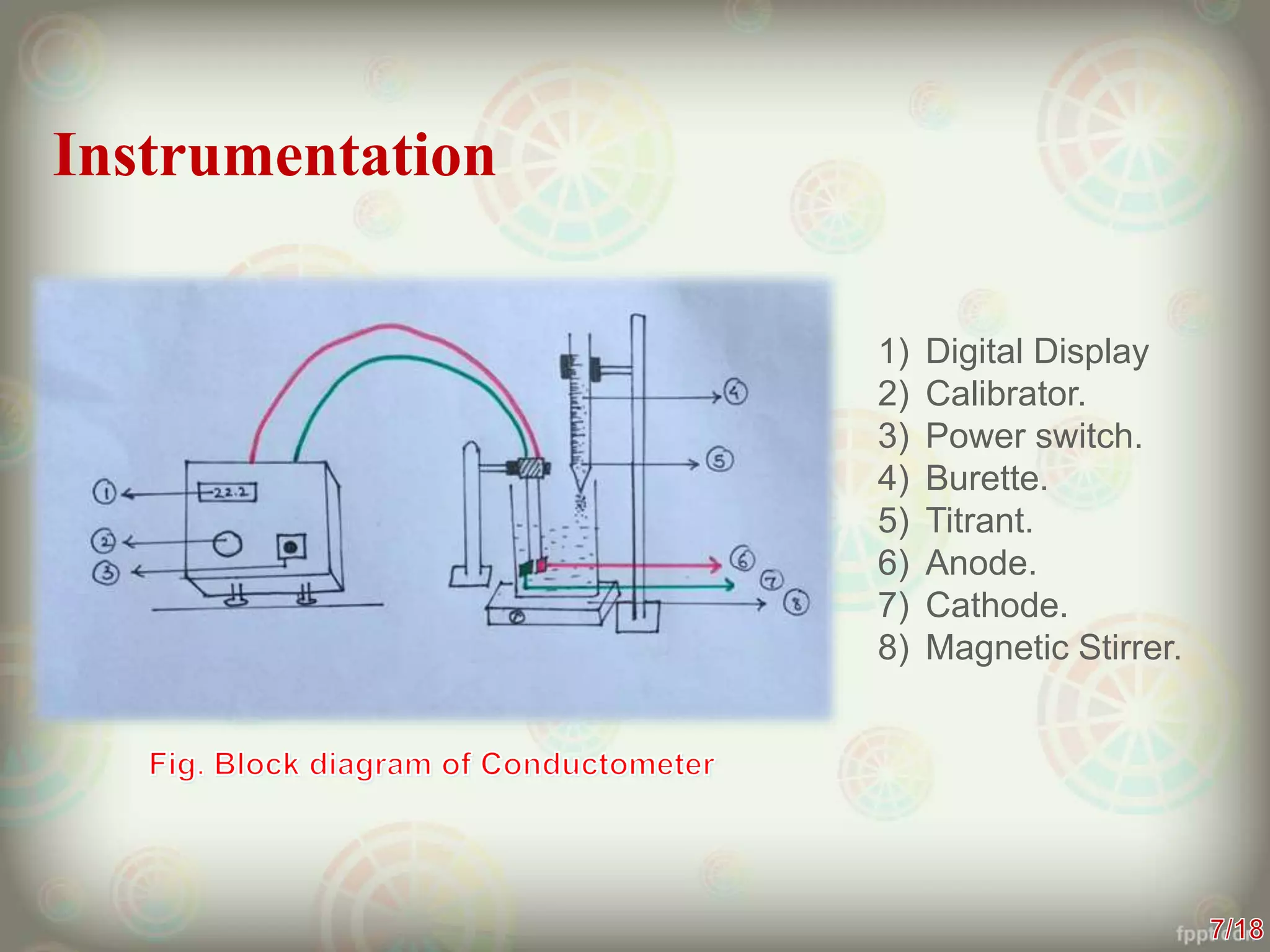
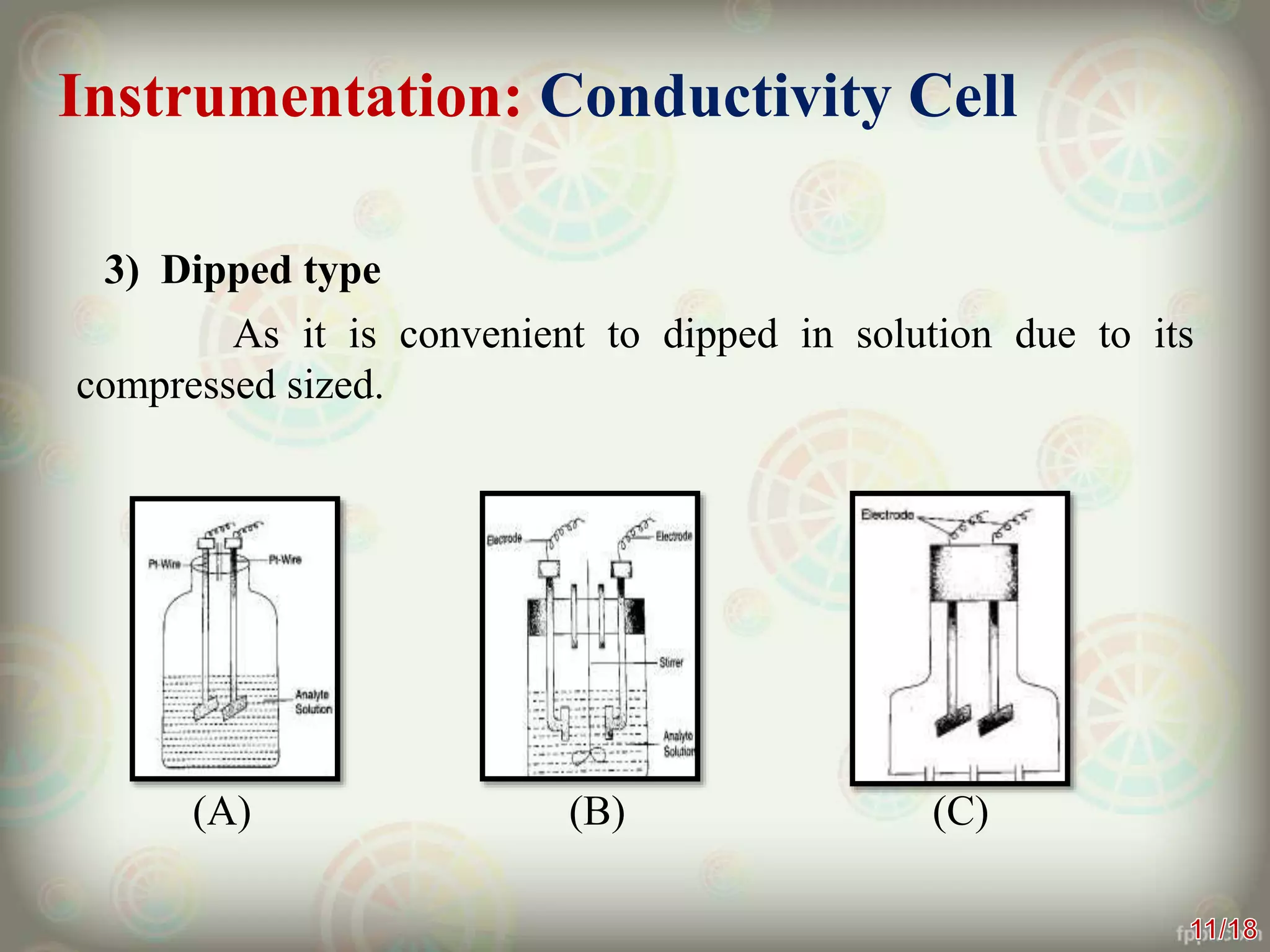
Conductometry is a technique that measures the electrical conductivity of a solution during a chemical reaction or titration. It works on the principle that conductivity changes as ions are replaced by other ions. The instrumentation includes a conductivity cell with electrodes, a current source, and a conductivity meter. Conductometry has applications in determining water quality, solubility of salts, and as an analytical technique for titrations. It provides accurate results but is limited for some redox titrations where hydronium ion concentration masks conductivity changes.