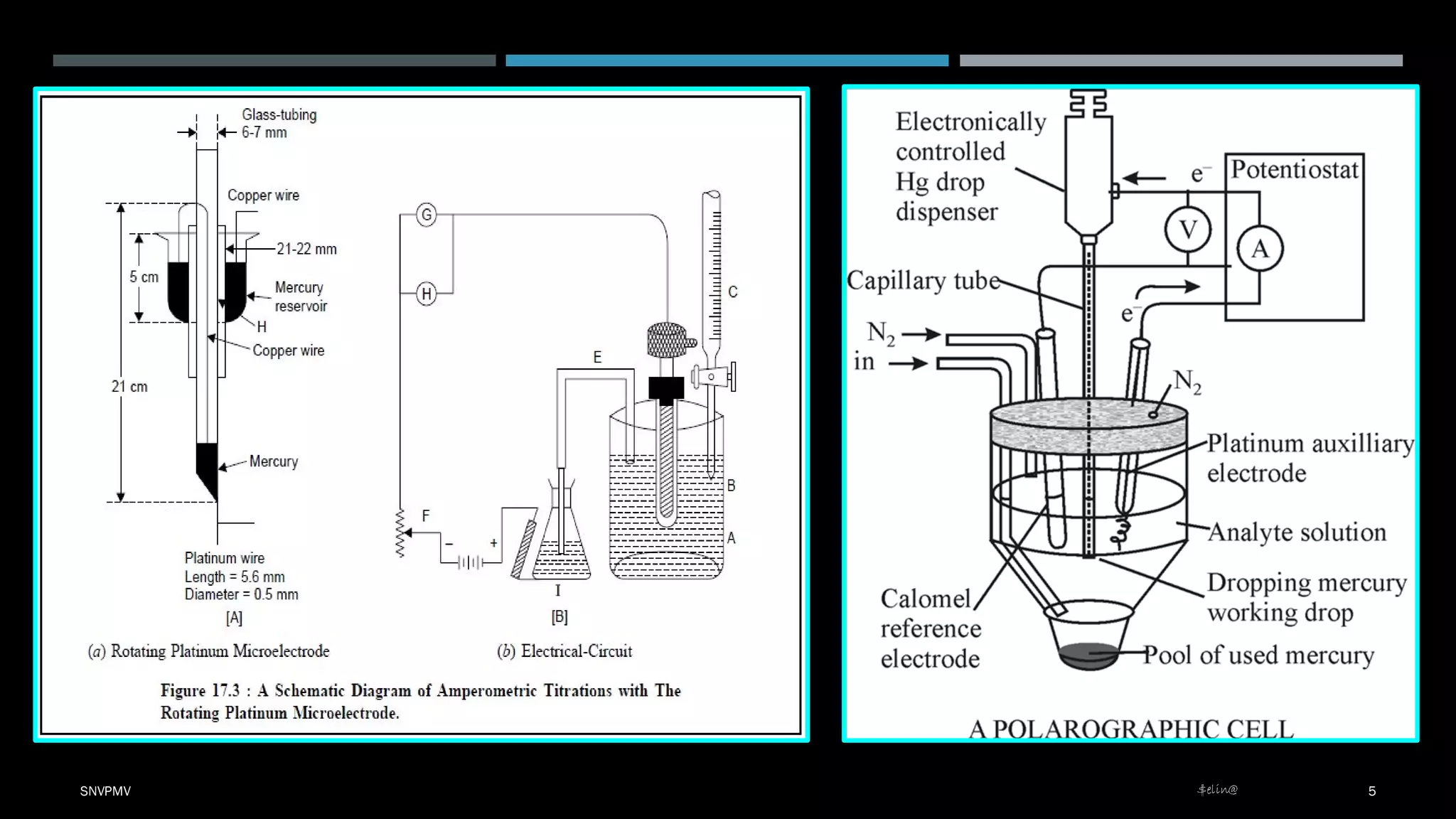
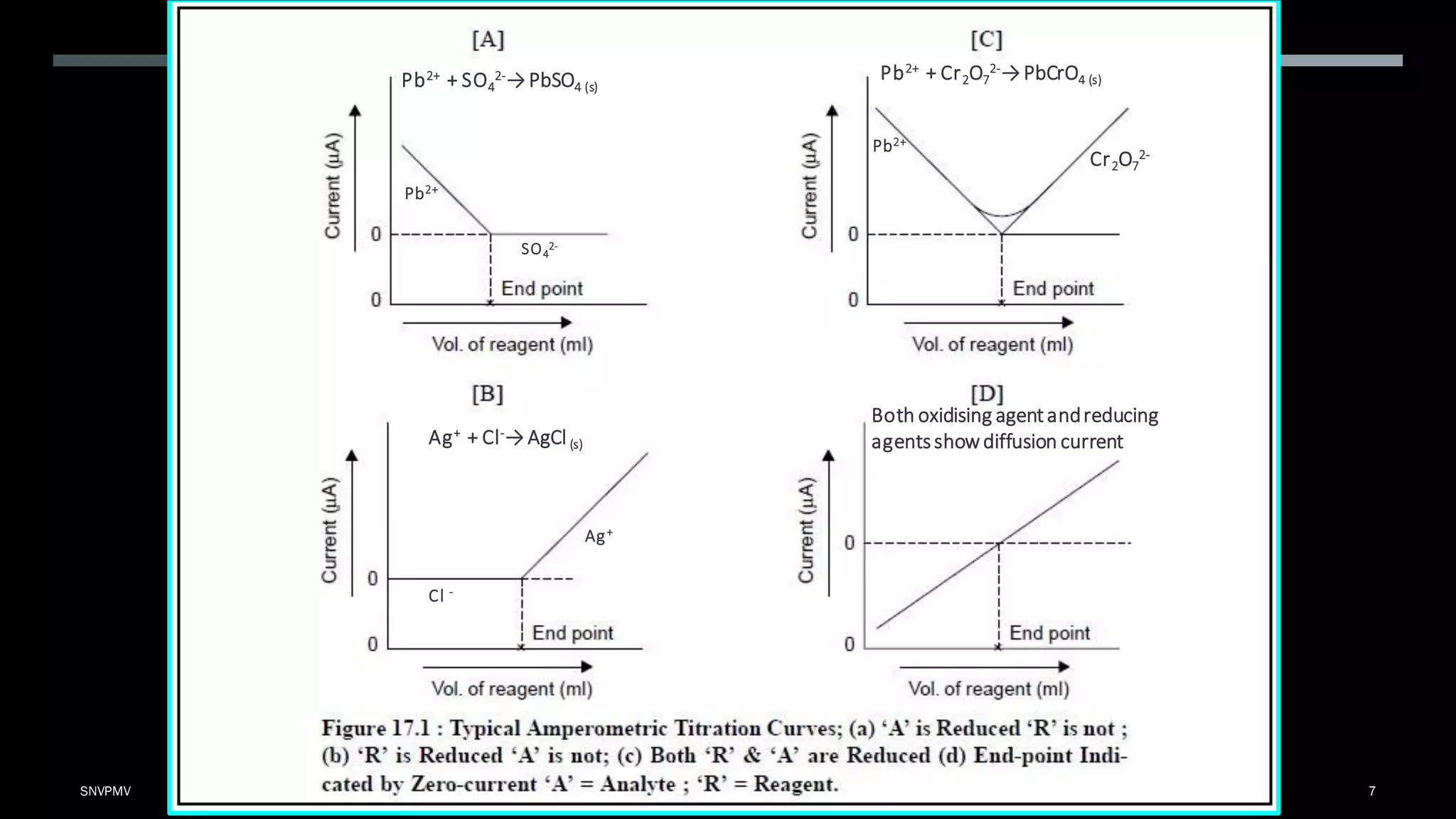
Amperometric titration is a technique where the potential between a polarizable working electrode and a non-polarizable reference electrode is kept constant. During titration, the diffusion current is measured, which changes as the concentration of the electroreducible ion changes. At the endpoint, there is a sharp change in the diffusion current. Amperometric titrations can be performed between an electroreducible ion and a non-electroreducible ion, or between two electroreducible ions. The titration conditions require that the titrant, titrate, or both be electroreducible, and the applied potential corresponds to the limiting current.







![DETERMINATION OF WATER USING KARL FISCHER TECHNIQUE
◘ Karl Fischer titration is a widely used analytical method for quantifying watercontentin a variety of products.
ROH + SO2 + R’N → [R’NH]SO3R + H2O + I2 + 2R’N → 2[R’NH]I + [R’NH]SO4R
[alcohol] [base] [alkylsulfite salt] [water] [iodine] [hydroiodic acid salt] [alkylsulfate salt]
◘ The alcohol reacts with sulfur dioxide (SO2) and base to form an intermediate alkylsulfitesalt, which is then
oxidized by iodine to an alkylsulfate salt.
◘ This oxidation reaction consumes water.
◘ The reactive alcohol is typically methanol or 2-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)ethanol, alsoknown as diethylene glycol
monoethyl ether (DEGEE), or another suitable alcohol.
◘ Classic Karl Fisher reagentscontainedpyridine, a noxious carcinogen, as the base. The reagentsmost
frequently used today are pyridine-free and containimidazole or primary amines instead.
◘ Water and iodine are consumed in a 1:1 ratio in the abovereaction.
◘ Once all of the waterpresent is consumed, the presence of excess iodine is detected amperometrically by
the titrator’s indicatorelectrode (double platinumelectrode). That signals the end-point of the titration.
◘ The amount of water present in the sample is calculatedbased on the concentration of iodine in the Karl
Fisher titrating reagent (i.e., titer) and the amount of Karl Fisher Reagent consumed in the titration.
SNVPMV $elin@ 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amperometry-200508084547/75/Amperometry-10-2048.jpg)



