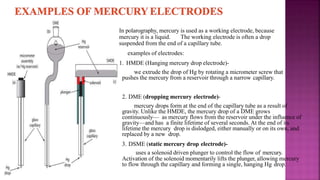
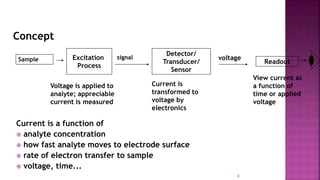
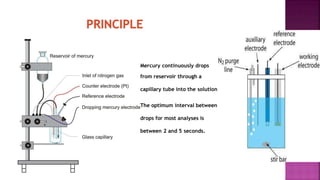
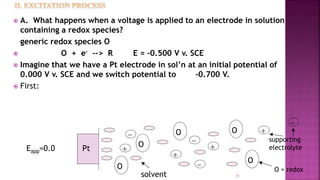
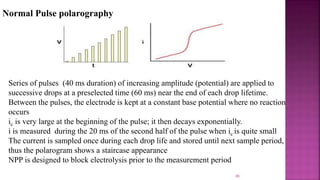
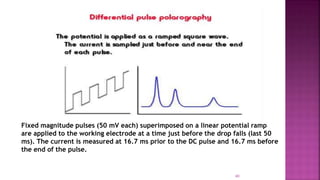
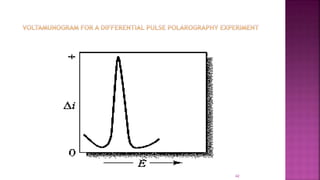
This document discusses polarography, which is a technique for analyzing solutions using two electrodes - a dropping mercury working electrode and a reference electrode. It provides details on:
1. How polarography works by applying a voltage to induce a redox reaction and measuring the resulting current.
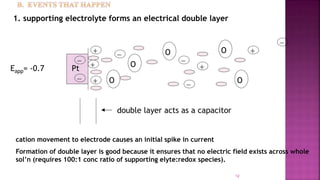
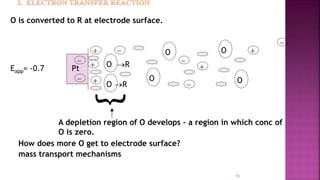
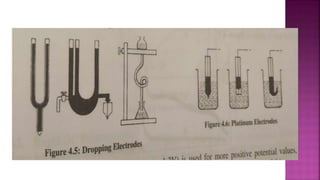
2. The components needed, including the dropping mercury electrode, reference electrode, and a supporting electrolyte.
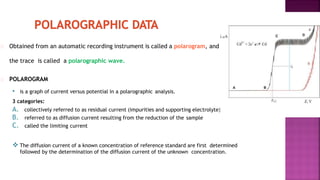
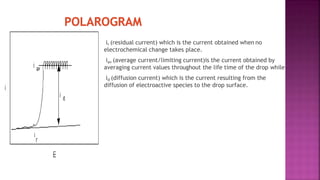
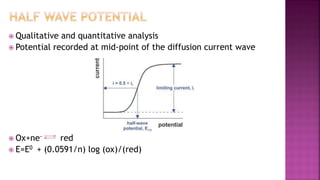
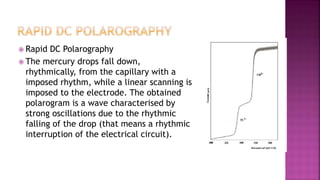
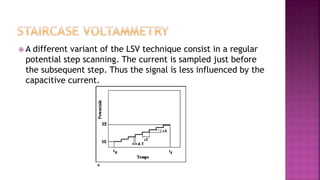
3. How polarograms are generated by plotting current vs. applied voltage and the different regions that can be seen on a polarogram.
4. Factors that influence the diffusion current measured, such as concentration of the analyte, diffusion coefficient, and drop lifetime. Equations for calculating diffusion current are also presented.