Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a potentiodynamic electrochemical measurement that involves the linear ramping of a working electrode's potential to study redox processes and electron transfer reactions in a solution. The technique utilizes a three-electrode system comprising a working electrode, reference electrode, and counter electrode, each serving distinct roles in measuring current and potential in electrochemical experiments. The document details types of CV, the setup of an electrochemical cell, and a practical lab experiment demonstrating the method using specific reagents and conditions.



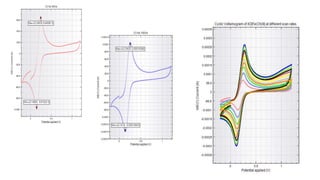
![Understanding : A Voltammogram & “Duck Shape”
• Here, the traces are called as voltammograms.
• When sweeped in the positive direction we get the anodic trace and in the negative
direction we get the cathodic trace.
• Lets consider the reaction
• [Fe(CN)6]3- + e- ⇌ [Fe(CN)6]4-
• At the starting potential, no current flows. If an oxidizable species is present, ia will
increase and continues till it reaches maximum which denotes that all the species has
been oxidized.
• Then it will again decrease till it reaches the background current level.
• Now, the potential is reversed and as potential is negatively sweeped, the now-high
concentrated oxidized species start to get reduced.
• So, ic reaches a maximum where all has been reduced and back to the background level.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyclicvoltammetry-210925084541/85/Cyclic-voltammetry-4-320.jpg)


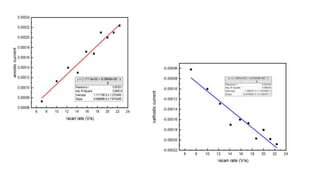
![In Lab
A 10-3 mM of K3[Fe(CN)6]3- was prepared in 0.1M KNO3 solution.
The reference electrode, here Ag/AgCl was prepared by immersing the Ag wire in a 0.05M KCl solution to
coat it with a greyish-white layer of chloride. Further, it was kept in a tube filled with agar-agar and KCl
solution. It was kept still for 24 hours for the equilibrium to maintain.
A Pt disc electrode and Pt flag electrode was used as WE and CE respectively.
It was arranged in a cell and the CV was taken for different scan rates from 50mV to 500mV.
The graph was plotted.
Values of ip,a, ip,c, Eo, Ec from the graph and Do was calculated from the Randles - Sevick equation.
ip = 0.446nFACo (
𝑛𝐹𝑣𝐷0
𝑅𝑇
)1/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyclicvoltammetry-210925084541/85/Cyclic-voltammetry-8-320.jpg)