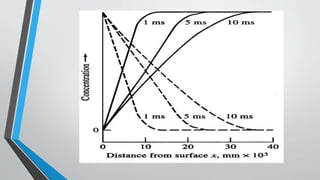
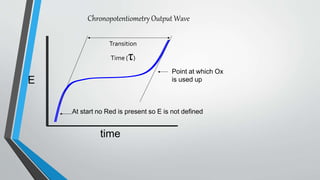
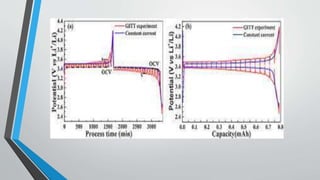
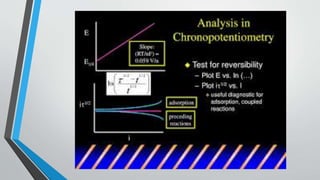
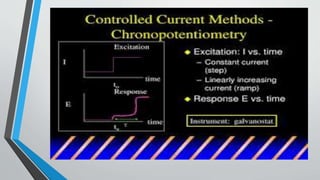
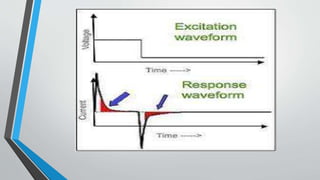
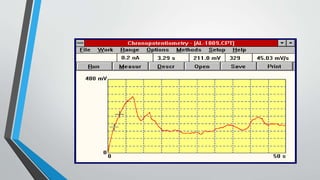
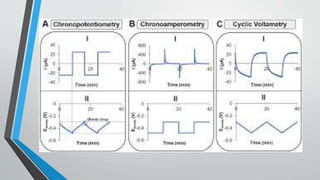
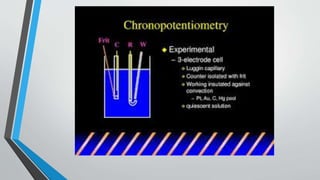
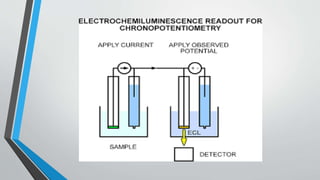
Chronopotentiometry is an electrochemical technique that applies a constant current between electrodes and measures the potential over time. It can be used to investigate electroporation of bilayer lipid membranes. When a constant current is applied, the potential gradually changes as oxidation and reduction reactions occur at the electrodes. Ultimately, the concentration of one species is depleted at the electrode surface, causing a rapid change in potential. Chronopotentiometry provides simple information about membrane pores but is not well-suited for studying capacitive currents.


![Theory of Chronopotentiometry
•A gradual change in E occurs as [Red] goes up and [Ox] goes
down (transition region) Ultimately the surface concentration of
Ox goes to zero & to sustain the constant current applied,
electrode potential makes a rapid change to the value required to
make a new process go](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronopotentiometry-210430140451/85/Chronopotentiometry-6-320.jpg)